
# **Atlas of the Human Brain**
This page intentionally left blank
# **Atlas of the Human Brain**
#### 4th edition
#### Jürgen K. Mai
Institute of Anatomy I, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany
#### Milan Majtanik
MR-X-Brain GmbH, Düsseldorf, Germany
#### George Paxinos
Sydney, Australia Neuroscience Research Australia and The University of New South Wales,


AMSTERDAM • BOSTON • HEIDELBERG • LONDON • NEW YORK • OXFORD • PARIS SAN DIEGO • SAN FRANCISCO • SINGAPORE • SYDNEY • TOKYO
Academic Press is an imprint of Elsevier
Academic Press is an imprint of Elsevier 125 London Wall, London EC2Y 5AS, UK 525 B Street, Suite 1800, San Diego, CA 92101-4495, USA 225 Wyman Street, Waltham, MA 02451, USA The Boulevard, Langford Lane, Kidlington, Oxford OX5 1GB, UK
Fourth edition
Copyright © 2016, 2008, 2004, 1995 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
This book and the individual contributions contained in it are protected under copyright by the Publisher (other than as may be noted herein).
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the Publisher. Details on how to seek permission, further information about the Publisher's permissions policies and our arrangements with organizations such as the Copyright Clearance Center and the Copyright Licensing Agency, can be found at our website: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
#### Notices
Knowledge and best practice in this field are constantly changing. As new research and experience broaden our understanding, changes in research methods, professional practices, or medical treatment may become necessary.
Practitioners and researchers must always rely on their own experience and knowledge in evaluating and using any information, methods, compounds, or experiments described herein. In using such information or methods they should be mindful of their own safety and the safety of others, including parties for whom they have a professional responsibility.
To the fullest extent of the law, neither the Publisher nor the authors, contributors, or editors, assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property as a matter of products liability, negligence or otherwise, or from any use or operation of any methods, products, instructions, or ideas contained in the material herein.
#### Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
A catalog record for this book is available from the Library of Congress
#### British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN: 978-0-12-802800-1
For information on all Academic Press publications visit our website at http://store.elsevier.com/

*Publisher:* Mica Haley *Acquisition Editor:* Mica Haley *Editorial Project Manager:* Kathy Padilla *Production Project Manager:* Julia Haynes
*Designer:* Alan Studholme
Printed and bound in the Far East
**IV**
# Contents
| Part 1: Three Atlases of the Brain in the Head | |
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----|
| 1.1 Materials and Methods | 1 |
| 1.1.1 Anatomical Preparations | 2 |
| 1.1.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | 2 |
| 1.1.3 Preparation and Photography of the Anatomical Slices | 2 |
| 1.1.4 Preparation of 100 µm Thick Frozen Histological Brain Sections | 2 |
| 1.1.5 Presentation of the Images for the Atlases of the Brain in the Head | 3 |
| 1.1.6 References | 5 |
| 1.2 Horizontal Atlas | 7 |
| 1.3 Coronal Atlas | 41 |
| 1.4 Sagittal Atlas | 69 |
| Part 2: Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space | 85 |
| 2.1 Materials and Methods | 86 |
| 2.1.1 The Brain | 86 |
| 2.1.2 Methods | 86 |
| 2.1.3 Earlier Histological, Morphometric, Immunohistochemical Studies | 86 |
| 2.1.4 Nomenclature | 86 |
| 2.1.5 Photographic Plates and Corresponding Diagrams | 86 |
| 2.1.6 Three-Dimensional Reconstructions | 86 |
| 2.1.7 Standardization | 87 |
| 2.1.8 Mapping of the Atlas Space to the Talairach Space | 87 |
| 2.1.9 Mapping of the Atlas Space to the MNI/ICBM2009b Template | 88 |
| 2.1.10 Atlas of the Human Brain (AHB) Reconstruction with MNI/ICBM2009b Shape Constrain | 89 |
| 2.1.11 Registration of the Histological Sections to the Reconstructed Volume | 90 |
| 2.1.12 Use of the Atlas for the Interpretation of Individual in vivo/in vitro Brains | 90 |
| 2.1.13 Mapping of the Cortex Areas | 90 |
| 2.1.14 Generation of the Linear Representation of Cortex "Stripes" | 91 |
| 2.1.15 Layout of the Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space | 91 |
| 2.1.16 References | 94 |
| 2.2 Surface Views | 95 |
| 2.3 Plates, Figures and Diagrams | 101 |
| 2.4 Diagrams with Reduced Detail | 400 |
| 2.4.1 Horizontal (axial) Diagrams | 401 |
| 2.4.2 Sagittal Diagrams | 409 |
| 2.5 Maps of Subcortical Areas | 416 |
| 2.5.1 Thalamus | 417 |
| 2.5.2 Hypothalamus | 427 |
| 2.6 Published Studies Referring to the Brain Represented in the Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space | 433 |
| 2.6.1 Histological, Morphometric and Histochemical Studies | 433 |
| 2.6.2 References | 439 |
| Index | |
| List of Structures | 440 |
| List of Abbreviations | 445 |
**V**
This page intentionally left blank
# Preface
The publication of the 4th Edition of Atlas of the Human Brain affords us the opportunity to include features which can be of assistance to the new fields of neuroscience – functional imaging, resting state imaging and tractography.
Totally new in this edition is the inclusion of Nissl plates with delineation of cortical areas (Brodmann's areas), the first time that these areas have been presented in serial histological sections.
This book consists of two major parts. They feature different aspects of brain morphology and topography.
# Part 1: Three Atlases of the Brain in the Head
They display the brain in the head sectioned in the three cardinal planes. It consists of serial 1-cm thick sections from three human heads that were previously scanned with MRI. Each head was sectioned either in the horizontal (axial), coronal, or sagittal plane. The sectioning of the brain in the skull ensures that no significant deformation of the brain occurred and allows correlation of bony landmarks, nerves, and blood vessels. In addition, included are X-ray images of the cadaver sections and MR-images from a healthy volunteer showing levels corresponding to those depicted in the *Atlas* plates.
# Part 2: Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space (AHB)
The AHB consists of a detailed myelo- and cytoarchitectonic atlas of the isolated brain in MNI space. It is represented by serial histological sections of one hemisphere with meticulous delineations. It displays 99 fiber-stained (myelin) sections accompanied by detailed diagrammatic delineations and 50 cell-stained (Nissl) sections of the right brain hemisphere.
This brain was selected because it was sectioned well and stained well by the great anatomists Oscar and Cécile Vogt and has been studied in the last 80 years by a number of scientists, including H. Brockhaus, R. Hassler, A. Hopf, W. Wahren and F. Sanides. Selected sections which can optionally shown by virtual microscopy as well as the published literature referring to this brain can be accessed at the free website: www.thehumanbrain.info.
The 4th edition of the *Atlas of the Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space* contains:
- 99 photographs of sections stained for myelin juxtaposed by 99 detailed diagrams.
- 50 sections stained for cell bodies, interposed at half the frequency of the myelin series. The cell-stained sections are not diagrammed but are accompanied by high resolution photographs of cortical areas.
- The photographs and diagrams represent the complete hemisphere and are placed in the MNI stereotaxic space.
- In the cell-stained (Nissl) plates cortical delineations (Brodmann's areas) (derived from Brodmann maps) are provided.
- Parts of cortical areas are displayed at high magnification on the facing page of full page Nissl sections. We selected preferentially those areas which are thought to correspond with those published by von Economo and Koskinas (1925).
- A novel way of depicting cortical areal pattern is used: the cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon is unfolded and presented linearly, in registration with the interpretation of earlier authors as we perceive their work.
- Low magnification diagrams in the horizontal (axial) and sagittal planes are included, calculated from the 3D model of the *Atlas* brain.
The magnification of the photographs is higher than the diagrams because in this way the photographs can be bled for the sake of greater resolution. Rostral to the genu of the corpus callosum and caudal to the splenium we used higher and varying magnification, dictated by the availability of space. Between the two anterior-posterior extremes of the corpus callosum we kept the magnification of the photographs constant.
# Reproduction of Figures by Users of the Atlas
As producer, J.K.M. is happy for the atlas figures to be reproduced in other publications and gives permission for the reproduction of any figure from the atlas in other publications for non-commercial scholarly purposes, provided that the atlas is cited. Permission from the publisher may be sought on-line via Copyright Clearance Center's Rightslink® service (http://www.copyright.com/rightsholders/ rightslink-permissions/) or contact the Elsevier Permissions Department: phone: (+1) 800-523-4069 x 3808, email: permissionshelpdesk@elsevier.com.
How to cite this book: Mai JK, Majtanik M and Paxinos G (2016). Atlas of the Human Brain 4th ed., Academic Press.
# Acknowledgements
This long lasting endeavour came to fruition because of the continued interest, and help of many persons. It is a pleasure to acknowledge the tremendous generosity of the late Prof. Adolf Hopf, the successor of Oskar Vogt. He nurtured this project from its inception. We thank Josef Assheuer for his major input to the first two editions. The authors received invaluable assistance in delineation from Herwig Lange (Cortex), Farhad Forutan (Thalamus), Ricardo Insausti (Temporal Lobe) and Yuri Koutcherov (Hypothalamus). We are greatly indebted to Azarias Karamanlidis (University of Thessaloniki, Greece) for valuable comments and scholarly advice on nomenclature and correcting a number of errors while preparing the Greek edition.
We are grateful to Christine Opfermann-Rüngeler and Laurentius Lanta for commitment to excellence in the preparation of artwork and design of the book. Ursula Lammersen has imaged our sections with the high resolution digital microscope with great skill and dedication. Special thanks go to Thomas Voß, Raul Grieben, Dominik Löchel, Jens Bongartz and Christoph Vogelbusch for invaluable work on mathematical modelling and image transformation algorithms referring to the *Atlas*. We have had the professional guidance of a talented editor, Mica Haley of Elsevier/ Academic Press who supported this edition with dedication.
We acknowledge support for this project from the Society of Friends and Supporters of the Heinrich-Heine-University at Düsseldorf. George Paxinos was supported by an NHMRC fellowship. The sponsorship by the Jörg Bernards-Stiftung, Cologne, and the private entrepreneurship by Miroslaw Pienkowski, Trinon GmbH, Karlsruhe was essential because none of the applications for support from the German research agencies were successful. In this we are in good company in that Korbinian Brodmann who was also refused funding by German funding bodies that should have supported him. Finally, our thoughts go with gratitude to those, who provided their bodies for educational and research purposes in anatomy.
**VII**
| DEDICATION: |
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| To Joseph Assheuer and Thomas Voß for their major contribution to the earlier editions of this work |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
**VIII**
# Part 1: Three Atlases of the Brain in the Head
#### Horizontal Atlas:


#### Coronal Atlas:

#### Sagittal Atlas:


**1**
# 1.1 Materials and Methods
In our understanding it is important to see the brain embedded into its environment. This part displays the brain in the head sectioned in three different cut angles. It consists of serial 1-cm thick sections from three human heads that were previously scanned with MRI. Each head was sectioned either in the horizontal (axial), coronal, or sagittal plane. The sectioning of the brain in the skull ensures that no significant deformation of the brain occurred and allows correlation of bony landmarks, nerves, and blood vessels. In addition, included are X-ray images of the cadaver sections and MR-images from a healthy volunteer showing levels corresponding to those depicted in the atlas plates.
## 1.1.1 Anatomical Preparations
**)%( oviv-ni )H(N / o**The three heads were obtained from bodies donated to the Department of Anatomy, Heinrich-Heine University of Düsseldorf. The studies were performed in accordance with established ethical standards. The cadavers were perfused via the radial veins first with physiological saline and then with fixative containing 10% formalin, glycerol, and Incidin (© Henkel, Düsseldorf). The heads were covered with linen and fixative to prevent drying out between MRI and freezing.
## 1.1.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
*MRI Scans:* MRI scans were performed in the horizontal, coronal, sagittal, and oblique coronal planes according to a standardized protocol (Assheuer et al., 1990). The corresponding section planes were defined by the intercommissural line and verticals intersecting this line in the center of the anterior and posterior commissures, except for the oblique coronal plane which was chosen to be parallel to the long axis of the brainstem (Meynert's plane).
*In vitro* imaging: MRI scans of the anatomical preparations are presented ahead of the macroscopic atlases. Scans and measurements were performed on a 0.15 Tesla superconductive magnet (Vista 2035, Picker International) in 1985. We used a multislice double-echo sequence [spin-echo sequence (SE) 5000/40/160] with four excitations to render proton (N(H))- and T2-weighted images. These scans are presented in the pages preceding the figures of the horizontal, coronal, and sagittal sections within the three *Atlases*).
In *vivo/in vitro* correlation was performed to determine the effect of the absence of blood flow, cessation of metabolism, fixation procedures and temperature on relaxation times, signal-to-noise ratio, and contrast. To perform this comparative analysis between living and post-mortem tissue, the heads of two volunteers and of two cadaver heads were scanned with the 0.15 Tesla superconductive magnet (Vista 2035, Picker International) using single-slice technique with SE and inversion recovery (IR) sequences with the following parameters: SE (TR: 200, 800, 1600, 3200, 6400 ms combined with TE: 30, 40, 60, 80, 120, 160 ms) and IR (TR: 620, 1240, 2480 ms combined with TI: 32, 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700 ms). The slice thickness was 5 mm with a matrix of 256 x 256 and a field of view of 250 mm.

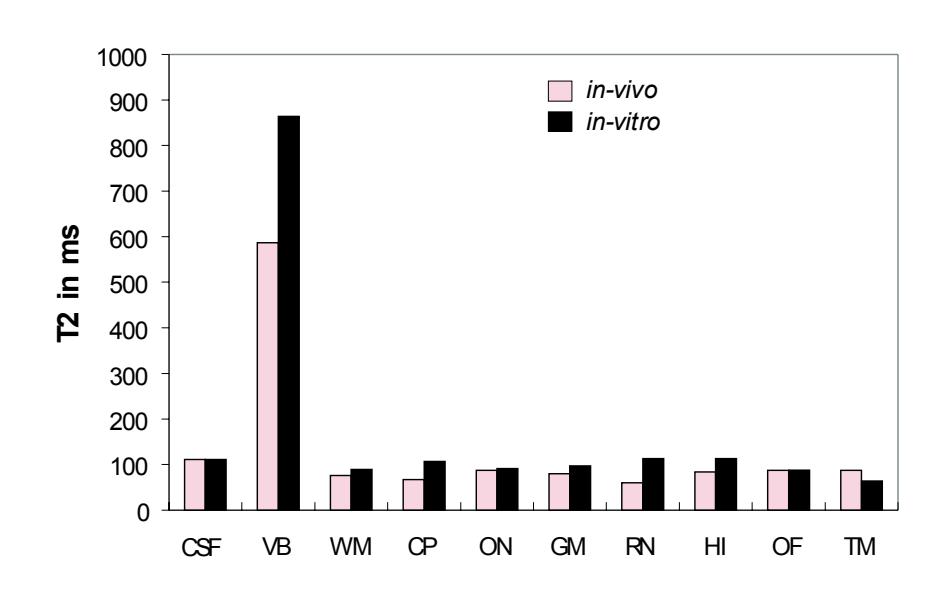
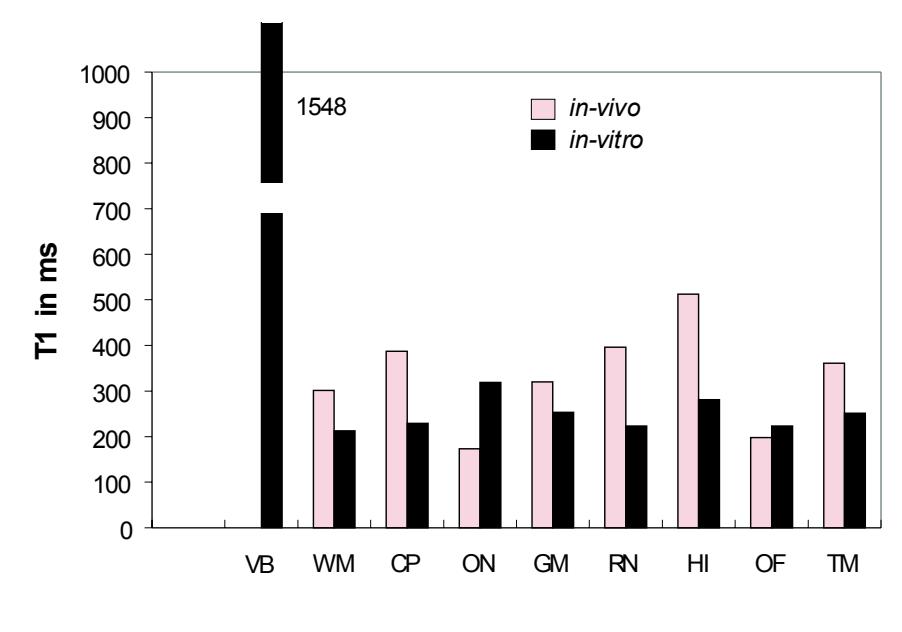
**Figure 1.1** Comparison between living and post-mortem tissue. T1 (spin-lattice relaxation) times, T2 (spin-spin relaxation) times, and N(H) values were measured from the same areas under *in vitro* and *in vivo* conditions. The N(H) values were calculated from SE-sequences (red squares) and IR-sequences (black squares). They are presented as quotient of *in vitro* values to *in vivo* values in %. Abbreviations: CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; VB: vitreous body; OF: orbital fat; ON: optic nerve; HI: hippocampus; WM: white matter; GM: gray matter, CP: cerebral peduncle; RN: red nucleus; TM: temporalis muscle. (Data from Longerich, 1989).
T1 (spin-lattice relaxation) times, T2 (spinspin relaxation) times, and N(H) (proton density) values of the *in vivo* and *in vitro* tissues are represented in Fig. 1.
Compared with the *in vivo* results, the *in vitro* tissues show large, nonlinear reduction in T1 relaxation times and N(H) values and small (negligible) changes in T2 relaxation times. A stable correlation exists between the *in vitro* and *in vivo* relaxation curves. For further details see Longerich (1989).
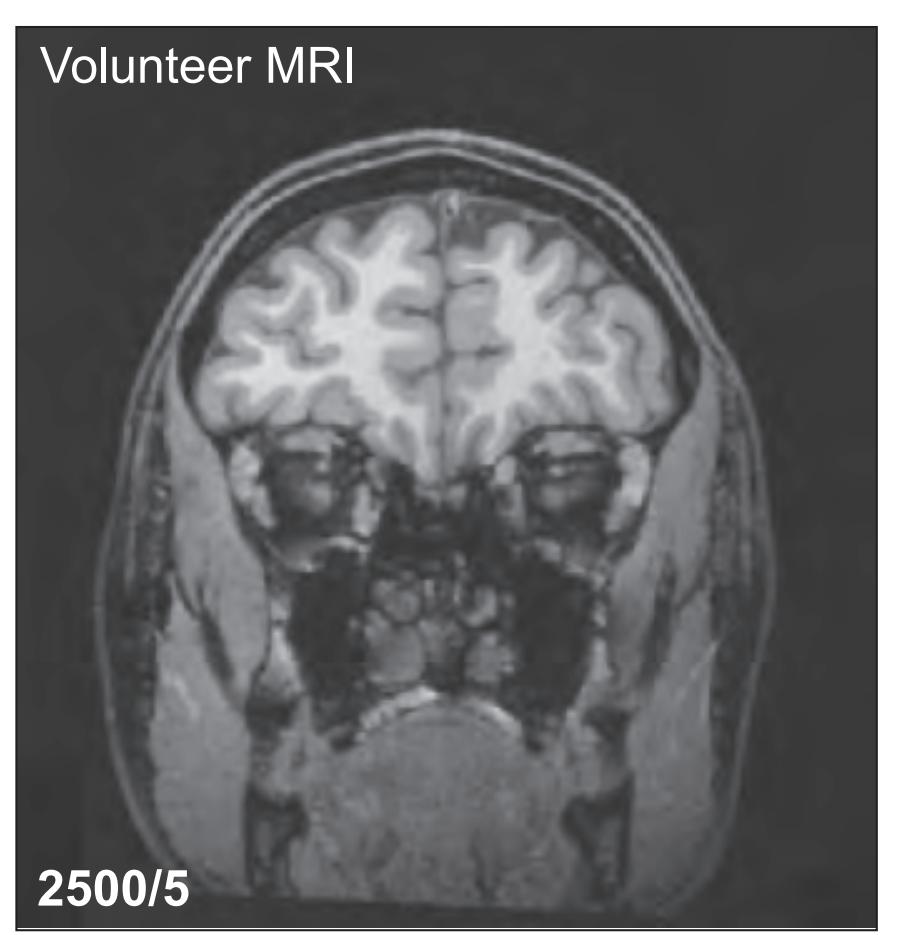
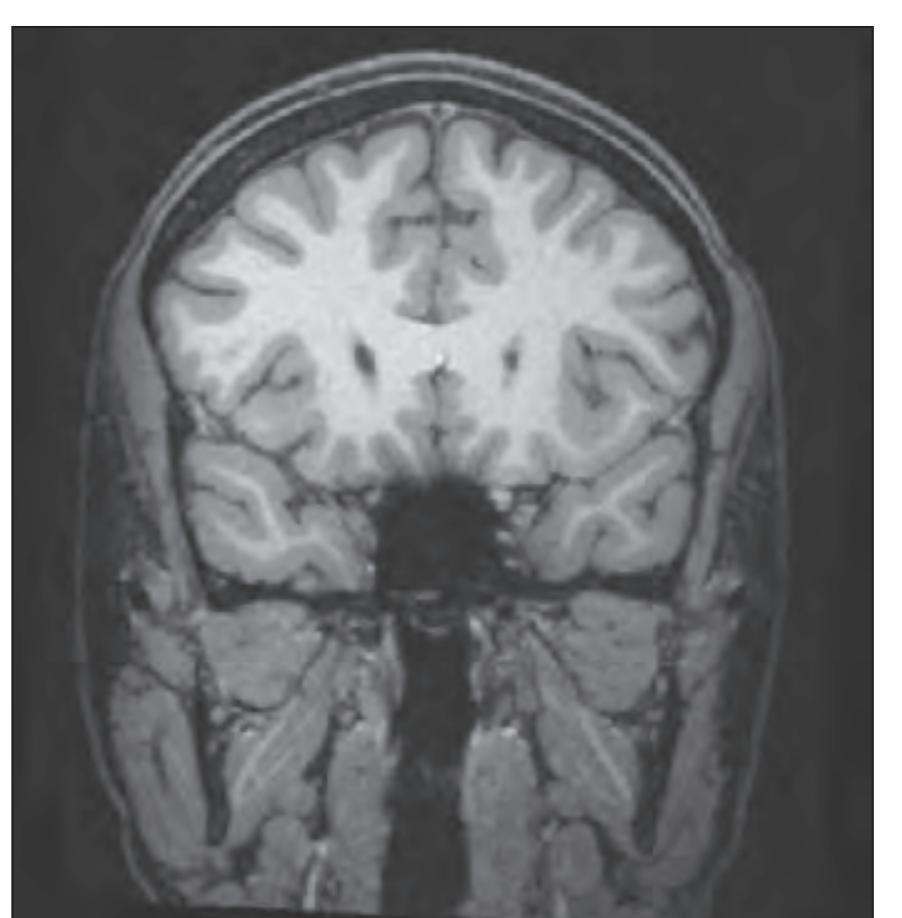
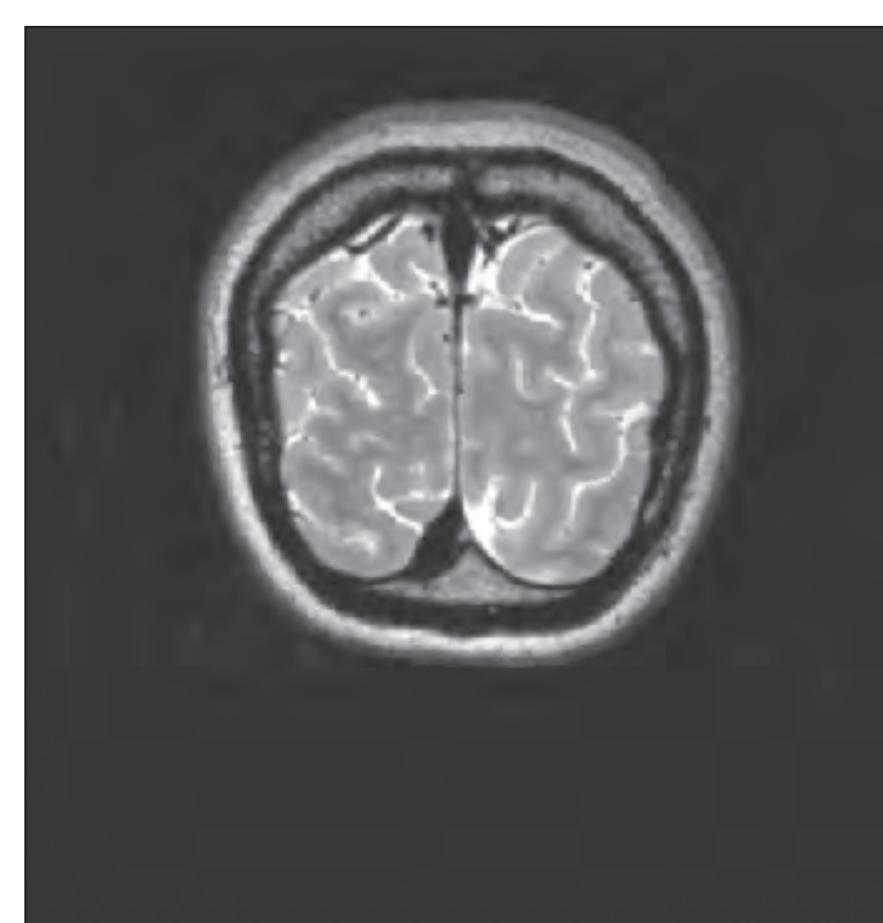
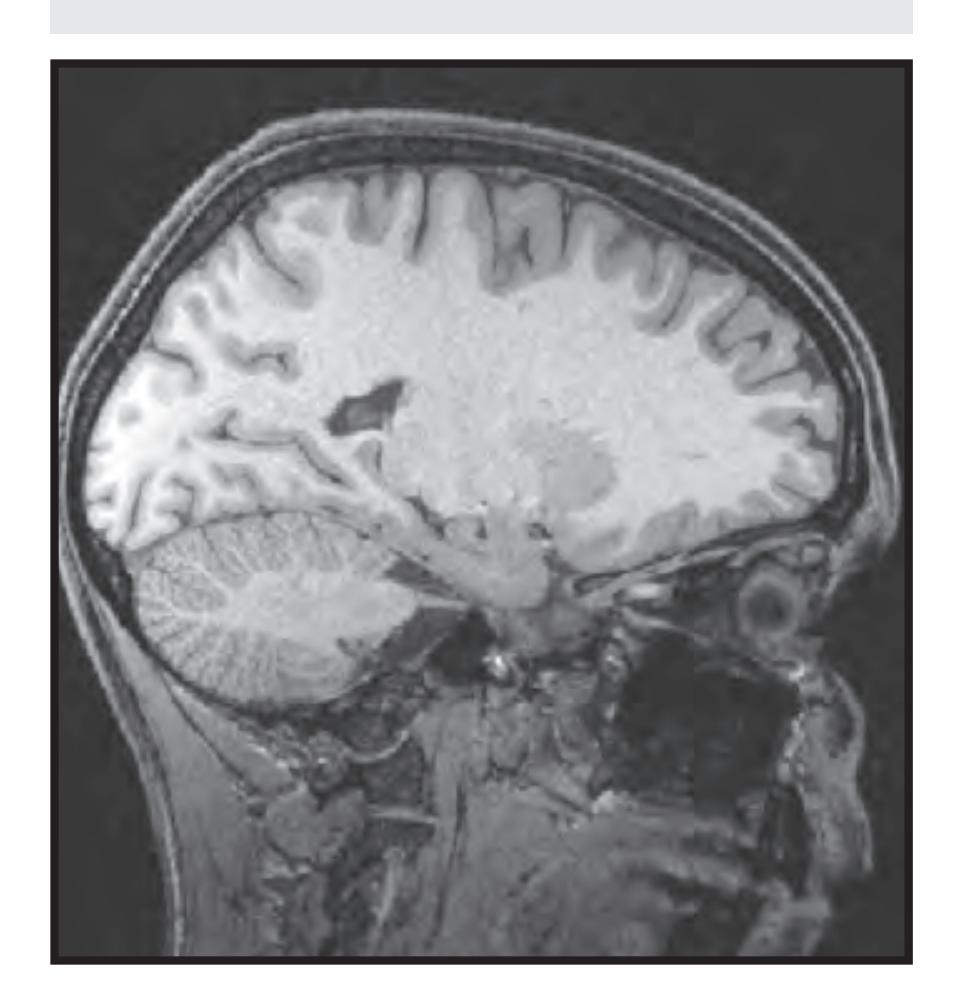
*In vivo* imaging: MRI scans of a healthy volunteer are presented at each atlas level. For *in vivo* imaging we used a 3 Tesla imager (Siemens Magnetom Trio) with the following protocols: TR 2500, TE 4.79 and TR 3000, TE 355. The slice thickness was 0.6 mm with a matrix of 320 x 320. These images are presented in Sections 1.2 to 1.4 facing each macroscopic anatomical section.
## 1.1.3 Preparation and Photography of the Anatomical Slices
Immediately after the MR scans, the heads were frozen in a -45°C freezer and later sliced at 1-cm thickness either in the horizontal, oblique coronal, and sagittal plane. The oblique coronal plane was angulated by –20°, such that the plane of the section is parallel to the brainstem axis and corresponds to the major ascending and descending fiber tracts.
The head slices were then photographed together with a scale bar. Each 1 cm slice was x-rayed separately. Its blood vessels were then filled with radio-opaque material and demonstrated by another x-ray. The course of the larger vessels within each slice was then drawn and combined with the x-ray. The resulting images are shown at the lowest panel in the left column next to the photos and diagrams of the slices (except for the horizontal plane).
Later, the brain slices were removed from the skull. The head and neck structures were dissected in order to demonstrate the topographic relations within the 1-cm slices. The 1-cm brain slices were mounted according to their *in vivo* situation to physically reconstruct the brain. After removal of the arachnoid mater photographs were made to document the gyrification pattern. These photographs form the basis of the diagrams preceding each of the three *Atlases of the Brain in the Head*, taking into account the 1-mm loss of tissue at every 1-cm level due to the sawing.
**2**
## 1.1.4 Preparation of 100 μm Thick Frozen Histological Brain Sections
After removal from the surrounding skull and photography of the assembled brain 1-cm slices, these were immersed for 48 hours in a fixative containing 4% formalin and 30% sucrose. Each slice was then positioned on a freezing stage (30 x 20 cm) of a microtome (Fig. 1.2a) and a mould was placed around it into which the mounting medium (methylcellulose dissolved in water and stained with various chromogens) was poured. After cooling down to -20°C, fiducial marks were made (Fig. 1.2b) and the blockface was photographed together with a scale bar prior to taking each section (Fig. 1.2c). Sections taken at 100-µm thickness were transferred to individual containers filled with phosphate-buffered saline (plus 30% sucrose). The photographs which were taken from the blockface aided correct mounting of the sections. All sections were mounted and then stained (with either toluidine blue or cresyl violet) for Nissl substance or (with hematoxylin or Sudan black B) for myelinated fibers. By means of the fiducial marks the single sections were compiled in a sequence from rostral to caudal. 3-D reconstructions were made from the blockface images obtained during the sectioning process using the AMIRA (© FEI Visualization Sciences Group) software system (Fig. 1.2d). In addition tracings of pial and ventricular surfaces as well as of the outlines of segmented internal structures were used for a vector model using a program developed by L. Teckhaus, MPI Dortmund.
# **a**



**Figure 1.2.** (a) Cryosectioning device consisting of the Tetrander ("Pantomikrotom"; see Vogt, 1905), a self-built freezing table, photograph stand (fixed to the vertical rectangle), and tube holder for dry ice. (b) Frozen tissue block overlaid with a 1 cm thick slab from plastic with drill holes providing a matrix of 1x1 cm distance and securing precise perpendicular orientation of cannulas used for punch marking. (c) Fixed slice of the hemisphere (represented in Section 2.2) embedded in methylcellulose and showing section surface with scales and punch marks (fiducial marks used later for topographic adjustment of sections). (d) Screenshot of the 3D reconstruction generated from the blockface images obtained during sectioning of the brain represented in Section 2.2).
## 1.1.5 Presentation of the Images for the Three Atlases of the Brain in the Head
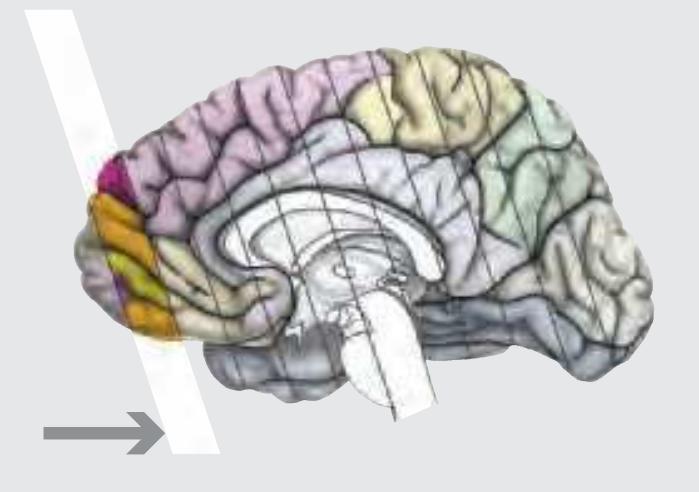
We represent the head with the brain in three different cut angles: horizontal/ axial, sagittal and coronal. The coronal section angle was not orthogonal to the others but tilted by -20° which results in a cut angle that is perpendicular to the brainstem (Meynert) axis. This displays the major ascending and descending long fiber tracts.
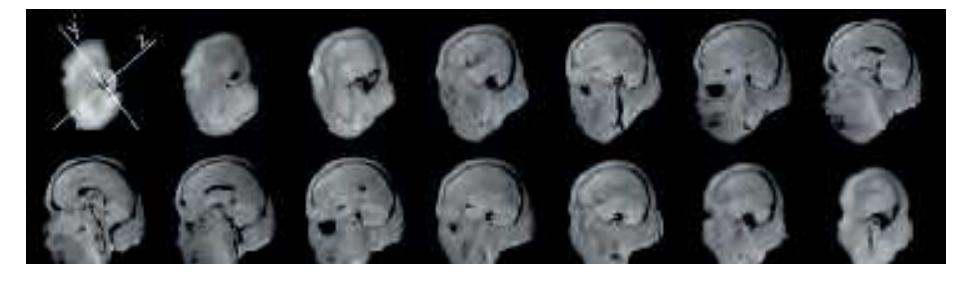
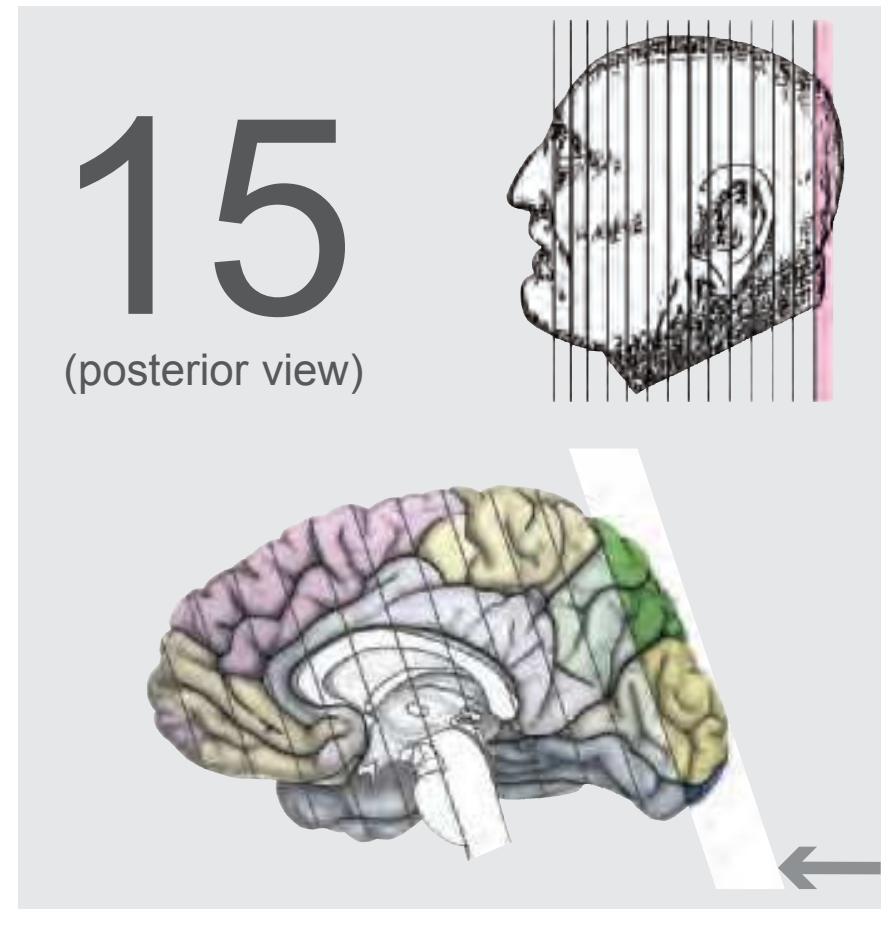
All representations of anatomical head and brain slices are mounted in the same way: Each *Atlas* begins with *in vitro* MR image series in all three cardinal planes of the unsectioned head on which it was based (Fig. 1.3).
Sagittal plane:
y´- direction:
z´- direction:

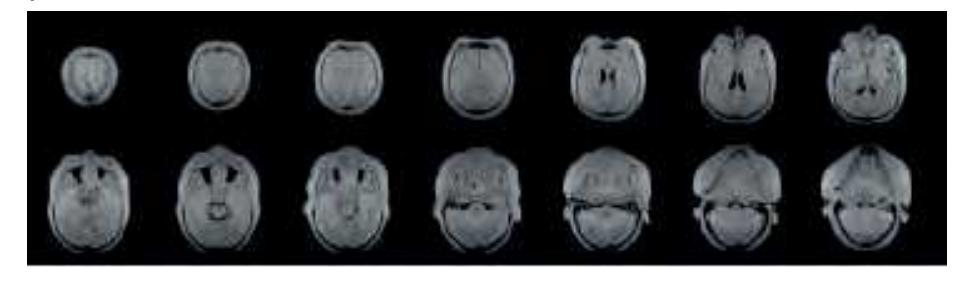
**Figure 1.3.** Each series of sections is headed by *in vitro* MR-images of the head which were taken prior to sectioning. To provide a comprehensive view of the head, MR-images are shown in all three orthogonal planes This allows a better orientation in the three-dimensional space and helps to recognize the topography of selected structures. The images appear in low quality because they were produced in the 1980-ties with one of the first commercial MR-systems.
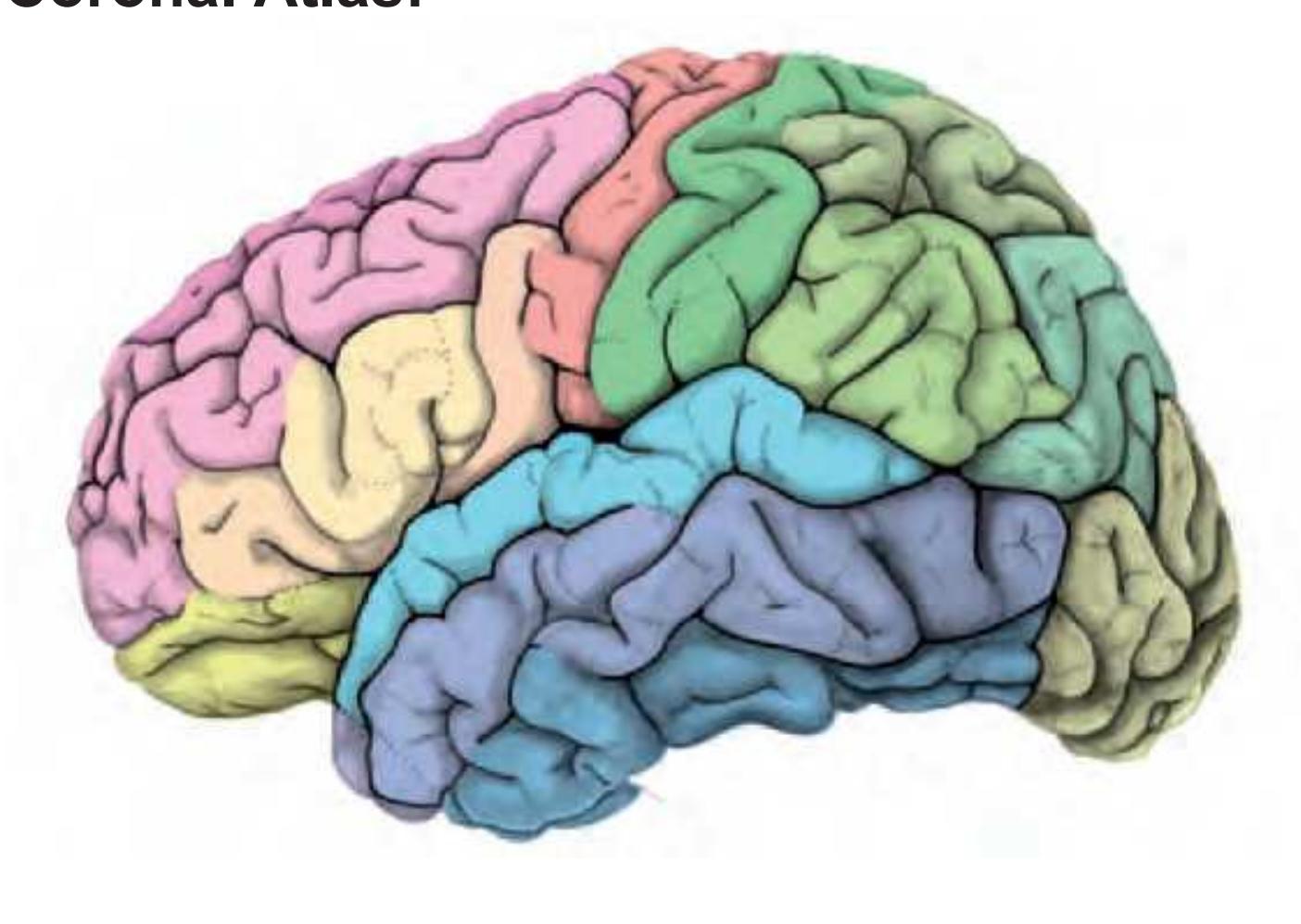
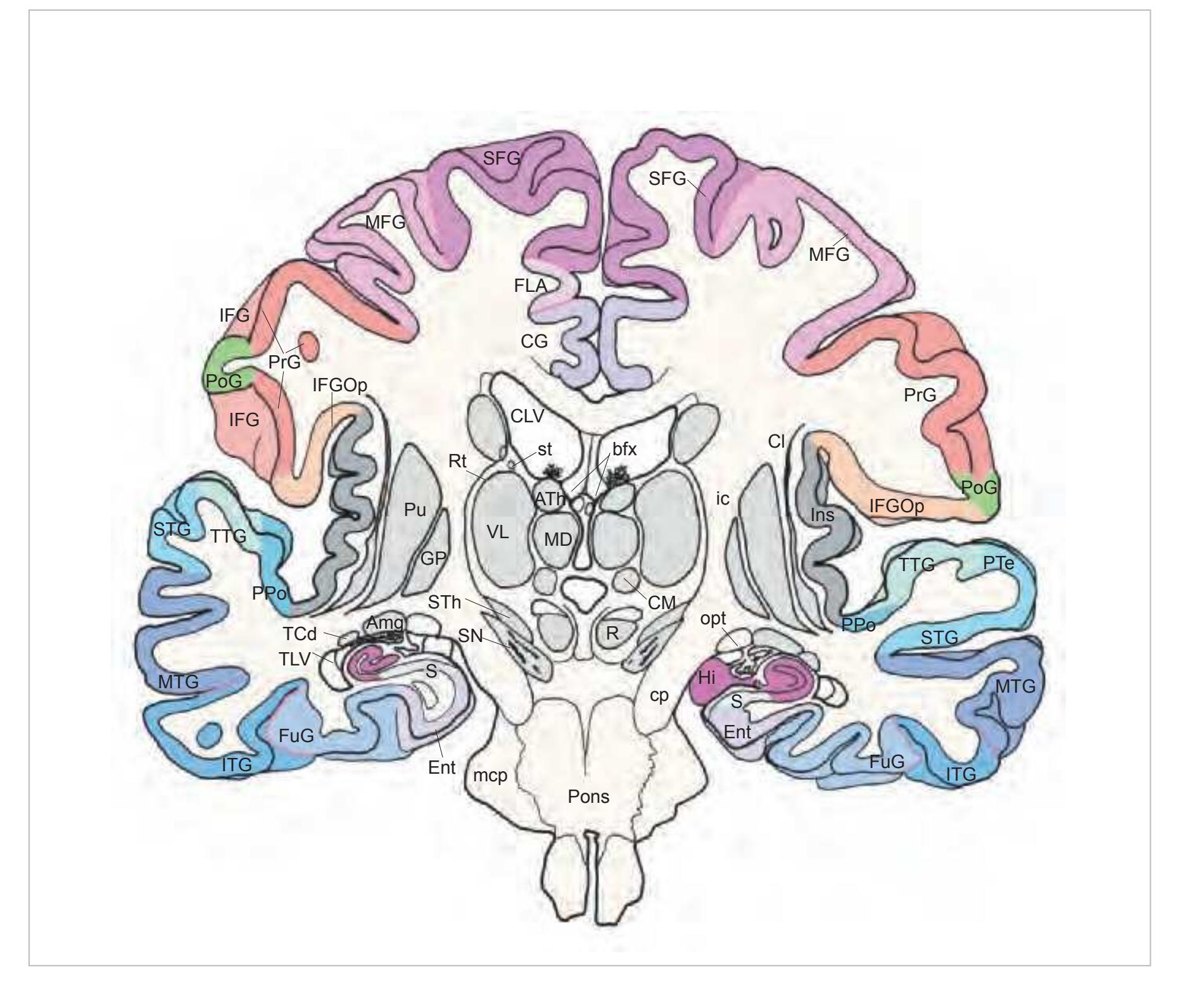
The following two pages within each of the horizontal, oblique coronal and sagittal atlases present surface views of the brains showing their gross morphology together with the delineation of the main gyri and sulci (Fig. 1.4 and 1.5). The gyri are consistently color-coded through the three *Atlases of the Brain in the Head* (see page 5).
The main part of each of these atlases represents the anatomical head and brain slices. They display surface views of 1-cm thick slices through the head either as photographs or colour-coded schematic drawing. Each physical page of the atlas represents one 1-cm thick slice, with the right hand page of the open book page (odd numbered page) displaying the anterior view of the slice and the back page
**3**

**Figure 1.4.** The page following the MR images depicts surface views of the brain. The mid-sagittal views, additionally, provide the stereotaxic proportional grid system of Talairach (Talairach and Tournoux, 1988). Every brain structure shown in the following sections can thus be adjusted to the coordinate system of the Talairach stereotaxic space (see section 2.1.8).
(even numbered page) displaying the posterior view of the same 1-cm slice. In this way, an open book page displays the facing surfaces of adjacent slices (Fig. 1.6). This allows the pursuit of any structure of interest throughout the series of sections. In an analogous way, for the horizontal atlas, the physical page displays the dorsal and ventral view of the same slice. In the coronal plane, the physical page

**Figure 1.5.** The next page presents the lateral and midsagittal views of the brain which has been sectioned, together with the placement of each 1-cm slice indicated. One of these section plans is placed (as "Locator") on each page of the atlas to indicate the location of the depicted slice.
shows the front view (drawing) and the back view (photograph) of the same slice. In the sagittal plane, the physical page displays the lateral and medial views of the same slice.
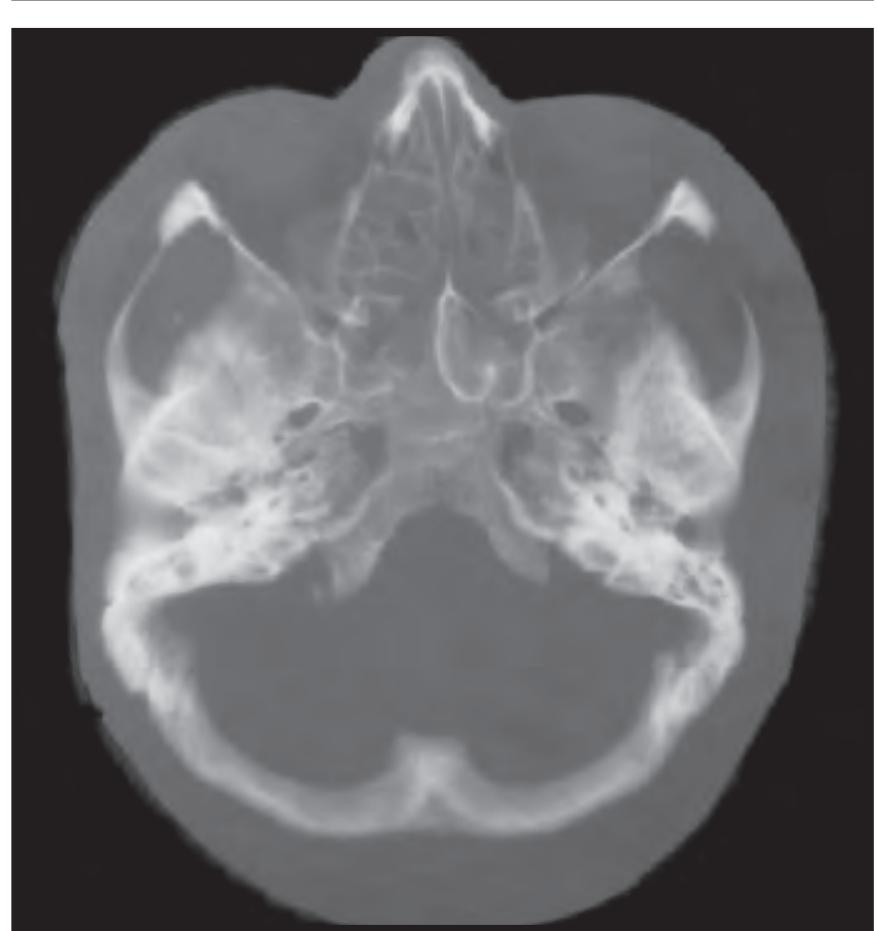
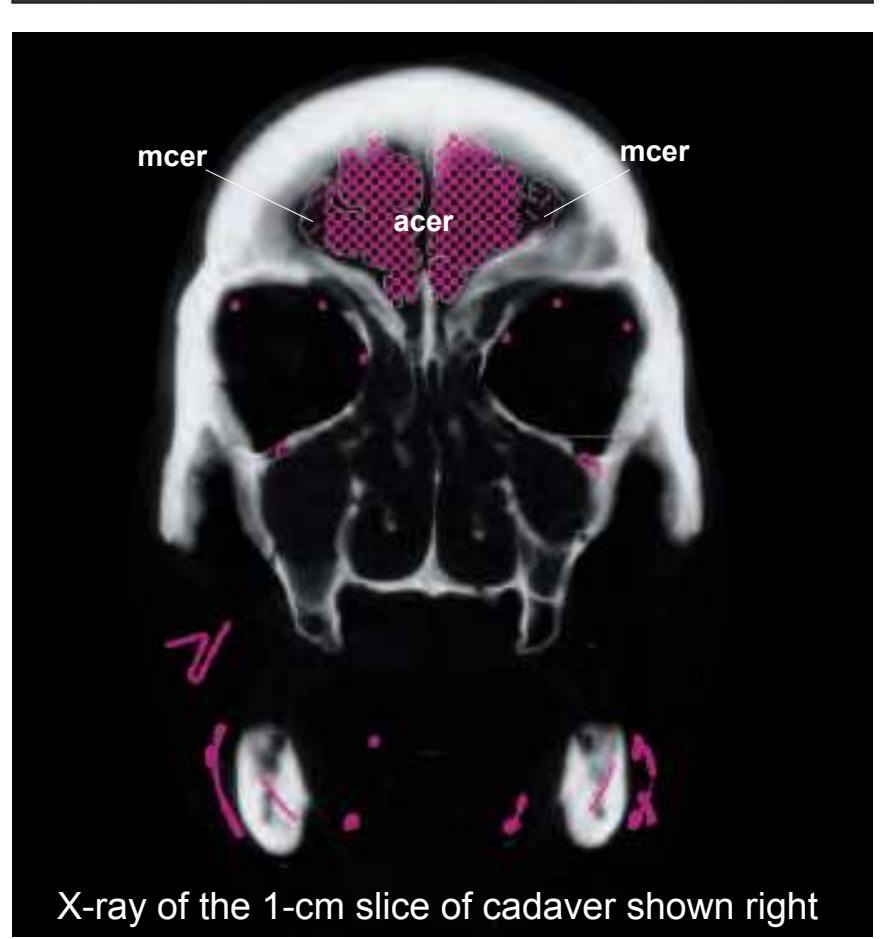
On the even-numbered pages the photographs and the corresponding drawings of the anatomical slices are supplemented by a radiogram of the 1-cm slice (bot-

**Figure 1.6.** The photographs and schematic drawings are mounted such that every section is seen from both sides. They are arranged on the pages in a consistent way: the open atlas (showing two pages) displays the opposing surfaces of the slices as if separated by the knife.
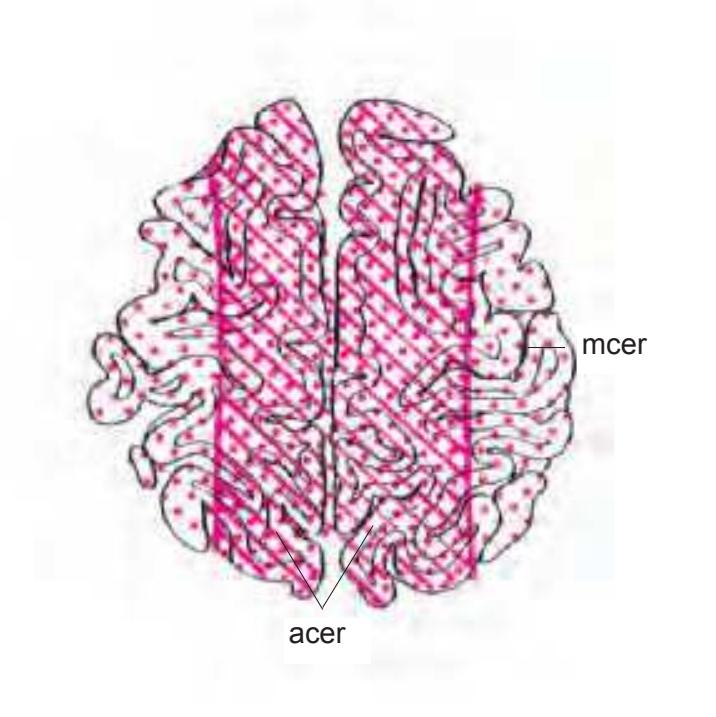
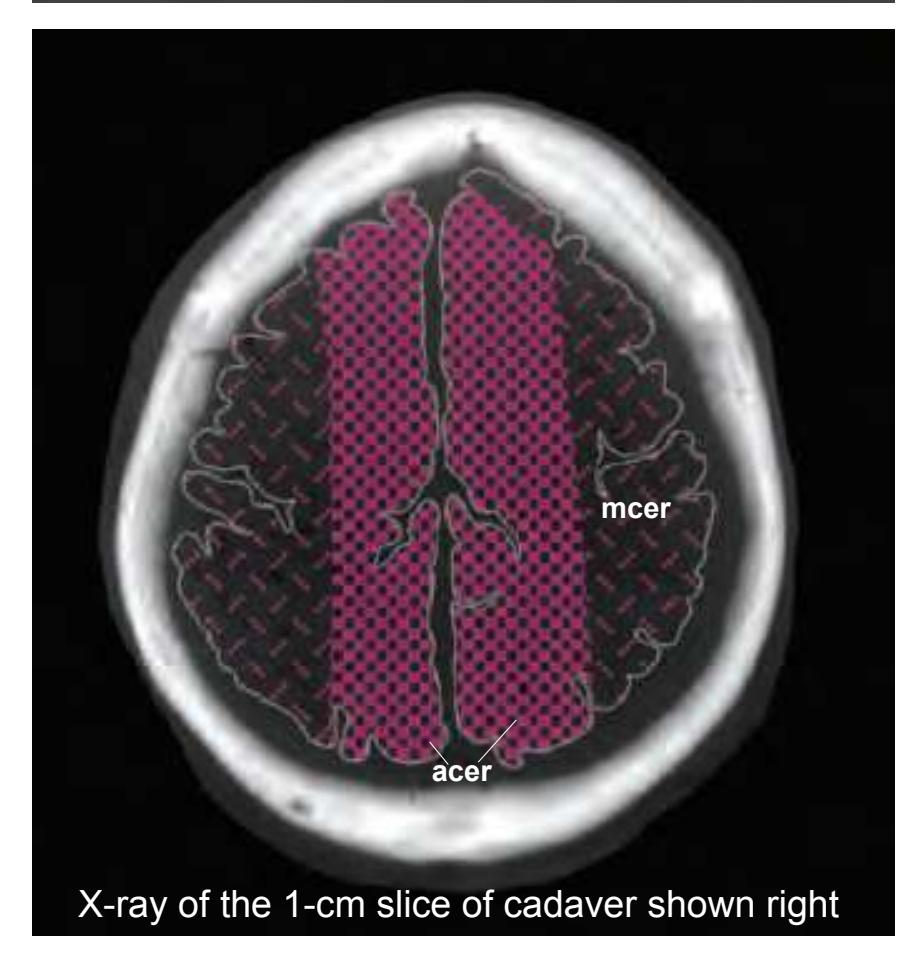
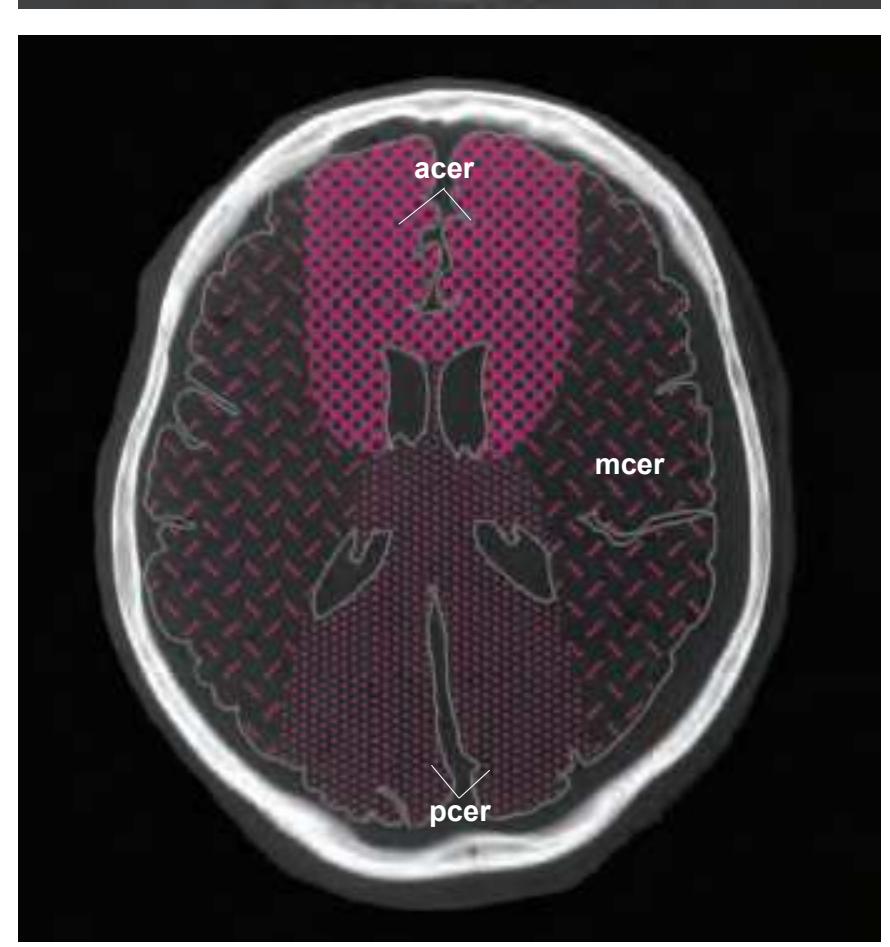
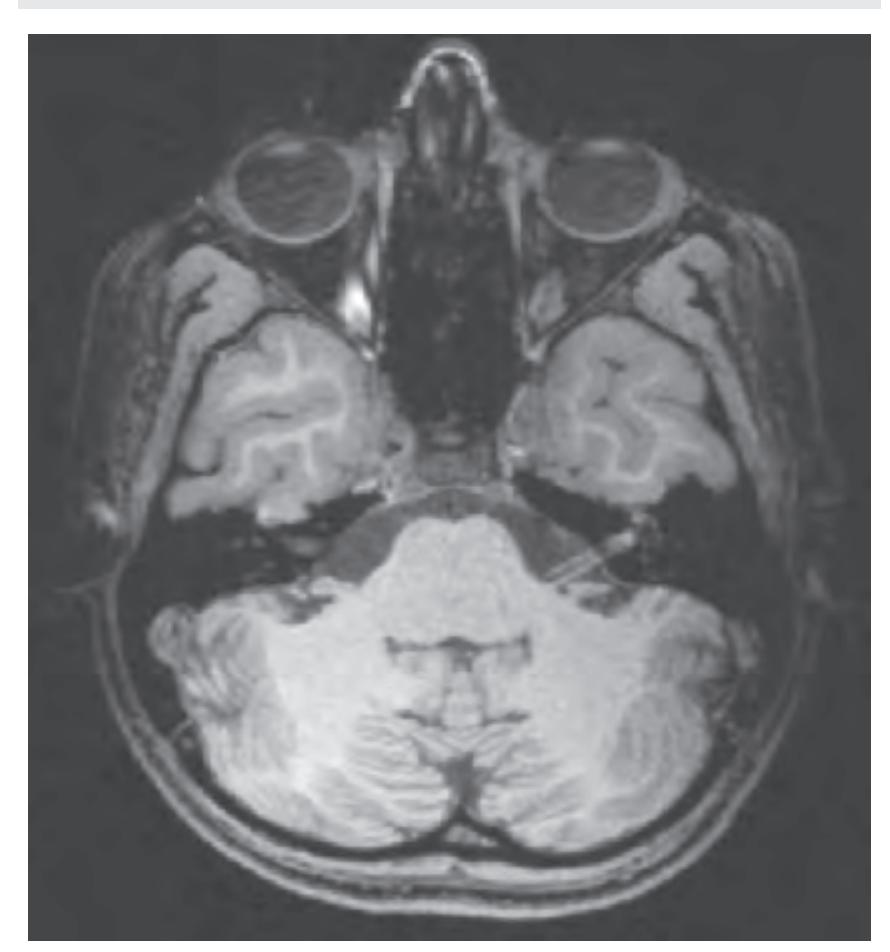
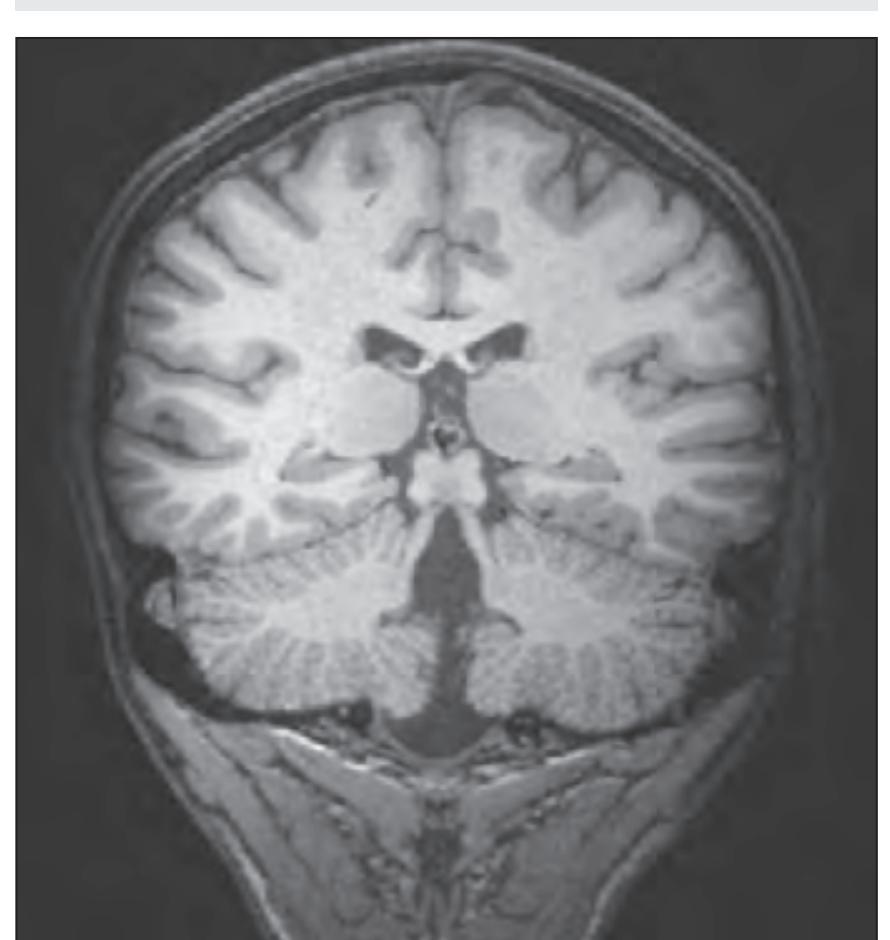
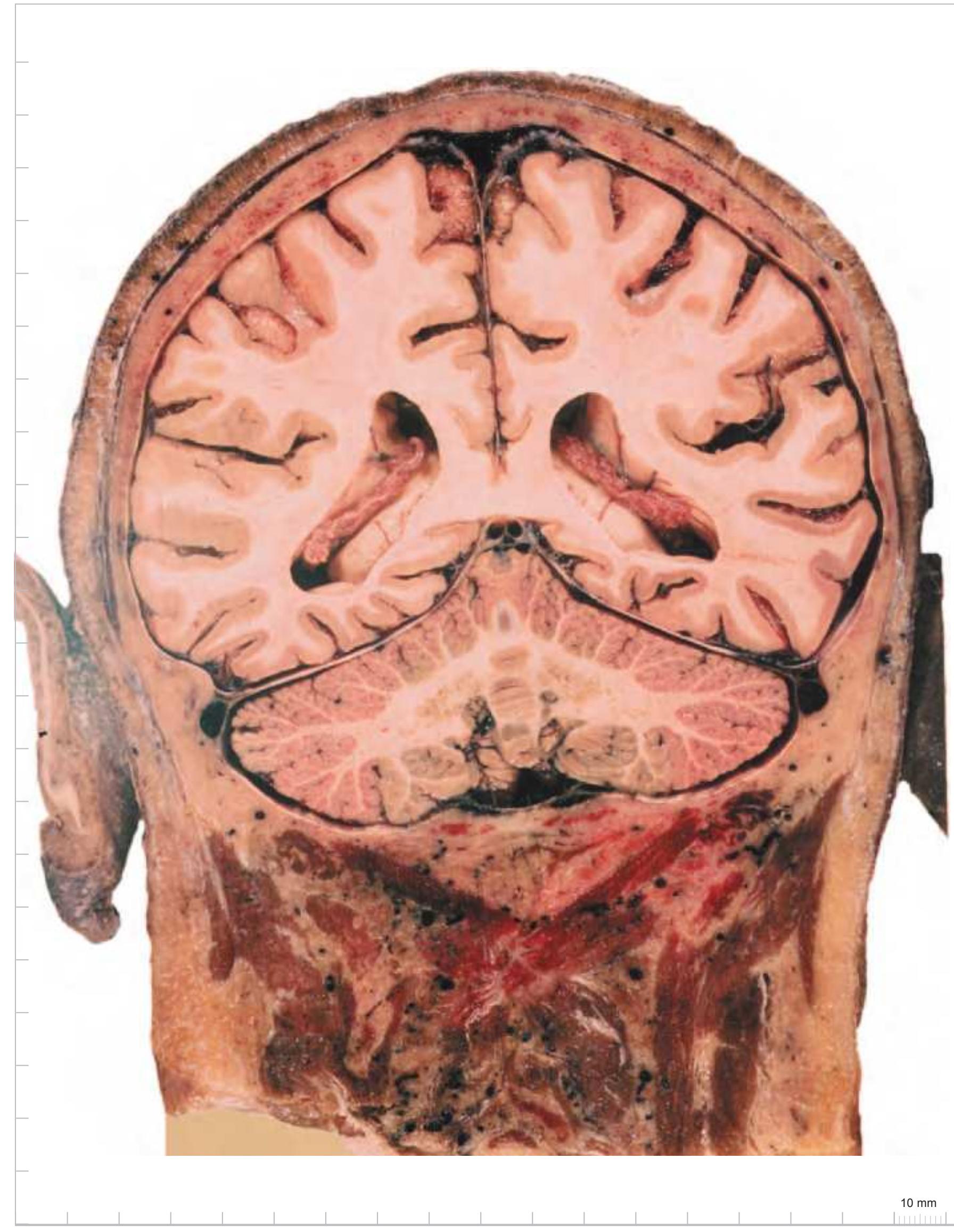
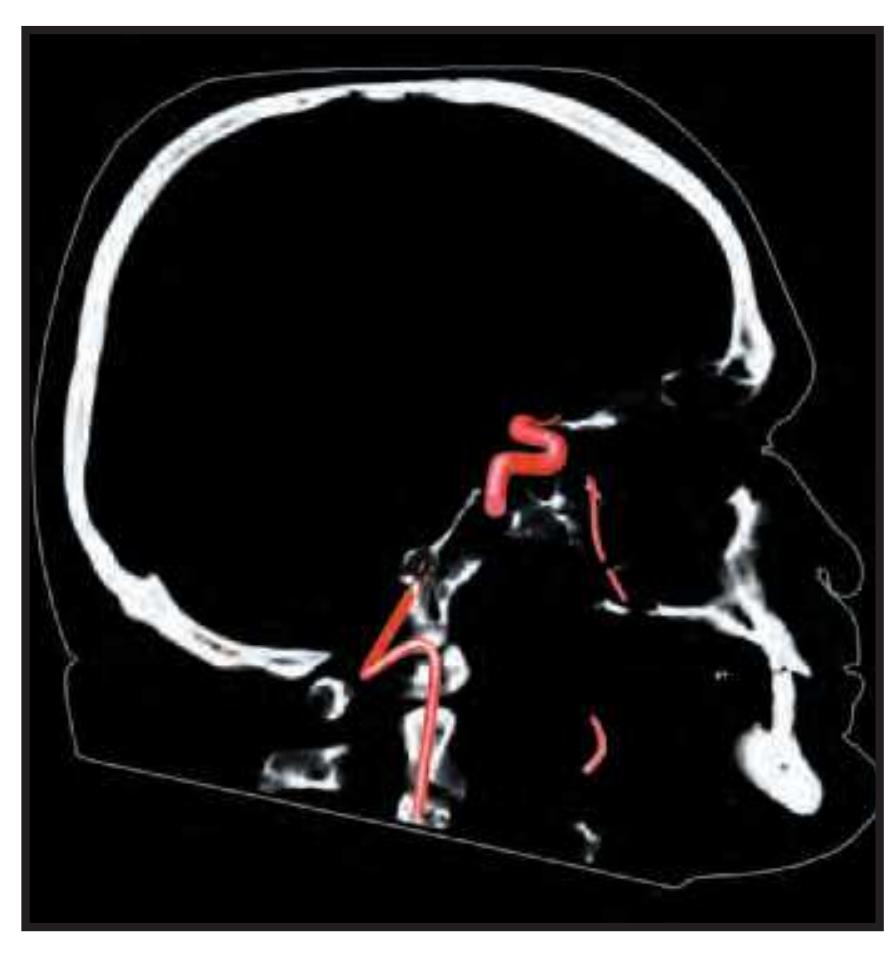
tom left) and by two MR-images of the corresponding location from a healthy, 25 year old volunteer. The MR-images differ with respect to T1, T2 and proton density (N(H)) contrast. The radiogram of the real section displays the vascular territories supplied by the main arteries and (in most sections) the segments of extracranial arteries which are located within the particular slice (Fig. 1.7).
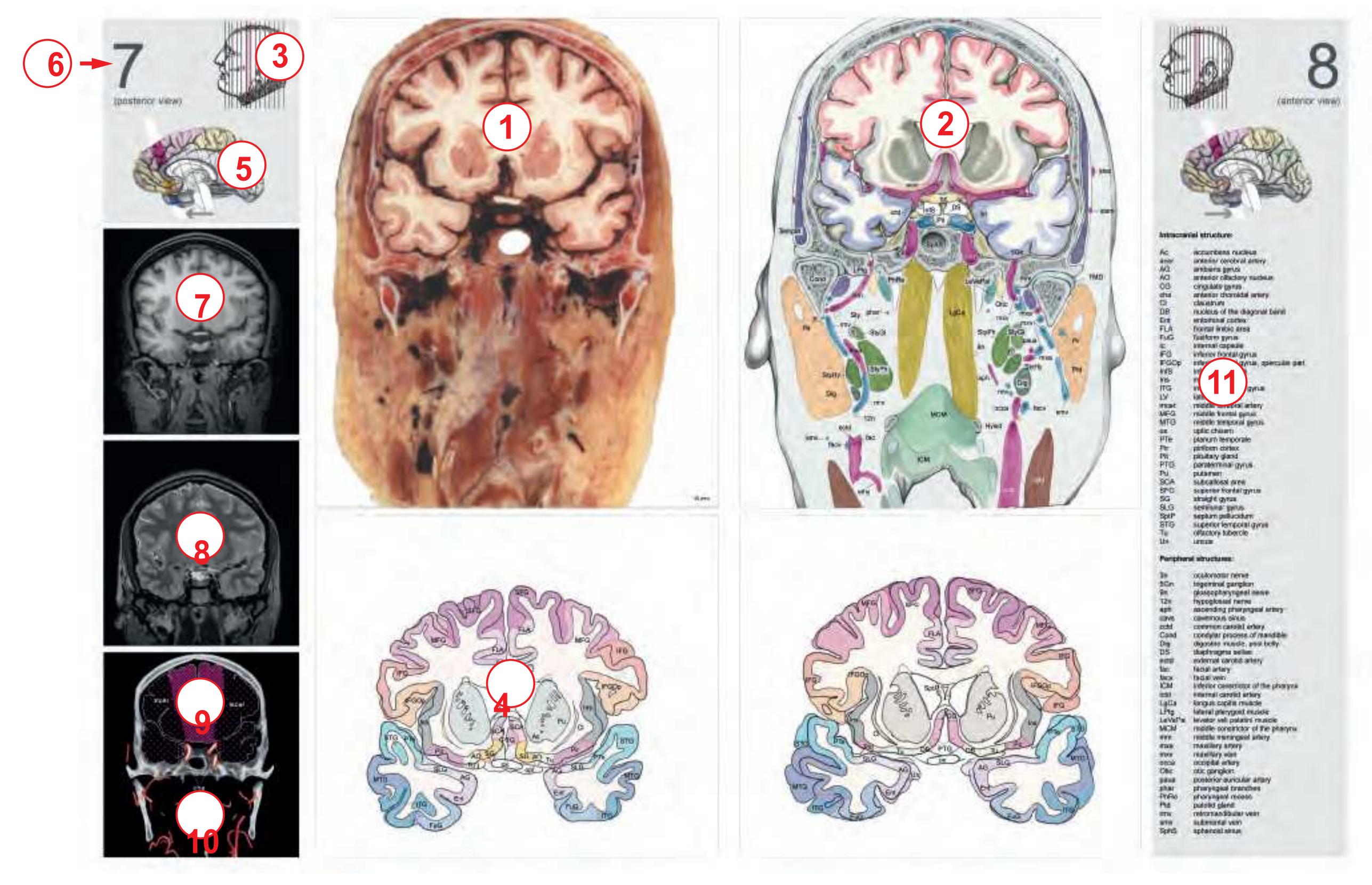
**Figure 1.7.** Layout of a typical double page in the three *Atlases of the Brain in the Head*. Photograph (1) and drawing (2) of the cut surface of 1-cm thick slices through the head and brain and the corresponding drawings of the brain after removal from the skull (4) are arranged in a way that displays the opposing surfaces of the slices. The locator on each page (3) indicates the position of the slice with the arrow pointing to the surface which is shown on this page. The position of the brain slices (4) is highlighted by the bar on the locator (5). In the diagrams the cortical gyri and sulci and subcortical struc-
tures are segmented and color coded (see next page) for easy registration with neighboring slices. On the even pages *in vivo* MR-images of a volunteer are shown which are carefully matched to the anatomic slice. (7,8). The scan parameters are indicated when they first appear in each *Atlas*. The radiograph of the demonstrated slice outlines the vascular territories supplied by the carotic and vertebral arteries (9) and segments of extracranial arteries which are located within the particular slice (10). The index (11) in the coronal and sagittal *Atlases* lists intracranial and extracranial structures separately.
**4**
We have tried to represent the images in a way that allows the structures to be easily followed throughout the section planes. One means is by the use of a consistent color scheme (see below). The other is the adjustment of the contour lines in the drawings in a way that they fit to the real 3D organization. Two examples, the 3D organization of the muscles of the head and neck and the organization of the fascia, as derived from *Atlas* figures, are presented in Fig. 1.8 and Fig. 1.9.

**Figure 1.8.** 3-dimensional reconstruction of muscles of the head and neck using segmentations of the macroscopic atlas. Source: Schumann (2006).
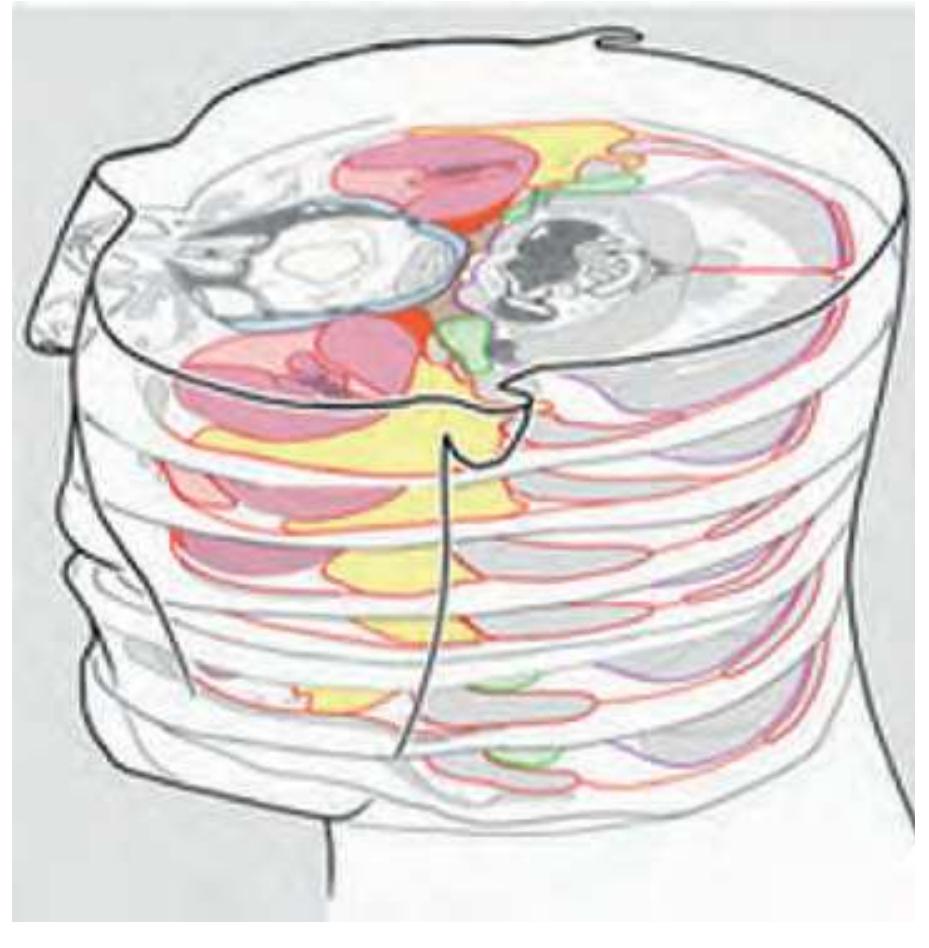
**Figure 1.9.** Alignment of serial drawings through the head and neck from the horizontal *Atlas* for visualization of fascial tissue spaces. Source: http://teaching.thehumanbrain.info/

## 1.1.6 References
Assheuer, J. Lanta, L., Longerich, U.J.J. Sievert, T. and Mai, J.K. Standardisierung der cerebralen Bilddarstellung in der Magnetresonanz tomographie (MRT). RöFo, 153: 296- 302 (1990).
Lange, H. and G. Thörner. Zur Neuroanatomie und Neuropathologie des Corpus striatum, Globus pallidus und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen. Thesis, University of Düsseldorf (1974).
Longerich, U. MRI-Untersuchungen an in-vivo und in-vitro Gehirngewebe: Einfluß von Fixierung und Temperatur auf das Relaxationsverhalten, die Protonendichte und das Kontrastverhalten. Thesis, University of Düsseldorf (1989).
Schumann. J. Segmentierung von Kopf-Halsmuskelstrukturen im MR-DICOM-Bild und deren 3D-Rekonstruktion. Thesis, University of Düsseldorf (2006).
Sievert, T. Topometrie des menschlichen Gehirns: Evaluation eines Verfahrens zur Integration morphologisch-funktioneller Daten aus histologischen Schnitten in die klinische Diagnostik. Thesis, University of Düsseldorf (1992).
Talairach, J., Tournoux P. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. G. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York (1988).
Vogt, O. Das Pantomikrotom des Neurobiologischen Laboratoriums. J. Psychol. Neurol. 6: 121- 125 (1905)
**5**
This page intentionally left blank
# 1.2 Horizontal Atlas of the Brain in the Head
**7**
#### Sagittal plane:

#### y´- direction:
#### z´- direction:

# MR-images of the head shown on the following pages.
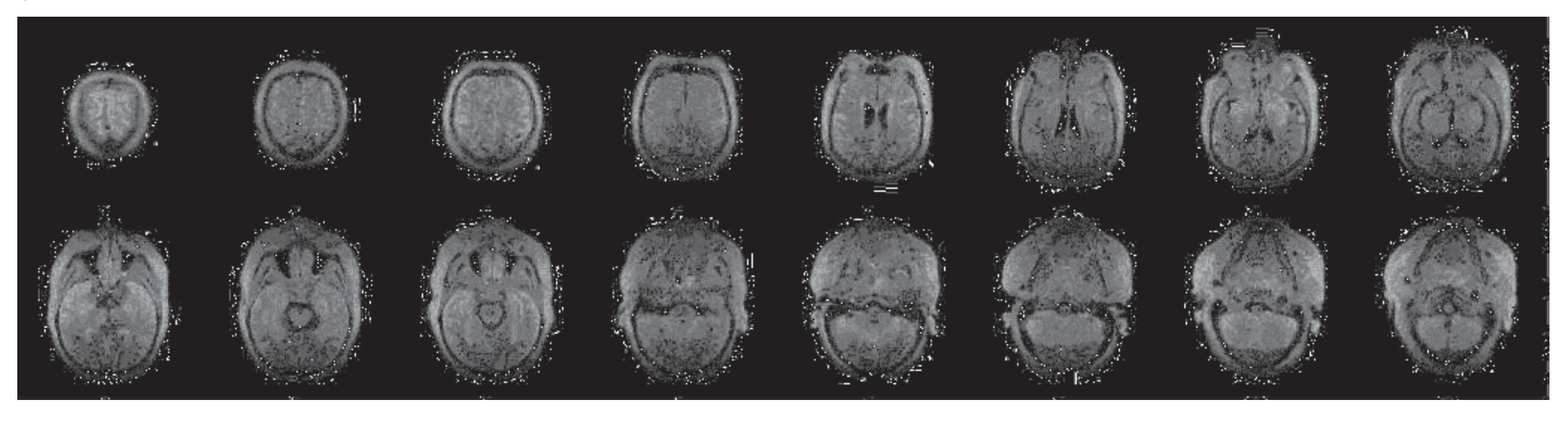
The head whose horizontal sections are depicted on pages 11-40 was imaged before sectioning. Parameters: 0.15 Tesla, matrix 256 x 256, field of view 25 cm, multi-slice, slice thickness 5 mm, 4 excitations, sequence: 5000/40. The contrast of these images is poor since they are highly proton-density (N(H)) weighted. The top panel presents the sagittal MRIs and specifies the planes of sectioning of the middle and lower panel. As can be seen the angle of sectioning of the two lower panels is about 45° tilted against the plane of sectioning for the anatomic slices. This was aimed to provide a more comprehensive view of the head.
**8**

Surface views of the brain which is shown in the subsequent pages. The most important gyri are delineated. The midsagittal views depict the brain with the stereotaxic space (ICL: intercommissural line, VCA: plane which is vertical to the intercommissural line at the level of the center of the anterior commissure).
**9**
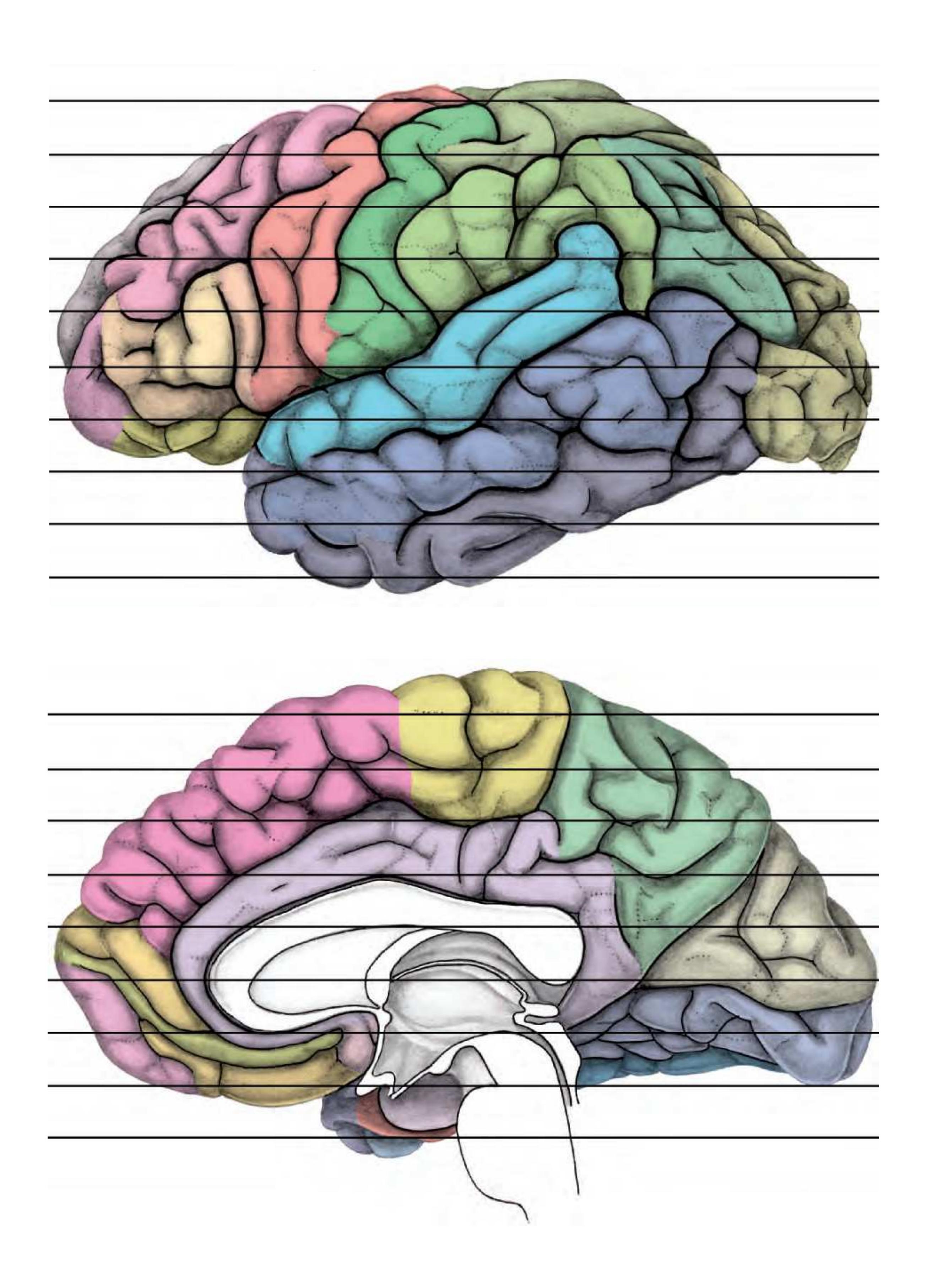
Surface views of the right hemisphere of the brain which has been sectioned in the horizontal plane as indicated. The drawing of the lateral aspect has been *mirror-imaged* in order to demonstrate the correspondence of section levels between convexity and midline structures.
**10**



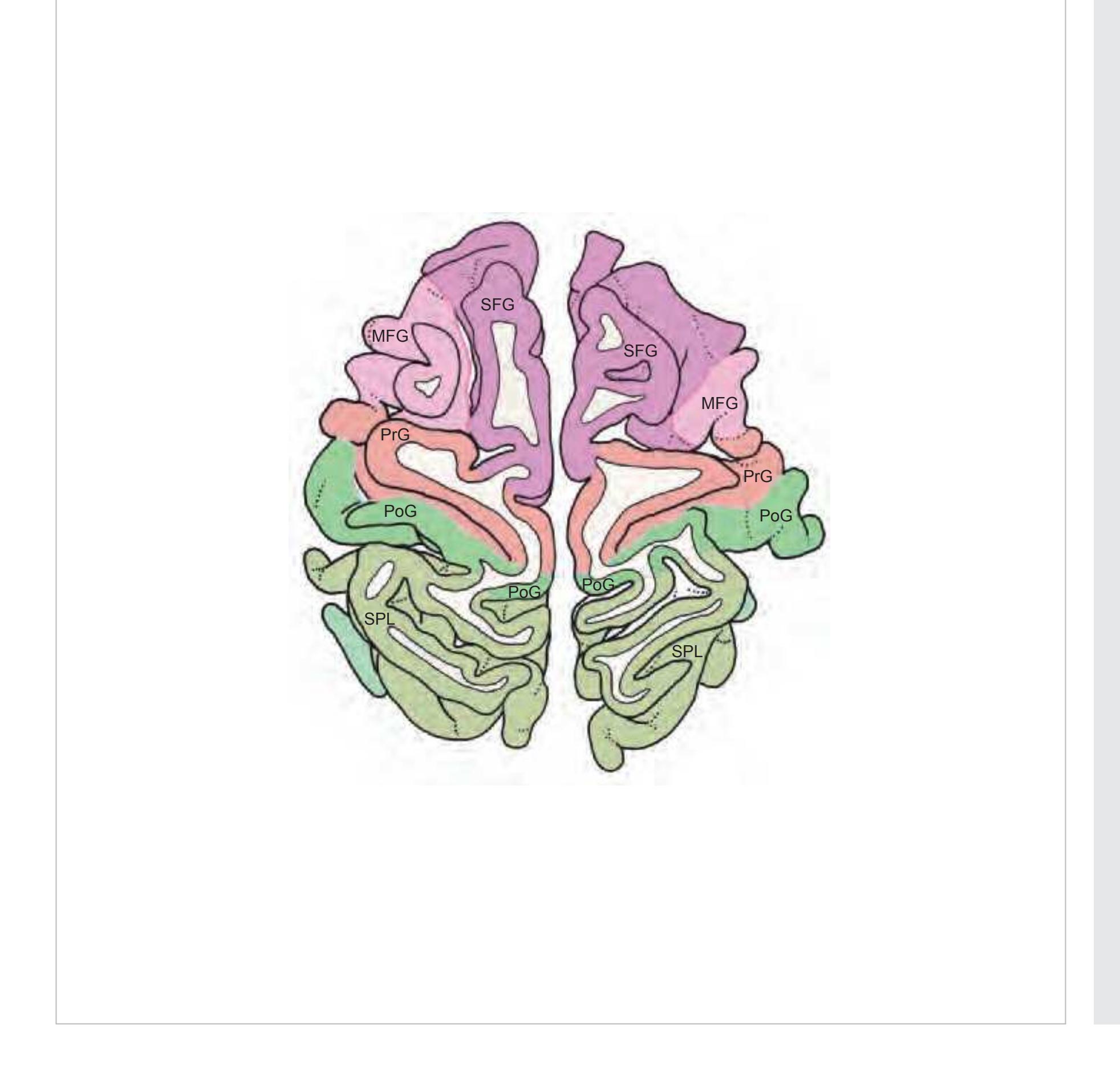
MFG middle frontal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
**11**





**12**

**13**





**14**

SPL superior parietal lobule

**15**




**16**

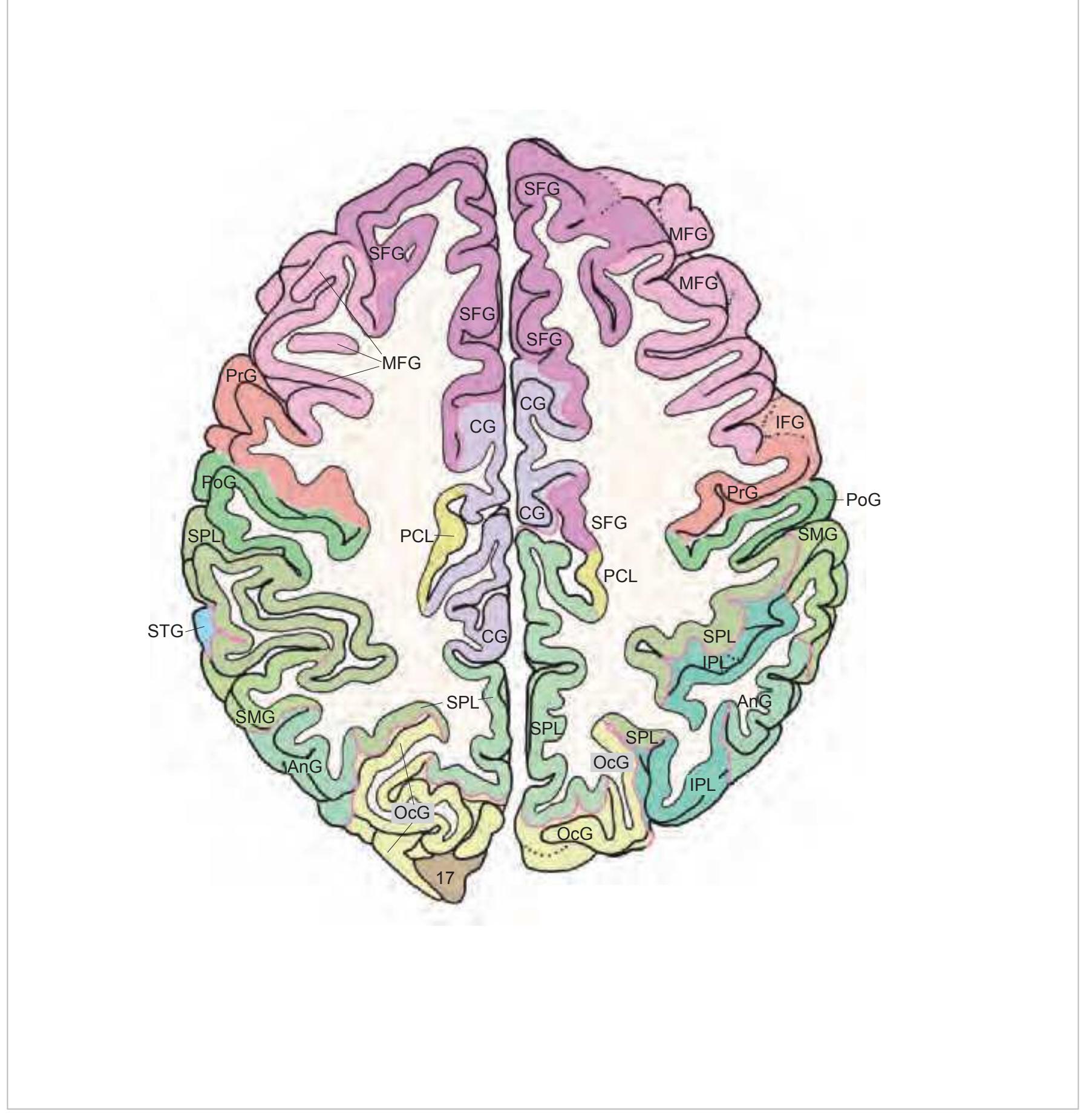

SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
**17**




**18**


IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IPL inferior parietal lobule LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri pcer posterior cerebral artery PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
**19**



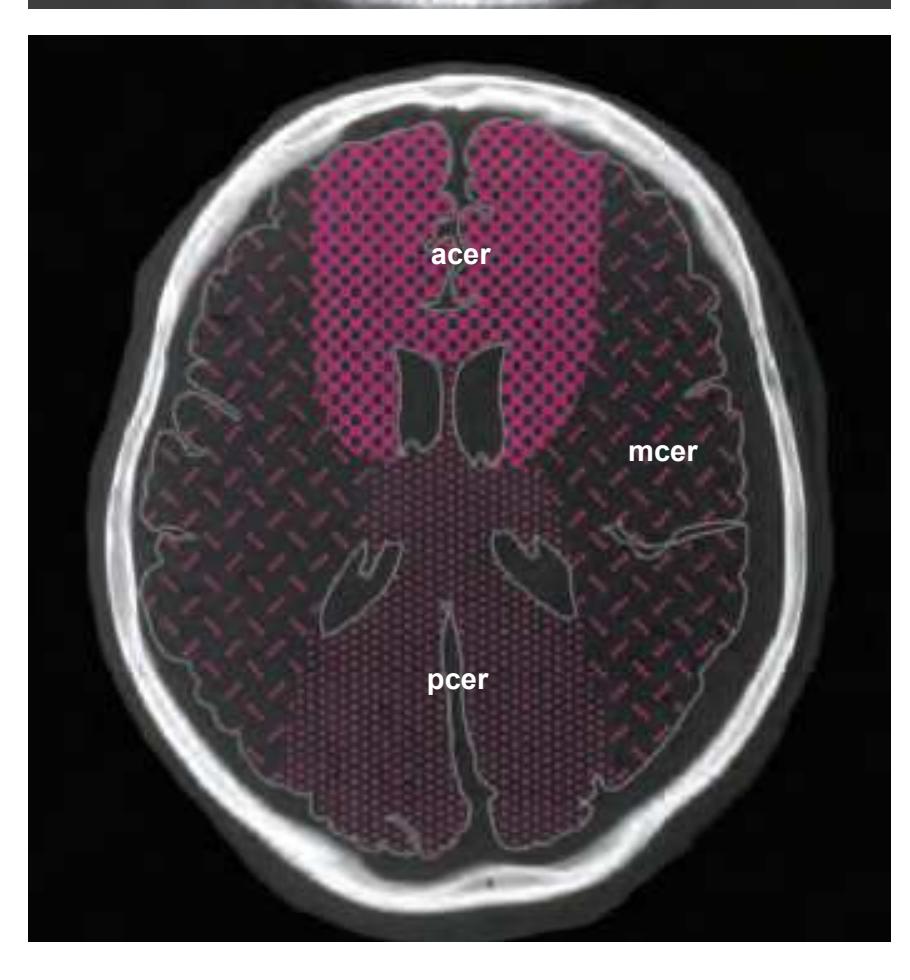


**20**



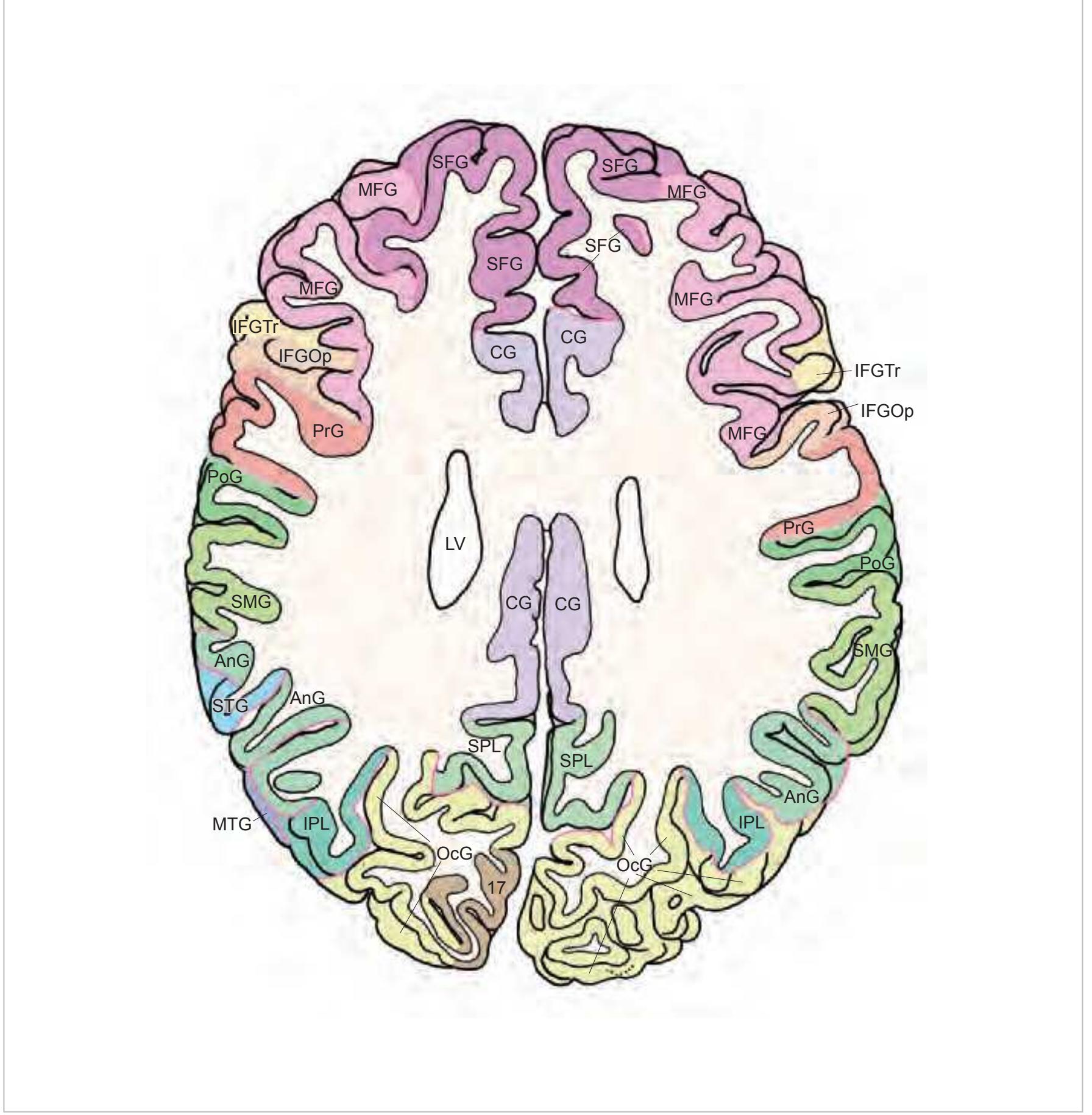
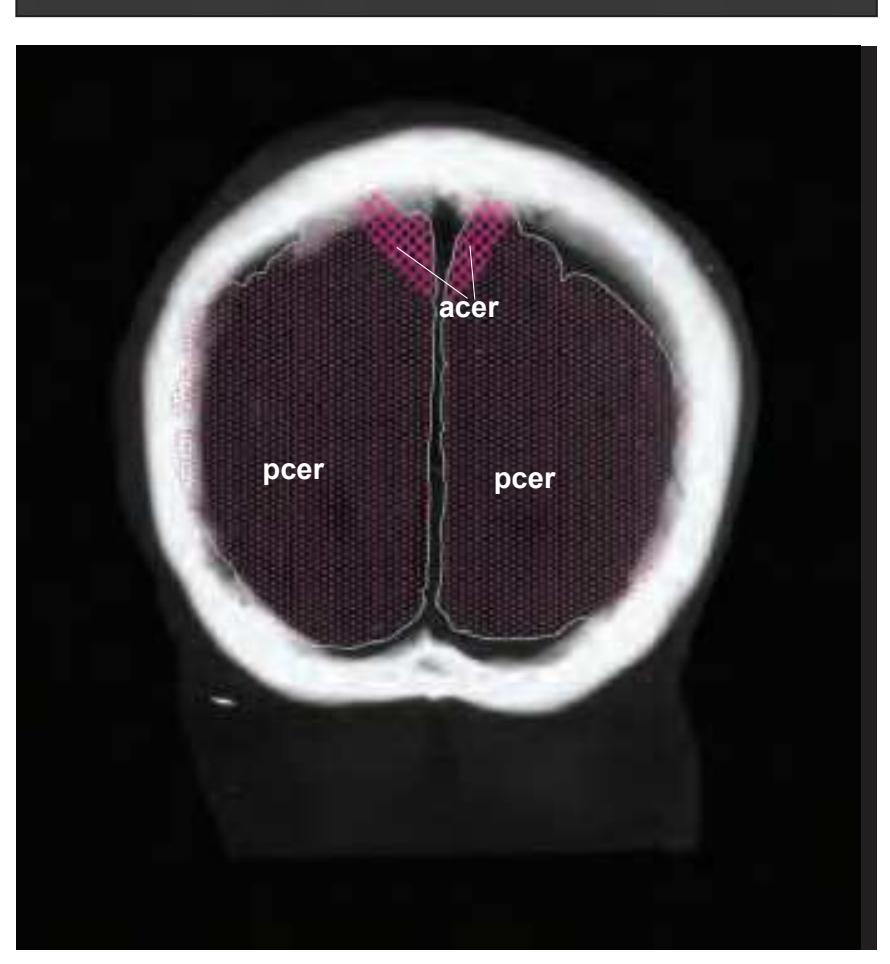
CG cingulate gyrus chpx choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle Cun cuneus FLV frontal horn of lateral ventricle fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum FOp frontal operculum fx fornix gcc genu of the corpus callosum HCd head of caudate nucleus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part Ins insula IPL inferior parietal lobule LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri OLV occipital horn of lateral ventricle pcer posterior cerebral artery PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale scc splenium of the corpus callosum SFG superior frontal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus sof superior occipitofrontal fasciculus st stria terminalis STG superior temporal gyrus TCd tail of caudate nucleus Th thalamus tsv thalamostriate vein TTG transverse temporal gyrus
3V third ventricle 17 striate area
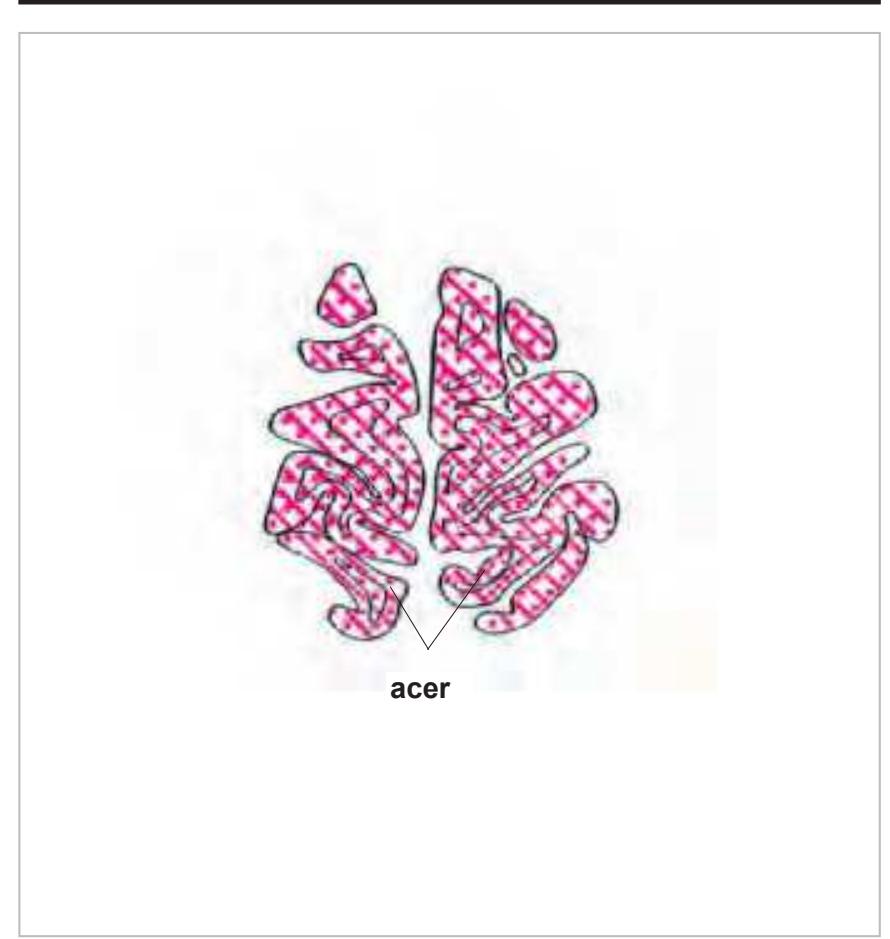
acer anterior cerebral artery
**21**



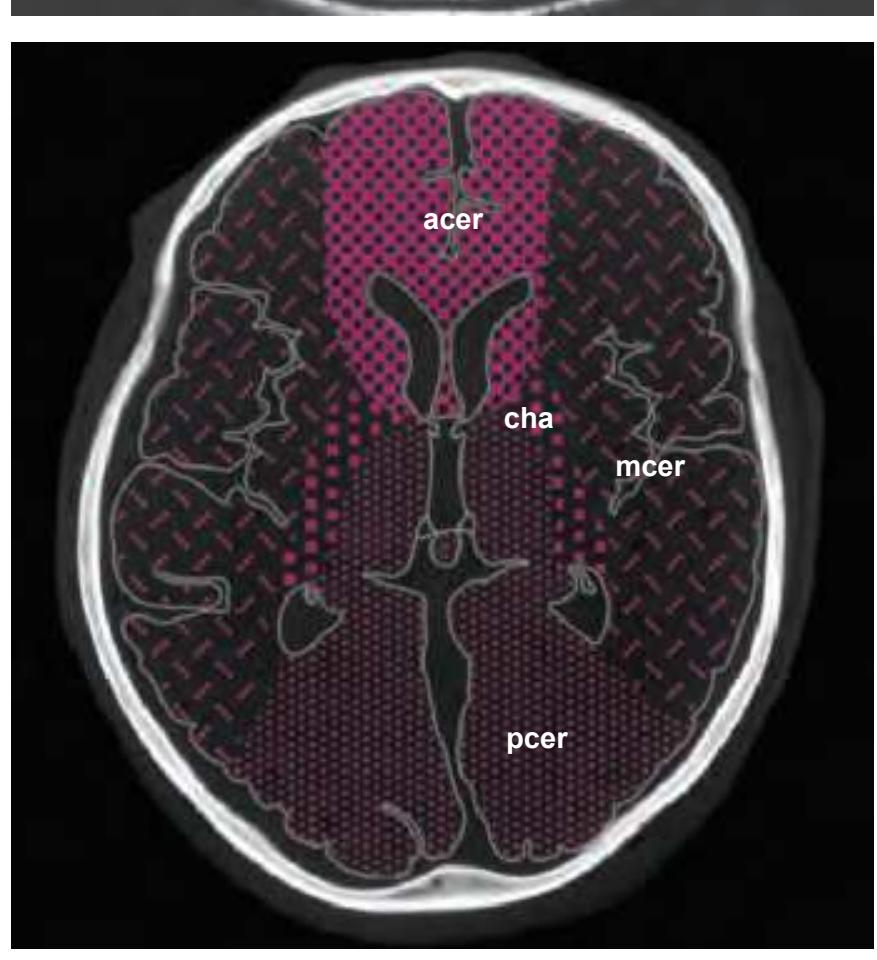


**22**


3V third ventricle 17 striate area acer anterior cerebral artery aic anterior limb of the internal capsule ATh anterior thalamic nucleus CG cingulate gyrus cha anterior choroidal artery chpx choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle Cl claustrum ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fi fimbria of the hippocampus FLV frontal horn of lateral ventricle FuG fusiform gyrus fx fornix gcc genu of the corpus callosum gic internal capsule, genu GP globus pallidus Hb habenula HCd head of caudate nucleus Hi hippocampus IFG inferior frontal gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri OLV occipital horn of lateral ventricle or optic radiation pcer posterior cerebral artery PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pi pineal gland pic posterior limb of the internal capsule PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pu putamen Pul pulvinar thalami SFG superior frontal gyrus sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis STG superior temporal gyrus TCd tail of caudate nucleus Th thalamus
TTG transverse temporal gyrus Ver vermis of cerebellum
**23**





**24**



sca superior cerebellar artery SN substantia nigra sta superficial temporal artery STG superior temporal gyrus stv superficial temporal vein Temp temporal bone TempM temporalis muscle tf temporal fascia
**25**

sta
10 mm
Temp
tv
pauv
ITG
OO
occ
sigs
lds
Occ
**26**



2n optic nerve 3n oculomotor nerve 4n trochlear nerve 4V fourth ventricle 5fr frontal nerve 5lac lacrimal nerve 5n trigeminal nerve acer anterior cerebral artery aica anterior inferior cerebellar artery Amg amygdala angv angular vein bas basilar artery cavs cavernous sinus CGal crista galli cha anterior choroidal artery PoCi pontocerebellar cistern CSCil corrugator supercilii muscle Ent entorhinal cortex FroN frontal bone, nasal part FroO frontal bone, orbital part Hi hippocampus ictd internal carotid artery ITG inferior temporal gyrus Lac lacrimal gland lds lambdoid suture LOTG lateral occipito-temporal gyrus LPal levator palpebrae superioris muscle LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery mmf middle meningeal artery, frontal branch MOTG medial occipito-temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus Occ occipital bone occ occipital artery, vein and nerve occs occipital sinus olf olfactory tract OO orbicularis oculi muscle OrG orbital gyrus ox optic chiasm PAM periamygdaloid cortex Par parietal bone pauv posterior auricular vein pcer posterior cerebral artery pcoma posterior communicating artery pica posterior inferior cerebellar artery Pit pituitary gland PoCi pontine cistern Pons pons sca superior cerebellar artery SG straight gyrus sigs sigmoid sinus SOb superior oblique muscle sophv superior ophthalmic vein Sph sphenoid bone sphps sphenoparietal sinus sphzg sphenozygomatic suture SRec superior rectus muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle sta superficial temporal artery sutra supratrochlear artery sutrn supratrochlear nerve sutrv supratrochlear vein Temp temporal bone TempM temporalis muscle
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
TP temporal pole tv temporal vein
**27**



**28**



10 (dorsal view)
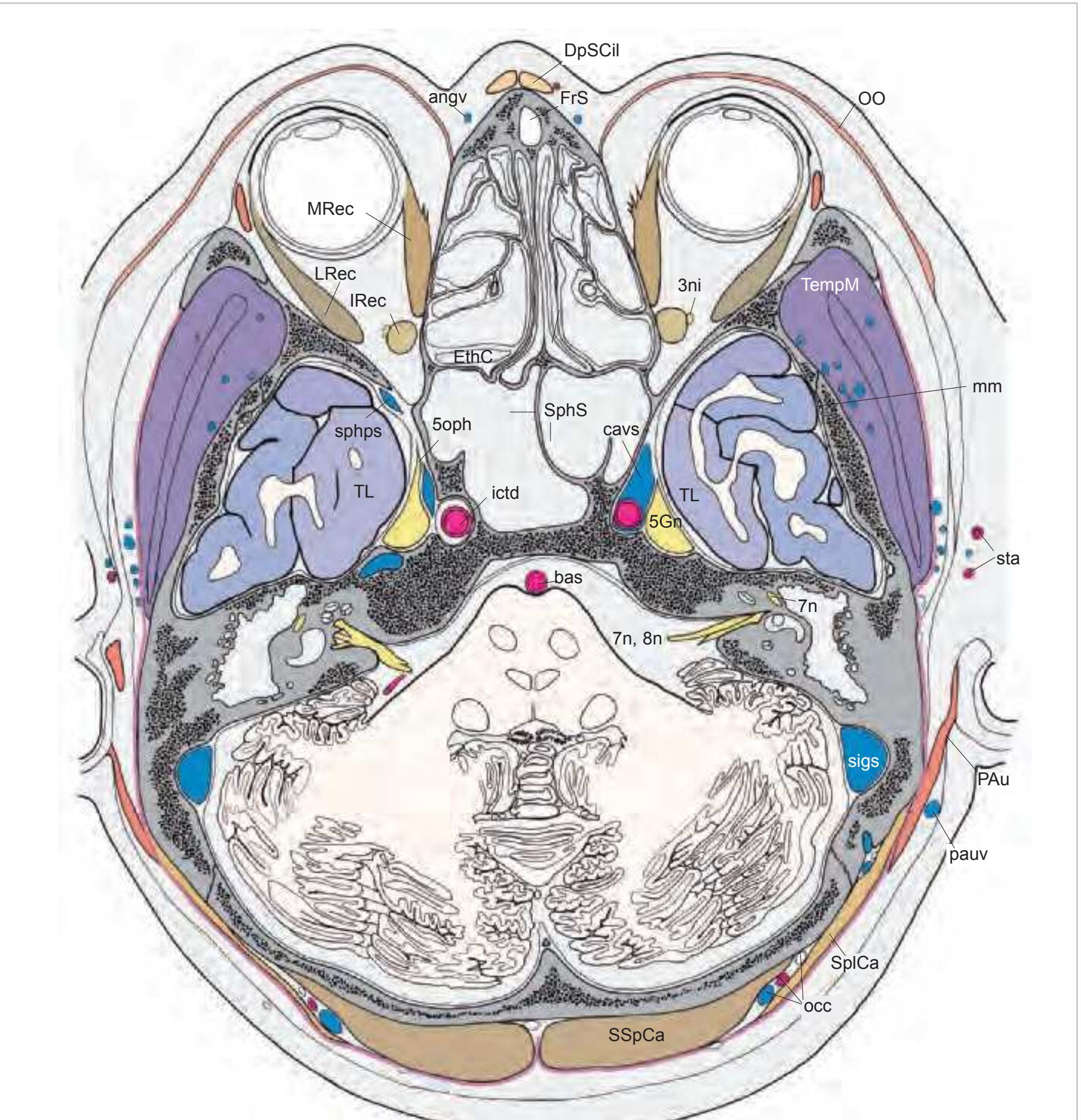
3ni oculomotor nerve (inferior branch) 4V fourth ventricle 5Gn trigeminal ganglion 5mx maxillary nerve 5oph ophthalmic nerve 7gp greater petrosal nerve 7n facial nerve 8n vestibulocochlear nerve anga angular artery angv angular vein bas basilar artery CAnT common anular tendon cavs cavernous sinus CilM ciliaris muscle DpSCil depressor supercilii muscle emi emissary vein EthC ethmoidal cell eye eyeball FrS frontal sinus gocn greater occipital nerve ictd internal carotid artery ipets inferior petrosal sinus IRec inferior rectus muscle lacv lacrimal vein LRec lateral rectus muscle mm middle meningeal artery MRec medial rectus muscle Na nasal bone nuf nuchal fascia Occ occipital bone occ occipital artery, vein and nerve ocm occipito-mastoid suture OO orbicularis oculi muscle PAu posterior auricular muscle pauv posterior auricular vein PoCi pontine cistern sca superior cerebellar artery sigs sigmoid sinus sophv superior ophthalmic vein Sph sphenoid bone sphps sphenoparietal sinus SphS sphenoid sinus SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle sta superficial temporal artery stv superficial temporal vein TempM temporalis muscle TempP temporal bone, petrosal part tf temporal fascia TL temporal lobe
tv temporal veins TyC tympanic cavity Zyg zygomatic bone
**29**





**30**


3ni oculomotor nerve (inferior branch)
(dorsal view) 11
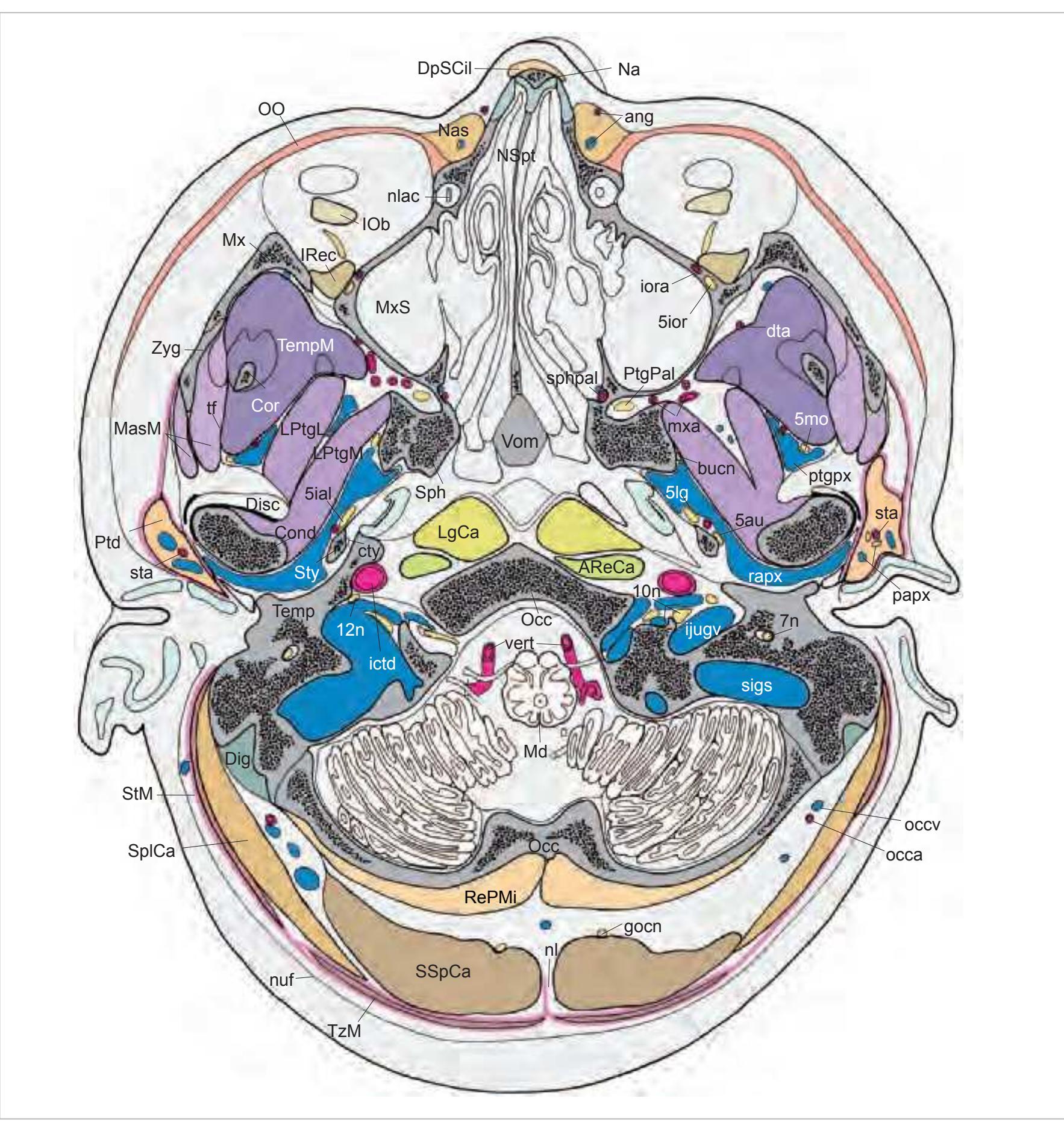
5au auriculotemporal nerve 5ial inferior alveolar nerve 5ior infraorbital nerve 5lg lingual nerve 5mo motor root of trigeminal nerve 7n facial nerve 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve ang angular artery and vein AReCa anterior rectus capitis muscle bucn buccal nerve Cond condylar process of mandible Cor coronoid process of the mandible cty chorda tympani Dig digastric muscle Disc articular disc of temporo-mandibular joint DpSCil depressor supercilii muscle dta deep temporal artery gocn greater occipital nerve ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein IOb inferior oblique muscle iora infraorbital artery IRec inferior rectus muscle LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LPtgL lateral pterygoid muscle, lateral belly LPtgM lateral pterygoid muscle, medial belly MasM masseter muscle Md medulla oblongata Mx maxilla mxa maxillary artery MxS maxillary sinus Na nasal bone Nas nasalis muscle nl nuchal ligament nlac nasolacrimal duct NSpt nasal septum nuf nuchal fascia Occ occipital bone occa occipital artery occv occipital vein OO orbicularis oculi muscle papx parotid plexus Ptd parotid gland PtgPal pterygopalatine ganglion ptgpx pterygoid plexus rapx retroarticular (venous) plexus RePMi rectus capitis posterior minor sigs sigmoid sinus Sph sphenoid bone sphpal sphenopalatine artery SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle sta superficial temporal artery StM sternomastoid muscle StT sternomastoid muscle, tendon Sty styloid process Temp temporal bone TempM temporalis muscle tf temporal fascia TzM trapezius muscle vert vertebral artery Vom vomer Zyg zygomatic bone
**31**

**32**



5ial inferior alveolar nerve
12 (dorsal view)
5ior infraorbital nerve 5lg lingual nerve 7n facial nerve 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve anga angular artery apala ascending palatine artery AReCa anterior rectus capitis muscle Atlas atlas AtOc atlanto-occipital joint bucn buccal nerve CAT cartilage of auditory tube cty chorda tympani DAx dens axis Dig digastric muscle dpala descending palatine artery dpc deep cervical artery and vein facv facial vein gocn greater occipital nerve ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein INaC inferior nasal concha iora infraorbital artery LAngO levator anguli oris muscle LeVePal levator veli palatini muscle LgCa longus capitis muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LLb levator labii superioris muscle LLbAN levator labii superioris alaeque nasi LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle LReCa lateral rectus capitis muscle Man mandible MasM masseter muscle MiZyg minor zygomaticus muscle MjAC major alar cartilage MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle MPtg medial pterygoid muscle Mx maxilla mxa maxillary artery Nas nasalis muscle nl nuchal ligament nuf nuchal fascia Occ occipital bone occa occipital artery OO orbicularis oculi muscle psa posterior superior alveolar artery psan posterior superior alveolar nerve Ptd parotid gland Ptg pterygoid process pvf prevertebral fascia RePMi rectus capitis posterior minor muscle RePMj rectus capitis posterior major muscle SalPh salpingopharyngeus muscle SCM superior constrictor of the pharynx SeC septal nasal cartilage SObCa superior oblique capitis muscle SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle sta superficial temporal artery StM sternomastoid muscle Sty styloid process StyPh stylopharyngeus muscle TempM temporalis muscle TeVePal tensor veli palatini muscle tfa transverse facial artery TzM trapezius muscle Uv uvula vert vertebral artery Vom vomer
Zyg zygomatic bone
**33**




**34**



13 (dorsal view)
5ior infraorbital nerve 5lg lingual nerve 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve apala ascending palatine artery Atlas atlas BucM buccinator muscle bucn buccal nerve cern2 cervical nerve 2 Dig digastric muscle dpc deep cervical artery and vein ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery facv facial vein gocn greater occipital nerve gpala greater palatine artery HPtg hamulus of the pterygoid bone ial inferior alveolar artery, vein, nerve iala inferior alveolar artery ialv inferior alveolar vein ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle ivvpx internal vertebral venous plexus LAngO levator anguli oris muscle LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LLb levator labii superioris muscle Man mandible MasM masseter muscle MiZyg minor zygomaticus muscle MjAC major alar cartilage MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle MPtg medial pterygoid muscle MScal middle scalenus muscle, insertion of levator scapulae muscle Mx maxilla Nas nasalis muscle nl nuchal ligament npal nasopalatine artery, incisive canal occa occipital artery occv occipital vein PalG palatine glands pau posterior auricular artery and vein Ptd parotid gland ptdd parotid duct
RePMj rectus capitis posterior major muscle rmv retromandibular vein SArS subarachnoid space SCM superior constrictor of the pharynx SeC septal nasal cartilage SpAx spinous process of axis Spinal spinal cord SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle StM sternomastoid muscle Sty styloid process StyGl styloglossus muscle StyHy stylohyoid muscle StyPh stylopharyngeus muscle TempM temporalis muscle TempT temporalis muscle, tendon TeVePal tensor veli palatini muscle TrPAt transverse process of the atlas
TzM trapezius muscle Uv uvula vert vertebral artery Vom vomer
**35**





**36**



5lg lingual nerve 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve all anterior longitudinal ligament apala ascending palatine artery aph ascending pharyngeal artery BucM buccinator muscle bucn buccal nerve Dig digastric muscle dpc deep cervical artery and vein ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery facv facial vein gocn greater occipital nerve gpala greater palatine artery HyGl hyoglossus muscle ial inferior alveolar artery, vein, nerve ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein IncC incisive canal w. nasopalatine artery InTrM intertransversarii muscles ISM interspinalis muscle LAngO levator anguli oris muscle LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LgsCe longissimus cervicis muscle LgsCeT longissimus cervicis muscle, tendon LSc levator scapulae muscle Ly lymph node Man mandible MasM masseter muscle MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle MPtg medial pterygoid muscle MScal middle scalenus muscle Mul multifidus muscle Mx maxilla MyHy mylohyoid muscle nuf nuchal fascia occa occipital artery OOr orbicularis oris muscle PalG palatine glands PalGl palatoglossus muscle Plat platysma Ptd parotid gland ptdd parotid duct rmv retromandibular vein S/MCM superior and middle constrictor of the pharynx ScalM scalenus muscle SCGn superior cervical ganglion SCM superior constrictor of the pharynx sln superior laryngeal nerve SM submandibular gland SpAx spinous process of axis SplCa splenius capitis muscle SplCe splenius cervicis muscle SpM spinalis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCe semispinalis cervicis muscle StM sternomastoid muscle StyGl styloglossus muscle StyHy stylohyoid muscle StyPh stylopharyngeus muscle Symp sympathetic trunk TzM trapezius muscle Uv uvula vert vertebral artery Vert3 third vertebra
Vert4 fourth vertebra
**37**


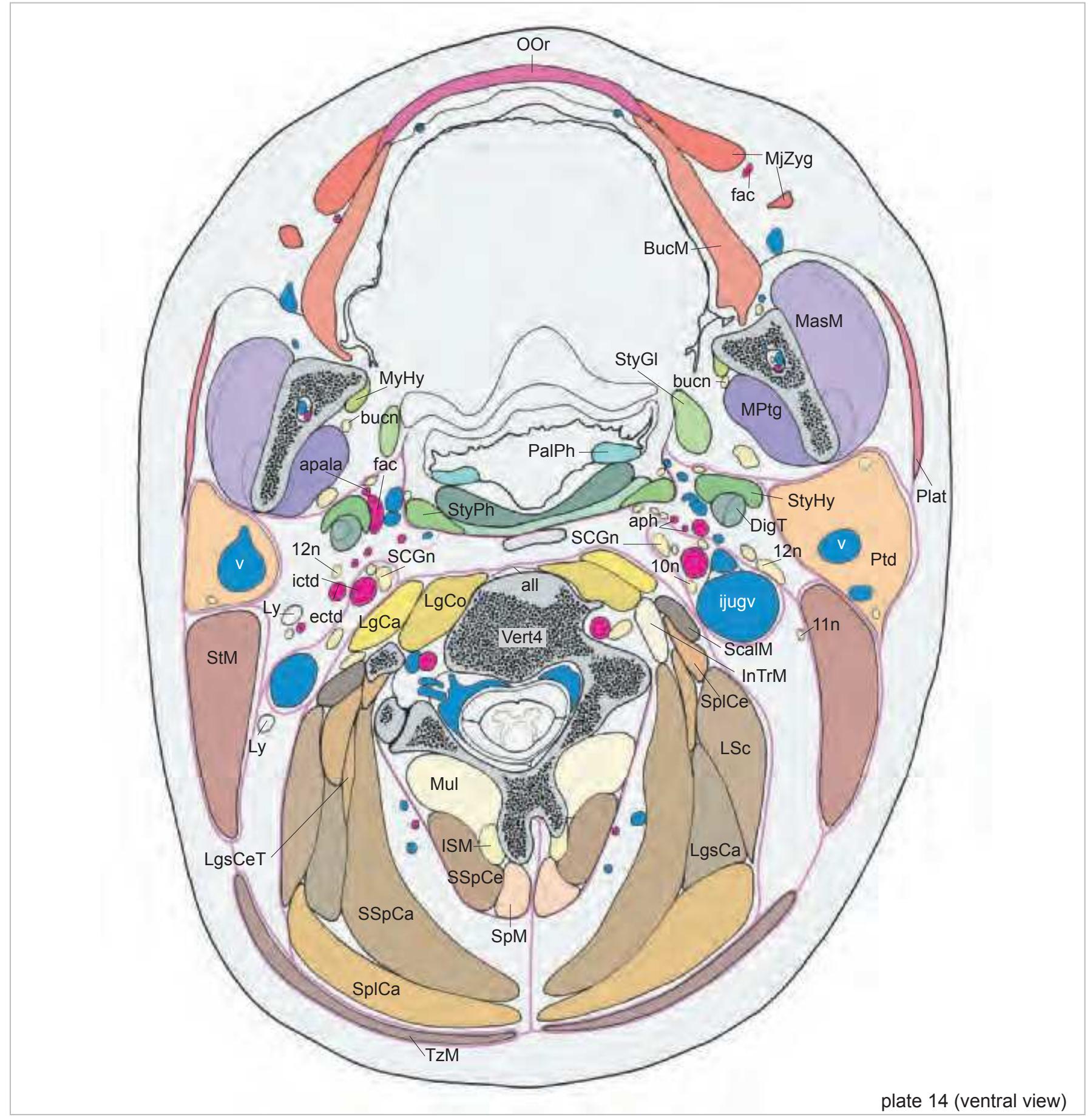
15
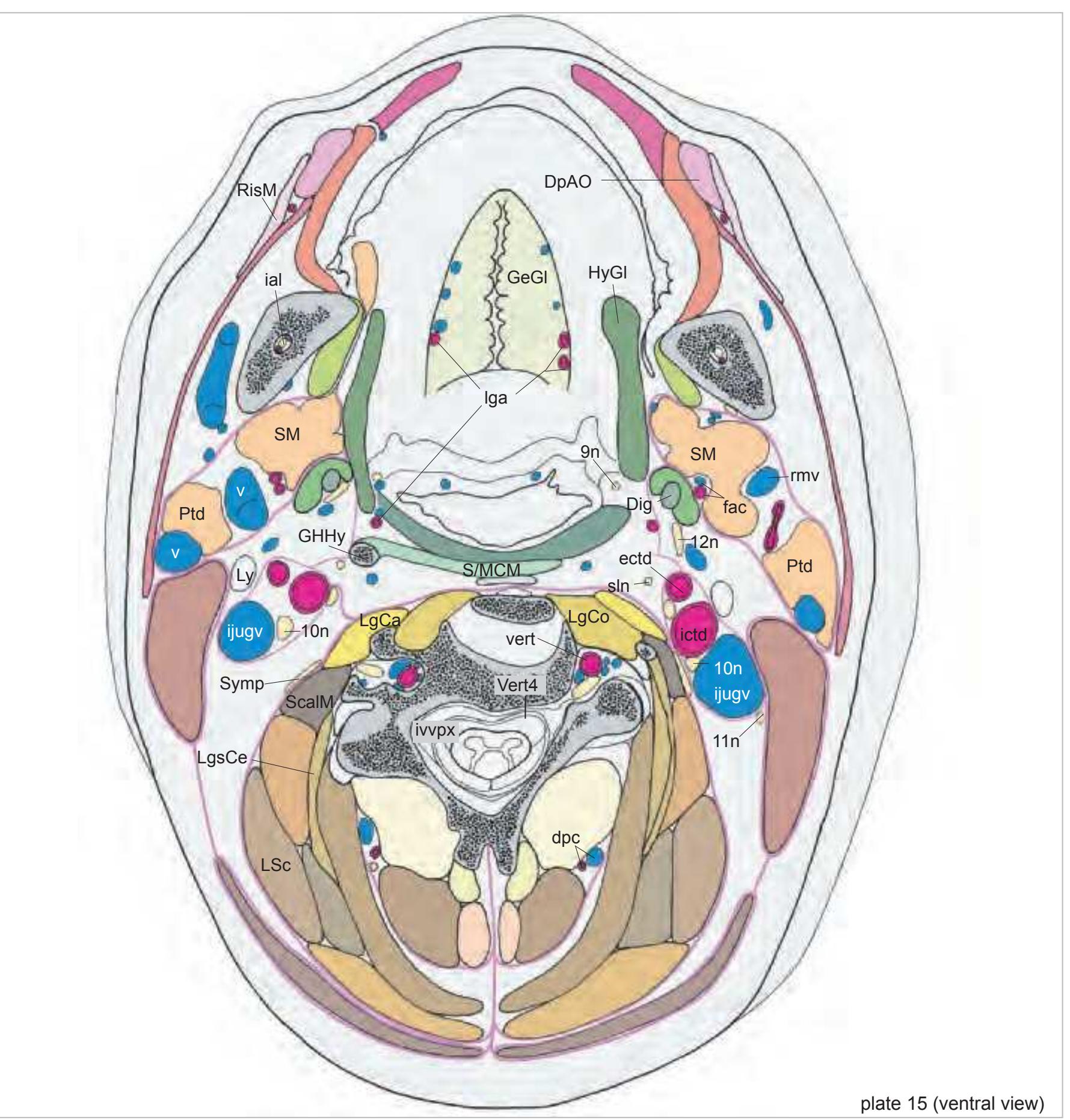
(ventral view) 9n glossopharyngeal nerve
10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve all anterior longitudinal ligament apala ascending palatine artery aph ascending pharyngeal artery BucM buccinator muscle bucn buccal nerve Dig digastric muscle DigT digastric muscle, tendon DpAO depressor anguli oris muscle dpc deep cervical artery and vein
ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery GeGl genioglossus muscle GHHy greater horn of hyoid bone
HyGl hyoglossus muscle ial inferior alveolar artery, vein, nerve
ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein InTrM intertransversarii muscles
ISM interspinalis muscle ivvpx internal vertebral venous plexus
lga lingual artery LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LgsCe longissimus cervicis muscle
LgsCeT longissimus cervicis muscle, tendon LSc levator scapulae muscle Ly lymph node MasM masseter muscle MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle MPtg medial pterygoid muscle
Mul multifidus muscle MyHy mylohyoid muscle OOr orbicularis oris muscle PalPh palatopharyngeus muscle Plat platysma
Ptd parotid gland RisM risorius muscle rmv retromandibular vein
S/MCM superior and middle constrictor of
the pharynx ScalM scalenus muscle SCGn superior cervical ganglion sln superior laryngeal nerve SM submandibular gland SplCa splenius capitis muscle SplCe splenius cervicis muscle SpM spinalis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCe semispinalis cervicis muscle
StM sternomastoid muscle StyGl styloglossus muscle StyHy stylohyoid muscle StyPh stylopharyngeus muscle Symp sympathetic trunk TzM trapezius muscle
v vein vert vertebral artery Vert4 fourth cervical vertebra
**38**



11n accessory nerve ancer ansa cervicalis
BucM buccinator muscle cctd common carotid artery cern cervical nerve cpx carotid plexus Dig digastric muscle DigT digastric muscle, tendon DpAO depressor anguli oris muscle dpc deep cervical artery and vein ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery (glandular branches) GeGl genioglossus muscle GHHy greater horn of hyoid bone HyGl hyoglossus muscle ICM inferior constrictor of the pharynx ictd internal carotid artery ijugv internal jugular vein ilab inferior labial artery and vein ISM interspinalis muscle Lg lingual gland lga lingual artery LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LgsCe longissimus cervicis muscle LSc levator scapulae muscle Ly lymph node Man mandible MCM middle constrictor of the pharynx Mul multifidus muscle MyHy mylohyoid muscle myhy mylohyoid nerve OOr orbicularis oris muscle Plat platysma RisM risorius muscle S/MCM superior and middle constrictor of the pharynx ScalM scalenus muscle SHThC superior horn of thyroid cartilage SL sublingual gland sln superior laryngeal nerve SM submandibular gland smd submandibular duct SplCa splenius capitis muscle SplCe splenius cervicis muscle SpM spinalis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCe semispinalis cervicis muscle sthy superior thyroid artery StM sternomastoid muscle StyHy stylohyoid muscle Symp sympathetic trunk ThHy thyrohyoid muscle ThHyMe thyrohyoid membrane TzM trapezius muscle v vein
Vert3 third cervical vertebra Vert4 fourth cervical vertebra Vert5 fifth cervical vertebra
**39**
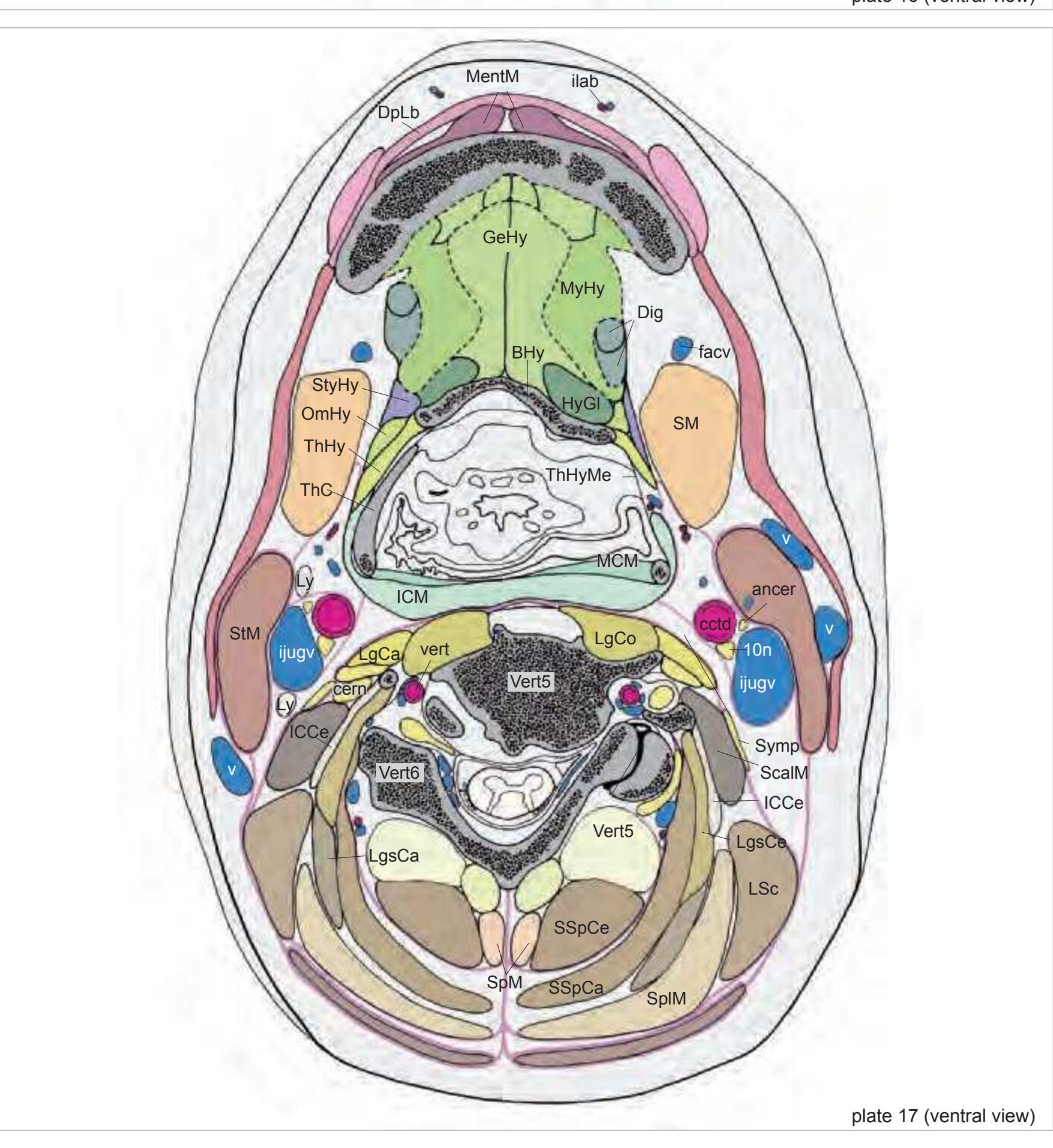
cern cervical nerve Dig digastric muscle DpAO depressor anguli oris muscle dpc deep cervical artery and vein DpLb depressor labii inferioris muscle fac facial artery (glandular branches) facv facial vein GeGl genioglossus muscle GeHy geniohyoid muscle GHHy greater horn of hyoid bone HyGl hyoglossus muscle ICCe iliocostalis cervicis muscle ICM inferior constrictor of the pharynx ijugv internal jugular vein ilab inferior labial artery and vein ISM interspinalis muscle lga lingual artery LgCa longus capitis muscle LgCo longus colli muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LgsCe longissimus cervicis muscle LSc levator scapulae muscle Ly lymph node
ManC mandibular canal MCM middle constrictor of the pharynx MentM mentalis muscle Mul multifidus muscle MyHy mylohyoid muscle
OmHy omohyoid muscle OOr orbicularis oris muscle Plat platysma
ScalM scalenus muscle SHThC superior horn of thyroid cartilage
SL sublingual gland sln superior laryngeal nerve SM submandibular gland smd submandibular duct SplCa splenius capitis muscle SplCe splenius cervicis muscle
SplM splenius capitis and cervicis muscle
SpM spinalis muscle
SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCe semispinalis cervicis muscle sthy superior thyroid artery StM sternomastoid muscle StyHy stylohyoid muscle Symp sympathetic trunk ThC thyroid cartilage ThHy thyrohyoid muscle ThHyMe thyrohyoid membrane
TrP4 transverse process of fourth vertebra
TzM trapezius muscle
v vein vert vertebral artery Vert4 fourth cervical vertebra Vert5 fifth cervical vertebra Vert6 sixth cervical vertebra

**40**
# 1.3 Coronal Atlas of the Brain in the Head
**41**
#### Sagittal plane:

#### y´- direction:

#### z´- direction:

# MR-images of the head shown on the following pages.
The head whose sections are depicted on the following pages was imaged in three orthgonal planes using the following parameters: 0.15 Tesla, matrix 256 x 256, field of view 25 cm, multislice, slice thickness 5 mm, 4 excitations, sequence: 5000/160. These heavy T2 weighted images highlight fluid-containing structures. Note that artificial fluid collections are visible in the nasal and paranasal cavities. The top panel presents the sagittal MRIs and specifies the planes of sectioning of the middle and lower panel. Orientation of these MRIs was based on the brainstem axis. Therefore the orientation of the coronal MRIs in the lower panel corresponds to the plane of cryo-sectioning of the head and direct comparisons can be made with photographs and diagrams of the following pages. The middle panel presents the horizontal MRIs from top to the bottom.
**42**

Surface views of the brain which is shown in the subsequent pages. The most important gyri are delineated. The midsagittal views depict the brain with the stereotaxic space.
**43**

Surface views of the left hemisphere of the brain which has been sectioned in the coronal plane (-20° angulation) as indicated. The drawing of the midsagittal view has been mirror-imaged in order to help identifying structures which lie in the same plane of sectioning with regard to the lateral and median view.
**44**
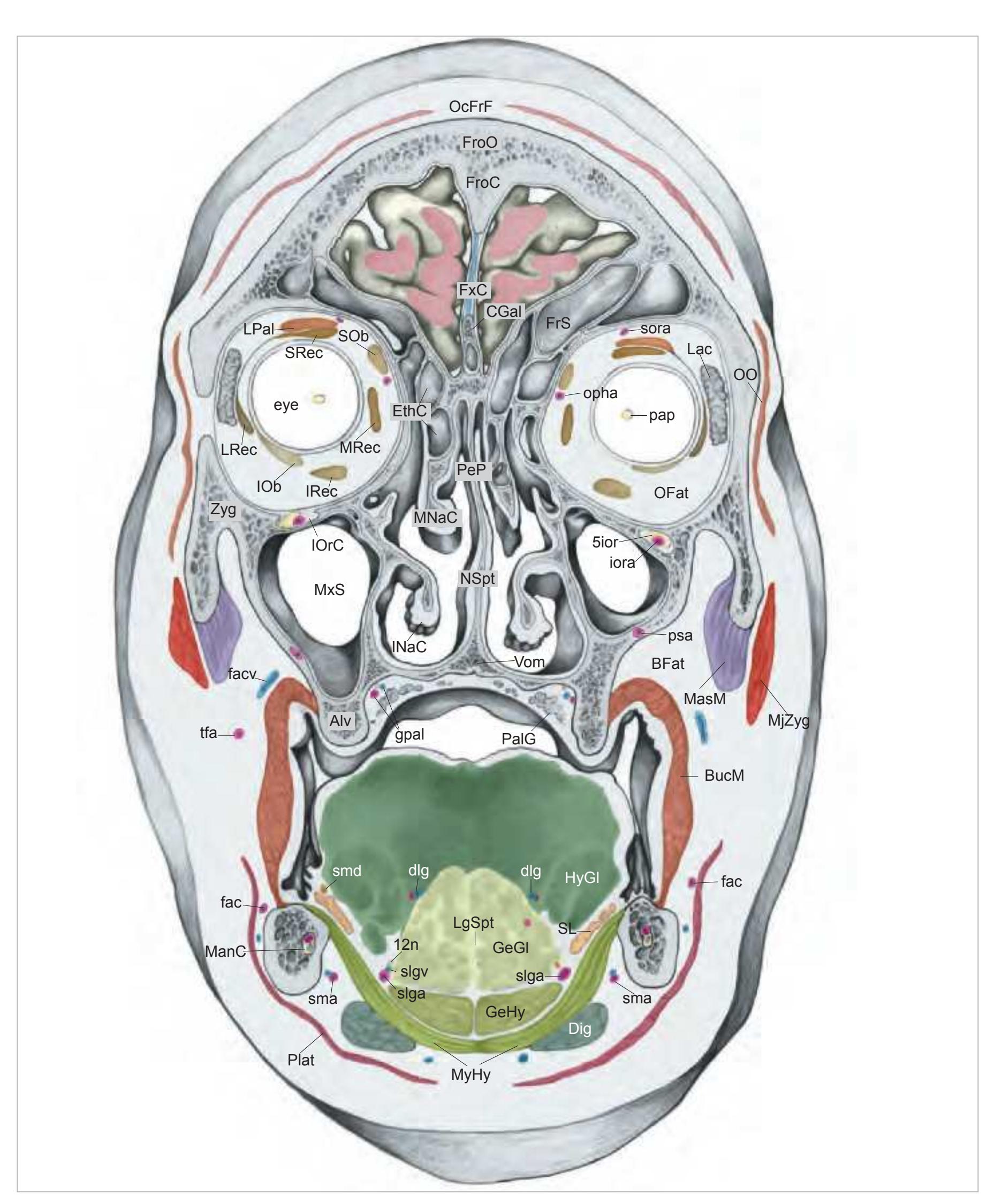
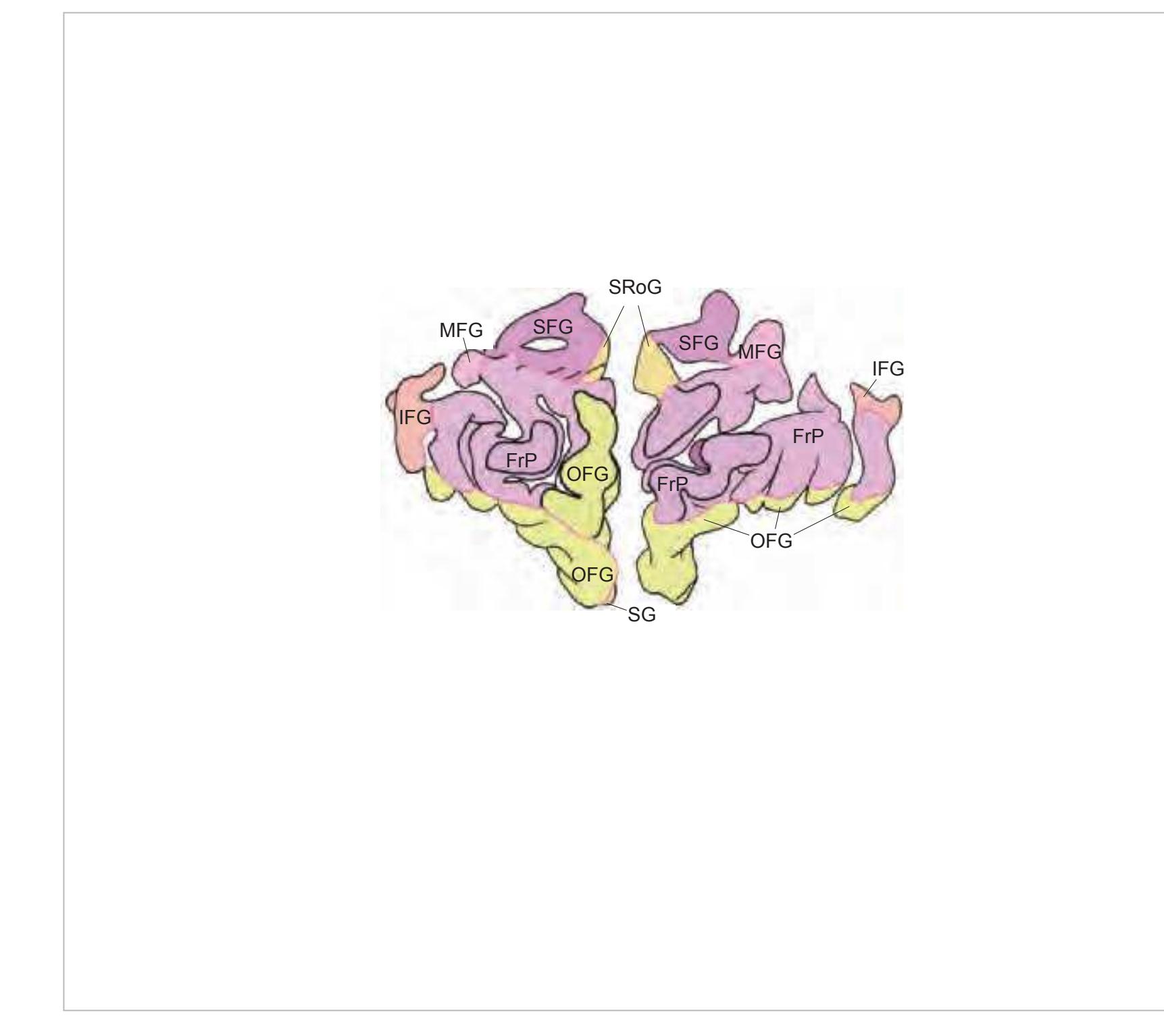
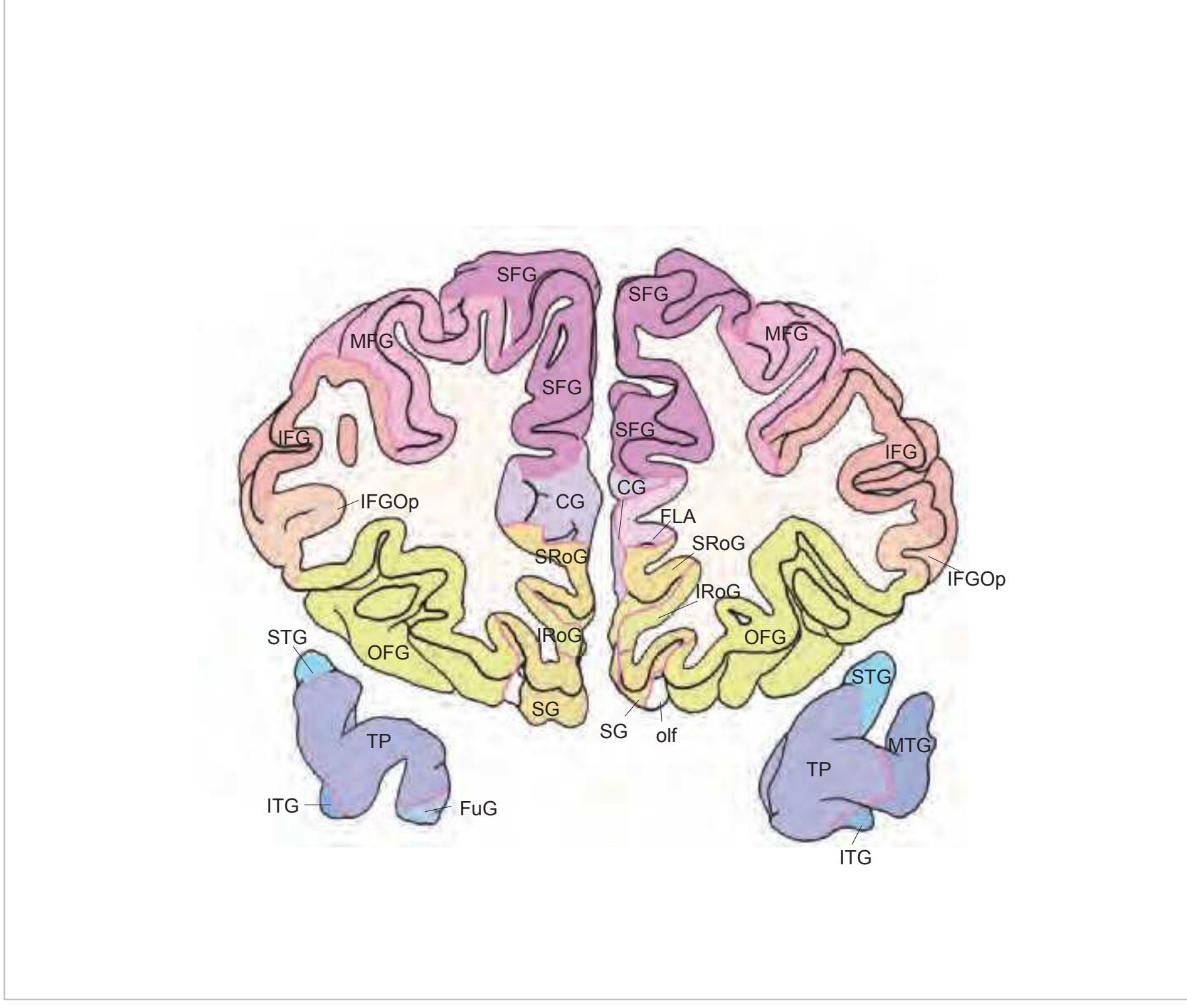
FrP frontopolar cortex FxC falx cerebri IFG inferior frontal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus OFG orbitofrontal gyri SFG superior frontal gyrus SG straight gyrus SRoG superior rostral gyrus
#### Peripheral structures:
5ior infraorbital nerve
12n hypoglossal nerve (lingual branch) Alv alveolar process of maxilla
BFat buccal fat pad
BucM buccinator muscle CGal crista galli
Dig digastric muscle, ant. belly
dlg deep lingual artery and vein EthC ethmoidal cell(s)
fac facial artery facv facial vein FroC frontal crest
FroO frontal bone, orbital part FrS frontal sinus
GeGl genioglossus muscle
GeHy geniohyoid muscle
gpal greater palatine artery, nerve, vein HyGl hyoglossus muscle
INaC inferior nasal concha IOb inferior oblique muscle iora infraorbital artery IOrC infraorbital canal IRec inferior rectus muscle Lac lacrimal gland
LgSpt lingual septum
LPal levator palpebrae superioris muscle
LRec lateral rectus muscle ManC mandibular canal MasM masseter muscle MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle MNaC middle nasal concha MRec medial rectus muscle
MxS maxillary sinus MyHy mylohyoid muscle NSpt nasal septum
OcFrF occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly
OFat orbital fat body OO orbicularis oculi muscle opha ophthalmic artery PalG palatine glands pap optic papilla PeP perpendicular plate
Plat platysma
psa posterior superior alveolar artery
SL sublingual gland slga sublingual artery slgv sublingual vein sma submental artery smd submandibular duct SOb superior oblique muscle sora supraorbital artery SRec superior rectus muscle tfa transverse facial artery
Vom vomer
Zyg zygomatic bone
**45**




**46**



(anterior view) 5
#### Intracranial structures:
acer anterior cerebral artery FrP frontopolar cortex FL frontal lobe IFG inferior frontal gyrus IRoG inferior rostral gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus OB olfactory bulb OFG orbitofrontal gyri SFG superior frontal gyrus SG straight gyrus SRoG superior rostral gyrus ssgs superior sagittal sinus
#### Peripheral structures:
2n optic nerve 5fr frontal nerve 5ior infraorbital nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve BMan body of mandible BucM buccinator muscle CGal crista galli cret central artery of retina
Dig digastric muscle, ant. belly dpala descending palatine artery dta deep temporal artery EthC ethmoidal cell fac facial artery facv facial vein
FroSq frontal bone, squamosal part
FrS frontal sinus GeGl genioglossus muscle GeHy geniohyoid muscle GPalF greater palatine foramen HyGl hyoglossus muscle
ial inferior alveolar artery, vein, nerve
iora infraorbital artery IOrC infraorbital canal IRec inferior rectus muscle lac lacrimal artery lga/lgv lingual artery / vein
LPal levator palpebrae superioris muscle
LRec lateral rectus muscle Ly submental lymph node ManC mandibular canal MasM masseter muscle MRec medial rectus muscle MxS maxillary sinus MyHy mylohyoid muscle
NSpt nasal septum
OcFrF occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly
OFat orbital fat body opha ophthalmic artery PalG palatine glands paln palatine nerve Plat platysma
psa posterior superior alveolar artery
ptdd parotid duct SL sublingual gland sma submental artery smd submandibular duct SOb superior oblique muscle SRec superior rectus muscle StHy sternohyoid muscle TempM temporalis muscle tfa transverse facial artery ZygA zygomatic arch
**47**






**48**


Lg lingual gland lga lingual artery lgv lingual vein LLPt lateral lamina of pterygoid process LPal levator palpebrae superioris muscle LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle LRec lateral rectus muscle Man mandible ManC mandibular canal MasM masseter muscle MLPt medial lamina of pterygoid process MPtg medial pterygoid muscle MRec medial rectus muscle mxa maxillary artery MxS maxillary sinus myhy mylohyoid nerve OmHy omohyoid muscle opha ophthalmic artery ophv ophthalmic vein Plat platysma pna posterior nasal artery ptdd parotid duct PtgPal pterygopalatine ganglion PtPF pterygopalatine fossa shl stylohyoid ligament smd submandibular duct SM submandibular gland SOb superior oblique muscle SPal soft palate staf superior temporal a., frontal branch
Remainder explained in Index of Abbreviations
**49**





**50**



acer anterior cerebral artery CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FLA frontal limbic area
FLV frontal horn of lateral ventricle
FuG fusiform gyrus IFG inferior frontal gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
IRoG inferior rostral gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OFG orbitofrontal gyri PTe planum temporale rcc rostrum of corpus callosum
SFG superior frontal gyrus SG straight gyrus SRoG superior rostral gyrus ssgs superior sagittal sinus STG superior temporal gyrus
TP temporal pole
# Peripheral structures:
2n optic nerve 3n oculomotor nerve 4n trochlear nerve 5ial inferior alveolar nerve 5lg lingual nerve 5mx maxillary nerve
6n abducens nerve or its root 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve AryE aryepiglotticus muscle Aud auditory tube
cavs cavernous sinus Dig digastric muscle, post belly
EGl epiglottis fac facial artery facv facial vein Hyoid hyoid bone
iala inferior alveolar artery ictd internal carotid artery inav internal nasal vein lga lingual artery lgv lingual vein
LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle
LeVePal levator veli palatini muscle
MasM masseter muscle
MCM middle constrictor of the pharynx mmf middle meningeal artery, frontal branch
MPtg medial pterygoid muscle mxa maxillary artery myhy mylohyoid nerve
OmHy omohyoid muscle PalPh palatopharyngeus muscle PalT palatine tonsil phar pharyngeal branches PirR piriform recess
ptdd parotid duct PtgC pterygoid canal ptgpx pterygoid plexus shl stylohyoid ligament SM submandibular gland smv submental vein
sphml sphenomandibular ligament staf superior temporal a., frontal branch
sthy superior thyroid artery StyGl styloglossus muscle
**51**





**52**



Ac accumbens nucleus acer anterior cerebral artery AG ambiens gyrus AO anterior olfactory nucleus CG cingulate gyrus cha anterior choroidal artery Cl claustrum DB nucleus of the diagonal band Ent entorhinal cortex FLA frontal limbic area FuG fusiform gyrus ic internal capsule IFG inferior frontal gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
InfS infundibular stalk Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus ox optic chiasm PTe planum temporale Pir piriform cortex Pit pituitary gland PTG paraterminal gyrus Pu putamen SCA subcallosal area SFG superior frontal gyrus SG straight gyrus
SLG semilunar gyrus SptP septum pellucidum STG superior temporal gyrus Tu olfactory tubercle
Un uncus
# Peripheral structures:
3n oculomotor nerve 5Gn trigeminal ganglion 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve aph ascending pharyngeal artery cavs cavernous sinus cctd common carotid artery Cond condylar process of mandible Dig digastric muscle, post belly DS diaphragma sellae ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery facv facial vein ICM inferior constrictor of the pharynx ictd internal carotid artery LgCa longus capitis muscle LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle LeVePal levator veli palatini muscle MCM middle constrictor of the pharynx mm middle meningeal artery mxa maxillary artery mxv maxillary vein occa occipital artery Otic otic ganglion
paua posterior auricular artery phar pharyngeal branches PhRe pharyngeal recess Ptd patotid gland rmv retromandibular vein smv submental vein SphS sphenoid sinus
**53**





**54**



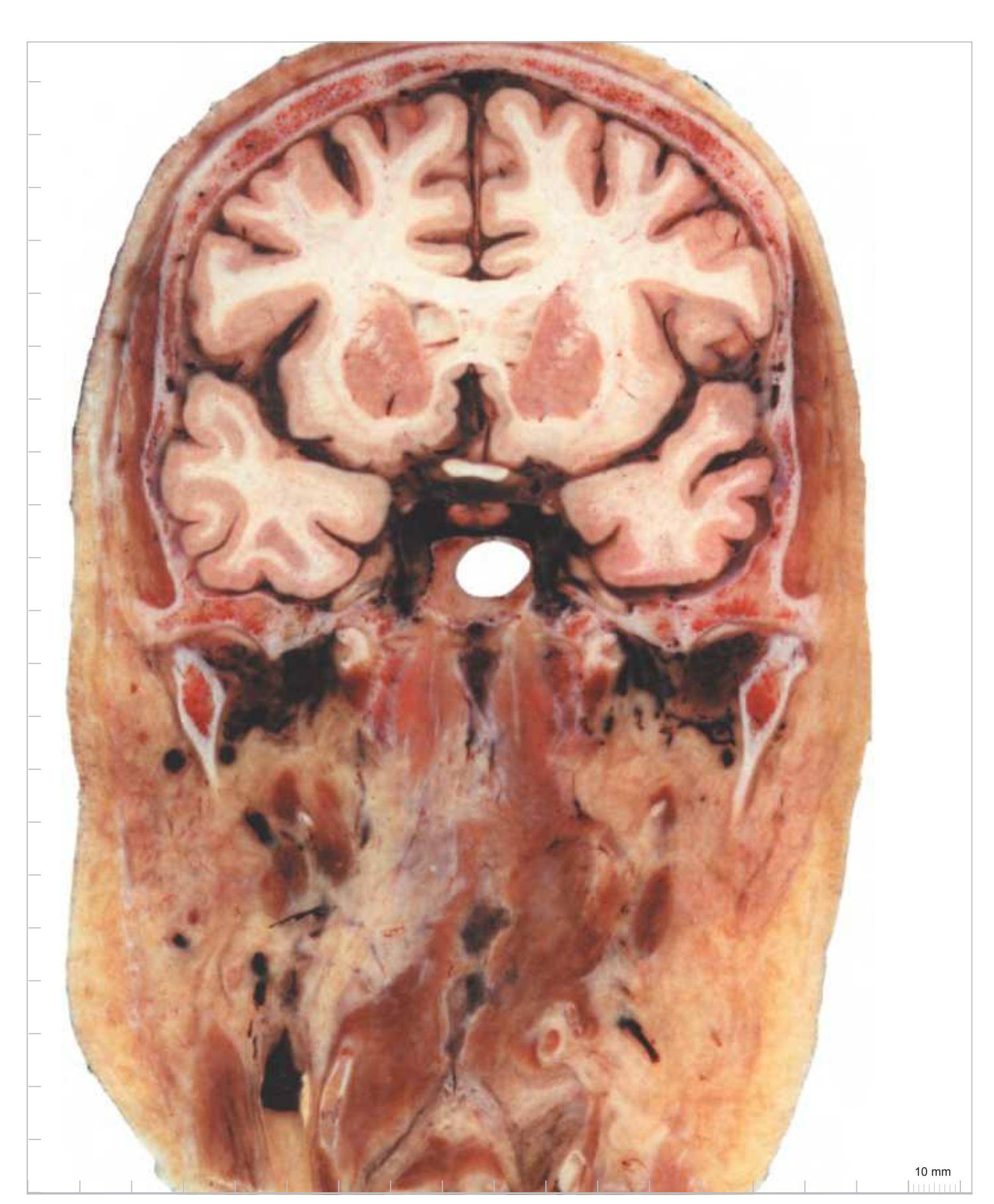
3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure acer anterior cerebral artery Amg amygdala ATh anterior thalamic nucleus cc corpus callosum ce central fissure
CG cingulate gyrus cha anterior choroidal artery Cl claustrum
CLV central part of lateral ventricle cp cerebral peduncle EGP external globus pallidus Ent entorhinal cortex FLA frontal limbic area FuG fusiform gyrus fx fornix
HCd head of caudate nucleus Hi hippocampus ic internal capsule
IFG inferior frontal gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
IGP internal globus pallidus
Ins insula
ipets inferior petrosal sinus IPF interpeduncular fossa isgs inferior sagittal sinus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MB mammillary body mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus opt optic tract
pcer posterior cerebral artery PoCi pontine cistern PoG postcentral gyrus PPo planum polare PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pu putamen
S subiculum SB striatal cell bridges sca superior cerebellar artery SFG superior frontal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TCd tail of caudate nucleus TL temporal lobe
TL
temporal lobe
TLV
temporal horn of l
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
TTG transverse temporal gyri Un uncus
# Peripheral structures:
3n oculomotor nerve or its root 5n trigeminal nerve 7gp greater petrosal nerve
7n facial nerve
9,10,11n glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves
aaua anterior auricular artery ACeIT anterior cervical intertransversarii muscles
ancer ansa cervicalis cctd common carotid artery cern2 cervical nerve 2 cerpx cervical plexus ejugv external jugular vein Dig digastric muscle ictd internal carotid artery
**55**




**56**



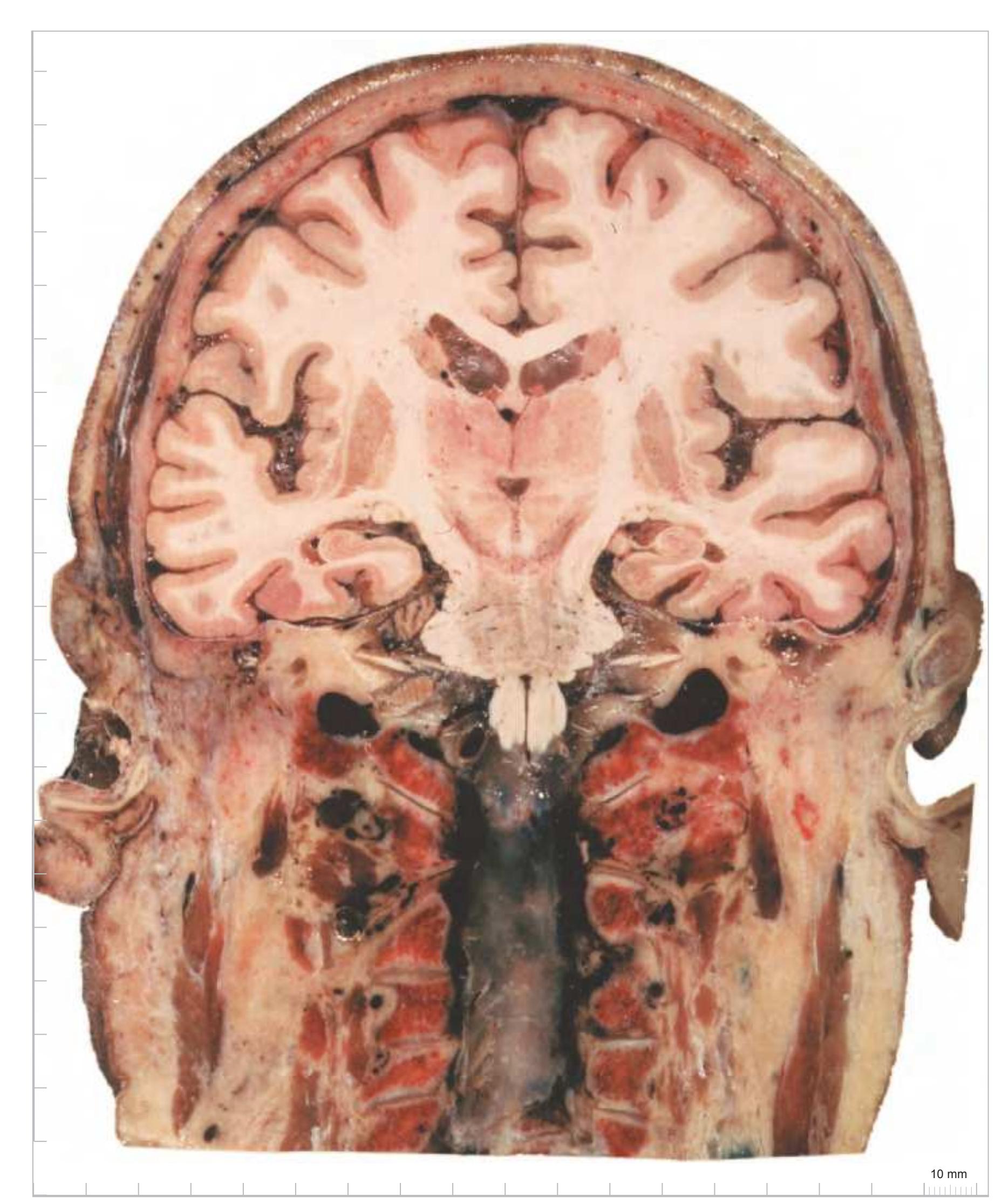
3V third ventricle acer anterior cerebral artery aica anterior inferior cerebellar artery Amg amygdala ATh anterior thalamic nucleus bfx body of fornix cc corpus callosum CG cingulate gyrus CH cerebellar hemisphere cha anterior choroidal artery chpx choroid plexus of the lat. ventricle Cl claustrum CLV central part of lateral ventricle CM centromedian thalamic nucleus cp cerebral peduncle dip diploic vein DSF dorsal superficial nucleus Ent entorhinal cortex FLA frontal limbic area FuG fusiform gyrus GP globus pallidus Hi hippocampus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula IO inferior olive isgs inferior sagittal sinus ITG inferior temporal gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery mcp middle cerebellar peduncle MD mediodorsal thalamic nucleus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
opt optic tract
ic internal capsule IFG inferior frontal gyrus
pcer posterior cerebral artery
pica posterior inferior cerebellar artery
PoG postcentral gyrus PPo planum polare PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pu putamen py pyramidal tract R red nucleus
Rt reticular thalamic nucleus S subiculum SB striatal cell bridges sca superior cerebellar artery SCC semicircular canals SFG superior frontal gyrus sigs sigmoid sinus SN substantia nigra spets superior petrosal sinus ssgs superior sagittal sinus STG superior temporal gyrus STh subthalamic nucleus TCb tentorium cerebelli TCd tail of caudate nucleus TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle TTG transverse temporal gyrus vert vertebral artery
**Peripheral structures:**
AtOc atlanto-occipital joint ijugv internal jugular vein, bulbus
VL ventral lateral thalamic nucleus
vr ventral root
**57**





**58**



3V third ventricle 4V fourth ventricle acer anterior cerebral artery argr arachnoid granulations BCd body of caudate nucleus bfx body of fornix cc corpus callosum CG cingulate gyrus CH cerebellar hemisphere cha anterior choroidal artery Ent entorhinal cortex
FuG fusiform gyrus fx fornix
Hi hippocampus icv internal cerebral vein
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
GrCi great (cerebellomedullary) cistern
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus LV lateral ventricle mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus occs occipital sinus
OcG occipital gyri
pcer posterior cerebral artery PCL paracentral lobule Pi pineal gland PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pul pulvinar thalami QP quadrigeminal plate Rt reticular thalamic nucleus S subiculum
SB striatal cell bridges sca superior cerebellar artery scc splenium of the corpus callosum SFG superior frontal gyrus
sigs sigmoid sinus
scp superior cerebellar peduncle SMV superior medullary velum st stria terminalis
STG superior temporal gyrus TCb tentorium cerebelli TCd tail of caudate nucleus Tec tectum of midbrain
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tsv thalamostriate vein TTG transverse temporal gyrus
Ver vermis of cerebellum
# Peripheral structures:
Atlas atlas Axis axis
emi emissary vein
IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle ivvpx internal vertebral venous plexus LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LSc levator scapulae muscle
mmp middle meningeal artery, parietal branch
Mul multifidus muscle occa occipital artery pauv posterior auricular vein ScalM scalenus muscle
SObCa superior oblique capitis muscle SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle StM sternomastoid muscle
**59**




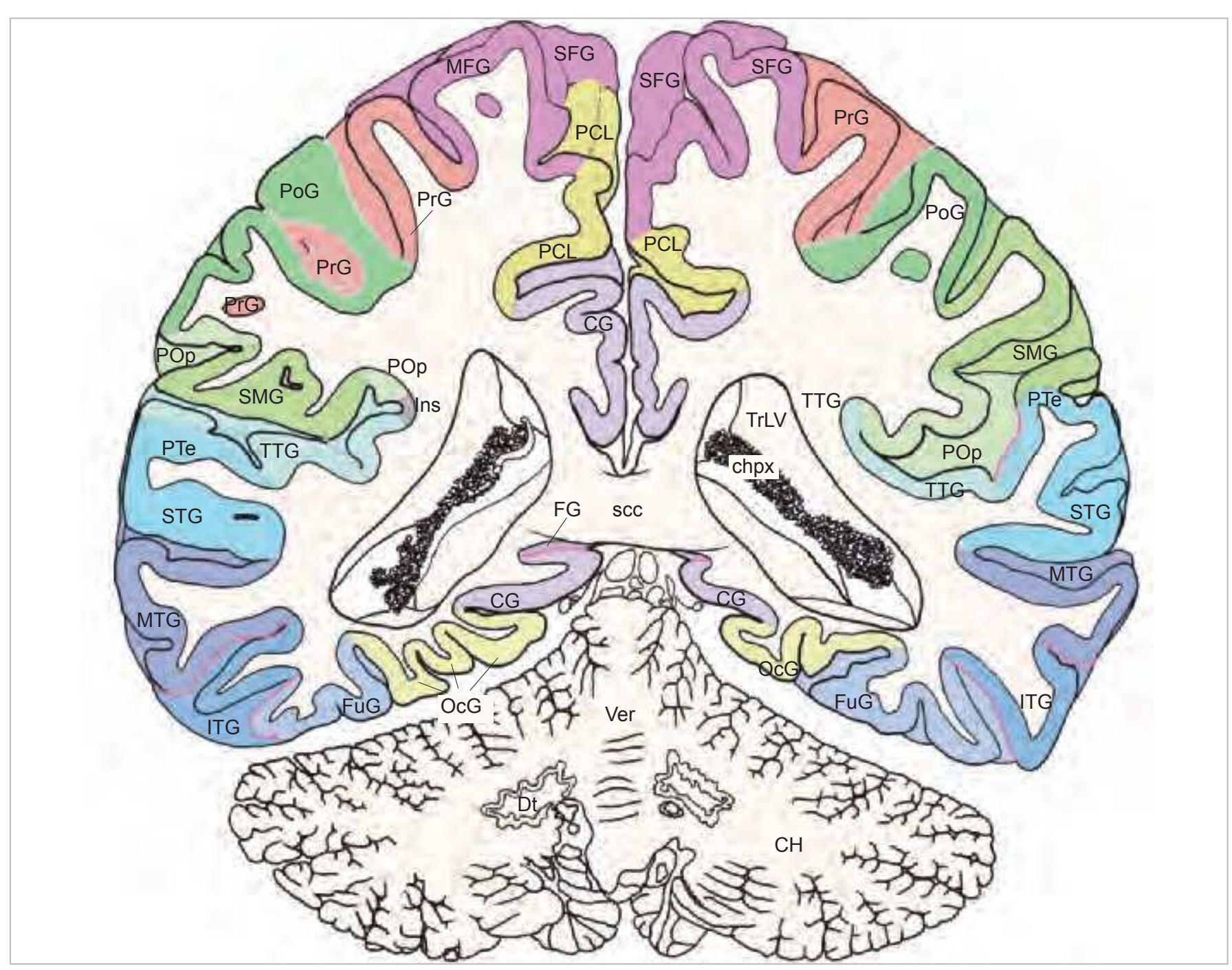
**60**

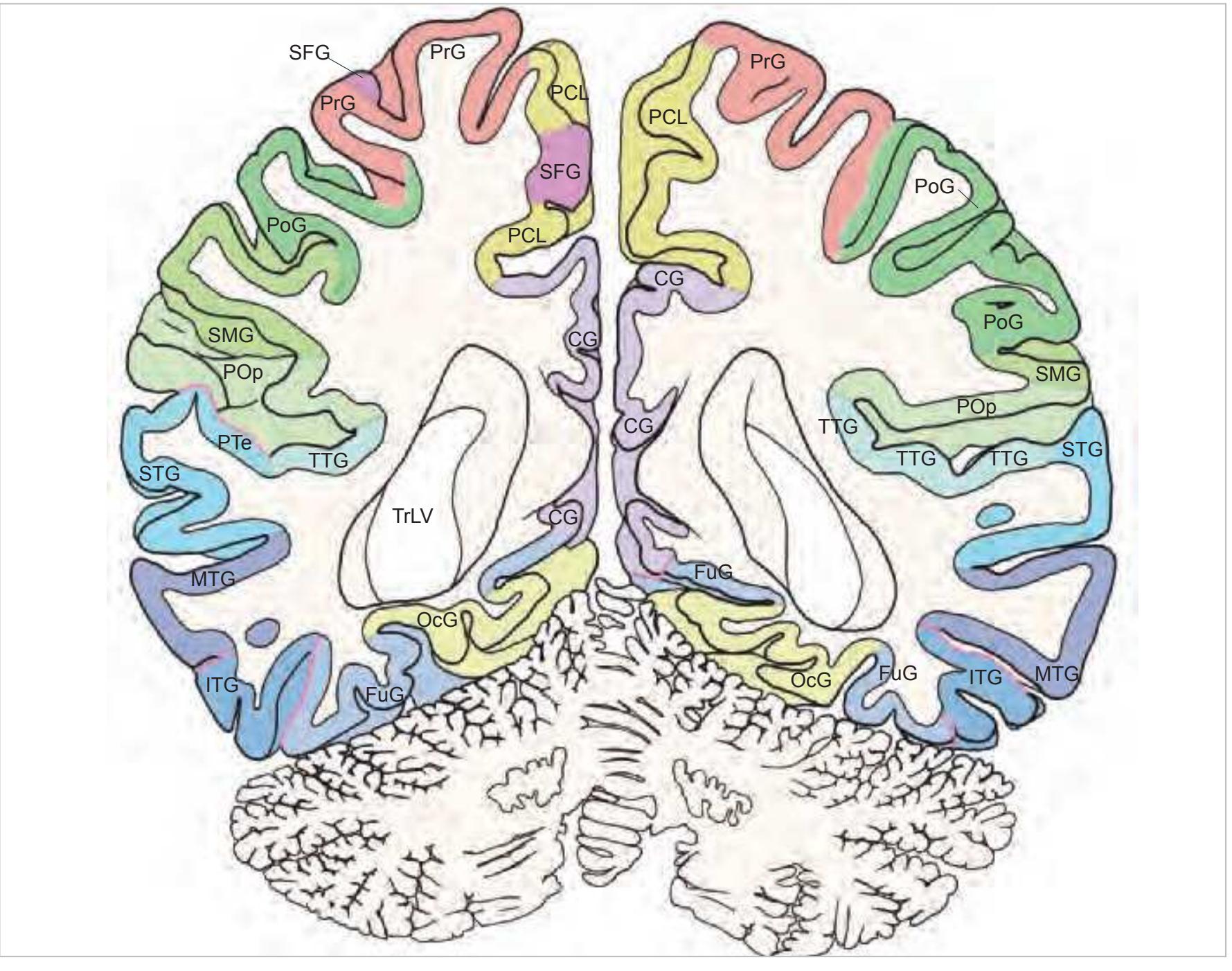

acer anterior cerebral artery CG cingulate gyrus CH cerebellar hemisphere
chpx choroid plexus of the lat. ventricle
Dt dentate nucleus FG fasciolar gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus occs occipital sinus
OcG occipital gyri
pcer posterior cerebral artery PCL paracentral lobule
pica posterior inferior cerebellar artery
PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale
scc splenium of the corpus callosum
SFG superior frontal gyrus sigs sigmoid sinus SMG supramarginal gyrus ss straight sinus STG superior temporal gyrus TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle TTG transverse temporal gyrus Ver vermis of cerebellum
# Peripheral structures:
emi emissary vein IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle occa occipital artery RePMi rectus capitis post. minor muscle RePMj rectus capitis post. major muscle SObCa superior oblique capitis muscle SpAx spinous process of axis SplCa splenius capitis muscle SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCe semispinalis cervicis muscle
StM sternomastoid muscle TempM temporalis muscle Vert3 third vertebra
CISM cervical interspinal muscle
**61**




**62**



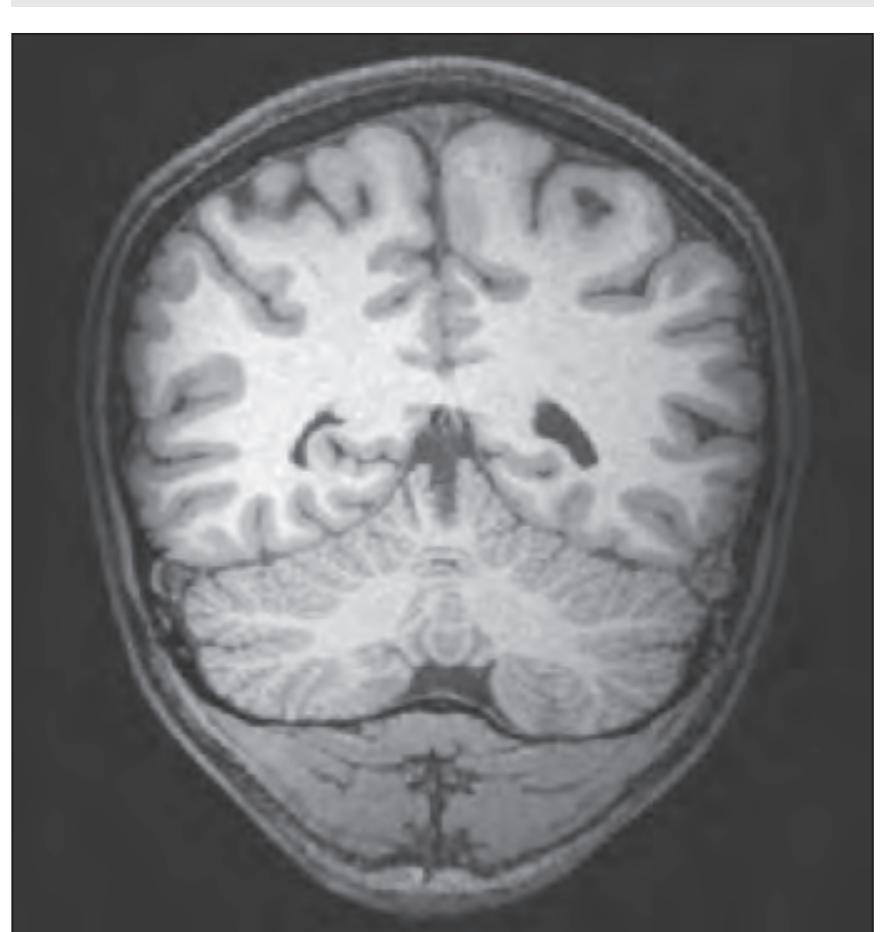
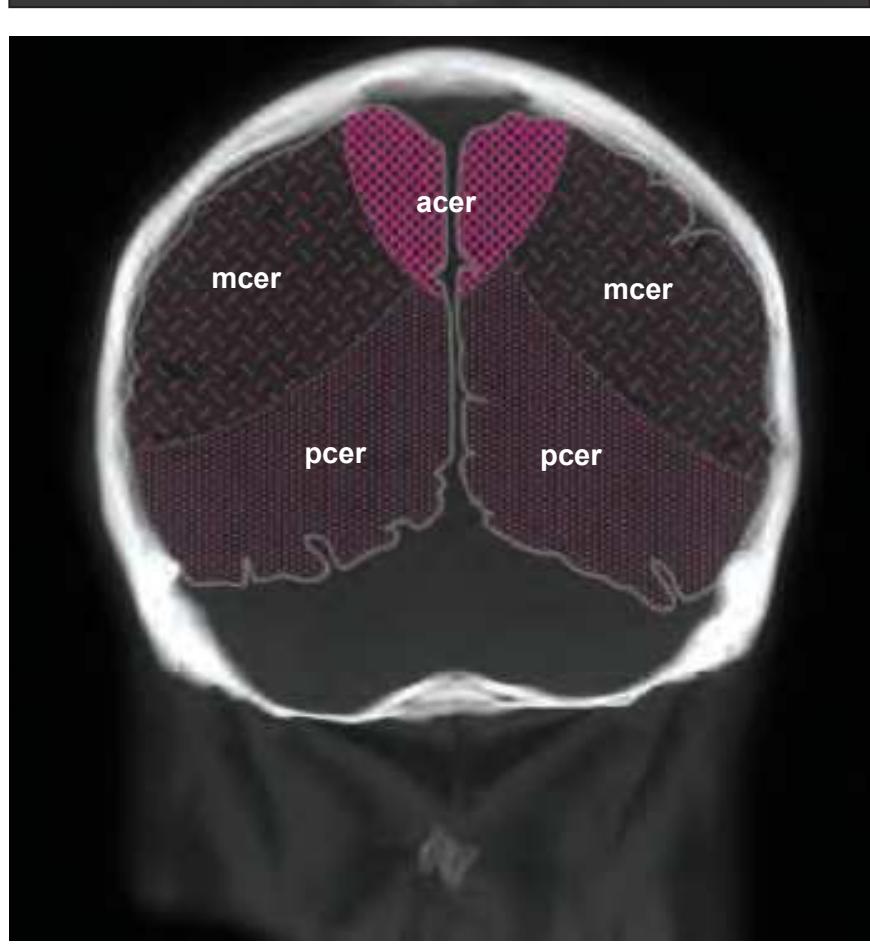
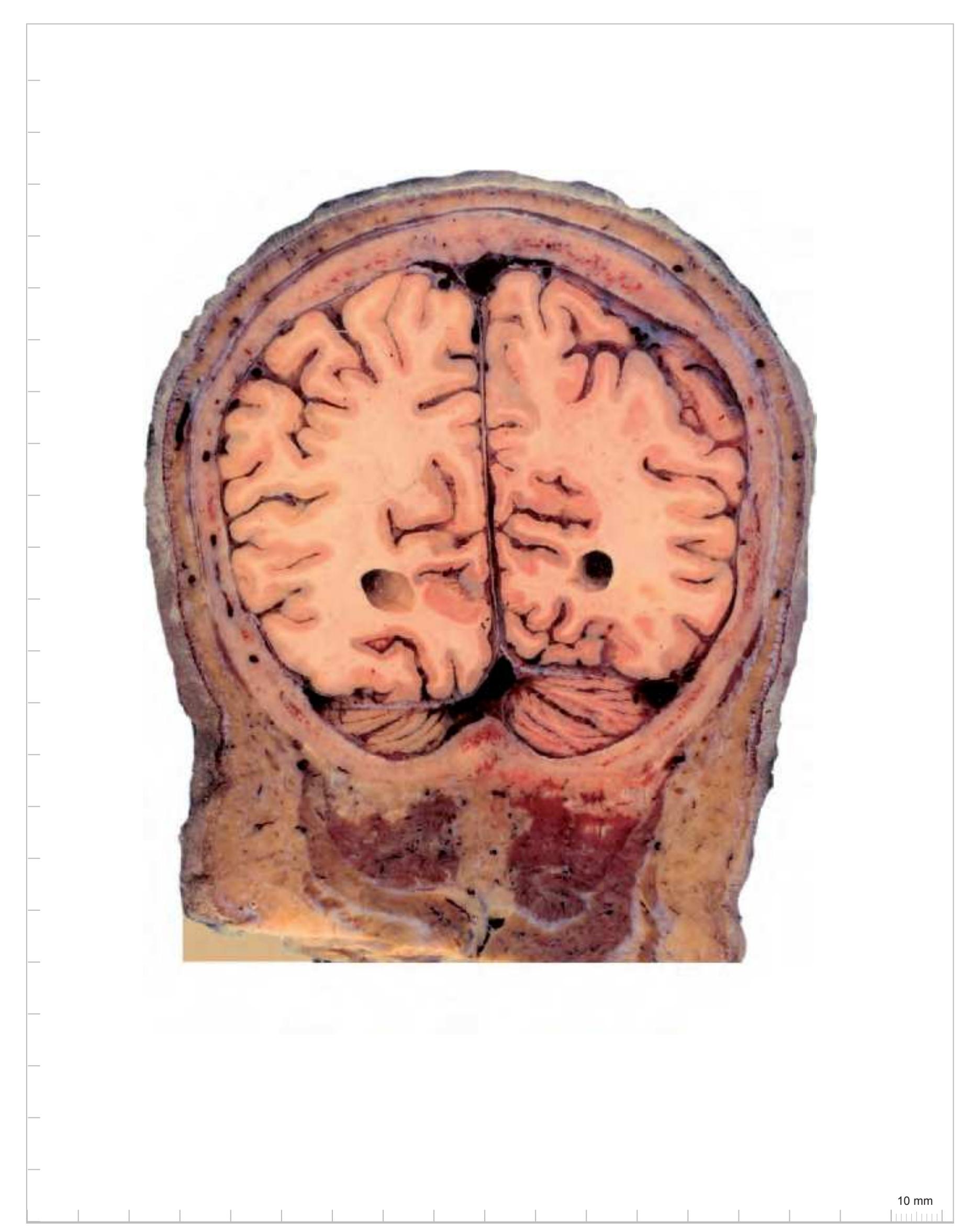
acer anterior cerebral artery AnG angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Cun cuneus FuG fusiform gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery MTG middle temporal gyrus occs occipital sinus
OcG occipital gyri OLV occipital horn of lateral ventricle pcer posterior cerebral artery
PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule ss straight sinus
ssgs superior sagittal sinus STG superior temporal gyrus trs transverse sinus
# Peripheral structures:
occa occipital artery
occv occipital vein RePMi rectus capitis post. minor muscle RePMj rectus capitis post. major muscle SplCa splenius capitis muscle
SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle StM sternomastoid muscle
**63**





**64**
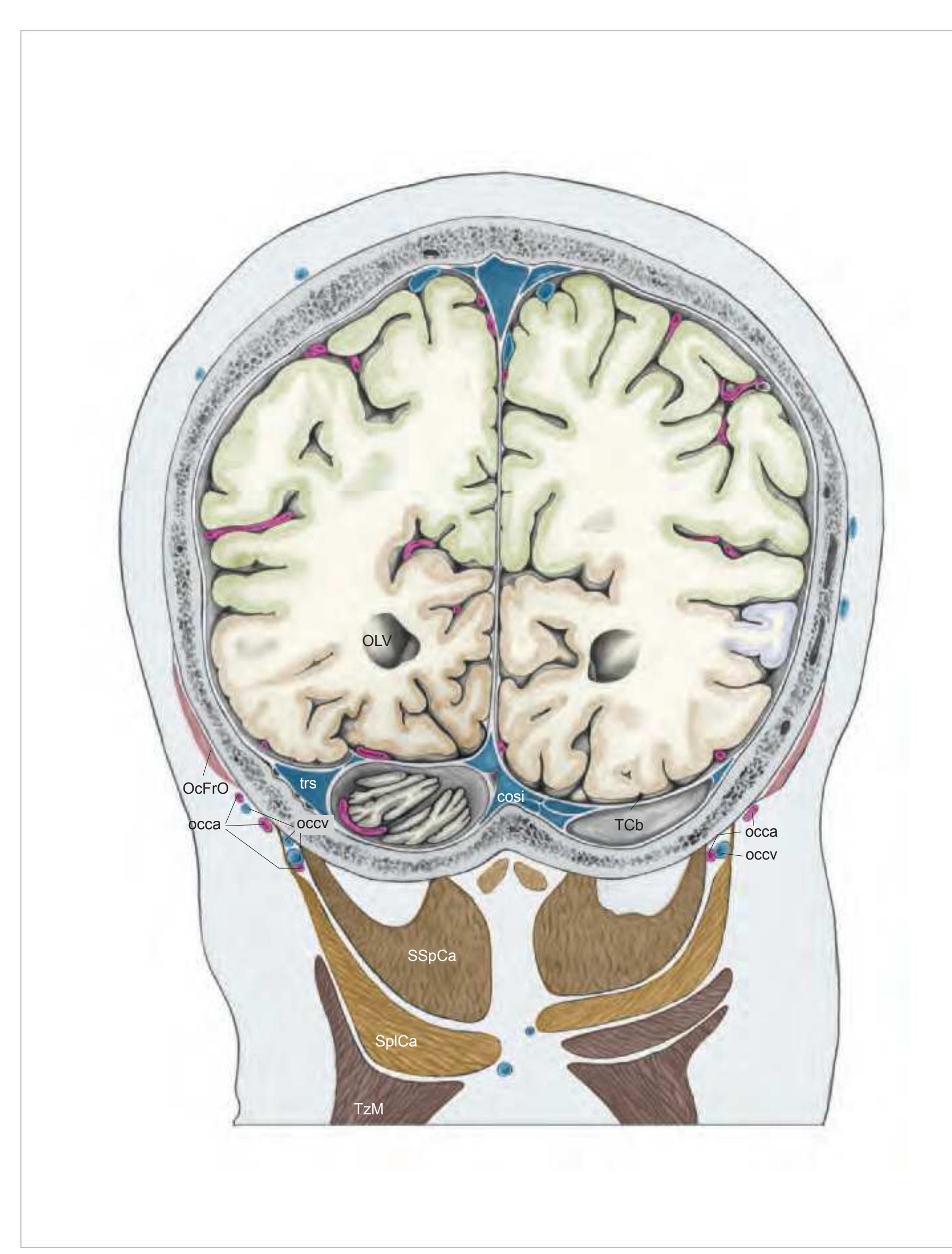


AnG angular gyrus cosi confluence of sinuses Cun cuneus FuG fusiform gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus mcer middle cerebral artery MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri OLV occipital horn of lateral ventricle pcer posterior cerebral artery PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus
acer anterior cerebral artery
PrG precentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TCb tentorium cerebelli trs transverse sinus
#### Peripheral structures:
occa occipital artery occv occipital vein
OcFrO occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly SplCa splenius capitis muscle
SSpCa semispinalis capitis muscle TzM trapezius muscle
**65**





**66**


17 striate area acer anterior cerebral artery AnG angular gyrus Cun cuneus
OcG occipital gyri pcer posterior cerebral artery
PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule ssgs superior sagittal sinus
#### Peripheral structures:
occa occipital artery
OcFrO occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly
TzM trapezius muscle

**67**




**68**
# 1.4 Sagittal Atlas of the Brain in the Head
# Cerebral structures:
17 striate area AnG angular gyrus Cun cuneus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus
SPL superior parietal lobule
**69**
#### Sagittal plane:
#### y´- direction:

#### z´- direction:

**MR-images (prior to sectioning) in three planes of the head from which one hemisphere is shown on the following pages.**
Parameters: 0.15 Tesla, matrix 256 x 256, field of view 25 cm, multi-slice, slice thickness 5 mm, 4 excitations, sequence: 5000/160. These heavy T2 weighted images highlight fluid-containing structures; uneven fluid collections (see lateral ventricles) are, therefore, visible. Note also that a dental prosthesis caused single void and deviation artefacts. The top panel presents the sagittal MRIs and specifies the planes of sectioning of the middle and lower panel. Orientation of these MRIs was based on the intercommissural line. Therefore, the orientation of the horizontal MRIs in the
middle panel corresponds to the plane of cryosectioning of the head. Direct comparisons can be made with in-vivo MRIs which accompany that series of sections. The lower panel presents the coronal MRIs.
**70**

Surface views of the left hemisphere which is shown in the subsequent pages. The drawings of the hemisphere are arranged such that they always show the same anterior-posterior orientation. The most important gyri are delineated. The midsagittal view depicts
the hemisphere with the Talairach space.
**71**


Surface views of the left hemisphere of the brain which has been sectioned in the sagittal plane as indicated. The drawing of the midsagittal view has been *mirror-imaged.*
**72**

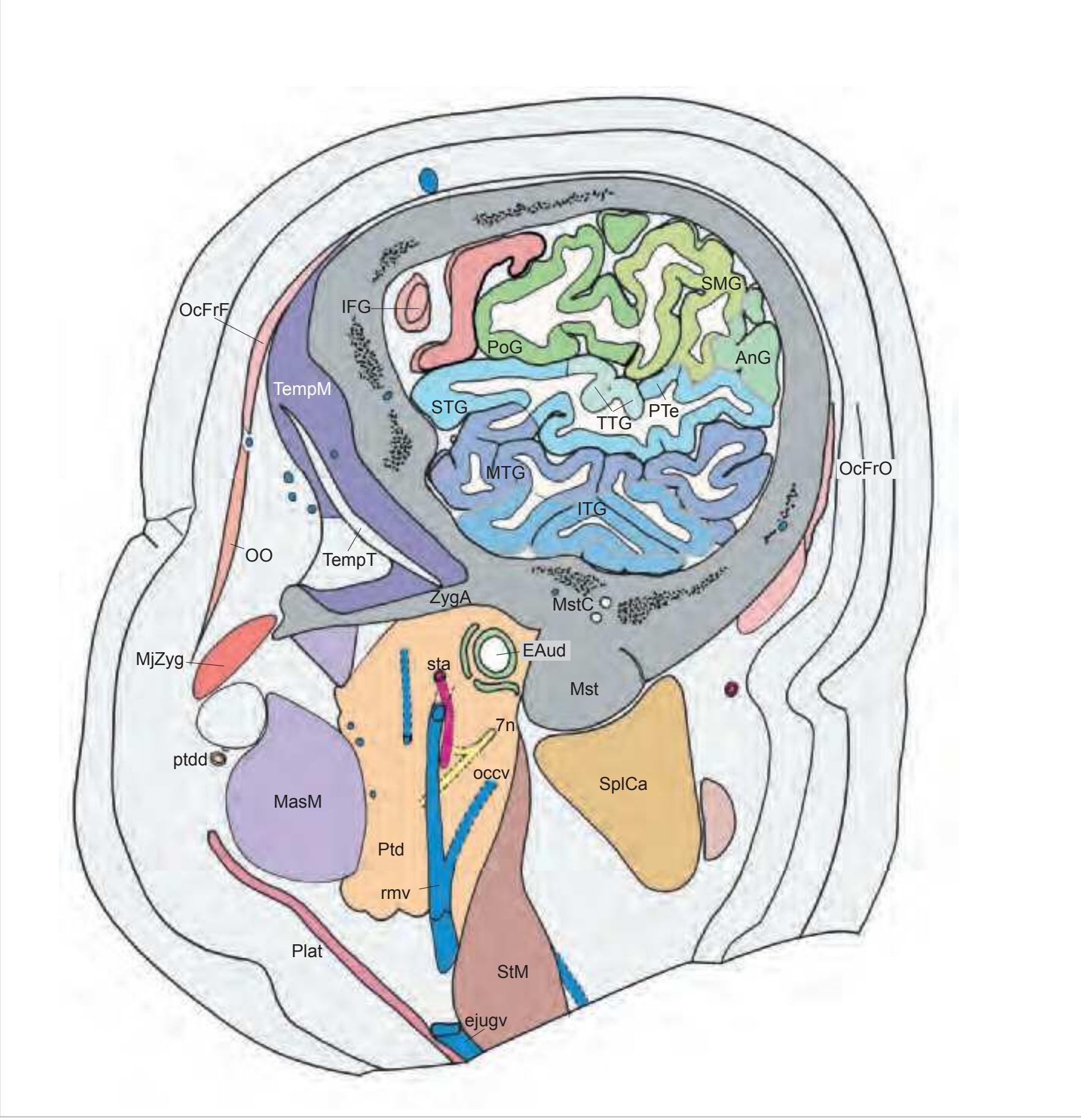

#### Intracranial structures:
| AnG | angular gyrus |
|-----|--------------------------|
| IFG | inferior frontal gyrus |
| ITG | inferior temporal gyrus |
| MTG | middle temporal gyrus |
| PoG | postcentral gyrus |
| PrG | precentral gyrus |
| PTe | planum temporale |
| SMG | supramarginal gyrus |
| STG | superior temporal gyrus |
| TTG | transverse temporal gyri |
#### Peripheral structures:
7n facial nerve
| EAud | external auditory meatus |
|-------|------------------------------------------|
| ejugv | external jugular vein |
| MasM | masseter muscle |
| MjZyg | major zygomaticus muscle |
| Mst | mastoid process of temporal bone |
| MstC | mastoid cells |
| occv | occipital vein |
| OcFrF | occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly |
| OcFrO | occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly |
OO orbicularis oculi muscle Plat platysma Ptd parotid gland ptdd parotid duct rmv retromandibular vein SplCa splenius capitis muscle sta superficial temporal artery
StM sternomastoid muscle TempM temporalis muscle TempT temporalis muscle, tendon ZygA zygomatic arch
**73**





**74**



#### Intracranial structures:
AnG angular gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus IFG inferior frontal gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale sigs sigmoid sinus SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TOp temporal operculum trs transverse sinus TTG transverse temporal gyri
#### Peripheral structures:
ATub articular tubercle Dig digastric muscle
Disc disk of temporo mandibular joint EAud external auditory meatus
ectd external carotid artery fac facial artery facv facial vein FroC frontal crest
LgsCa longissimus capitis muscle LReCa lateral rectus capitis muscle LSc levator scapulae muscle
Ly lymph node Man mandible ManF mandibular fossa MasM masseter muscle
MjZyg major zygomaticus muscle Mst mastoid process of temporal bone
MstC mastoid cells occa occipital artery occv occipital vein
OcFrF occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly OcFrO occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly
OO orbicularis oculi muscle
Plat platysma Ptd parotid gland ptdd parotid duct ptgpx pterygoid plexus rmv retromandibular vein SM submandibular gland SplCa splenius capitis muscle SphGW sphenoid, greater wing StM sternomastoid muscle StT sternomastoid muscle, tendon TempM temporalis muscle
TempT temporalis muscle, tendon
Zyg zygomatic bone
**75**




**76**



#### Intracranial structures:
FOp frontal operculum
| FuG | fusiform gyrus |
|-------|--------------------------|
| IFG | inferior frontal gyrus |
| Ins | insula |
| ipets | inferior petrosal sinus |
| ITG | inferior temporal gyrus |
| mcer | middle cerebral artery |
| MFG | middle frontal gyrus |
| MTG | middle temporal gyrus |
| OcG | occipital gyri |
| OFG | orbitofrontal gyri |
| PoG | postcentral gyrus |
| POp | parietal operculum |
| PrG | precentral gyrus |
| PTe | planum temporale |
| SMG | supramarginal gyrus |
| SPL | superior parietal lobule |
| STG | superior temporal gyrus |
| TOp | temporal operculum |
| trs | transverse sinus |
| TTG | transverse temporal gyri |
| Peripheral structures: | |
|------------------------|------------------------------------------|
| 5ial | inferior alveolar nerve |
| 5lg | lingual nerve |
| 9n | glossopharyngeal nerve |
| 10n | vagus nerve |
| 11n | accessory nerve |
| 12n | hypoglossal nerve or its root |
| BucM | buccinator muscle |
| Dig | digastric muscle |
| ectd | external carotid artery |
| fac | facial artery |
| facv | facial vein |
| iala | inferior alveolar artery |
| ictd | internal carotid artery |
| ijugv | internal jugular vein |
| IObCa | inferior oblique capitis muscle |
| LgsCa | longissimus capitis muscle |
| LPtg | lateral pterygoid muscle |
| Ly | lymph node |
| Man | mandible |
| MPtg | medial pterygoid muscle |
| mxa | maxillary artery |
| occa | occipital artery |
| OcFrF | occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly |
| OcFrO | occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly |
| OO | orbicularis oculi muscle |
| OOr | orbicularis oris muscle |
| Plat | platysma |
| Ptd | parotid gland |
| ptdd | parotid duct |
| ptgpx | pterygoid plexus |
| RePMj | rectus capitis posterior major muscle |
| rmv | retromandibular vein |
| ScalM | scalenus muscle |
| SCD | semicircular ducts |
| SM | submandibular gland |
| SObCa | superior oblique capitis muscle |
| SplCa | splenius capitis muscle |
| SplCe | splenius cervicis muscle |
| SphGW | sphenoid, greater wing |
| SSpCa | semispinalis capitis muscle |
| StyGl | styloglossus muscle |
| StyHy | stylohyoid muscle |
| StyPh | stylopharyngeus muscle |
| Symp | sympathetic trunk |
| TempM | temporalis muscle |
| TrPAt | transverse process of the atlas |
| TyC | tympanic cavity |
| TzM | trapezius muscle |
ZygM zygomatic muscles
**77**




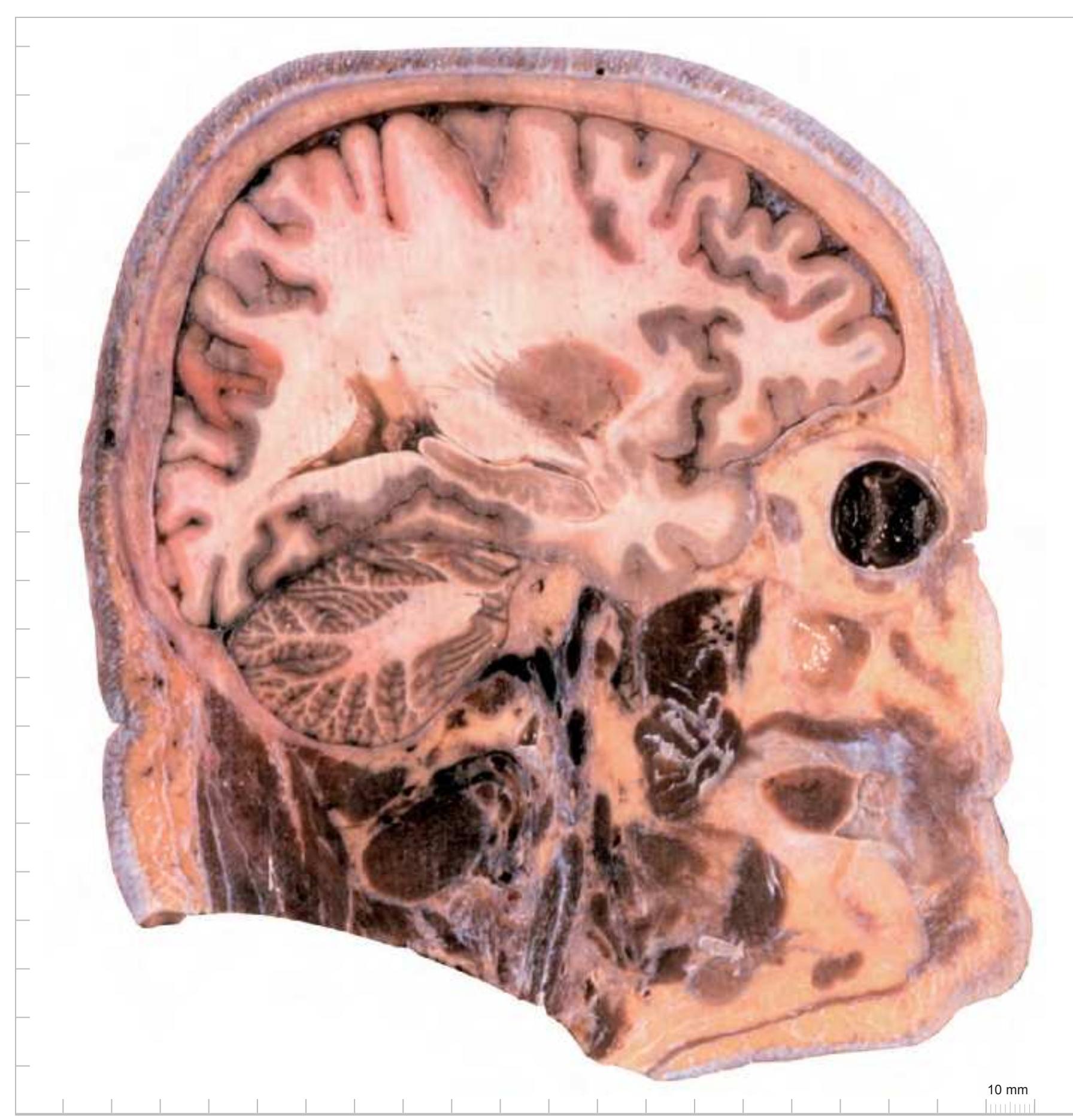

**78**



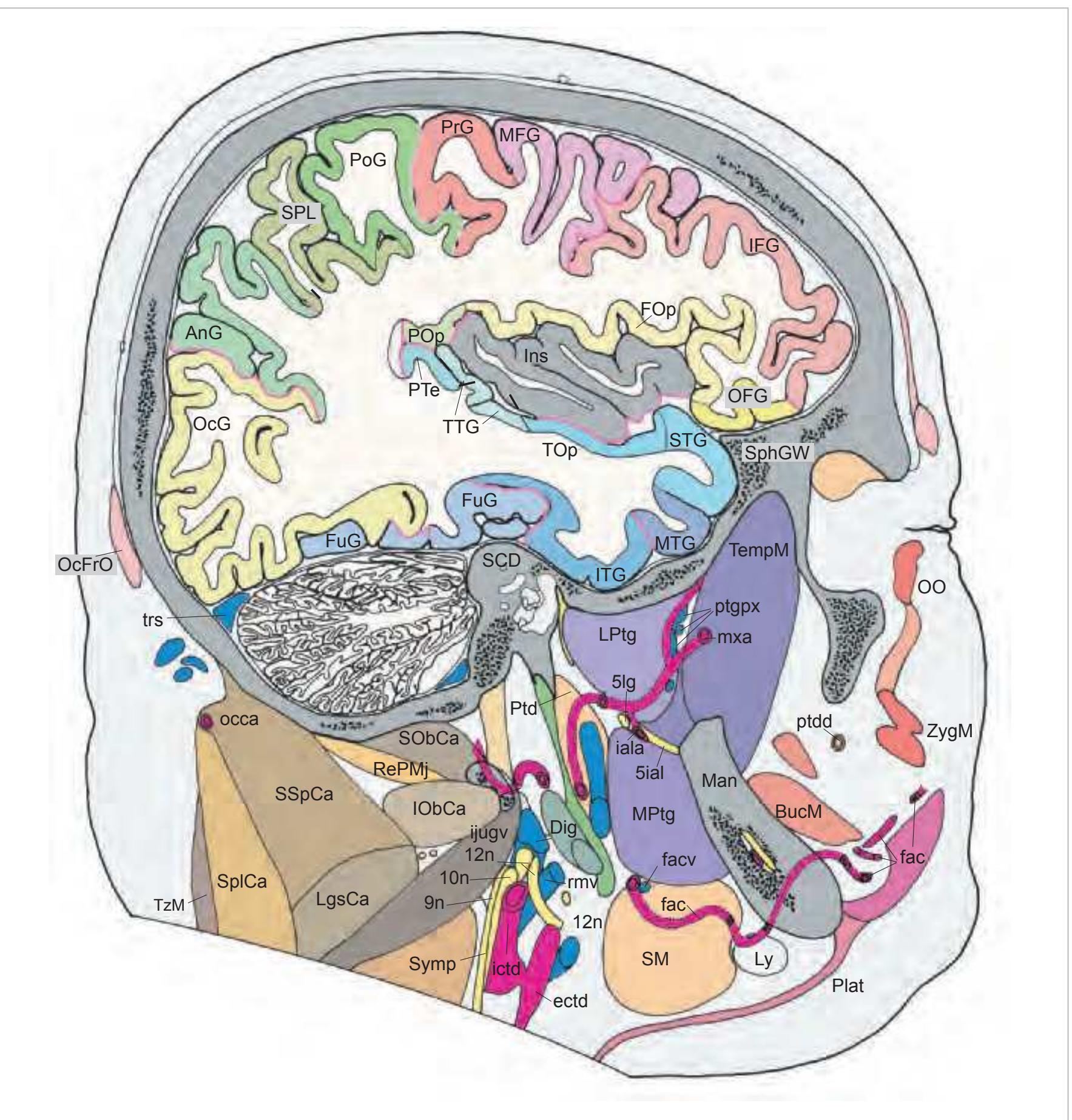
#### Intracranial structures:
ac anterior commissure AIn agranular insular cortex (claustro-cortex insularis) Amg amygdala
aud auditory radiation Cb cerebellum Cl claustrum DG dentate gyrus
fi fimbria of the the hippocampus
FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus GP globus pallidus Hi hippocampus IFG inferior frontal gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LG lateral geniculate nucleus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri OFG orbitofrontal gyri
LV occipital horn of lateral v
OLV occipital horn of lateral ventricle or optic radiation PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus Pu putamen Pul pulvinar thalami SFG superior frontal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule st stria terminalis
STG superior temporal gyrus TCd tail of caudate nucleus
thr thalamic radiation (corona radiata)
TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
# Peripheral structures:
5ial inferior alveolar nerve 5ior infraorbital nerve 5lg lingual nerve 5man mandibular nerve 9n glossopharyngeal nerve 10n vagus nerve 11n accessory nerve 12n hypoglossal nerve Aud auditory tube BucM buccinator muscle Dig digastric muscle DigT digastric muscle, tendon DpAO depressor anguli oris muscle DpLb depressor labii inferioris muscle
fac facial artery facv facial vein
gocn greater occipital nerve IAud internal auditory meatus ictd internal carotid artery
ijugv internal jugular vein & sigmoid sinus IOb inferior oblique muscle
IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle iora infraorbital artery
IOrF infraorbital foramen ivvpx internal vertebral venous plexus
JugP jugular process lab labial artery
LAngO levator anguli oris muscle
lga lingual artery LgC longus capitis and colli muscles
lgv lingual vein
LLb levator labii superioris muscle LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle LRec lateral rectus muscle SM submandibular gland socv suboccipital venous plexus
Remainder explained in Index of Abbreviations
**79**





**80**
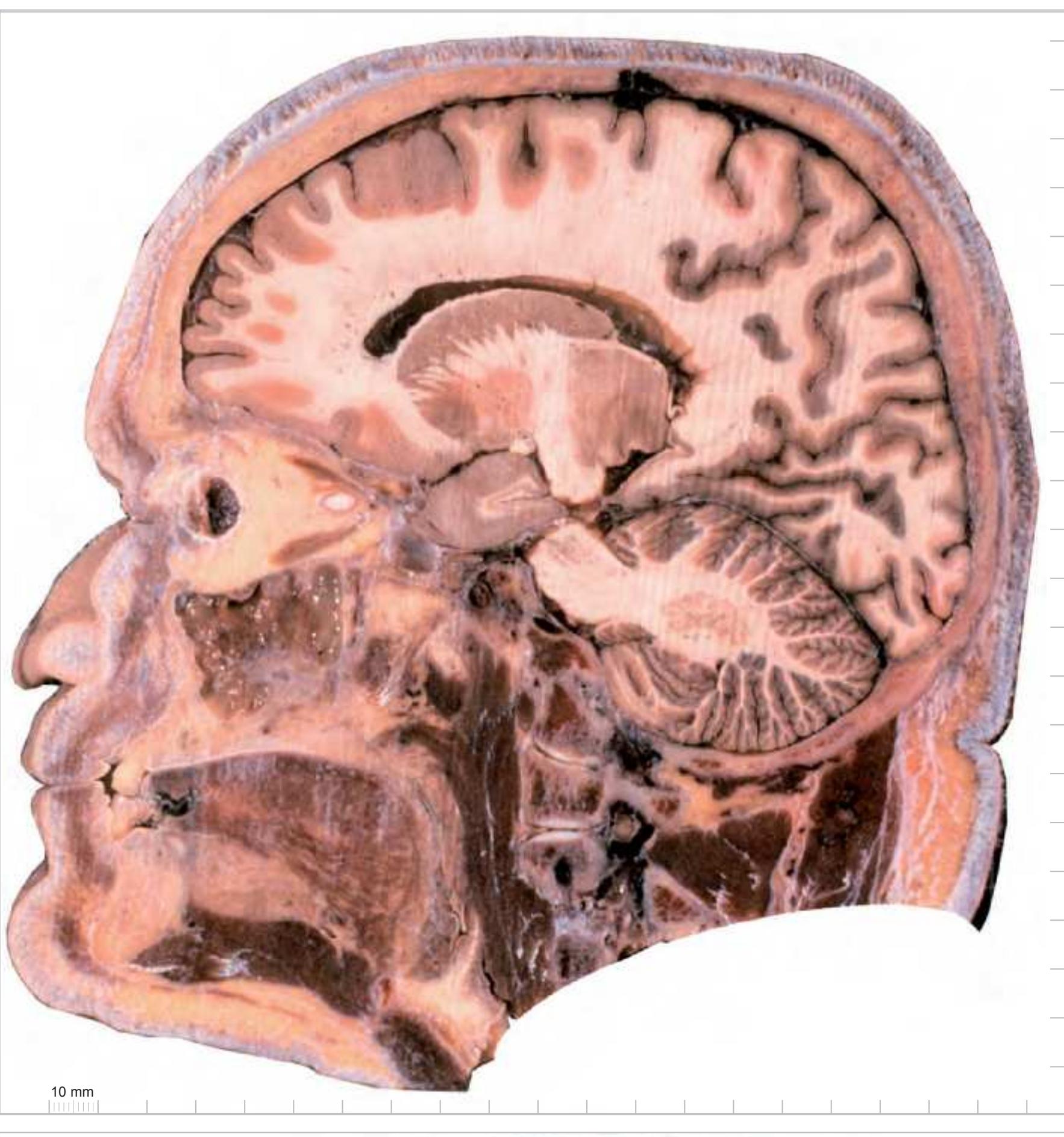


#### Intracranial structures:
| 5n | trigeminal nerve |
|----|---------------------|
| ac | anterior commissure |
AIn agranular insular cortex (claustro-
cortex insularis)
alv alveus of hippocampus
Amg amygdala Cb cerebellum Cd caudate nucleus CG cingulate gyrus
cp cerebral peduncle Cun cuneus DG dentate gyrus FG fasciolar gyrus
FuG fusiform gyrus GP globus pallidus Hi hippocampus ic internal capsule ipets inferior petrosal sinus LgG lingual gyrus
Li limen insulae LTh lateral thalamic nuclear region mcp middle cerebellar peduncle
MFG middle frontal gyrus MG medial geniculate nucleus
OcG occipital gyri OFG orbitofrontal gyri opt optic tract
PAM periamygdaloid cortex
PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pir piriform cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus Pu putamen Pul pulvinar SB striatal cell bridges
SFG superior frontal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule st stria terminalis Th thalamus
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
# Peripheral structures:
2n optic nerve 5Gn trigeminal ganglion 5nc nasociliary nerve 12C hypoglossal canal 12n hypoglossal nerve
AReCa anterior rectus capitis muscle AtOc atlanto-occipital joint
Aud auditory tube cern (1-3) cervical nerve (1-3) Dig digastric muscle, ant. belly dpala descending palatine artery
EGl epiglottis
gocn greater occipital nerve HyGl hyoglossus muscle
Hyoid hyoid bone ictd internal carotid artery IOb inferior oblique muscle IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle
lga lingual artery LeVePal levator veli palatini muscle
LgC longus capitis and colli muscles LgFo lingual follicle
LPal levator palpebrae superioris muscle
MPtg medial pterygoid muscle MRec medial rectus muscle Mul multifidus muscle mxa maxillary artery
MxS maxillary sinus SCMPP superior constrictor of the pharynx,
pterygopharyngeal part StHy sternohyoid muscle
Remainder explained in Index of Abbreviations
**81**





**82**

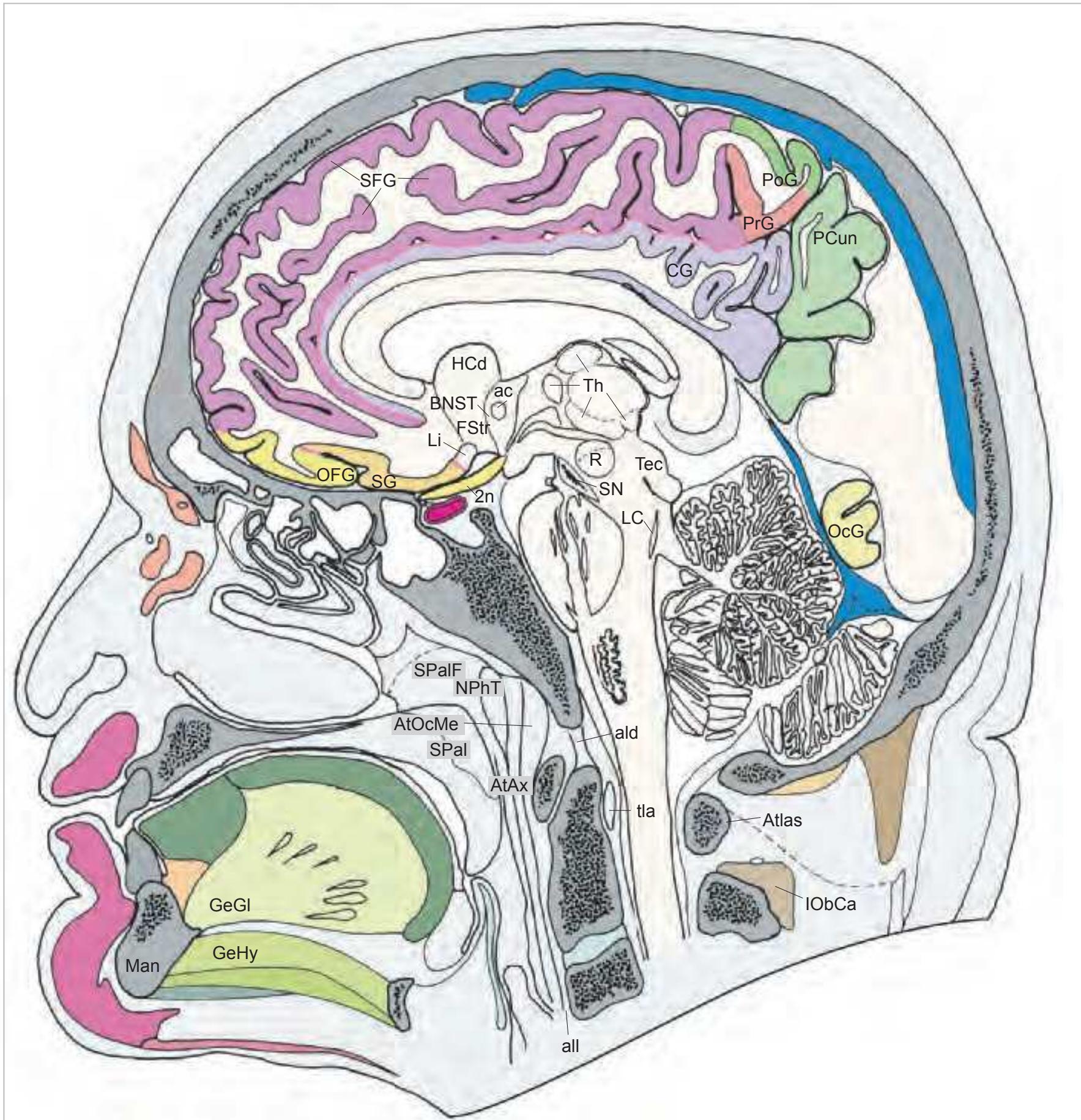

#### Intracranial structures:
2n optic nerve ac anterior commissure
BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
cc corpus callosum CG cingulate gyrus
CM centromedian thalamic nucleus DSF dorsal superficial nucleus
FStr fundus striati
HCd head of caudate nucleus
ic internal capsule IO inferior olive
IPF interpe duncular fossa LC locus coeruleus Li limen insulae
LTh lateral thalamic nuclear region and
reticular nucleus
MD mediodorsal thalamic nucleus OcG occipital gyri
OFG orbitofrontal gyri PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus
Pons pons PrG precentral gyrus
Pul pulvinar R red nucleus SFG superior frontal gyrus SG straight gyrus SN substantia nigra st stria terminalis Tec tectum of midbrain
Th thalamus
# Peripheral structures:
AAT anterior arch of atlas ald apical ligament of dens all anterior longitudinal ligament AtAx altanto-axial membrane Atlas atlas
AtOcMe atlanto-occipital membrane
Axis axis DAx dens axis Dig digastric muscle EGl epiglottis GeGl genioglossus muscle GeHy geniohyoid muscle ictd internal carotid artery IObCa inferior oblique capitis muscle
Man mandible Mx maxilla
MyHy mylohyoid muscle NPhT nasopharyngeal tonsil oaud opening of auditory tube
Occ occipital bone
OcFrF occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly OOr orbicularis oris muscle
Oral oral cavity
PAT posterior arch of atlas
Plat platysma smd submandibular duct SPal soft palate
SPalF salpingopalatine fold SPhF salpingopharyngeal fold tla transverse ligament of atlas
TLev torus levatorius TTub torus tubarius
**83**




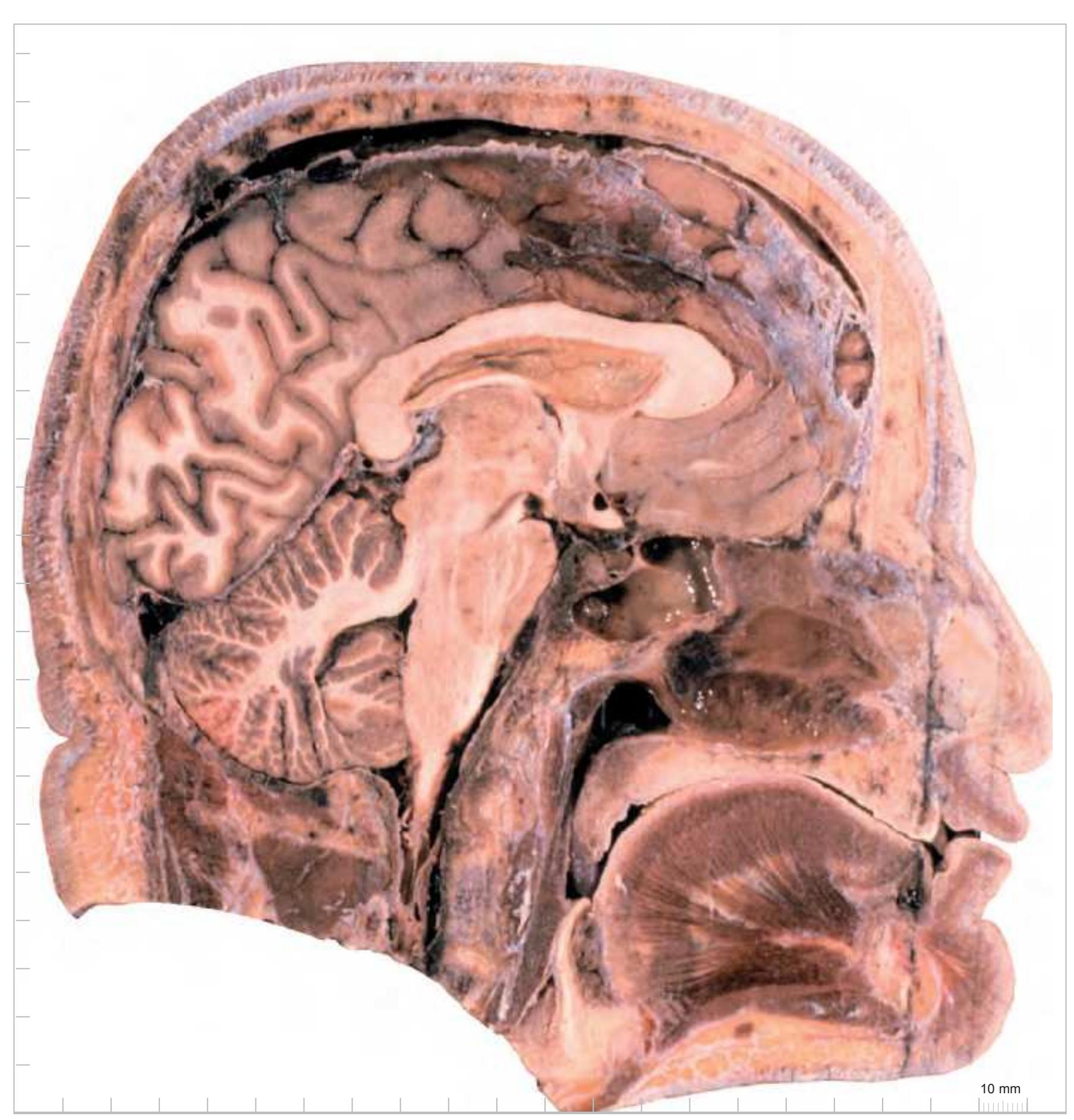

**84**
# Part 2: Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space
**85**
# 2.1 Material and Methods
## 2.1.1 The Brain
The *Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space (AHB)* is based on the right hemisphere of a 24-year-old male (1905-1929). The cause of death was hypovolemic shock and the death to fixation interval was 3 hours. This brain belongs to the Vogt-collection of Düsseldorf. The brain weight at autopsy was 1383 g, the fresh volume was 1316.3 cm3 (see more details in Published Studies, Section 2.6). The values of some linear measurements for the fixed brain are given in Fig. 2.2. The external morphology of the formalin-fixed brain is shown on pages 95 to 97. This brain was selected because it was sectioned well and stained well by the great anatomists Oscar and Cécil Vogt and has been studied in the ensuing years by a number of scientists, including the Vogts, H. Brockhaus, R. Hassler, W. Wahren, F. Sanides and A. Hopf. In this *Atlas* we display the mylo- and cytoarchitecture of the right brain hemisphere accompanied by detailed diagrammatic delineations.
## 2.1.2 Methods
#### Histological Procedures:
The brain was cut by O. Vogt into five blocks oriented vertically to the intercommissural plane before being embedded in paraffin. Serial frontal (coronal) sections of 20 μm thickness were prepared. Most sections were stained with either cresyl violet or hematoxylin. Some additional sections remained unstained and we processed them immunohistochemically (e.g., substance P; see Section 2.6). Since the first and the last paraffin sections of each block were only partially recovered, we have drawn the approximate outlines of these sections by using photographs of the cut surface of the individual blocks, which were taken before sectioning.
#### Estimates of Volume Changes:
Volume changes occurring during autopsy, fixation and embedding in paraffin provide major obstacles in comparing sections with the *in vivo* condition. In the *Atlas* brain, the volume changes due to formalin fixation are negligible because the brain volume at the fixation time corresponds to the values determined at autopsy (Longerich, 1989). It is, therefore, reasonable to assume that the dimensions of the formalin fixed brain (Fig. 2.2) represent the *in vivo* condition. The overall volumetric changes that occurred during the histological preparation (due to dehydration, paraffin embedding, cutting, and mounting of the sections) were calculated in two ways: first, by estimating the extent of shrinkage artefacts on scaled photographs. The 1:1 scaled photographs of the surface views of the fixed brain and of the block-face were correlated with the histological sections. The transformation of the histological sections according to the shrinkage calculated revealed no appreciable nonlinear changes (Sievert, 1992). Second, by determination of the differences in the linear dimensions between the fixed, unembedded hemisphere (scaled photographs) and the serially sectioned hemisphere (Lange and Thörner, 1974) (see Section 2.6).
For application as a reference brain, interindividual variability and shrinkage artefacts are the foremost variables that must be considered. The degree of shrinkage artefacts revealed no appreciable nonlinear changes (Sievert, 1992). Therefore, we are confident that our image data meet the condition of a reference atlas, hereby providing detailed histological data.
# 2.1.3 Earlier Histological, Morphometric and Immunohistochemical Studies
Numerous descriptive and quantitative studies were performed on sections from the brain represented in the *Atlas*. The relevant descriptive studies and morphometric data (fresh volume, volume of serial sections, numeric cell density, volumetric cell density, and absolute cell numbers of cortical divisions and subcortical nuclei) have been listed together with references in Section 2.6. Please note, that in several publications features or data of this brain were compared to other brains. Full text of most of these studies is found on the free website: www. thehumanbrain.info in an editable format.
## 2.1.4 Nomenclature
Considering the obvious need for a stable neuroanatomical nomenclature, we have decided to use the abbreviation system of Paxinos and colleagues because it is consistently used in atlases of various animals, used by many experts in the field of neuroscience and in the companion volume of this atlas, "The Human Nervous System" (Mai and Paxinos, 2012).
# 2.1.5 Photographic Plates and Corresponding Diagrams
The Atlas contains:
• 99 photographs of sections stained for myelin juxtaposed by 99 detailed diagrams. • 50 photographs of sections stained for cell bodies, interposed at half the frequency of the myelin series. All photographs and diagrams are adjusted to the MNI stereotaxic space (see below).
The magnification of the photographs is higher than the diagrams because in this way the photographs can be bled for the sake of greater resolution. Rostral to the genu of the corpus callosum and caudal to the splenium we used higher and varying magnification, dictated by the availability of space. Between these two levels we kept the magnification constant.
The cell stained (Nissl) sections are not diagramed but are accompanied by high resolution photographs of cortical areas on the facing page of full page Nissl sections. These areas were selected to fit those depicted and described in the work of von Economo and Koskinas (1925). This provides the possibility to compare the histological features of the closely corresponding regions and to read the very detailed descriptions which accompany their photographs.
Additionally, the cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon is unfolded and presented linearly as "stripes" in registration with the interpretation of earlier authors as we perceive their work (Section 2.14). Because any position within these stripes has a precise relation to the coordinates of the MNI-space, delineations of cortex areas derived from other classes of research can be registered. By this option any region of interest can be mapped within these stripes and compared with existing entries.
# 2.1.6 Three-Dimensional Reconstructions
For the 3-D analysis we used "contourlines" to define pial and ventricular surfaces, borderlines around identified nuclei and their subdivisions (e.g. basal ganglia, amygdala, basal nuclear complex, hypothalamus and thalamus), and delineations of some compact fiber tracts (optic tract, anterior commissure, h1- and h2-fascicles, inferior thalamic peduncle) from 385
**86**

**Figure 2.1.** Generation of the 3D model of the human brain structures from the delineations and manual segmentations of histological sections which are represented in the *Atlas*. (a) Sections from the *Atlas* are aligned in the stereotaxic space and the borders of the nuclei of the anterior group of the thalamus are defined. (b) The cross-section areas of the anterior nuclei and of the paratenial nucleus located in front of the plane of the depicted myelin section (considering steadiness and consistency of the borderlines of neighboring sections). (c) Representation of relevant neighborhood relations. (d) 3D model of the anterior nuclei and their topographical situation. (e) The 3D model embedded within the MNI space (modified from Mai and Forutan, 2012).
sections of one hemisphere (Fig. 2.1). The correct segmentation of individual structures was not derived from a single class of research. We considered results from a range of conventional and immuno-stained sections from many other brains, including evaluations of more than 50 developing brains and a large number of brain sections from Pathology and from the Vogt-collection. We have always respected the results from the numerous cyto- and myeloarchitectonic studies that were previously performed on the represented brain and have used as often as possible the original delineations provided by these earlier workers. Generally, the consistency of the drawings, section-to-section, was of higher importance than a precise correspondence between the photographs and the drawings.
For each model structure separate voxel and surface representations were constructed (Mai and Majtanik, 2013). This reconstruction became embedded into the 3D template of the human brain developed from the *"3D- Atlas of the Human Brain"* (3D-AHB) (Mai and Majtanik, 2014).
# 2.1.7 Standardization
Our *Atlas* uses a reference system where the brain space is defined metrically with the zero point (= point 0/0/0) for all three dimensions being the center of the anterior commissure (Fig. 2.3a). The morphologic data of the hemispheres, therefore, are handled as coordinate points in this 3-D (metric) grid as X- (mediolateral), Y- (vertical), and Z- (fronto-occipital) coordinates (Fig. 2.3b). Scaling of the photographs and accompanying diagrams are accordingly provided in metric coordinates.
#### Data and Measurements:
The major linear dimensions of the *Atlas of the Human Brain (AHB)* are provided in Fig. 2.2. We defined the stereotaxic space by the midsagittal plane and the perpendicular plane which passes through the center of the anterior and posterior commissures, respectively (Assheuer et al., 1990). We have used the plane through the centers of the commissures (intercommisural plane, ICP) because of its established use in neurosurgery and its easier definition if compared with points at the limiting border of each commissure (see Tamraz and Comair, 2000). The vertical planes (VAC, VPC) pass through the centers of the anterior and posterior commissure, respectively. The distance between VAC and VPC is 28 mm.
This stereotaxic coordinate system can be directly spatially registered to the dimensions of alternative coordinate spaces e.g. the Talairach Atlas or the MNI/ICBM templates.
# 2.1.8 Mapping of the Atlas Space to the Talairach-Space
In order to facilitate the comparison of the original Talairach structural labelings, effort has been made to transform the dimensions of this individual brain to the Talairach stereotaxic space (Talairach and Szikla, 1967; Talairach and Tournoux, 1988). In the last edition of our *Atlas of the Human Brain* (2008) we have applied linear transformation of the *Atlas* brain into the Talairach and Tournoux (T&T) standard proportional grid system. This approach is problematic for several reasons. First, the *Atlas* was prepared from the brain of a 24 year old male person; the T&T atlas is based on the brain of a 60 year old female. Second, not all linear dimensions of the *Atlas-* and the T&T-brains are exactly congruent. As illustrated in Fig. 2.2 the linear mediolateral and fronto-occipital dimensions of the formalin-fixed *Atlas* brain correspond to those of the T&Tbrain. The vertical dimension, however, is reduced with respect to the distance below and above the ICL (Sievert, 1992). Third, the distances of the stereotaxic grid along the orthogonal planes have different values with respect to the Talairach space reported 1967 and 1968, respectively. Finally, and most important, is the use of different baselines (see below).
To make the linear dimensions between both atlases directly comparable, we have adjusted the vertical dimension of the *Atlas-*brain to that of the T&T-brain (Fig. 2.2). In the first edition of the *Atlas* (1995), we showed two scalings on the schematic diagrams, indicating the different dimension as illustrated by the green arrows in Fig. 2.2. One scale provided the vertical dimension of the stained histological sections, the other the calculated dimensions according to the standard dimensions of the T&T space. In the last edition (2008), we showed the diagrams in the (transformed) dimension of the T&T space. The photographs of the myelin-stained sections remained without linear distortion and showed the original, unchanged dimension.
**87**
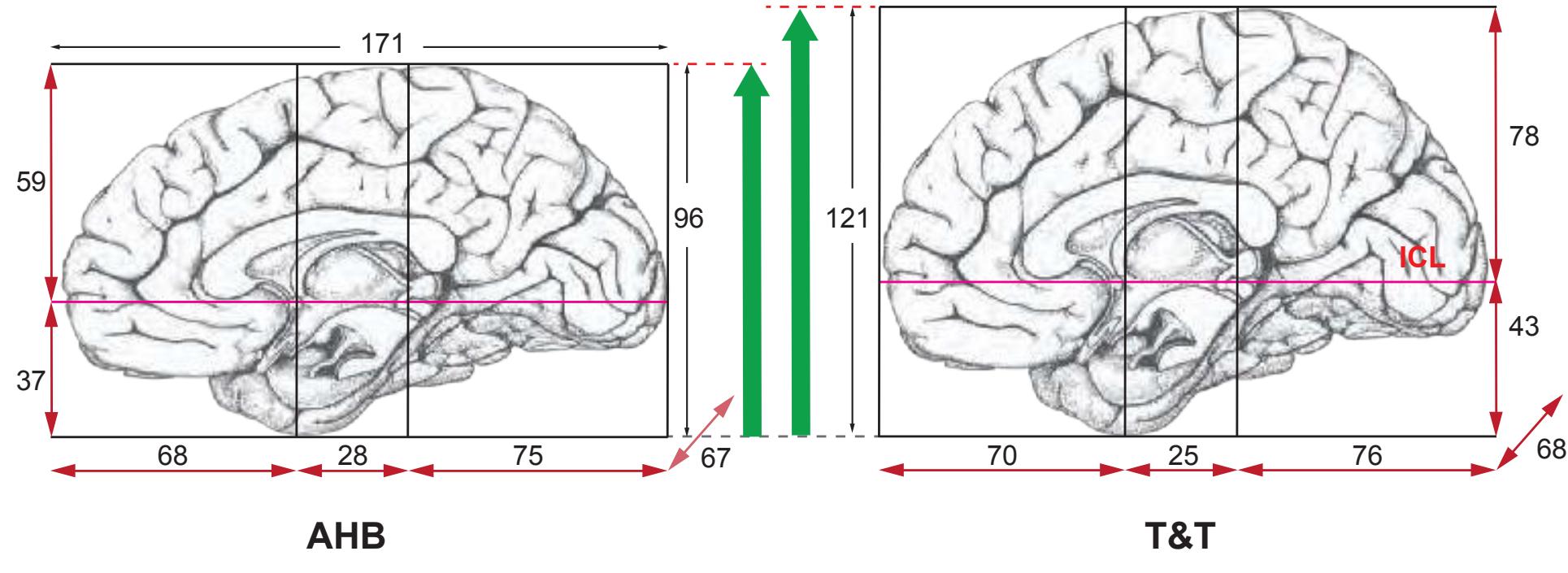
**Figure 2.2.** Graphic representation of the formalin-fixed *Atlas* brain before embedding (left) and after transformation into the Talairach and Tournoux standard proportional grid system (right). The linear dimensions of the orthogonal reference lines (in mm) are indicated. The linear anterior-posterior and medio-lateral dimensions of the formalin-fixed brain correspond well to the values of the Talairach space. The vertical dimension is, however, reduced (green arrows) (Sütfels, 2011).
If maps from the *Atlas*- and the T&T-brain are compared at the same section levels, differences in various areas are obvious (Fig. 2.4). These result from the different slopes of the stereotaxic baseline used for the standardization procedure. The *Atlas* space is based on the intercommissural line (ICL), which passes through the centers of the anterior (AC) and posterior (PC) commissure, respectively. The vertical line of the anterior commissure (VAC) extends orthogonally through the center of the AC (Assheuer et al., 1990). The T&T space is based on the bicommissural line (BCL). This line connects the upper border of the anterior commissure with the lower border of the posterior commissure. VAC and VCP orient perpendicular to the BCL from the posterior and anterior margins of the AC and PC, respectively (Fig. 2.3.a). Consequently, the zero point (intersection of the commissural line and VAC) of both coordinate systems locate differently (center of AC versus posterior margin of AC). Distance values between both commissures and especially the representation of section content are different.
Fig. 2.3a demonstrates the differences in the geometry of both systems and the main consequences:
- The origin of the coordinate system is different. That leads to a shift of corresponding coordinate points. For example, the values for the AC-PC distance differ albeit the actual distance is equal. If the diameter of the anterior commissure is calculated with 2-3 mm, the coordinate zero-point of the T&T-Atlas is 1 to 1.5 mm posterior. This is the distance, by which structures along the anterior-posterior axis are shifted.
- The different slope of the commissural lines (ICL or BCL) leads to a different representation of the frontal plane (Fig. 2.4).
• The limited matching between the histological features from both atlases is best visualized if actual sections with the same coordinate points are compared. Fig. 2.4 shows the consequences with respect to the dimension and content illustrated at three section levels: in front of the anterior commissure, between both commissures and posterior to the posterior commissure.
171


**Figure 2.3.** a) Comparison between the intercommissural line (ICL) and the bicommisural line (BCL) and the consequence with respect to the orthogonal frontal section plane. b) The orientation between both stereotaxic frames of the AHB and the T&T is different (Sütfels, 2011).
The overlays of diagrams taken from the T&T-atlas and from this *Atlas* at corresponding levels along the fronto-occipital axis (y in the T&T-; z in the *Atlas* brain) illustrate that the different slope of the BCL in the T&T and of the ICL in the *Atlas* brain results in a shift along the vertical axis of each image pair that is dependent in extent from the distance from the crossing point of the two baselines (ICL and BCL) (Fig. 2.4). The figures demonstrate that the different geometry due to the standardization protocols used precludes the direct correspondence of coordinates (ROIs), especially distant to the midcommissural point. The discrepancy between the Talairach coordinates and those from the *Atlas* makes the correlation of ROIs with anatomic structures difficult and therefore not all published coordinates refer to the same neuroanatomical region (Sütfels, 2011). However, since the Talairach coordinates can be converted into MNI coordinates (Lancaster et al., 2007; Laird et al., 2010) this platform provides the possibility for (indirect) comparison with our *Atlas* in the MNI space (see below).
Because of the limitations ensuing from comparison between our *Atlas* and the atlas from Talairach and Tournoux (1988) we have in this edition tried to compare the *Atlas* with the information provided by the MNI standard space.
# 2.1.9 Mapping of the Atlas Space to the MNI/ ICBM2009b Template
The MNI defines a new standard brain by using a large series of MRI scans on normal controls. The MNI152 6th generation standard space consists of multiple linear and nonlinear averages of 152 normal MRI scans from the MNI152 database that were transformed into a symmetric model in the Talairach space (Collins, 2012; Evans et al., 1992, 1993). The new MNI/ICBM2009 spaces are a set of unbiased non-linear averages of the MNI152 database with both high-spatial resolution and high signal-to-noise ratio. This space is not biased by the deviations of any single brain (Fonov et al., 2011).
The construction of MNI/ICBM2009 involved multiple iterations of a process where, at each iteration, individual MRIs were non-linearly fitted to the average template from the previous iteration, starting with the MNI152 linear template. Furthermore, a specific age-based subpopulation of subjects became created. The scans within each group were then automatically re-registered to the stereotaxic space target template with an iterative nonlinear co-registration algorithm applied to obtain the group averages (Fonov et al., 2011).
In the present edition of the *Atlas* registration was made to comply with the MNI space (see Fig.2.5). Not only the diagrams but also the photographs of the original histological brain sections were nonlinearly registered to fit that space with respect to its dimensions.
The MNI brain is significantly different in shape compared with the *Atlas* brain. The MNI template is larger than the *Atlas* brain, especially along the dorso-ventral
**88**

**Figure 2.4.** Topographic correlation of images from the Talairach atlas and from the *Atlas* brain. The different slopes of the baseline (ICL and BCL) of the standardization protocols yield a shift along the vertical axis of both image spaces that is dependent in extent from the distance from the crossing point of the two baselines (compare to figure 2.3a). This precludes direct correspondence of coordinates (ROIs). (a) Corresponding section planes located 12 mm anterior to the AC. Panel D (y = +12 mm) of the T & T overlaid to the *Atlas* plate 22 (z = -12.5 mm) of the AHB. The plane of section is 12 mm anterior to the anterior commissure. The image visualizes the effect of the increasing distance between the BCL (T & T) and ICL (AHB). The outer contours and subcortical structures show a generally good congruence between the T & T and the *Atlas* templates. However, of the outer contours (broken line) and the location of the putamen (green) and caudate nucleus (yellow) of the T & T panel are shifted ventrally if both images are aligned on the ICL. (b) Panel D\_E (y = 0 mm ) of the T & T and corresponding panel 32 (z = 0.0 mm ) of the AHB at the center of the anterior commissure. The superimposed diagrams from both atlases show a good agreement of the subcortical structures; the outer brain contours, however show appreciable differences. (c) Overlay of panel E ( y = -12 mm) of the T & T and the corresponding plate 44 (z = 13.3 mm) of the AHB. Rather good congruence of the superimposed diagrams due to the location of both diagrams at the point of intersection of the ICL and the BCL, respectively (adapted from Sütfels, 2011).
axis by about 30 mm and along the anterior-posterior axis by about 10 mm. In the MNI space the center of the anterior commissure (AC) is about 4.5 mm more ventral and 2.5 mm more anterior than the origin [0,0,0] of the MNI template (MNI AC coordinates = [0, -2.5, -4.5]) (Fig.2.5b). It is also noteworthy that the ICL plane is not exactly horizontal.
Due to the restriction of the deformation fields for the slice-to-slice reconstruction (slice orientation of the *Atlas* is constant) a perfect global conversion of 3D-AHB to MNI coordinates is somewhat complicated. Therefore we performed a two stage mapping of the *Atlas* to the MNI152/ ICBM2009b symmetric brain template provided by the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) (Mai and Majtanik, 2013). To this end a shape constrained 3D reconstruction of the *Atlas* has been created.
# 2.1.10 AHB Reconstruction with MNI/ ICBM2009b Shape Constrain
The 3D reconstruction of the *Atlas of the Human Brain in Stereotaxic (MNI) Space (AHB)* was created from delineations of 358 coronal slices with maximal sliceto-slice distance of 0,4 mm. For the 3D reconstruction of the AHB we employed our novel geometric shape constrained 3D reconstruction algorithm for serial sections (Mai and Majtanik, 2014). This algorithm creates a specific 3D-AHB reconstruction such that it corresponds to the MNI/ICBM-2009b space. A single geometric shape constrain defines a homologous structure in the AHB and in the MNI brain that will be perfectly matched during the nonlinear part of the reconstruction process. The geometric constrains can be defined as a set of one, two or tree dimensional structures (1D, 2D or 3D constrains).


**Figure 2.5.** (a) Linear dimensions of the *Atlas* brain after transformation to the MNI-dimensions (AHB-MNI). (b) Composite showing the MNI template projected to the midsaggital view of the AHB-MNI. The blue arrows point to the x/y/z center of the coordinates of both stereotaxic spaces. MNI/ICBM2009b brain, ©1993–2004 Louis Collins, McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University.

**Figure 2.6** Corresponding landmarks between MNI/ ICBM2009b brain (top) and AHB brain (bottom). For the generation of the geometric shape constrains the following landmarks marked by black vertical lines were used: anterior-posterior extension of the brain, AC, PC, pole of the temporal lobe, and the extension of the corpus callosum. MNI/ICBM2009b brain: ©1993–2004 Louis Collins, McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University.
The 3D reconstruction was performed in 2 stages: the linear and the nonlinear stage. During the first stage we created a sliceto-slice linearly registered *Atlas* volume and a corresponding brain segmentation of the ICBM2009b brain. In this step 1D and 3D geometric constrains were defined (Fig. 2.6). The set of 1D landmarks consisted of the anterior-posterior extension of the brain, AC, PC, pole of the temporal lobe, and the extension of the corpus callosum. As 3D volume constrains we used the overall shape of the brain, ventricles, corpus callosum, optic tract, lateral and medial geniculate bodies, septum, mammillary bodies. Since the deformation fields during the slice-to-slice reconstruction are restricted to the 2D coronal plane we generated for each slice a corresponding slice from the 3D constrain volumes and used them in the next nonlinear step of the reconstruction.
The slice-to-slice registration was followed by a global nonlinear stage. Each slice was nonlinearly registered to the neighboring slices. Simultaneously, the geometric constrains for each slice were aligned. After the initial match a high resolution iterative optimization procedure was applied to ensure perfect match between **89**
the geometric volumes and the structures of the *AHB*. We used an optimized sequence of tree multimodal measures during this high resolution step. The resulting 3D volume along with the corresponding MNI MRI slices were used to register the histological sections into the MNI/ISBM2009b space.
# 2.1.11 Registration of the Histological Sections to the Reconstructed Volume
Prior to the registraton an intensity correction algorithm was employed for optimization of the histological data accounting for staining inhomogeneities and deformations such as shearing, local compression, tearing. Missing parts of the slices were reconstructed either from neighboring slices or by means of inpainting algorithm. We have indicated the reconstructed areas by grey broken lines in the fiber-stained sections.
A total of 99 fiber and 50 cell stained


**Figure 2.7.** Myelin stained section (top left) at the level of the anterior commissure registered to the corresponding MNI slice (top right). Below: color coded composite of both images: myelin stained section (green), MNI slice (red). MNI brain; ©1993–2004 Louis Collins, Mc-Connell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University.
high resolution slices were registered to the 3D AHB reconstruction by means of the multimodal registration procedure. In the first step the slices were registered to the corresponding sections from the 3D reconstruction. The next step consisted of local high resolution multimodal registration of the subcortical part of the slice to the corresponding MNI section. For the registration of the plates to the MNI space we used a pseudo-grey level representation of the schemata.v


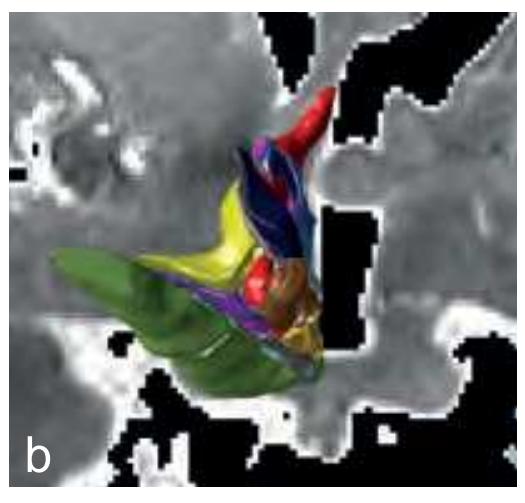

**Figure 2.8.** Examples of the automatic correlation between the histomorphologic and MR-image datasets. (a) Registration of the human thalamus model from Mai and Forutan (2012) to the MNI template. (b) Registration of the human hypothalamus model from Y. Koutcherov (see page 427) to a formalin fixed autopsy brain with severe pathological changes due to infarction. After transformation the borders of *Atlas*-regions are shown as overlay on the individual MRimages in any chosen plane. The precision of the registration can be controlled and can - if necessary - be interactively adjusted. This procedure uses no probability maps and preserves the original MR data. Therefore, the high original resolution by MRI is retained. Any point within the (individual) MR-brain can be back-registered by the transformation matrix to the *Atlas* brain and used for intra- and extramural communication. (Data from Mai and Majtanik, 2014).
# 2.1.12 Use of the Atlas for the Interpretation of Individual in vivo Brains
Figure 2.8 shows examples of the automatic correlation between the histomorphologic and MR-image datasets. For the *Atlas* being registrered to a standard MR-dataset an automatic two stage processing pipeline is used.
In the first stage the 3D *Atlas* template is registered to the target brain with standard 1mm resolution. This stage uses a T1-weighted and optionally a co-registered T2-weighted MR image of the patient's brain as an input. First, an automatic localization of the anatomical landmarks AC and PC derived from Pallavaram et al. (2009) is performed. In the next step image intensities are corrected and normalized. The preprocessing ends with an intensity-based segmentation of the brain (white and gray matter) and of the ventricles. Further, a standard resolution (1mm) *Atlas* registration is performed by three registrations with increasing degrees of freedom (DOF), rigid (6 DOF), affine (12 DOF) and non-linear diffeomorphic registration. Each registration type uses a coarse-to-fine approach and smooth-tosharp refinement similar to the one described in Haegelen et al. (2013).
The accuracy and the robustness of the used algorithms are critical for the precision of the resulting *Atlas-*based segmentation. With the standard 1mm MR resolution the description details of the deformation fields are not sufficient. Therefore a second high resolution stage is executed. In the second stage a Gaussian volume mask corresponding to a region-of-interest (ROI) around the target and surrounding structures (thalamus, striatum, ...) are defined in the patients MR and in the *Atlas* template space. The ROIs are super-sampled to a resolution of 0.1 mm. The ROIs are coregistered using diffeomorphic registration algorithms (Beg et al., 2005). In this high resolution stage the results of the first stage are locally optimized with a sequence of multi-modal distance measures to perfectly match computer identified control volumes.
After the registration the borders of *Atlas*regions are shown as overlay on the individual MR-images in any chosen plane and can - if necessary - become adjusted to relevant landmarks. This procedure uses no probability maps and maintains the original MR data. Therefore, the high original resolution by MRI is retained (Fig. 2.8).
Registration of the 3D-MRI into the MNI space facilitates the precise identification, localization and characterization of anatomical cortical and subcortical regions in MNI normalized datasets.
Because the transformation matrix is known any point within the MR-brain can be correlated to the *Atlas* brain. The 3D-AHB can thus serve as registry of the corresponding coordinates and as module for the integration of databank entries.
# 2.1.13 Mapping of the Cortex Areas
Since many reports of ROIs have been correlated with the Brodmann areas we have used these delineations for correlation with the histology of the brain sections.

**Figure 2.9.** Brodmann (1909) parcellations of the cortex surface-registered to the 3D-AHB. The 3D-AHB is shown in three different representations: fiducial, very inflated and as flat map. (Data from Mai and Majtanik, 2014).
**90**
*Preparation of the Brodmann Areas:* The photographs of the cell-stained sections and the schematic drawings show delineations of the cortex which are based on the original maps of Brodmann (1909). We have used the surface-based maps that were generated (in Caret) by Van Essen (Van Essen, 2005, Van Essen et al. 2012) but we have induced a modification by manually estimating areal boundaries on the *Atlas* brain and transferring them onto the surface of the 3D reconstruction.
The same procedure as for mapping the Brodmann areas has been applied for the registration of the von Economo and Koskinas surface-based maps. The resulting areal boundaries are not shown on the sections or diagrams but are indicated on the linear representation of the cortical ribbon ("stripes", Section 2.1.14).
The Brodmann and von Economo and Koskinas surface-based maps were generated by manually estimating areal boundaries on the 3D reconstructed *AHB* using as a reference the classical drawings from these authors. Further, the reconstructed *3D-AHB* was surface-registered to the PALS12 atlas of Van Essen by open source software Caret (Van Essen 2005, Van Essen et al., 2012). The Brodmann and von Economo and Koskinas parcellations of the cortex were then projected onto the flat map cortex representation of the *AHB*. The cortical parcellation of the cortex represented by the flatmaps of the PALS12 atlas was back-transformed to the *AHB* by means of inverse deformation fields.
Since the insula and the areal boundaries of the orbitofrontal cortex are not sufficiently delineated in the Brodmann map we have included the insula as defined by the circular sulcus and have used the delineations of Öngur et al. (2003) from the PALS12 atlas flat map representations for the parcellation of the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex (Öngur et al. 2003, Van Essen et al. 2012).
#### Flat Map Registration and Transformation to the Atlas Slices:
For the projection of the cortical parcellations to the 2D sections we generated a coronal section through the *3D-AHB* surface representation at the corresponding position. From the intersection of the surface with the coronal cutting plane a linear contour representation of the parcellation was generated and transferred to the histological section. For the schemata and Nissl stained sections the parcellations from Brodmann (1909) and Öngür et al. (2003) were adopted.

**Figure 2.10.** Linear representation of the cortex as "stripes". The left figure shows the MNI-registered cell-stained slice with delineated Brodmann areas. The right-sighted cartoon depicts the "unwrapping" of the cortex into stripes. The stripes are defined as straight bands of "unfolded" cortex together with parcellation bands (a). The stripe segment depicted in (b) represents the cortex between the two blue marking lines in (a). The small segment indicated be asterisks is shown at different magnifications in the left-sided figure and in a-c (red boxed area\*\*.) Functional area delineations are shown at the bottom of the stripe at (b).
We are very aware that the representation of the borders indicating areal boundaries of "original" Brodmann areas is at present only best guess and needs confirmation or changes depending on more accurate methodological studies. This will be aided by additional features that update the structural and functional analysis of the sections:
- (i) We make the the original cell- and fiber-stained sections available at high magnification in the internet (www.thehumanbrain.info).
- (ii) On the facing page of each full page Nissl section we present photographs showing small sectors of cortical areas that are displayed at high magnification to allow the study of the cytoarchitectonic characteristics. We selected preferentially those areas which are thought to correspond with the photographs published by von Economo and Koskinas (1925). This has the advantage that their descriptions can be evaluated with respect to correspondence or conflicts. Thus, the user of the *AHB* can profit from their monumental work of more than 800 pages and their histological atlas.
- (iii) As a novel way of depicting cortical areal pattern we show the cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon unfolded in a linear presentation (see 2.1.10 and 2.2.12). This representation maintains the x/y/z coordinates of the brain space and allows the easy registration of the interpretation of other authors and of regions of interest provided by imaging techniques.
# 2.1.14 Generation of the Linear Representation of Cortex "Stripes"
For mapping, documentation and comparison between differing interpretations of cortex areas and inclusion of activation areas (ROIs) we produced linear representations of the cortex (Fig. 2.10).
The linearization is based on a solution of the Laplace equation between inner and outer contour, and resampling of the cortex along the traverses. We call this linear representation a *stripe*. The stripe is a band that represents equally spaced sampling of the cortex. For the *AHB* we present the stripe representations of the Brodmann and von Economo and Koskinas cortex parcellations supplemented by the parcellations of Öngür et al. (2003). We also show a stripe with the representation of the gyri and sulci which aides the orientation and localization of the areas involved. The presentation of linear cortex stripes adjusts the different regions of interest into common coordinates and allows easy comparison of different results reported at common coordinate points or regions.
# 2.1.15 The Layout of the Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Stereotaxic Atlas in MNI Space
The main part of the "*Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Stereotaxic Atlas"* consists of 99 fiber-stained (myelin) plates and their graphic interpretation, both mounted on facing pages (Fig. 2.11).
**91**

**Figure 2.11.** Open page view of the *Atlas* depicting the layout with the fiber-stained (myelin) sections (1) and corresponding diagrams (2) on facing pages. The colors of the cortex of the myelin section illustrate the gyral and sulcal anatomy. Since the interpretation of the cortical surface is more detailed than in the three *Atlases of the Brain in the Head* the color coding is not always exactly matching between the *Atlases*. The colors outlining the cortex on the right-sided diagram (2) illustrate the Brodmann areas. The locators (3,4), accordingly, show the anatomical cortex map (on the even numbered pages) and the Brodmann map as generated from automatic registration (on the odd numbered pages). Note that

the size of the photographs and of the diagrams are not identical (see next page). The section level is indicated first, by the serial plate number (5) second, by the vertical bar in the locators, third, by the section and slice number (6) and finally, most important, by values next to the locator (7,8). The MNI-position gives the distance from the center of the anterior commisure in the MNI space; the *ICL*-position refers to the distance from the center of the anterior commissure (y=0) of the *Atlas* brain; MCP indicates the distance from the midcommissural point of the ICL of the *Atlas* brain.
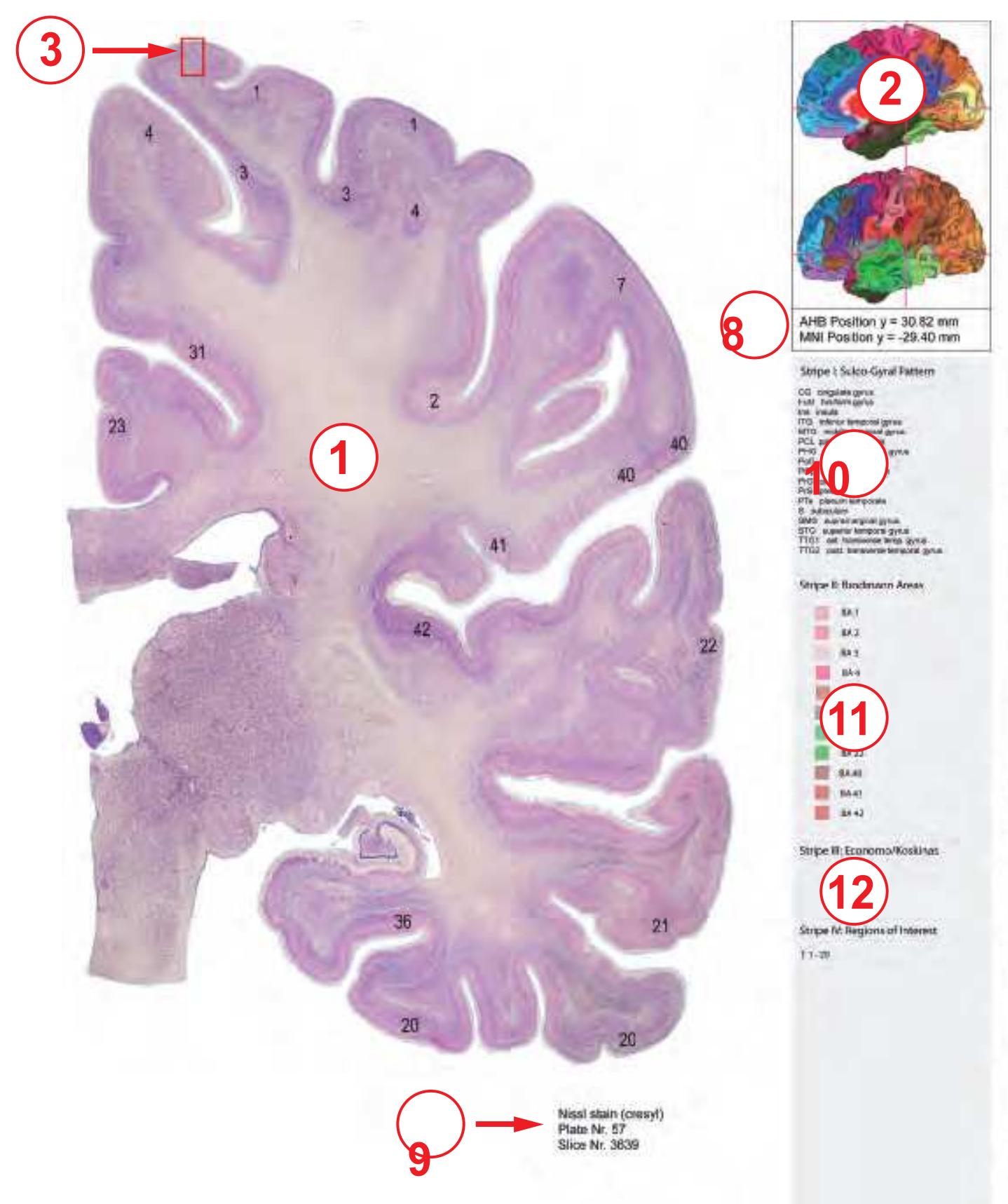
Figure 2.12. Layout of the pages presenting the photographs of the cell-stained (Nissl) sections and accompanying features. The delineated and numbered cortex areas on the cell-stained (Nissl) photographs indicate the Brodmann areas (1). The locators (2) show the midsagittal and lateral views of the brain with the Brodmann parcellations as fiducial representation (compare to Fig. 2.9). The boxed area (3) indicates the segment of cortex which is depicted at high magnification on the right side (4). The location of this segment was selected to correspond to a photograph from the von Economo and Koskinas atlas illustrating the cytoarchitecture of this region (5). In the lower half the cortical cytoarchistripes (7) separately. **92**

tectonic ribbon is unfolded and presented linearly (6). The bands which are seen below the cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon (7) provide the sequence of the sulcal-gyral organization, the Brodmann areas, the von Economo and Koskinas areas and interpretations from other authors. The location of the section is indicated by the vertical bar in the locator (2), the values indicating the distance from the center of the anterior commissure of the *AHB* and MNI coordinates (8) and the successive section number (9). The legend is subdivided (10, 11, 12) and lists the features referring to the bands below the
Interdigitated within the existing myelin plates we have included fifty cell-stained (Nissl) plates. All photographs of the celland fiber-stained sections as well as the drawings have been transformed to fit the MNI-space (Section 2.1.9).
The magnification of the photographs is the same at section levels which show the corpus callosum. Anterior to the rostrum and posterior to the splenium the magnification is higher and varying, dictated by the availability of space.
Because the arrangement of the plates, diagrams and additional information may be difficult to follow, we shortly describe the layout of this part of the *Atlas* (Figs. 2.11 and 2.12).
In the *photographs of the fiber-stained (myelin) sections* we have indicated the gyral and sulcal anatomy. The colors distinguishing cortical regions indicate the surface anatomy as presented on pages 95-97.
The *photographs of the cell-stained (Nissl) sections* display the functional cortical delineations derived from Brodmann maps as generated by the semi-automatic mapping procedure from the 3D reconstruction of the *Atlas* hemisphere in the MNI-stereotaxic space (Section 2.1.13).
Within the *schematic drawings* we also provide the Brodmann areas.
Therefore, an open book side where the myeloarchitecture with the sulcal and gyral pattern is represented on the left side, the right side shows diagrams at the same section levels with the Brodmann areas together with the subcortical architecture (Fig. 2.11).
On the page opposite to the full page Nissl-plates small sectors of the cortex are displayed at high magnification. We selected areas which are thought to correspond with those published by von Economo and Koskinas (1925). The selected image from these authors is presented at low magnification (Fig. 2.12). Text and tables from von Economo and Koskinas are recently masterly translated, revised and edited by L. C. Triarhou (von Economo and Koskinas, 2008, 2009).
In the lower half of the page we depict the cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon unfolded and presented linearly (Fig. 2.12). This presentation allows the synoptic registration of results from different sources. This arrangement makes possible to bring any x/y/z coordinate or region of interest in registry with existing entries and to correlate them with the cyto- and myeloarchitecture of the specified regions.
Since the cortical ribbon can not always be shown as a single uninterrupted band, it may be broken into several segments. Begin and direction of each stripe, however, are indicated within every Nissl-section and the topography is comprehensible by correlation with the sulco-gyral pattern (that is provided in the uppermost stripe).
Next to the locators and the serial plate number we provide the position of the photographs and diagrams of the sections by three distance measures with regard to the anterior-posterior position in the brain space: MNI, ICL and MCP, respectively.
*ICL and MCP* correspond to the distance along the intercommissural line of the native *Atlas* brain, not registered to the MNI-space. The ICL and MCP values indicate the position of each section either with respect to the center of the anterior commissure (ICL) or to the midcommissural point (MCP). Both values allow comparison with the previous editions of the *Atlas*.
The MNI value provides the distance from the center of anterior commissure in the MNI space (see section 2.1.10).
Due to the different anterior-posterior extension of the Atlas (171 mm) and the MNI brain (181 mm), respectively, the ICL and MNI values may differ (figure 2.13).
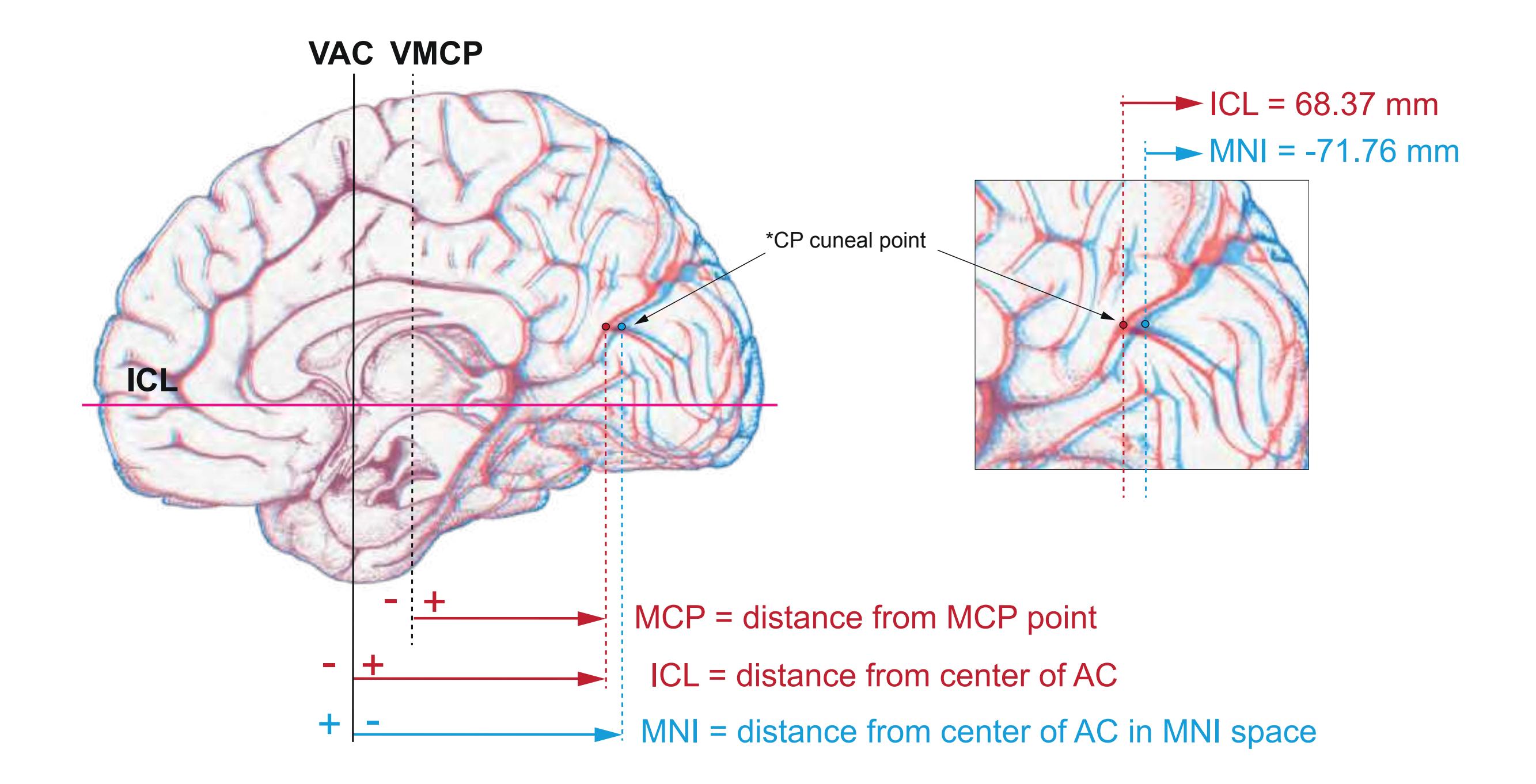
Figure 2.13. Midsagital view of the *Atlas* in the stereotaxic space of the printed *Atlas* (red) and of the Atlas brain registered to the MNI brain (blue). In both instances the point of reference [0,0,0] is located in the center of the anterior commissure (crossing of ICL and VAC). The right image shows the enlarged area around the cuneal point \*CP together with the ICL and MNI distances. Abbreviations: ICL intercommissural line, MCP midcommissural
point, MNI coordinate system of the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI/ICBM2009b brain, ©1993–2004 Louis Collins, McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University), VAC vertical through the anterior commisure, VMCP vertical through the midcommissural point.
**93**
**2.1.16 References**
- Assheuer, J., Lanta, L., Longerich, U.J.J., Sievert, T., Mai J.K. (1990) Standardisierung der cerebralen Bilddarstellung in der Magnetresonanztomographie (MRT). RöFo, 153: 296-302.
- Beg, M. F., Miller, M. I., Trouve, A., Younes, L. (2005) Computing large deformation metric mapping via geodesic flows of diffeomorphisms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 61: 139–157.
- Brodmann, K. (1909). Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde. Leipzig: Barth.
- Collins, D.L. (2012) Montreal Neurological Institite (MNI) stereotaxic space. In: The human cerebral cortex. Ed. Petrides, M.: Academic Press/ Elsevier, San Diego, pp. 11-17.
- Evans, A. C., Collins, D. L., Milner, B. (1992) An MRI-based stereotactic atlas from 250 young normal subjects. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 18: 408.
- Evans, A. C., Collins, D. L., Mills, S. R., Brown E. D., Kelly, R. L. Peters, T. M. (1993) 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes, Proc. IEEE-Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 1813-1817.
- Fonov, V., Evans, A.C., Botteron, K., Almli, C.R., McKinstry, R.C., Collins, D.L., and Brain Development Cooperative Group. (2011) Unbiased average age-appropriate atlases for pediatric studies. Neuroimage 54(1): 313-327.
- Haegelen, C., Coupé, P., Fonov, V., Guizard, N., Jannin, P., Morandi, X., Collins, D.L. (2013) Automated segmentation of basal ganglia and deep brain structures in MRI of Parkinson's disease. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 8(1): 99-110.
- Laird et al., (2010) Comparison of the disparity between Talairach and MNI coordinates in functional neuroimaging data: Validation of the Lancaster transform. Neuroimage 51(2): 677–683.
- Lancaster, J.L., Tordesillas-Gutiérrez, D., Martinez, M., Salinas, F., Evans, A., Zilles, K., Mazziotta, J.C., Fox, P.T. (2007) Bias between MNI and Talairach coordinates analyzed using the ICBM-152 brain template. Human Brain Mapp. 28(11) 1194-1205.
- Lange, H., Thörner G. (1974) Zur Neuroanatomie und Neuropathologie des Corpus striatum, Globus pallidus und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen. Thesis, University Duesseldorf.
- Löchel, D. (2007) Morphologische multimodale Bildanpassung. Thesis, University of Duesseldorf.
- Longerich, U. (1989) MRI-Untersuchungen an in-vivo und in-vitro Gehirngewebe: Einfluß von Fixierung und Temperatur auf das Relaxationsverhalten, die Protonendichte und das Kontrastverhalten. Thesis, University of Duesseldorf.
- Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G. (2012) The Human Nervous System, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego.
- Mai, J.K., Forutan, F. (2012) Thalamus. In: Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G. (Eds) The Human Nervous System, 3rd Ed. San Diego: Academic Press/Elsevier, pp. 618-677.
- Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M. (2013) Registraton of the Atlas of the Human Brain to MNI/ ICBM brain templates. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. No. 197.02.
- Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M. (2014) Cortex Cytoarchitecture and Functional Areas in the MNI-Registered "Atlas of the Human Brain": Implications for Diagnostics. Federation of European Neuroscience Societies (FENS) Abstr. No. 3616.
- Mai, J.K. and Paxinos, G. (2012) The Human Nervous System, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego.
- Öngür, D., Ferry, A.T., Price, J.L. (2003) Architectonic subdivisionof the human orbital and medial prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol,460(3): 425-449.
- Pallavaram, S., Dawant, B.M., Koyama, T., Yu, H., Neimat, J., Konrad, P.E., D'Haese, P.F. (2009) Validation of a fully automatic method for the routine selection of the anterior and posterior commissures in magnetic resonance images. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87(3):148-154.
- Sievert, T. (1992) Topometrie des menschlichen Gehirns: Evaluation eines Verfahrens zur Integration morphologisch-funktioneller Daten aus histologischen Schnitten in die klinische Diagnostik. Thesis, University of Duesseldorf.
- Sütfels, S. (2011) Anatomische Zuordnung funktioneller MRT- und PET-Daten von subkortikalen Hirnarealen im Talairach-Raum - Anwendung eines serienschnittbasierten Atlassystems. Thesis, University of Duesseldorf.
- Talairach, J., Szikla G. (1967) Atlas d' Anatomie stereotaxique du Telencephale. Masson & Cie. Paris.
- Talairach, J., Tournoux P. (1988) Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain. G. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York.
- Tamraz, J.C., Comair, Y.G. (2000) Atlas of Regional Anatomy of the Brain Using MRI: With Functional Correlations. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- Van Essen, D.C. (2005) A population-average, landmark- and surface-based(pals) atlas of human cerebral cortex. Neuroimage, 28(3): 635-662.
- Van Essen, D.C., Dierker, D.L. (2007) Surface-based and probabilistic atlases of primate cerebral cortex. Neuron 56(2): 209-225.
- Van Essen, D.C., Glasser, M.F., Dierker, D.L., Harwell, J., Coalson T. (2012) Parcellations and hemispheric asymmetries of human cerebral cortex analyzed on surface-based atlases. Cereb. Cortex 22(10): 2241-2262.
- Vogt, O. (1905) Das Pantomikrotom des Neurobiologischen Laboratoriums. J. Psychol. Neurol. 6: 121-125.
- von Economo, C., Koskinas, G.N. (1925) Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des Erwachsenen Menschen: Textband und Atlas mit 112 Mikrophotographischen Tafeln. Springer, Vienna.
- von Economo, C., Koskinas, G.N. (2008) Atlas of cytoarchitectonics of the adult human cerebral cortex (translated, revised and edited by L.C. Triarhou). Basel, S. Karger.
- von Economo, C., Koskinas, G.N. (2009) Cellular structure of the human cerebral cortex (translated and edited by L.C. Triarhou). Basel, S. Karger.
**94**
# 2.2 Surface Views
AAnG angular gyrus AOrG anterior orbital gyrus aos-i anterior occipital sulcus, inferior ramus aos-s anterior occipital sulcus, superior ramus apa posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt); (precuneal limiting sulcus) asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus atcos anterior transverse collateral sulcus BSt brainstem ccs calcarine sulcus ce central sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus Ent entorhinal gyrus fd frontal dimple FMG frontomarginal gyrus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FuG fusiform gyrus IFG-Op inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFG-Or inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part
IFG-Tr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus IOG inferior occipital gyrus ios inferior occipital sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus ISG inferior sagittal gyrus its inferior temporal sulcus ITG inferior temporal gyrus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus LgG lingual gyrus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus lus lunate sulcus MFG middle frontal gyrus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus ops occipitopolar sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcs postcentral sulcus PHG parahippocampal gyrus POc-a parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-p parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus polfs preolfactory transverse sulcus ppa posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt) PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus prop preopercular sulcus prs precentral sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus PSt parastriate area ptcos posterior transverse collateral sulcus ras radiate sulcus rcs-i retrocalcrine sulcus, inferior branch rcs-s retrocalcrine sulcus, superior branch
SFG superior frontal gyrus
SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus SG straight gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus sos superior orbital sulcus SPL superior parietal lobule sprs superior precentral sulcus SSG-a superior sagittal gyrus, anterior part SSG-p superior sagittal gyrus, posterior part sss superior saggital sulcus (v.Economo/Koskinas) STG superior temporal gyrus sts superior temporal sulcus tos transverse occipital sulcus tos-l transverse occipital sulcus, lateral ramus tos-m transverse occipital sulcus, medial ramus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone TPG temporopolar gyrus Un uncus us uncal sulcus
**95**
acus sulcus acusticus angs angular sulcus aos anterior occipital sulcus aos-s anterior occipital sulcus, superior ramus aos-i anterior occipital sulcus, inferior ramus apa posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt); (precuneal limiting sulcus) ASCe anterior subcentral gyrus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus COp central operculum (Rolandi) dgs diagonal sulcus FMG frontomarginal gyrus fmps frontal paramidline sulcus fms frontomarginal sulcus FOp frontal operculum fors fronto-orbital sulcus FP frontal pole FrP frontoplolar gyrus IFG inferior frontal gyrus IFG-asc inferior frontal gyrus, ascending part IFG-ba inferior frontal gyrus, basilar part IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part ifs inferior frontal sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
impII second intermediate parietal sulcus
ipcs inferior postcentral sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus ips-a intraparietal sulcus, ascending segment ips-d intraparietal sulcus, descending segment ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment ITG inferior temporal gyrus its inferior temporal sulcus its-a inferior temporal sulcus, anterior segment its-p inferior temporal sulcus, posterior segment lf lateral fissure lf-a lateral fissure, anterior segment lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal segment lf-m lateral fissure, middle segment lf-p lateral fissure, posterior segment lf-v lateral fissure, vertical segment lors lateral orbital sulcus los lateral occipital sulcus LuG lunate gyrus lus lunate sulcus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcP occipital pole OrG orbital gyri pacs paracentral sulcus PAnG posterior angular gyrus pcs postcentral sulcus pi preoccipital notch
POc-a parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-p parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum pof parieto-occipital fissure ppms posterior paramidline sulcus ppa posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt) PrG precentral gyrus prs precentral sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus PSCe posterior subcentral gyrus ras radiate sulcus (Eberstaller) SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus sfs superior frontal sulcus SMG supramarginal gyrus sms supramarginal sulcus SOG superior occipital gyrus sos superior occipital sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus SPL superior parietal lobule sprs superior precentral sulcus STG superior temporal gyrus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
tos-m transverse occipital sulcus, medial ramus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
TP temporal pole ts triangular sulcus
tvt transverse temporal sulcus
sts-a superior temporal sulcus, anterior segment
segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior sts-p superior temporal sulcus, posterior segment
**96**

| *X
cuneolingual gyrus (in depth) (-> Ribas) | frs | fragmentosus sulcus | MTG | medial temporal gyrus | PTG | paraterminal gyrus |
|------------------------------------------------------------|-------|-------------------------------------------------|--------|-------------------------------------------------|-------|-----------------------------------------------|
| 1p
olfactory peduncle | FuG | fusiform gyrus | OcP | occipital pole | pts | paraterminal sulcus |
| ac
anterior commissure | GA | ambiens gyrus | olfs | olfactory sulcus | rcc | rostrum of corpus callosum |
| acals
accessory callosal sulcus | gcc | genu of corpus callosum | ops | occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of Seitz) | rcs-i | retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch |
| ACC
anterior cingulate cortex | GDe | gyrus descendens (Ecker) | pacs | paracentral sulcus | rcs-s | retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch |
| acs
calcarine sulcus, anterior part | ICg | isthmus of cungulate gyrus | pc | posterior commissure | rhs | rhinal sulcus |
| aMCC
anterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) | IFGOr | inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part | PCA | precommissural archicortex | RoG | rostral gyrus |
| AOrG
anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus | IFGTr | inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part | PCC | posterior cingulate cortex (B.Vogt) | ros | rostral sulcus |
| AOrG-l
anterior (intermediate) orbital g., lateral part | IFPG | inferior frontopolar gyrus | pcf | paracentral fossa | ros-i | rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch |
| AOrG-m
anterior (intermediate) orbital g., medial part | ifps | inferior frontopolar sulcus | PCg | paracingulate gyrus | ros-s | rostral sulcus, superior (upper) branch |
| apa
posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt); (precuneal | ILgG | inferior lingual gyrus | pcgs | paracingulate sulcus | RSG | gyri limbici retrospleniales (vonEconomo) |
| limiting sulcus) | IOG | inferior occipital gyrus | PCL | paracentral lobule | sbps | subparietal sulcus |
| aps
anterior parolfactory sulcus | iors | intermediate orbital sulcus | pcs | precentral sulcus | SCA | subcallosal area |
| asos
accessory supraorbital sulcus | ios | inferior occipital sulcus | PCun | precuneus | scc | splenium of corpus callosum |
| atcos
anterior transverse collateral sulcus | ISG | inferior sagittal gyrus | PHG | parahippocampal gyrus | scs | subcalcarine sulcus |
| bcc
body of corpus callosum | isgs | inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior) | pi | preoccipital incisure | SFGM | superior frontal gyrus, medial division |
| cals
callosal sulcus | ITG | inferior temporal gyrus | pMCC | posterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) | SFPG | superior frontopolar gyrus |
| ccs
calcarine sulcus, central part | its | inferior temporal sulcus | PMOL | posteromedial orbital lobule | sfps | superior frontopolar sulcus |
| ce
central sulcus | lf-h | lateral fissure, horizontal | POc-a | occipitoparietal arch, anterior part | SG | straight gyrus |
| CG
cingulate gyrus | LFuG | lateral fusiform gyrus | POc-p | occipitoparietal arch, posterior part | SLgG | superior lingual gyrus |
| cgs-a
cingulate sulcus, anterior part | LgG | lingual gyrus | pof | parieto-occipital fissure | SOG | superior occiptal gyrus |
| cgs-i
inferior cingulate sulcus | lgs | lingual sulcus | PoG | postcentral gyrus | sors | supraorbital sulcus |
| cgs-mg
marginal ramus of cingulate sulcus | LOrG | lateral orbital gyrus | polfs | preolfactory transverse sulcus | sos | superior occipital sulcus |
| cgs-p
cingulate sulcus, posterior part | lors | lateral orbital sulcus | POrG | posterior orbital gyrus | SPL | superior parietal lobule |
| cos
collateral sulcus (medial occipitotemporal s.) | lots | lateral occipitotemporal sulcus | pors | posterior orbital sulcus | SSG | superior sagittal gyrus |
| cos-o
collateral sulcus, occipital ramus | LPHT | lingual-parahippocampal transition area | pors-m | posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch | sss | superior sagittal sulcus (v.Economo/Koskinas) |
| cos-ph
collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus | mfms | medial frontomarginal sulcus | posc | postreme subcallosal sulcus | TIG | transverse insular gyrus |
| cos-t
collateral sulcus, temporal ramus | MFPG | middle frontopolar gyrus | ppa | posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt) | tors | transverse orbital sulcus |
| culs
cuneal limiting sulcus | mfs | midfusiform sulcus | pps | posterior parolfactory sulcus | TPG | temporopolar gyrus |
| Cun
cuneus | MFuG | medial fusiform gyrus | PRC | perirhinal cortex | Un | uncus |
| Ent
entorhinal gyrus | MOrG | medial orbital gyrus | PrG | precentral gyrus | us | uncal sulcus |
| FMG
frontomarginal gyrus | mors | middle orbital sulcus | PSR | perisplenial region | | |
**97**
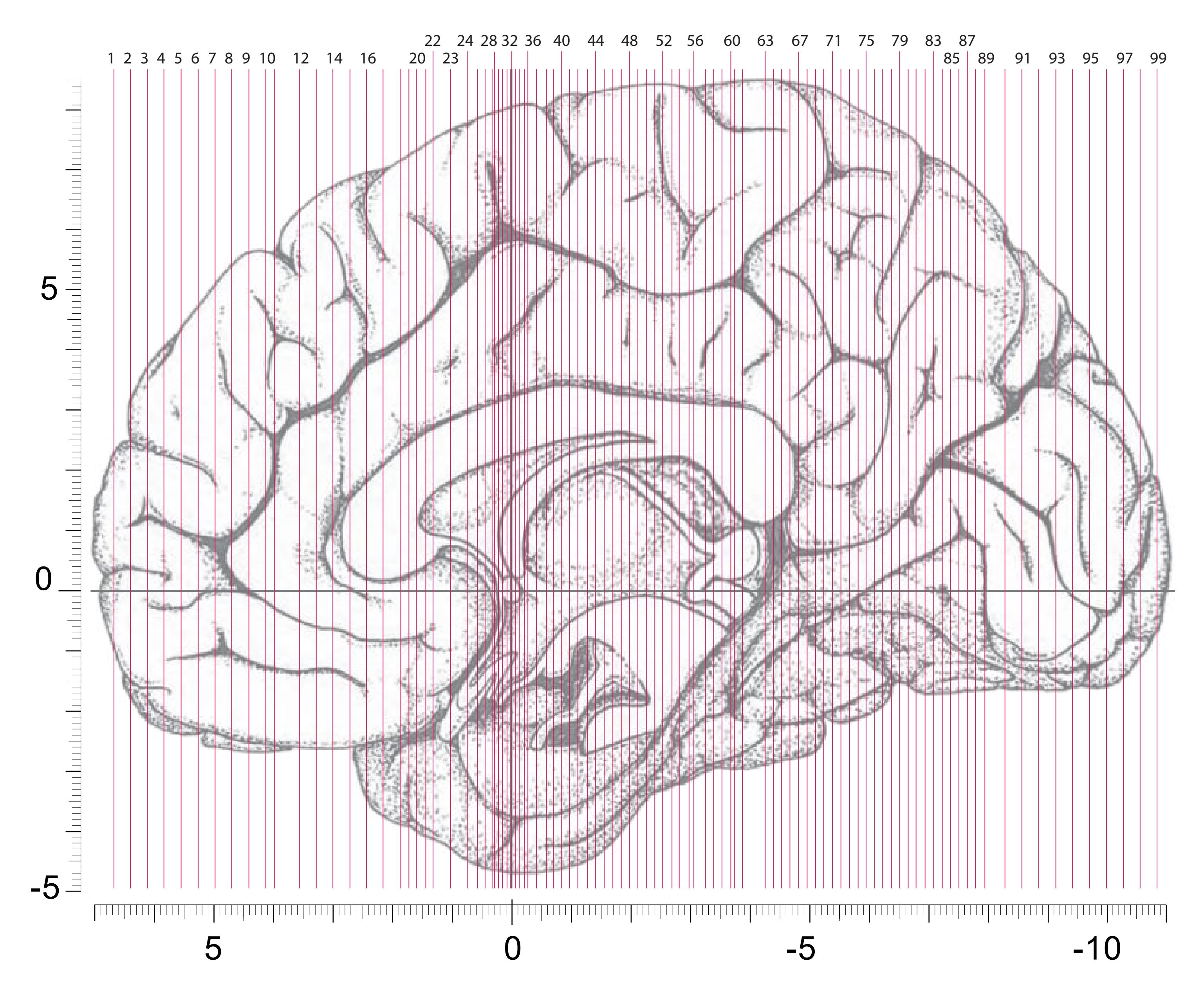
Location of the following 99 fiber-stained (myelin) sections and accompanying high detail diagrams. The diagram on this side shows the dimensions of the MNI-transformed unsectioned brain. "0" marks the vertical through the center of the anterior commissure. A negative sign signifies sections posteriorly to the center of anterior
commissure (AC). Rostral and caudal to the corpus callosum we used higher and varying magnification, dictated by the availability of space. Between the two anterior-posterior extremes of the corpus callosum we kept the magnificaiton constant.
**98**
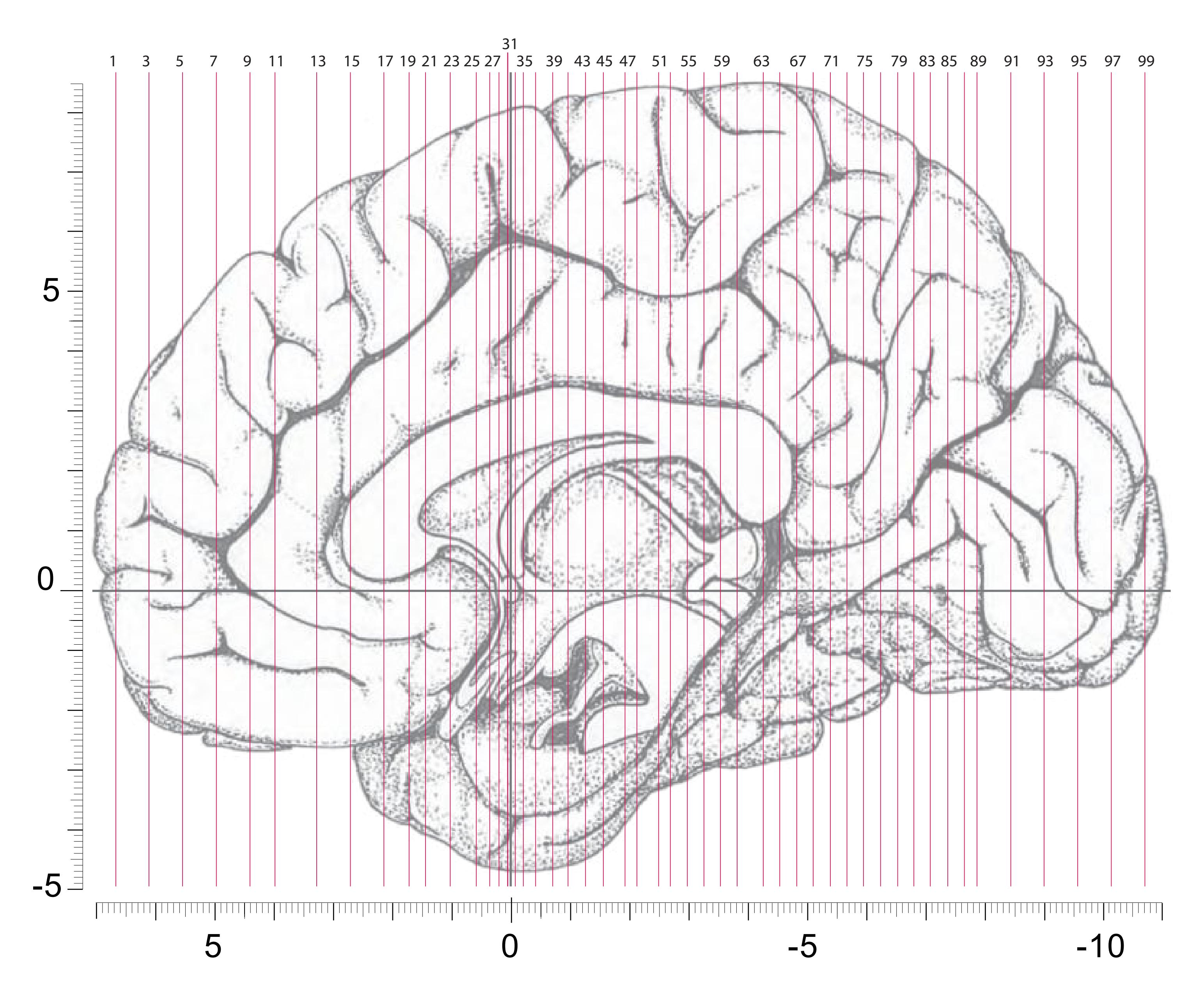
Location of the 50 cell-stained (Nissl) sections. The diagram shows the dimensions of the MNI-transformed unsectioned brain.
**99**
This page intentionally left blank
# 2.3 Plates, Figures and Diagrams

Sulci and Gyri

Brodmann (1909)
von Economo and Koskinas (1925)
The figures demonstrating the cortical delineations by Brodmann and von Economo and Koskinas are based on the surface registration of their published diagrams to the *3D-AHB* as described in sections 2.1.13 and not on dedicated cytoarchitectonic analysis.
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis BA5 area praeparietalis BA6 area frontalis agranularis BA7 area parietalis superior BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis BA10 area frontopolaris BA11 area praefrontalis
BA12 area praefrontalis BA13-16 fields 13-16 correspond to the
insular cortex BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis BA25 area subgenualis
BA26 area ectosplenialis BA27 area praesubicularis
BA28 area entorhinalis BA29 area retrolimbica granularis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis BA33 area praegenualis
BA34 area entorhinalis dorsalis BA35 area perirhinalis BA36 area ectorhinalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis BA38 area temporopolaris BA39 area angularis BA40 area supramarginalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis BA44 area opercularis BA45 area triangularis BA46 area frontalis media
BA47 area orbitalis BA48 area retrosubicularis BA49 area parasubicularis BA51 area prepiriformis
BA52 area parainsularis
Öngür et.al. (2003)
OP Architectonic areas of the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex adopted from Öngür et al., (2003).
OP {10, 11, 47/12, 13,14,24,25,32,47} OP\_AON anterior olfactory nucleus
OP\_G gustatory cortex OP\_I agranular insular cortex OP\_PRCO precentral opercular area
# BA\*
BA\* indicates a mismatch between the delineations of Brodmann and those registered from the publication from Öngur et al., (2003). It signifies the extension of the Brodmann area as compared to the territory defined by Öngür et al., (2003).
# Brodmann Areas The 54 Principal Areas of von Economo and Koskinas (1925)
# Lobus frontalis F
FA Area praecentralis FB Area frontalis agranularis
FC Area frontalis intermedia FD Area frontalis granularis FE Area frontopolaris
# Regio orbitalis
FF Area orbitalis (granularis) FG Area gyri recta (Area recta)
FH Area praefrontalis FI Area frontoinsularis FK Area piriformis frontalis FL Area parolfactoria
FM Area geniculata FN Area praecommissuralis
# Lobus limbicus L
LA Area limbica ant. agr. LB1 Area ultracingularis ant. LB2 Area indusei
LC1 Area cingularis post. dorsalis LC2 Area cingularis post. ventral. LC3 Area cingularis limit. post. LD Area retrosplenialis agranul.
LE Area retrosplenialis granulosa LF1 Area ultracingularis post. LF2 Area (ultracingularis) obtecta
# Lobus insulae I
IA Area insulae praecentralis IB Area insulae postcentralis
IC Area orbito-insularis ID Area insularis piriformis
**Lobus parietalis P** PA1 Area postcentralis gigantopyramidalis
PB2 Area postcentralis oralis simplex PC Area postcentralis intermedia
PD Area postcentralis caudalis PE Area parietalis superior
PF Area supramarginalis PG Area angularis
PH Area parietalis (temporo-occipitalis) basalis
#### Lobus occipitalis O OA Area peristriata
OB Area parastriata OC Area striata (granulosa)
# Lobus temporalis T
TA Area temporalis sup.
TB Area supratemporalis magnocellularis simplex
TC Area supratemporalis granulosa
TD Area supratemporalis intercalata TE Area temporalalis propria
TF Area fusiformis TH Area hippocampotemporalis
TG Area temporopolaris TI Area piriformis temporalis
TK Area substantiae perforatae post.
# Lobus limbicus inferior H
HA Area uncinata
HB Area parauncinata
HC Area rhinalis limitans HD Area praesubicularis granulosa
HE Area pyramidalis
HF Area fasciae dentatae
**101**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
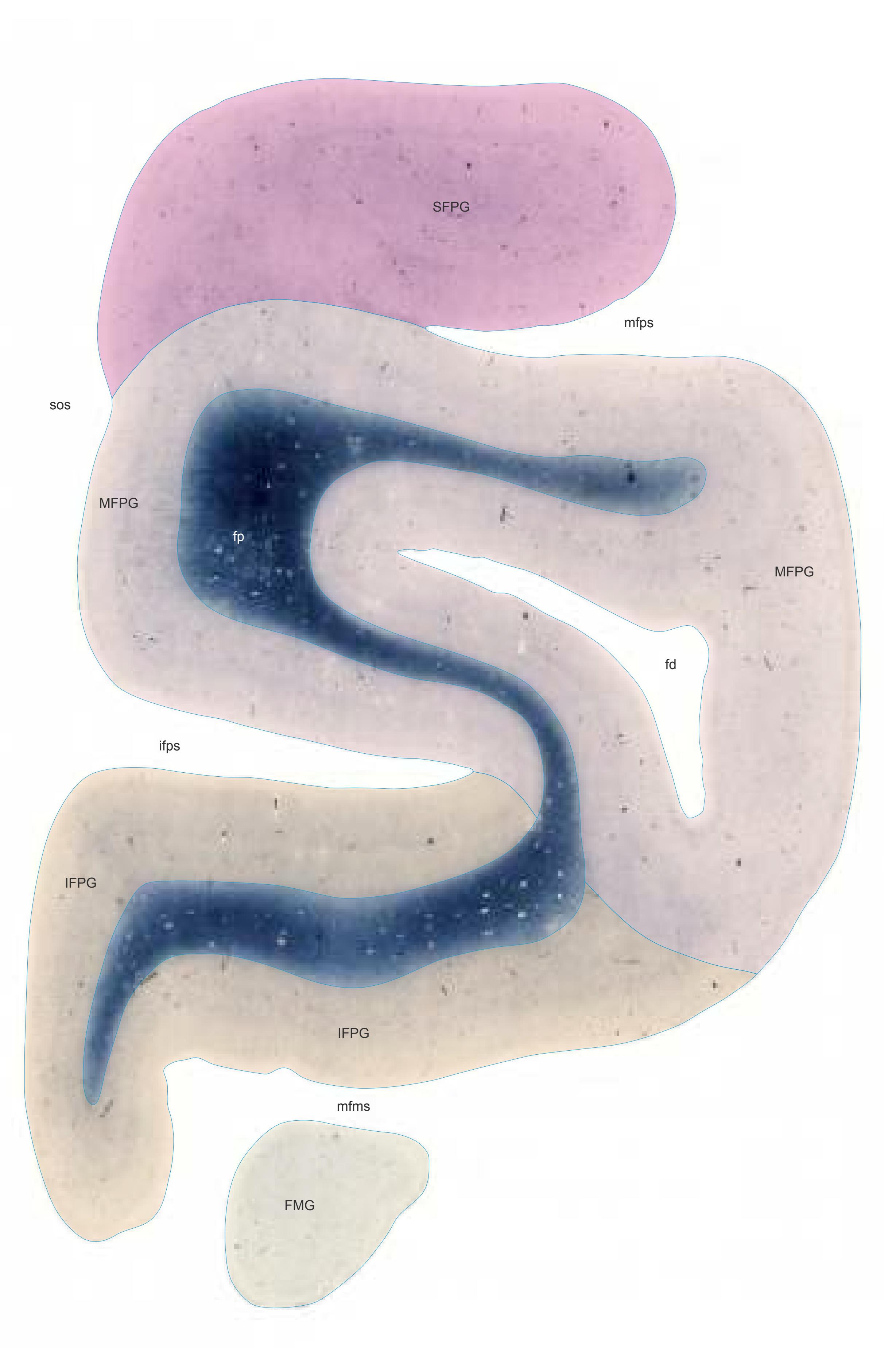

MNI Position y = 66.21 mm AHB Position y = -63.03 mm
## Gyri
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
#### Sulci
fd frontopolar dimple ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
# Fibers
fp frontopolar fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 1 Slice Nr. 138
**102**

1
ICL: -63.03 MCP: -77.77 MNI: 66.21

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101 ) BA\*10 see p. 101 OP 10 area defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
fd frontal dimple fps frontopolar sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus sos superior occipital sulcus
**103**


MNI Position y = 66.16 mm AHB Position y = -62.98 mm
# Gyral Pattern
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
- BA10 area frontopolaris
- OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FD granular frontal area FE frontopolar area
# Regions of Interest
-
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 1 Slice Nr. 140
**104**
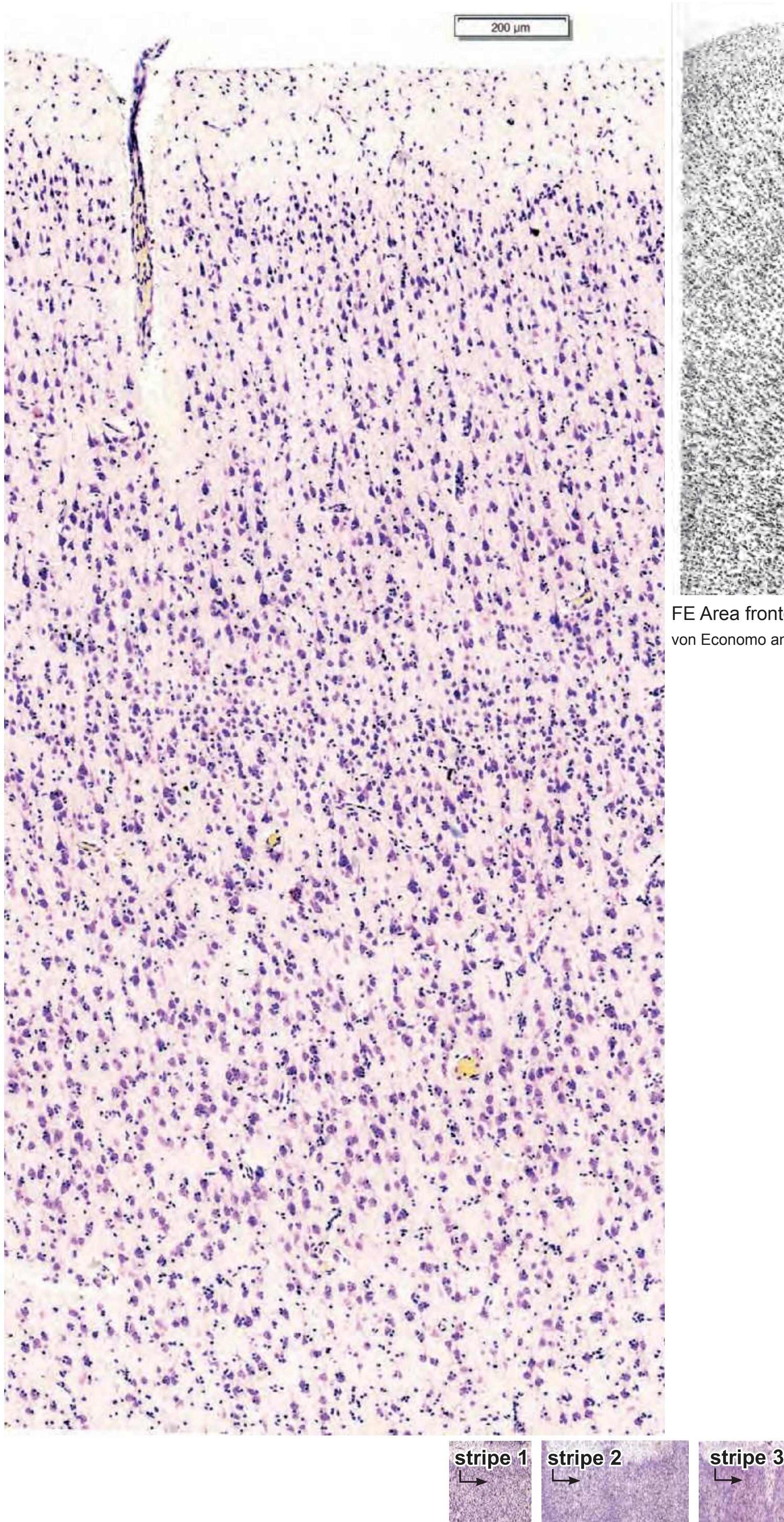

FE Area frontopolaris von Economo and Koskinas (1925) Plate XXXI (31)

Brodmann areas von Economo Regions of Interest


**105**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


MNI Position y = 63.45 mm AHB Position y = -60.41 mm
## Gyri
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
# Sulci
fd frontopolar dimple ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
## Fibers
fp frontopolar fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 2 Slice Nr. 236
**106**

2
ICL: -60.41 MCP: -75.15 MNI: 63.45

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10 see p. 101
ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus OP10, 11 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sos superior occipital sulcus
**107**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


MNI Position y = 60.64 mm AHB Position y = -57.73 mm
## Gyri
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
## Sulci
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus pos praeolfactory sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior part sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
# Fibers
fp frontopolar fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 3 Slice Nr. 336
**108**

ICL: -57.73 MCP: -72.47 MNI: 60.64

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10 see p. 101
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus OP10,11,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) pos praeolfactory sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch sfps superior frontopolar sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus sos superior occipital sulcus
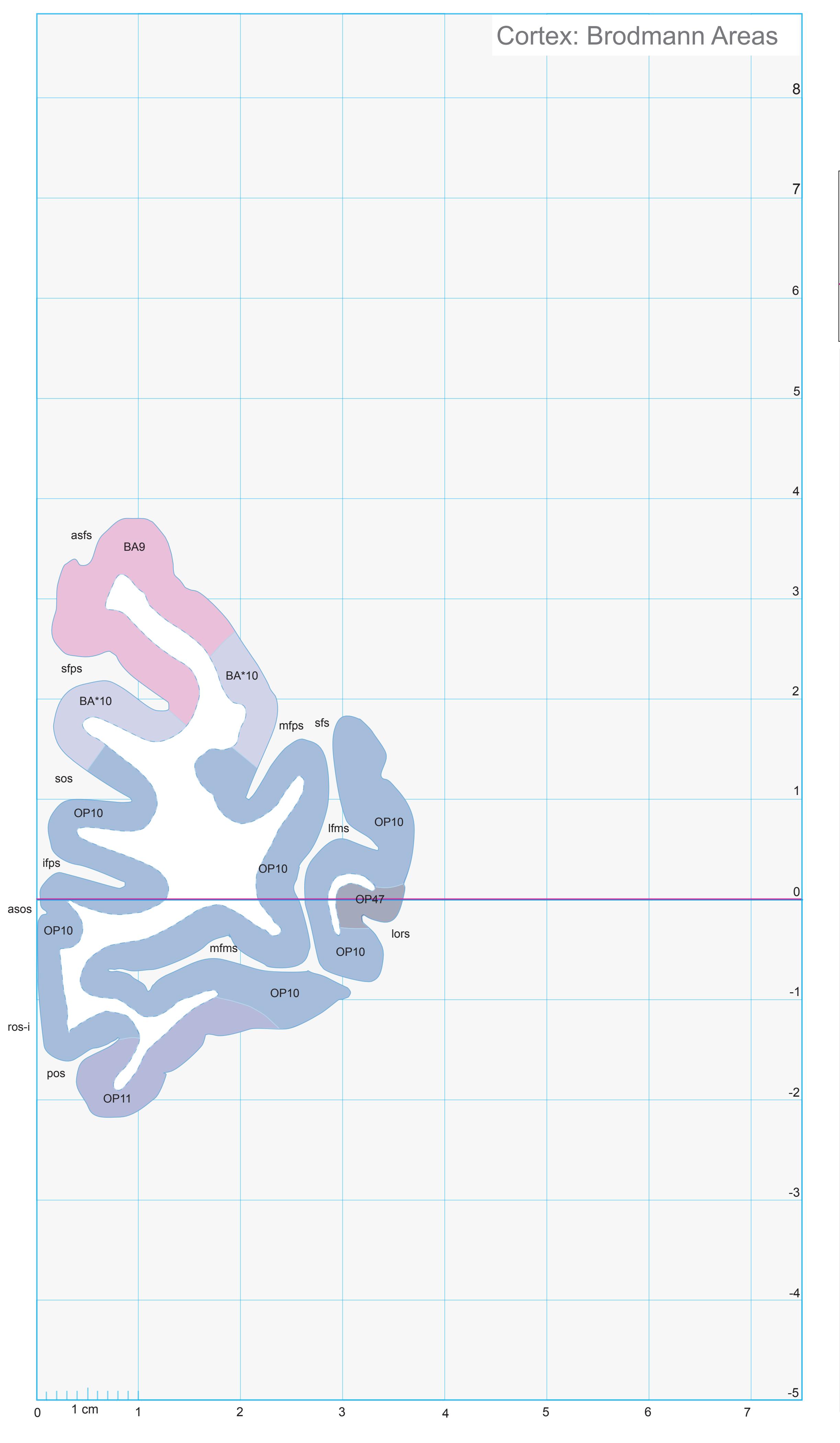
**109**

Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 3 Slice Nr. 337
MNI Position y = 60.61 mm AHB Position y = -57.70 mm
# Gyral Pattern
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
- BA9 area frontalis granularis
- BA10 area frontopolaris
- OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP11 area 11 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FD granular frontal area FE frontopolar area FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular orbital area
# Regions of Interest
-
**110**

**111**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci

Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 4 Slice Nr. 434

MNI Position y = 57.91 mm AHB Position y = -55.10 mm
## Gyri
FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG medial frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
#### Sulci
SG straight gyrus
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus mors medial orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pos praeolfactory sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior part sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
# Fibers
fp frontopolar fibers
**112**

4
ICL: -55.10 MCP: -69.84 MNI: 57.91

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10 see p. 101
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifps inferior frontopolar sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mors middle orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,11,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) pos praeolfactory sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch
sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sos superior occipital sulcus
**113**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
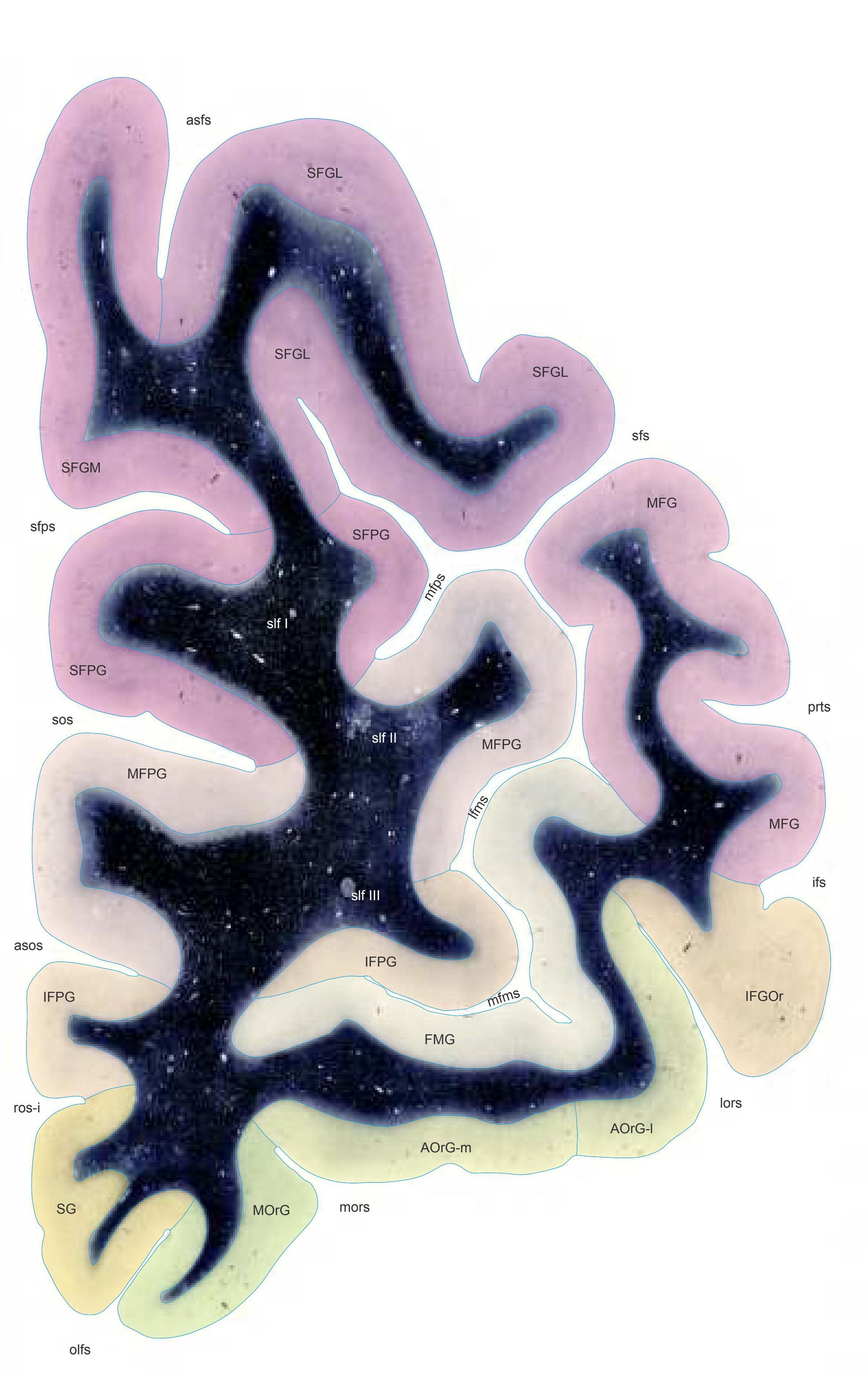


MNI Position y = 55.01 mm AHB Position y = -52.37 mm
# Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG medial frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus
# Sulci
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mfps middle frontopolar sulcus mors medial orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior part sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
# Fibers
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
**114**
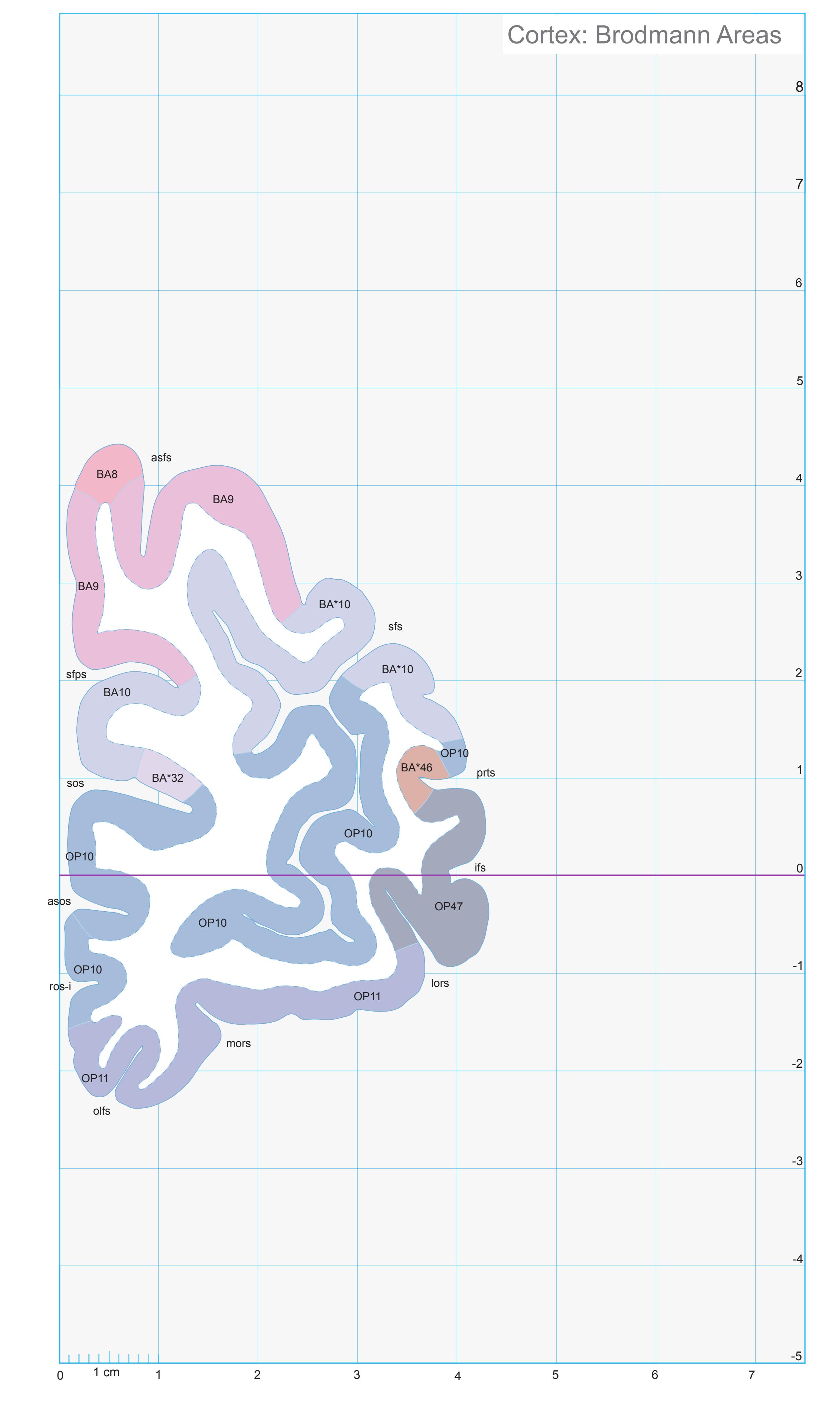
5
ICL: -52.37 MCP: -67.11 MNI: 55.01

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10,32,46 see p. 101
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mors middle orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus OP 10,11,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
sos superior occipital sulcus
**115**

Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 5 Slice Nr. 537
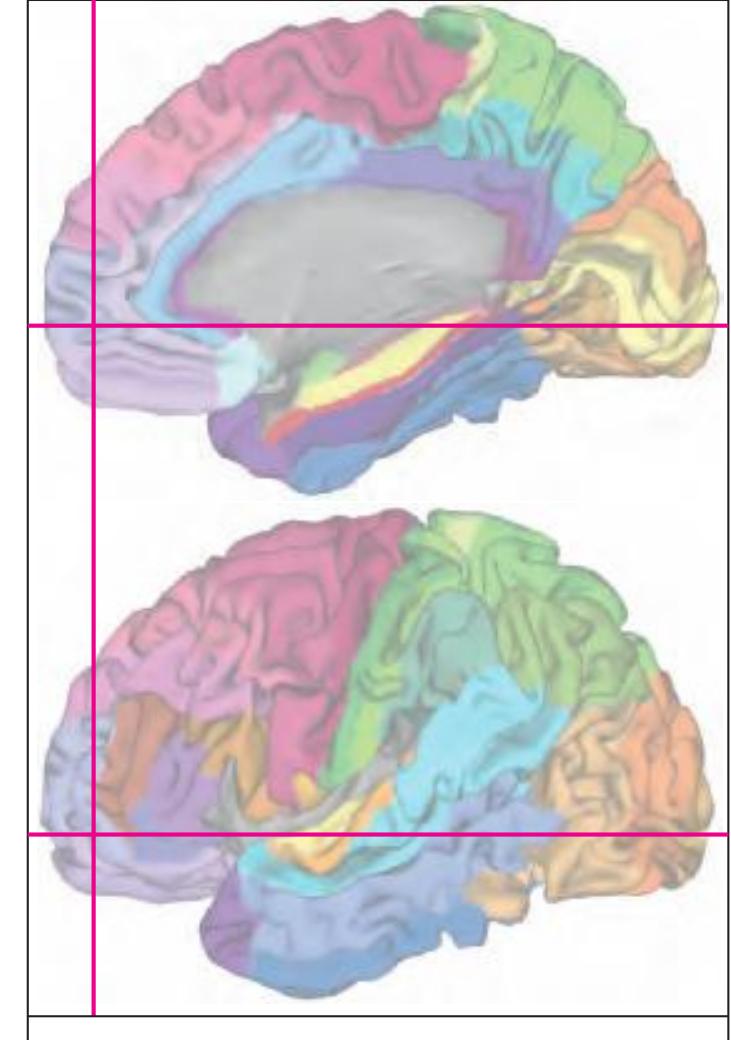
MNI Position y = 54.98 mm AHB Position y = -52.34 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus MFG medial frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
- BA8 area frontalis intermedia
- BA9 area frontalis granularis
- BA10 area frontopolaris
- BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
- BA46 area frontalis media OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP11 area 11 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003) BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
- of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FD granular frontal area FDdelta middle granular frontal area
FE frontopolar area FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular orbital area
FG area of straight gyrus (area recta)
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
**116**

**117**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


## Gyri
AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part CG cingulate gyrus FMG frontomarginal gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part
## Sulci
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mfms medial frontomarginal sulcus mors medial orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior part sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 6 Slice Nr. 637
**118**
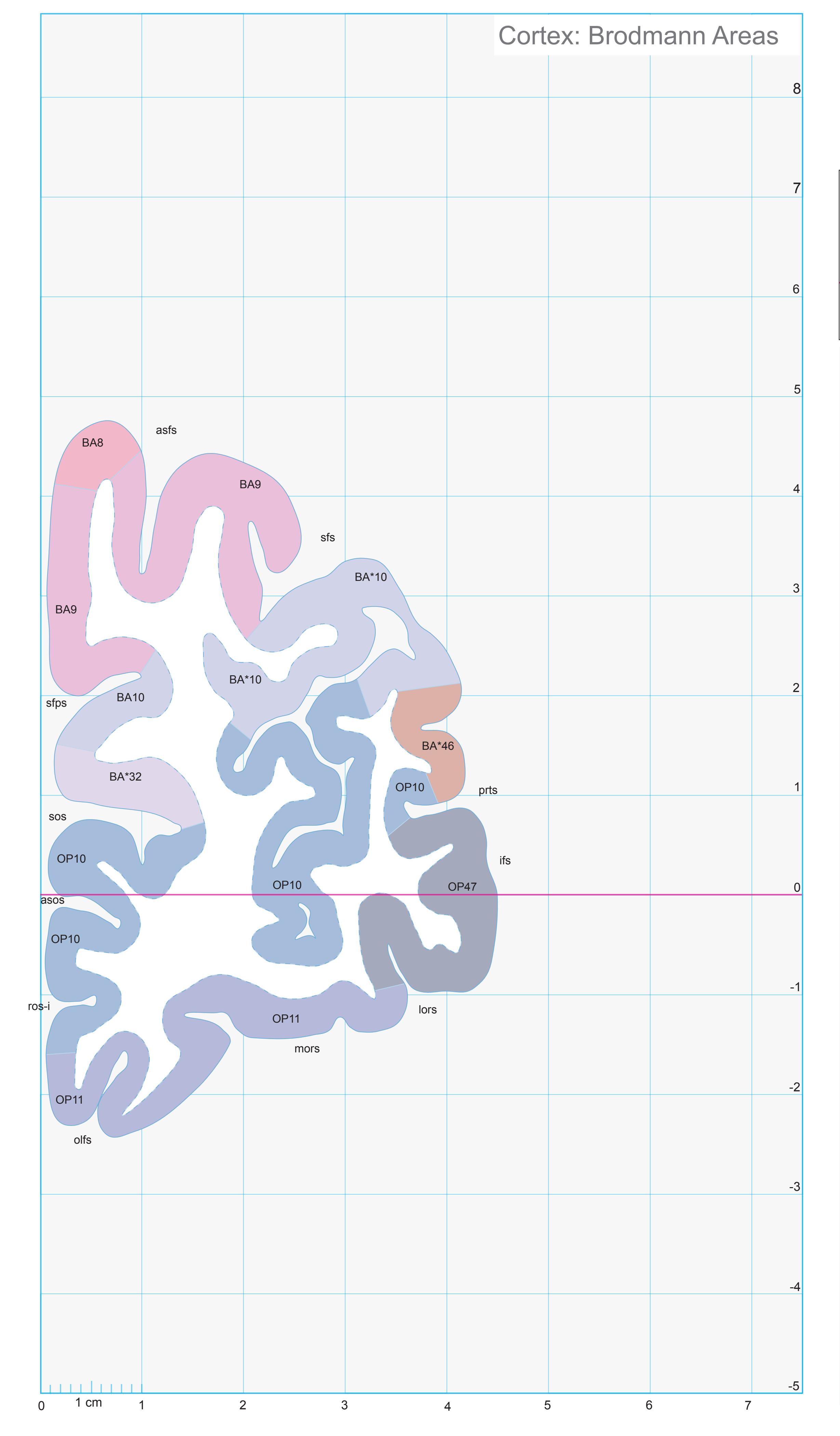

ICL: -49.66 MCP: -64.40 MNI: 52.16
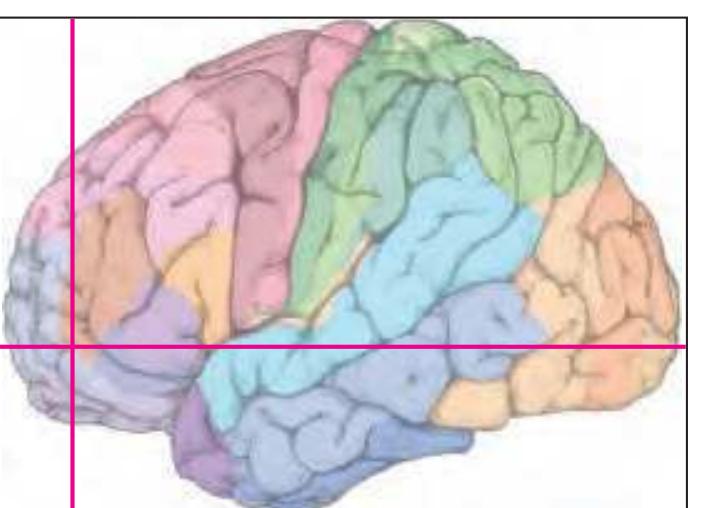
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10,32,46 see p. 101
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mors middle orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus OP 10,11,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) prts pretriangular sulcus ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
sos superior occipital sulcus
**119**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci

Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 7 Slice Nr. 737

MNI Position y = 49.35 mm AHB Position y = -46.98 mm
## Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus
## Sulci
SG straight gyrus
ramus asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus asos accessory supraorbital sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part ifs inferior frontal sulcus lfms lateral frontomarginal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus mors medial orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus ras radiate sulcus
ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior part sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**120**
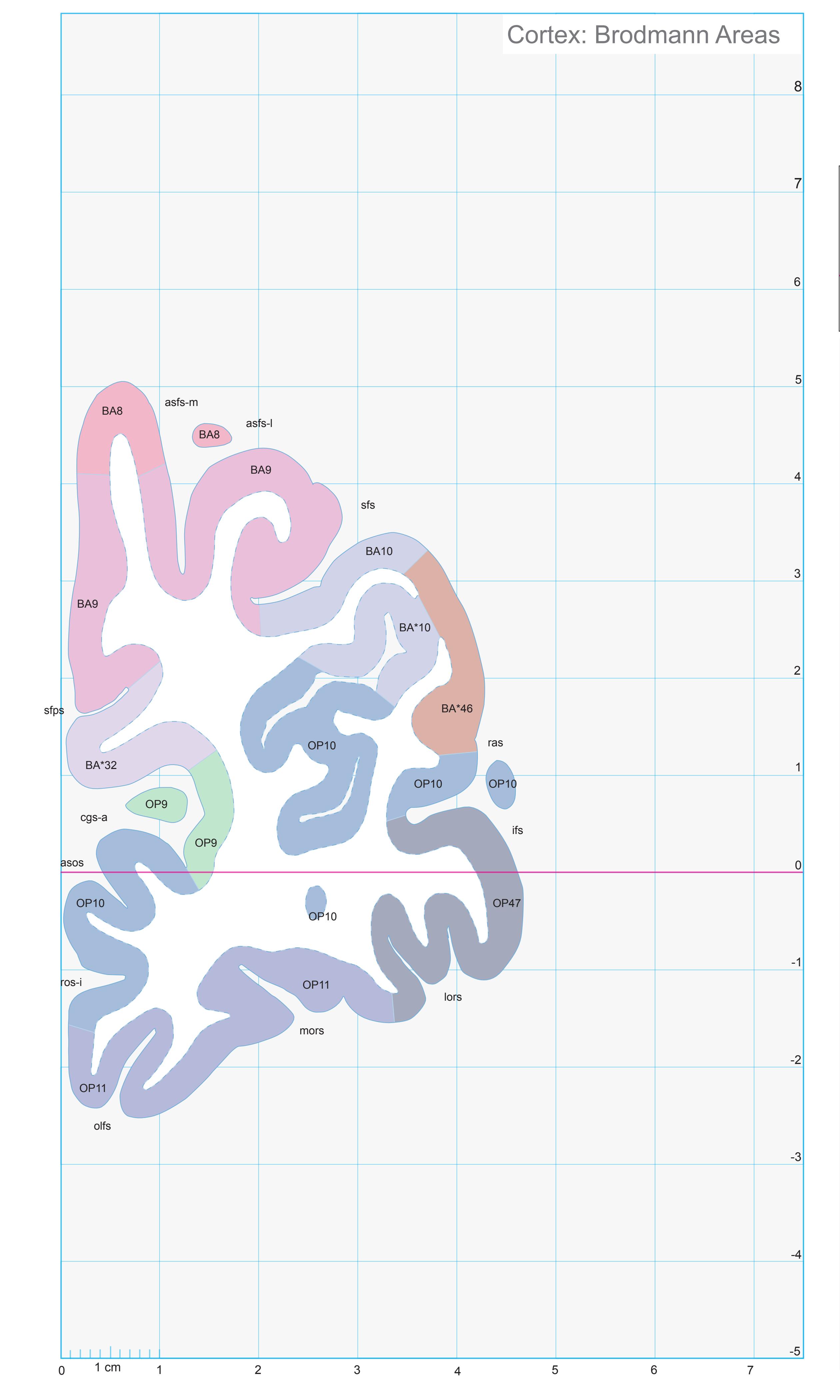
7
ICL: -46.98 MCP: -61.72 MNI: 49.35

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10,32,46 see p. 101
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus
asos accessory supraorbital sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. ifs inferior frontal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus
mors middle orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus OP 9,10,11,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
ras radiate sulcus (Eberstaller) ros-i rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch sfps superior frontopolar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
**121**
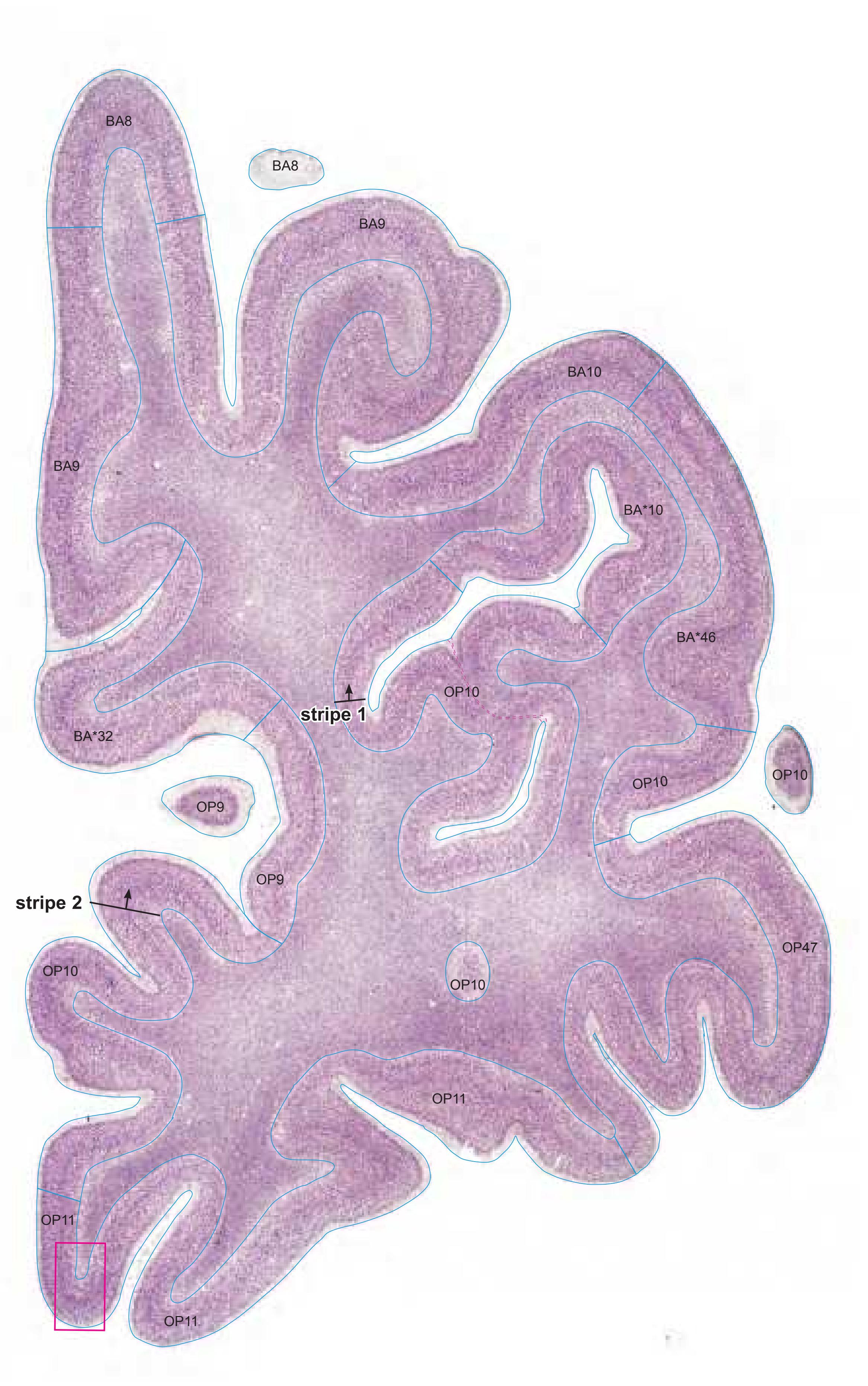


MNI Position y = 49.32 mm AHB Position y = -46.95 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part
CG cingulate gyrus
IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus
MOrG medial orbital gyrus
RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA10 area frontopolaris
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA46 area frontalis media OP9 area 9 ( by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP11 area 11 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003) BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FD granular frontal area
FDdelta middle granular frontal area
FE frontopolar area FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FG area of straight gyrus (area recta)
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
**122**

# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
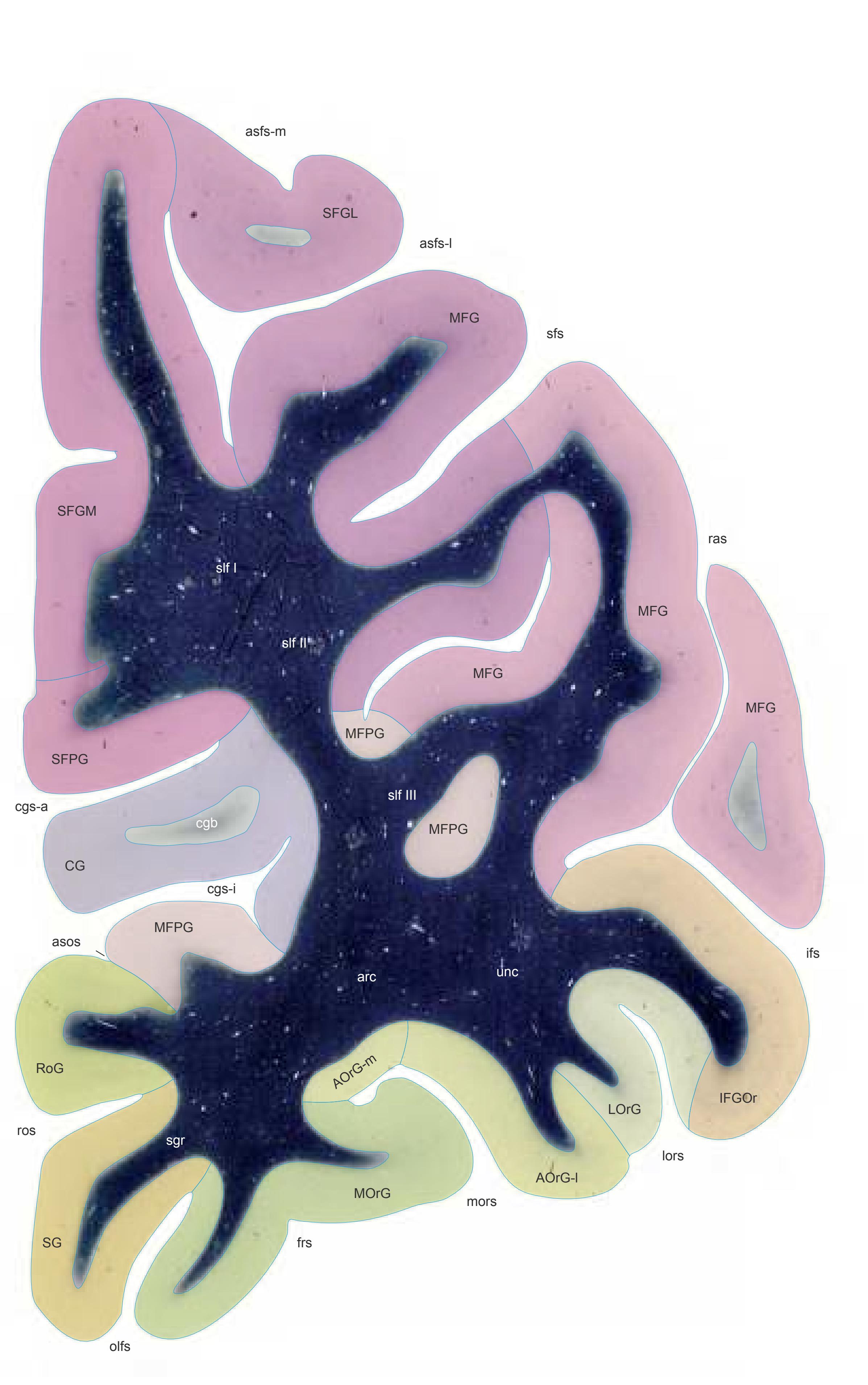


MNI Position y = 46.53 mm AHB Position y = -44.35 mm
#### Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus
MOrG medial orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus
# Sulci
asos accessory supraorbital sulcus asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part frs fragmentosus sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lors lateral orbital sulcus
mors medial orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus
ras radiate sulcus ros rostral sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
unc uncinate fascicle
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
**124**


ICL: -44.35 MCP: -59.09 MNI: 46.53

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA10,32,46 see p. 101
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral
ramus asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial
ramus
asos accessory supraorbital sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus
frs fragmentosus sulcus
ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lors lateral orbital sulcus
mors middle orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus
OP 9,10,11,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
ras radiate sulcus (Eberstaller)
ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
**125**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
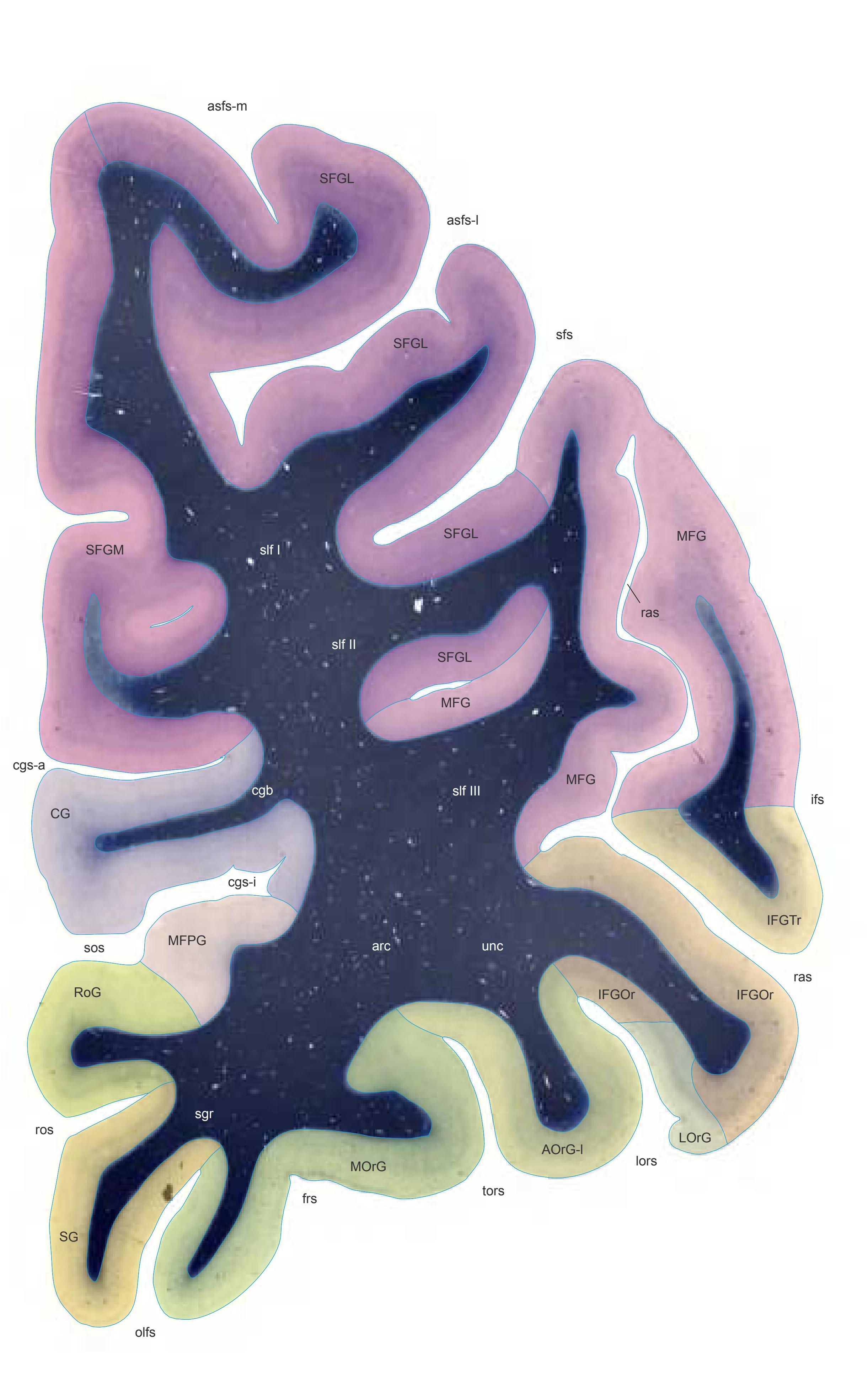
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 9 Slice Nr. 937

MNI Position y = 43.72 mm AHB Position y = -41.62 mm
# Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
## Sulci
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part frs fragmentosus sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lors lateral orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus ras radiate sulcus ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus sos supraorbital sulcus tors transverse orbital sulcus
unc uncinate fascicle
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
**126**


ICL: -41.62 MCP: -56.36 MNI: 43.72
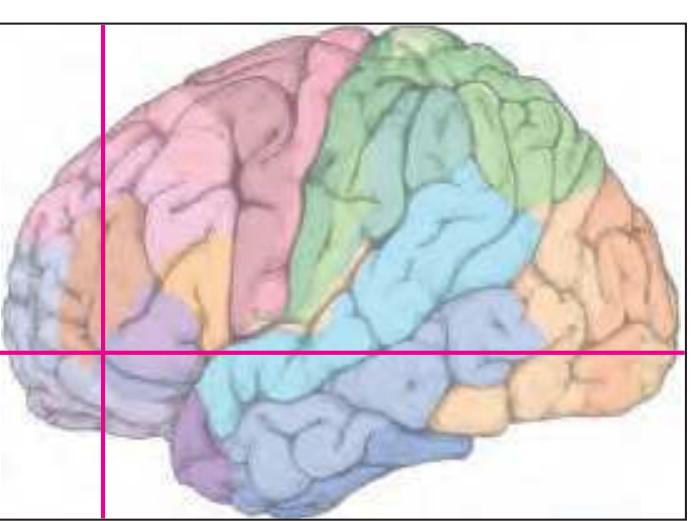
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA32,46 see p. 101
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus
frs fragmentosus sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus
lors lateral orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus
OP 9,10,11,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
sos superior occipital sulcus tors transverse orbital sulcus
**127**
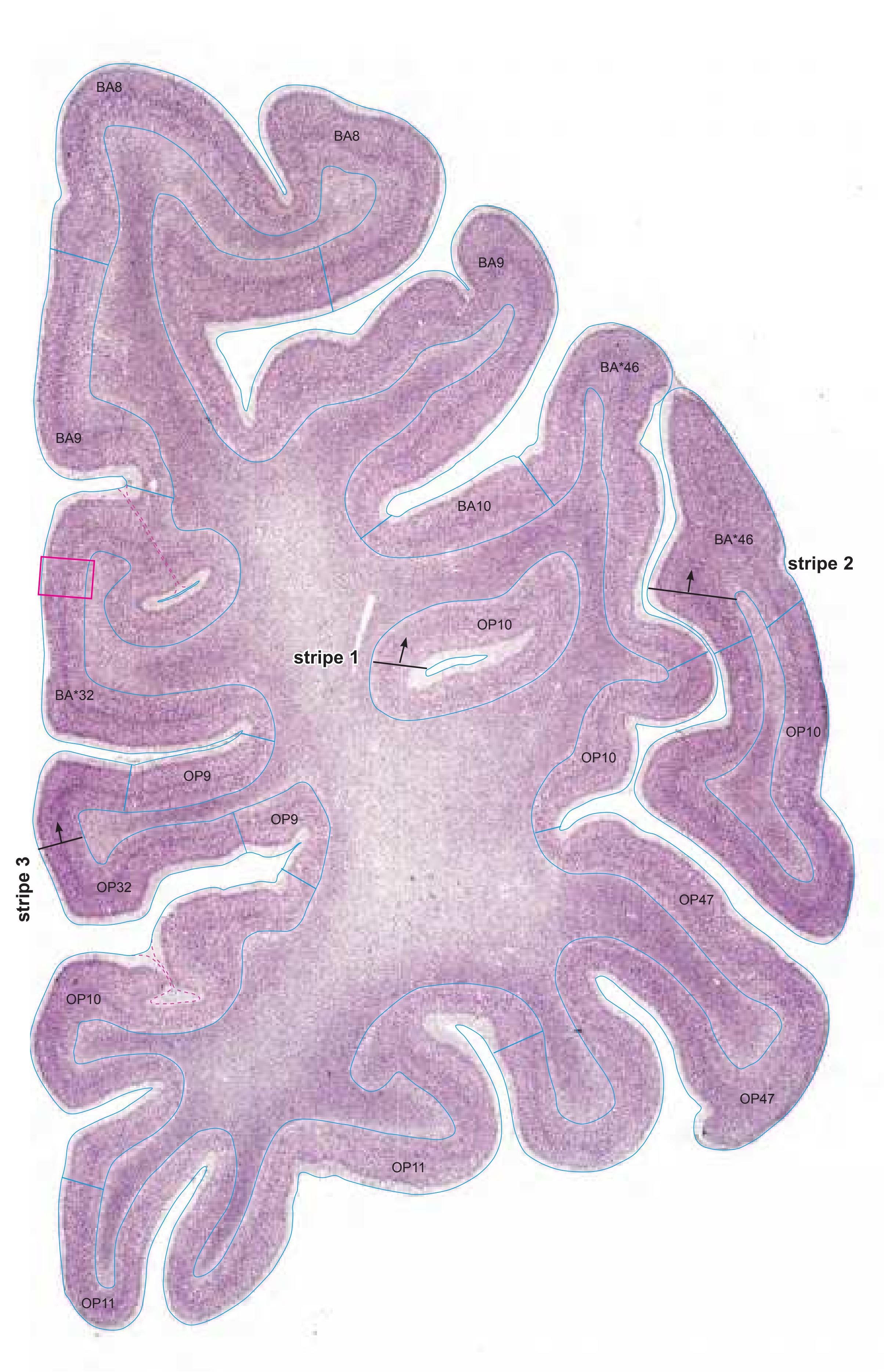

MNI Position y = 43.69 mm AHB Position y = -41.59 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus
MOrG medial orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
- BA8 area frontalis intermedia
- BA9 area frontalis granularis
- BA10 area frontopolaris
- BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
- BA46 area frontalis media
- OP9 area 9 ( by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP11 area 11 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP32 area 32 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FD granular frontal area
FDdelta middle granular frontal area FDgamma+op triangular and opercular
granular frontal area
FE frontopolar area
FEL limbic frontopolar area
FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular orbital area
FG area of straight gyrus (area recta)
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
p24 posterior division of BA24
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 9 Slice Nr. 938
**128**

# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


MNI Position y = 40.93 mm AHB Position y = -38.94 mm
#### Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
# Sulci
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part
frs fragmentosus sulcus
ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lors lateral orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus
ras radiate sulcus ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
tors transverse orbital sulcus
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle
sgr radiation of straight gyrus
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
unc uncinate fascicle
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 10 Slice Nr. 1037
**130**

10
ICL: -38.94 MCP: -53.68 MNI: 40.93

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA32,46 see p. 101
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial
ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus
frs fragmentosus sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus
lors lateral orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus
OP 9,10,11,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
tors transverse orbital sulcus
**131**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
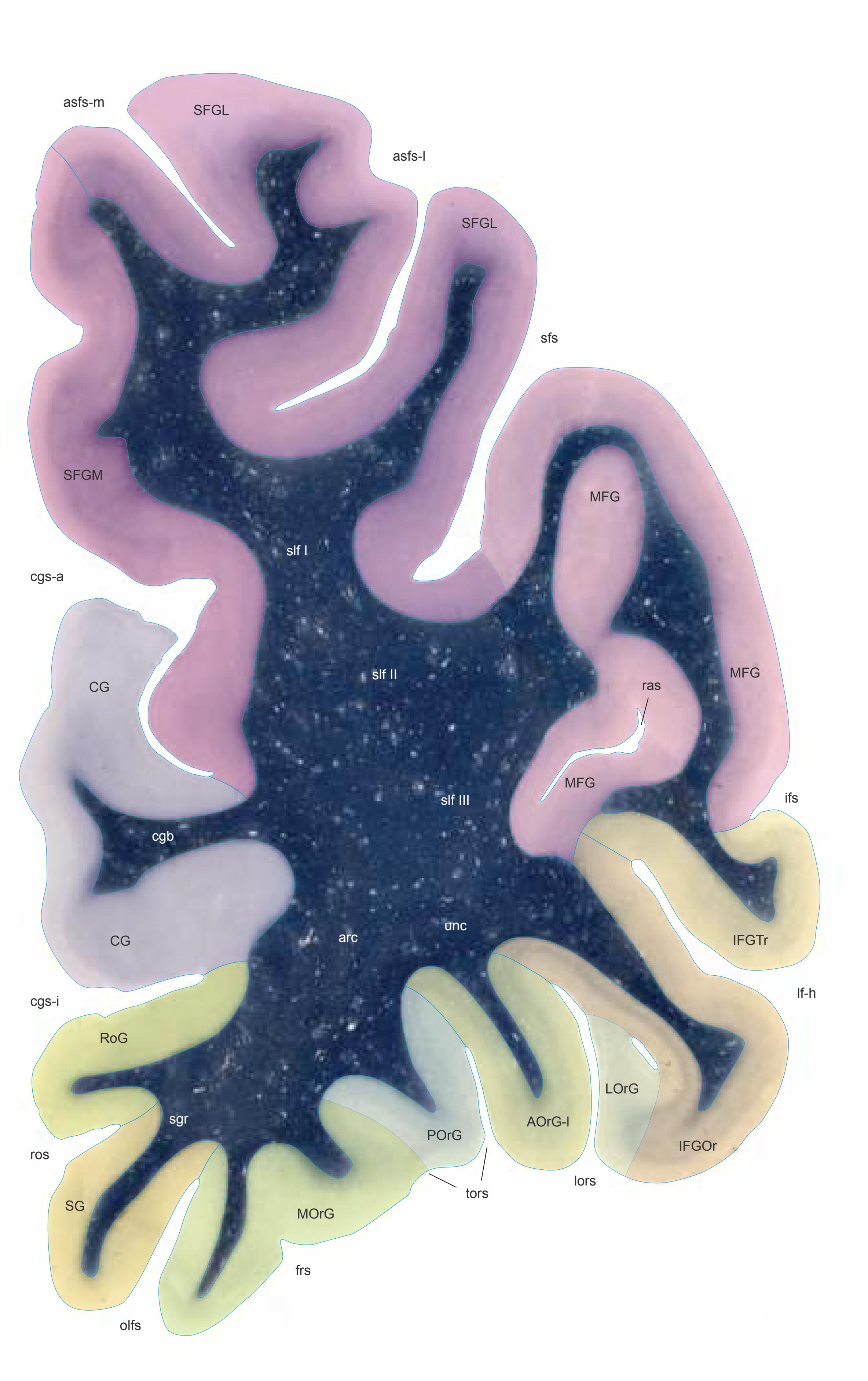


MNI Position y = 39.44 mm AHB Position y = -37.54 mm
# Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part
CG cingulate gyrus
IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SG straight gyrus
## Sulci
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial
ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part
cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part
frs fragmentosus sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure
lors lateral orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus ras radiate sulcus
ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus tors transverse orbital sulcus
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle
cgb cingulum bundle
sgr radiation of straight gyrus
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
unc uncinate fascicle
Slice Nr. 1089
**132**
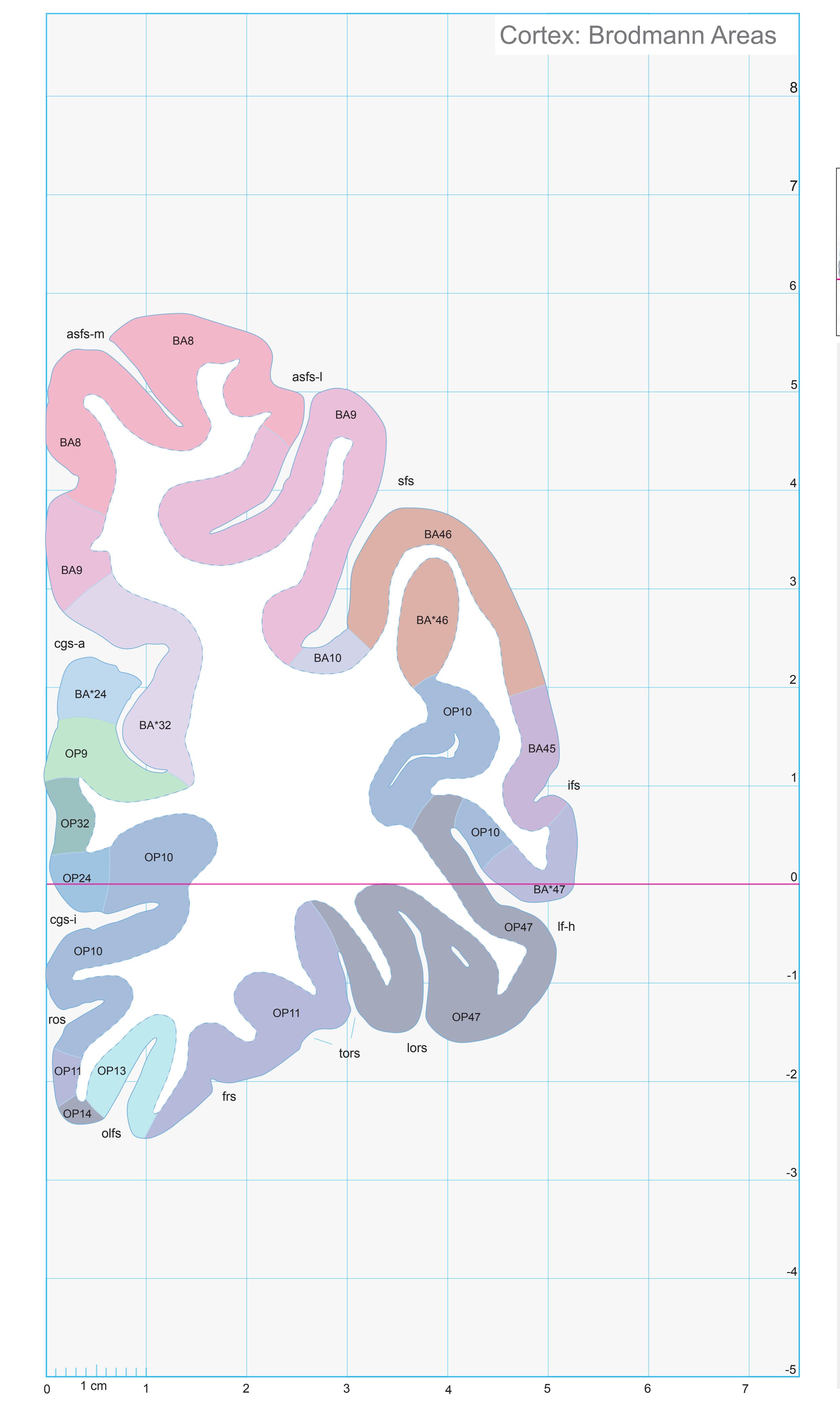
11
ICL: -37.54 MCP: -52.28 MNI: 39.44

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA24,32,46,47 see p. 101
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial
ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus frs fragmentosus sulcus
ifs inferior frontal sulcus
lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus
lors lateral orbital sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus
OP 9,10,11,13,24,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
tors transverse orbital sulcus
**133**
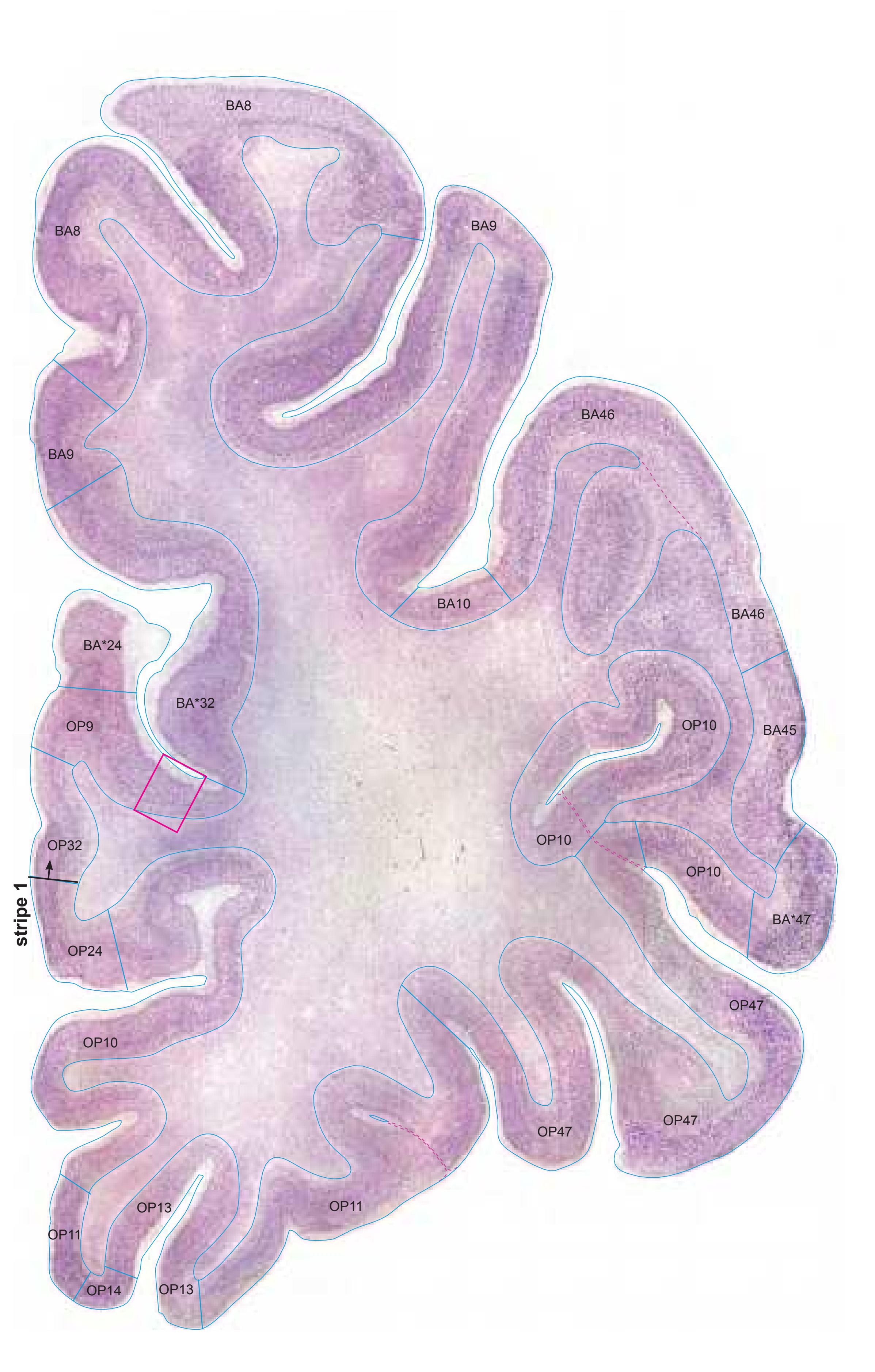
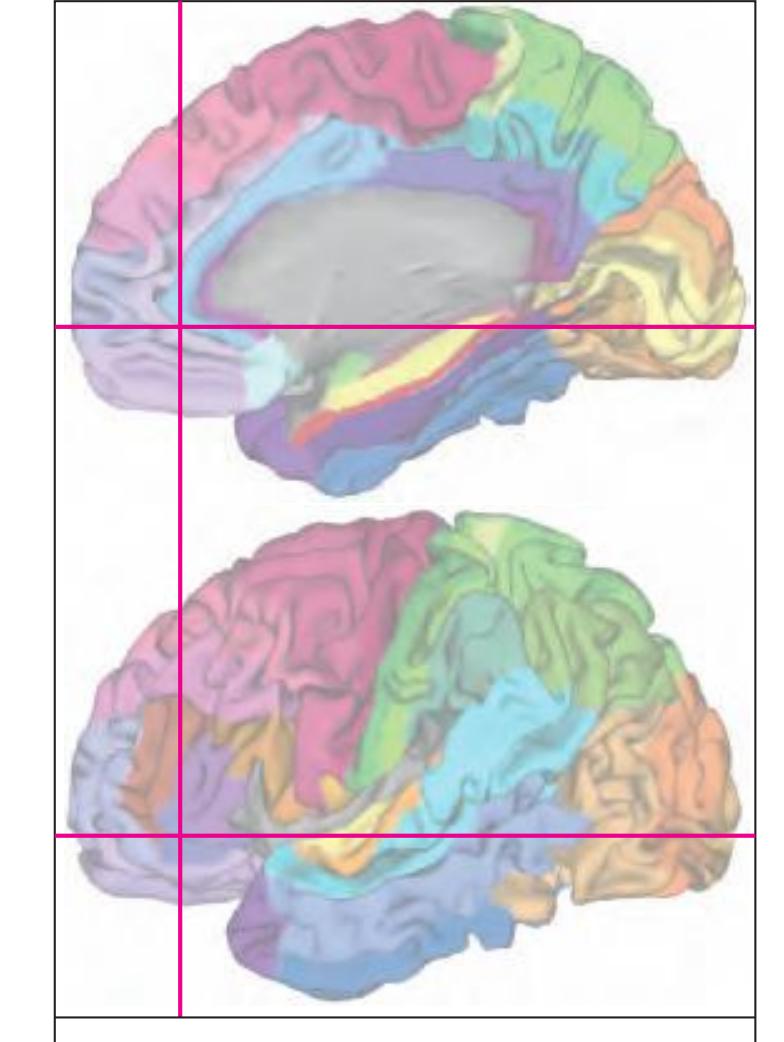
MNI Position y = 39.50 mm AHB Position y = -37.60 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part
CG cingulate gyrus
IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part
IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MOrG medial orbital gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus
RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SG straight gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA10 area frontopolaris
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA45 area triangularis
BA46 area frontalis media
BA47 area orbitalis
OP9 area 9 ( by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP11 area 11 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP24 area 24 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP32 area 32 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area FD granular frontal area
FDgamma+op triangular and opercular
granular frontal area FE frontopolar area
FEL limbic frontopolar area
FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FG area of straight gyrus (area recta) FH prefrontal area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
33 frontal division of BA33
p24 posterior division of BA24 s32 subregion of area 24
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 11 Slice Nr. 1087
**134**
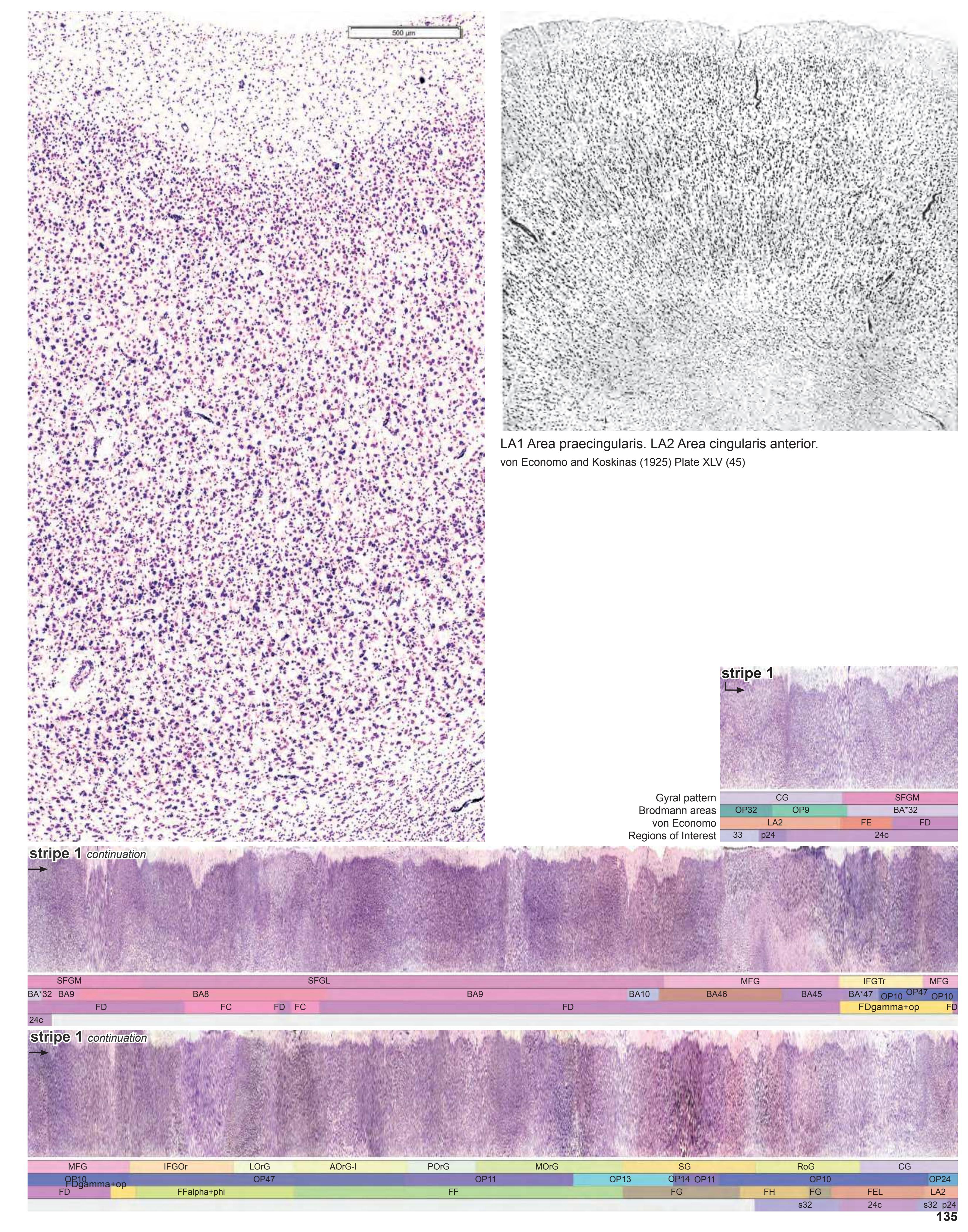
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci



MNI Position y = 35.30 mm AHB Position y = -33.61 mm
## Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
# Sulci
acals accessory callosal sulcus asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part frs fragmentosus sulcus
ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lors lateral orbital sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors posterior orbital sulcus ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus tors transverse orbital sulcus
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**136**

12
ICL: -33.61 MCP: -48.35 MNI: 35.30

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA24,47 see p. 101
acals accessory callosal sulcus cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus OP10,11,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
**137**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci

Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 13 Slice Nr. 1336

MNI Position y = 32.66 mm AHB Position y = -30.93 mm
# Gyri
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus
IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus
SG straight gyrus
RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
# Sulci
acals accessory callosal sulcus
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus
lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus
pors posterior orbital sulcus ros rostral sulcus
sfs superior frontal sulcus
unc uncinate fascicle
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle racc radiation of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
**138**

13
ICL: -30.93 MCP: -45.67 MNI: 32.66

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA33,47 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle acals accessory callosal sulcus asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral
ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür
et.al. (2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus racc radiation of corpus callosum ros rostral sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
**139**

Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 13 Slice Nr. 1335

MNI Position y = 32.52 mm AHB Position y = -30.95 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part CG cingulate gyrus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part
IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus
RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA45 area triangularis
BA46 area frontalis media
BA47 area orbitalis
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP24 area 24 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FC intermediate frontal area
FD granular frontal area
FDgamma+op triangular and opercular granular frontal area FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FG area of straight gyrus (area recta) FH prefrontal area
FHL parolfactory prefrontal area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
32 frontal division of BA32
33 frontal division of BA33
p24 posterior division of BA24 s24 superior division of BA24
**140**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci



MNI Position y = 29.73 mm AHB Position y = -28.30 mm
#### Gyri
CG cingulate gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
TIG transverse insular gyrus
### Sulci
acals accessory callosal sulcus asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part ifs inferior frontal sulcus
imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus pcgs paracingulate sulcus
pors posterior orbital sulcus ros rostral sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
# Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle racc radiation of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**142**

ICL: -28.30 MCP: -43.04 MNI: 29.73

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA33,47 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus
fmi forceps minor of corpus callosum
ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus
lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus
lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure lors lateral orbital sulcus
OP10,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
pors posterior orbital sulcus
racc radiation of corpus callosum
ros rostral sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum
sfs superior frontal sulcus
SGl substantia gliosa
**143**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci



MNI Position y = 26.88 mm AHB Position y = -25.59 mm
CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus
acals accessory callosal sulcus cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf lateral fissure lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m middle transverse olfactory sulcus ros rostral sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
1p olfactory peduncle arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**144**

ICL: -25.59 MCP: -40.33 MNI: 26.88

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA45 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. fmi forceps minor of corpus callosum gcc genu of corpus callosum ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch racc radiation of corpus callosum ros rostral sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus
SGl substantia gliosa
**145**


MNI Position y = 26.86 mm AHB Position y = -25.57 mm
# Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus
BOp basal operculum
CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part
IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus
PCG precallosal gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus
RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SG straight gyrus
TIG transverse insular gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA44 area opercularis
BA45 area triangularis
BA46 area frontalis media
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP24 area 24 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Ongur et al. 2003)
OP. PRCO. precentral opercular area
OP\_PRCO precentral opercular area (by Öngür et al. 2003)
TPCm, medial temporal lobe
memory system
TPCm medial temporopolar cortex BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
of areas OP10-47
# von Economo and Koskinas
FB agranular frontal area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
FD granular frontal area FDgamma+op triangular and opercular
granular frontal area FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FH prefrontal area FHL parolfactory prefrontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area
#### TG temporo polar area Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24c subregion of BA 24
32 frontal division of BA32
33 frontal division of BA33 a24c' anterior division of BA24
p24 posterior division of BA24
s24 superior division of BA24
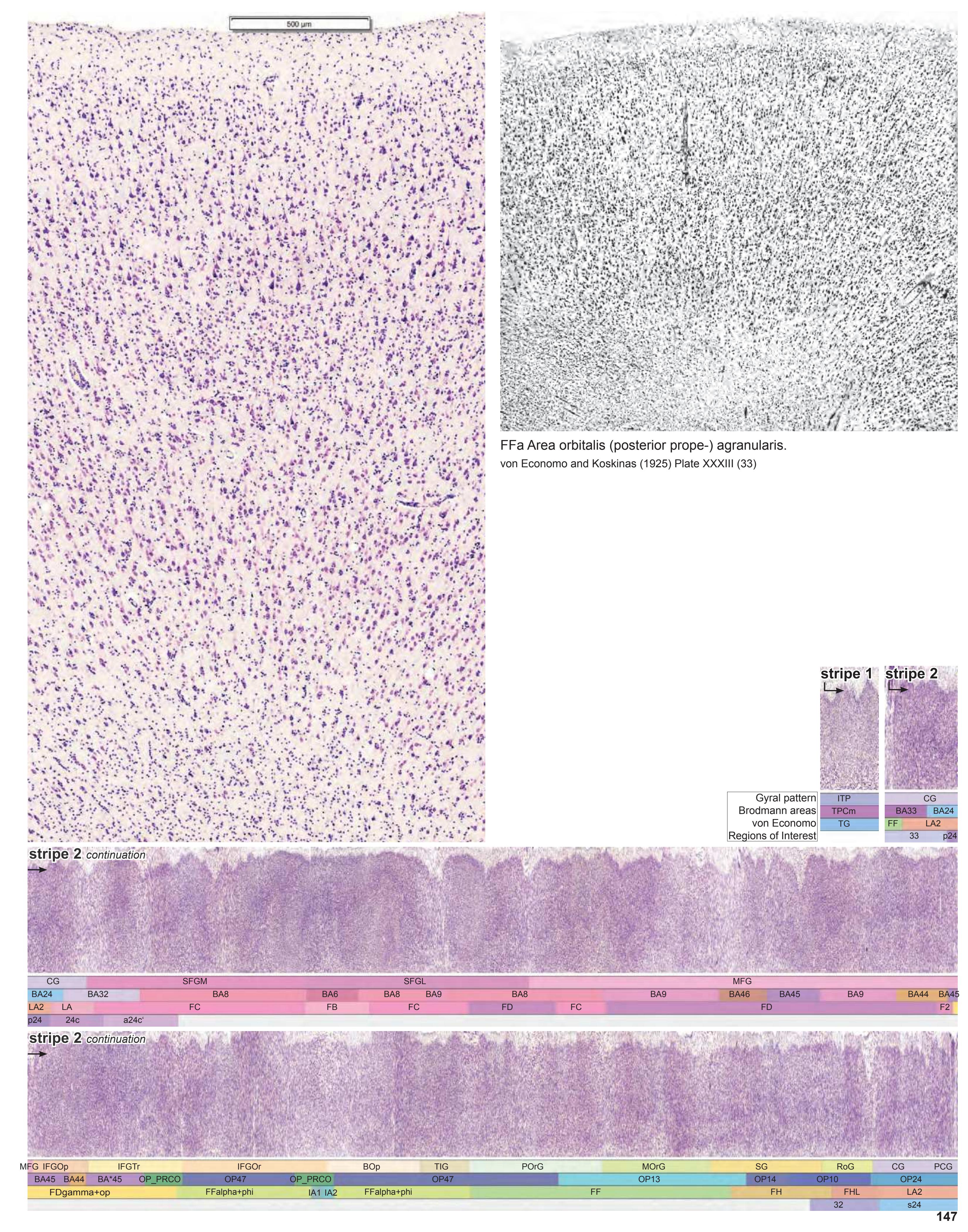
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


AHB Position y = -22.97 mm
CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus
acals accessory callosal sulcus cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part ifs inferior frontal sulcus imfs intermediate frontal sulcus lf lateral fissure lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m middle transverse olfactory sulcus ros rostral sulcus Fibers
Sulci
1p olfactory peduncle acr anterior corona radiata arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle sfs superior frontal sulcus
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 16 Slice Nr. 1633
**148**
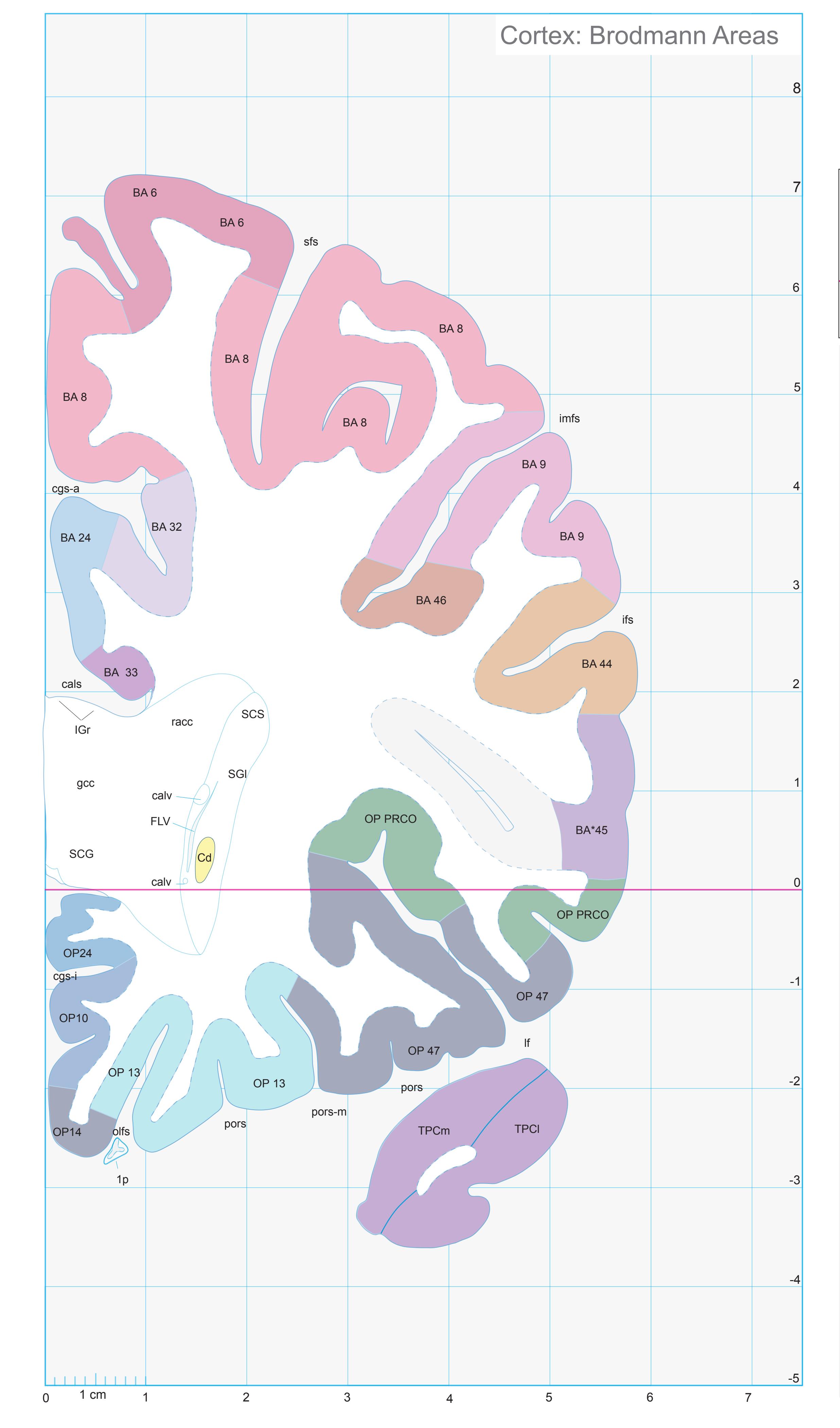
ICL: -22.97 MCP: -37.71 MNI: 24.07

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA45 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein Cd caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle gcc genu of corpus callosum ifs inferior frontal sulcus IGr indusium griseum imfs intermediate frontal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch
racc radiation of corpus callosum SCG cingulate gyrus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
**149**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


MNI Position y = 21.28 mm AHB Position y = -20.34 mm
AOI Area orbitoinsularis CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SG straight gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPC tempopolar cotex
TIG transverse insular gyru
TPC tempopolar cotex
Sulci Fibers Gyri
acals accessory callosal sulcus cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lf lateral fissure lf-h horizontal ramus of lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m middle transverse olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus ros rostral sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
1p olfactory peduncle aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
unc uncinate fascicle
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 17 Slice Nr. 1731
**150**

ICL: -20.34 MCP: -35.08 MNI: 21.28
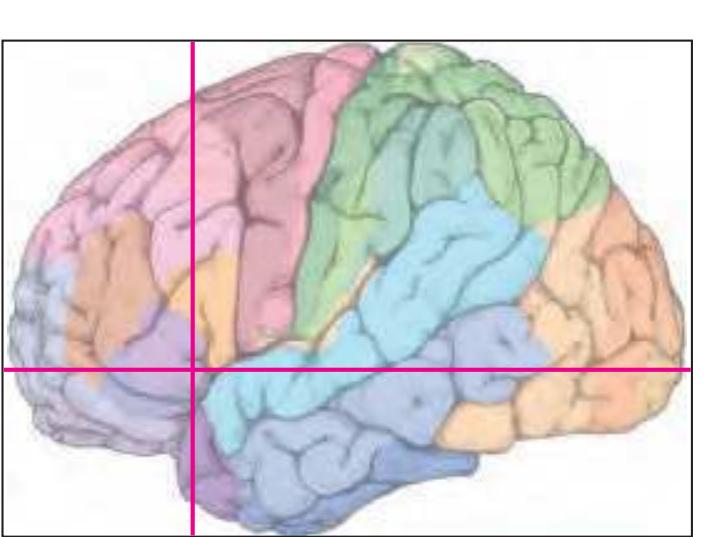
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
1p olfactory peduncle AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region) cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus Cl claustrum
ex extreme capsule fpms frontal paramidline sulcus gcc genu of corpus callosum ifs inferior frontal sulcus
IGr indusium griseum lf-h lateral fissure, horizontal ramus
lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus
OP10,13,14,24,47 areas defined by Öngür
et.al. (2003) OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003)
pors posterior orbital sulcus pors-m posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch Pu putamen
racc radiation of corpus callosum ros rostral sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
sts superior temporal sulcus
**151**


MNI Position y = 21.26 mm AHB Position y = -20.23 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AOI Area orbitoinsularis
CG cingulate gyrus
BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus
FOp frontal operculum
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part
IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part
IG insular gyrus
ITP inferior temporopolar region
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus
POrG posterior orbital gyrus
PPo planum polare
RoG rostral gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
SG straight gyrus
TIG transverse insular gyrus
TPC tempopolar cotex
#### Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA44 area opercularis


BA45 area triangularis
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP24 area 24 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_PRCO precentral opercular area (by Öngür et al. 2003)
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FB agranular frontal area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area FD granular frontal area
FDgamma+op triangular and opercular
granular frontal area
FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FH prefrontal area FHL parolfactory prefrontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area TA superior temporal area
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
25 BA25
33 frontal division of BA33
a24c' anterior division of BA24
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33 p24 posterior division of BA24
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 17 Slice Nr. 1735
**152**

# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


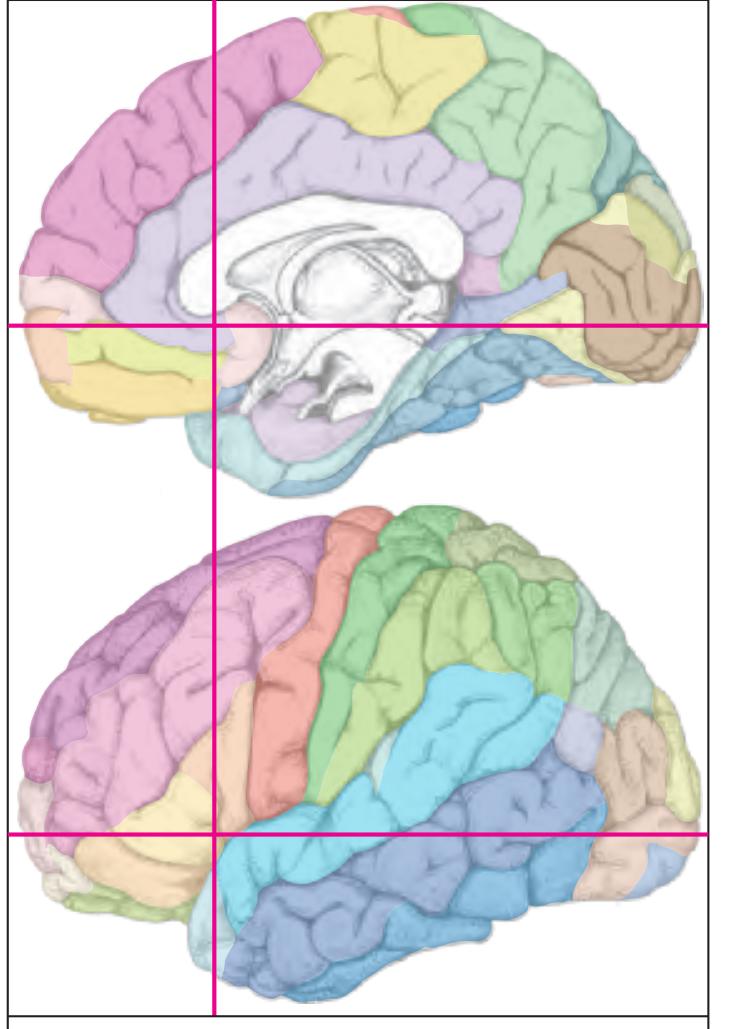
MNI Position y = 18.41 mm AHB Position y = -17.53 mm
AOI Area orbitoinsularis CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus IP insular pole ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare RoG rostral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPC tempopolar cortex
acas accessory callosal sulcus cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part dgs diagonal sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus lf lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure olfs olfactory sulcus pors transverse olfactory sulcus pors-m middle transverse olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
Sulci
Fibers Gyri
1p olfactory peduncle aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum rcc rostrum of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**154**

ICL: -17.53 MCP: -32.27 MNI: 18.41

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle
AcL accumbens n., lateral p.
AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region)
cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein
CdL lateral caudate n.
CdM medial caudate n.
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus
Cl claustrum
ec external capsule
ex extreme capsule
FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle
fpms frontal paramidline sulcus
FPu fundus region of putamen
gcc genu of corpus callosum
ifs inferior frontal sulcus IGr indusium griseum
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure
olfs olfactory sulcus
OP10,13,24,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
et. al. (200
G. gustatc
OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003)
OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped
from Öngür et. al. 2003) ps polas sulcus
Pu putamen
racc radiation of corpus callosum SB striatal cell bridge
scal subcallosal fc
SCS subcallosal stratum
sfs superior frontal sulcus
SGl substantia gliosa sof superior occipitofrontal fasciculus
sts superior temporal sulcus
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
**155**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
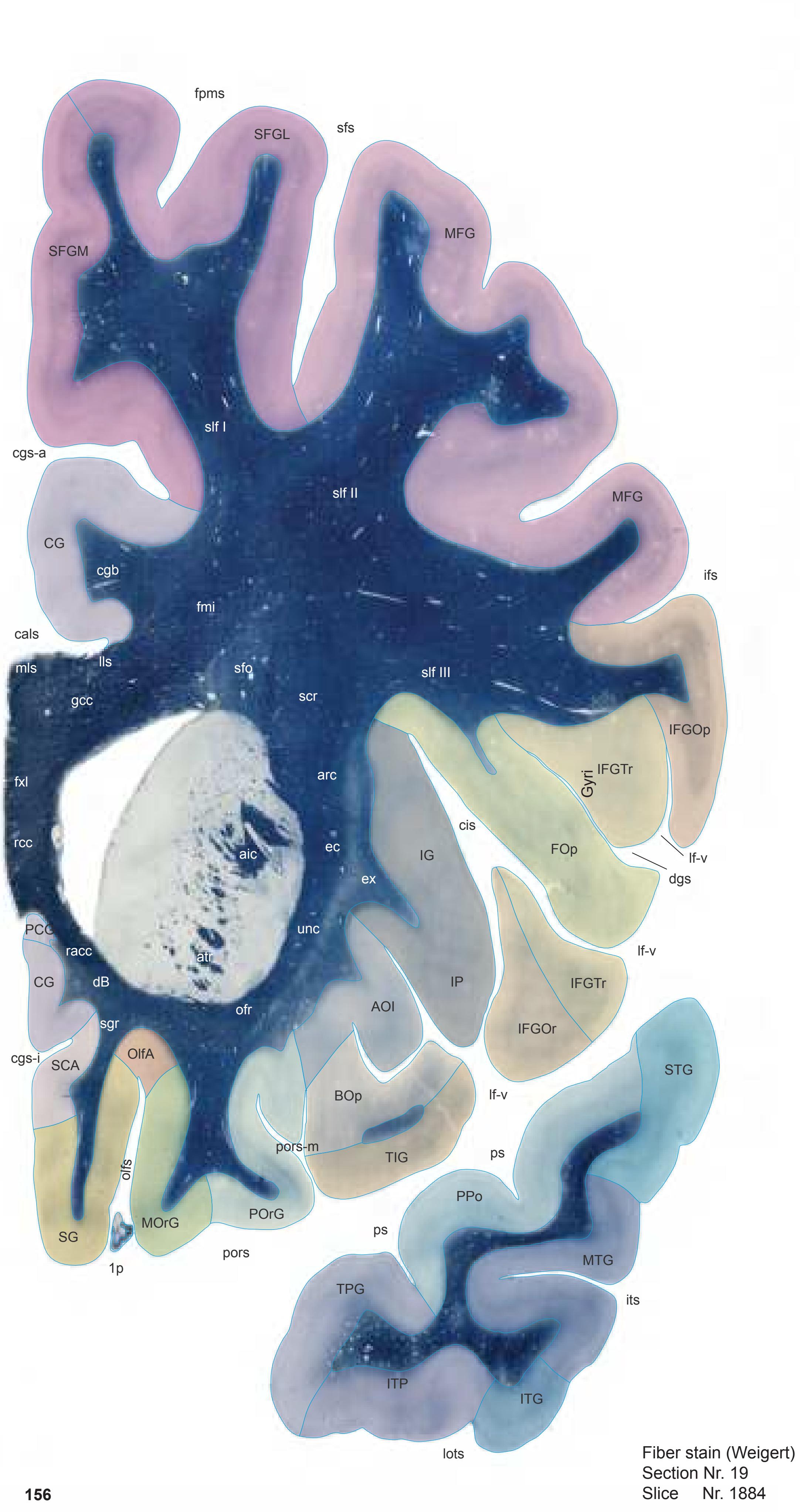
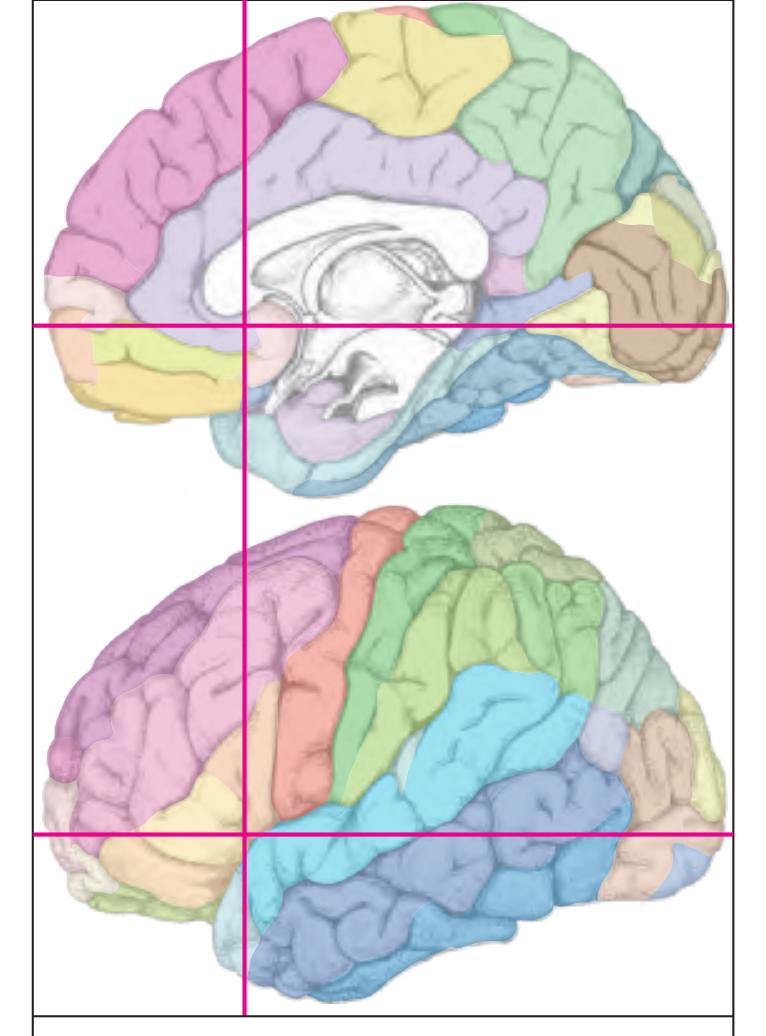
MNI Position y = 17.06 mm AHB Position y = -16.24 mm
AOI Area orbitoinsularis CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus IP insular pole ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part cis circular sulcus dgs diagonal sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus (f2) its inferior temporal sulcus lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors transverse olfactory sulcus pors-m middle transverse olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus Fibers
Sulci
1p olfactory peduncle aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fxl fornix longus gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum rcc rostrum of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle sfs superior frontal sulcus
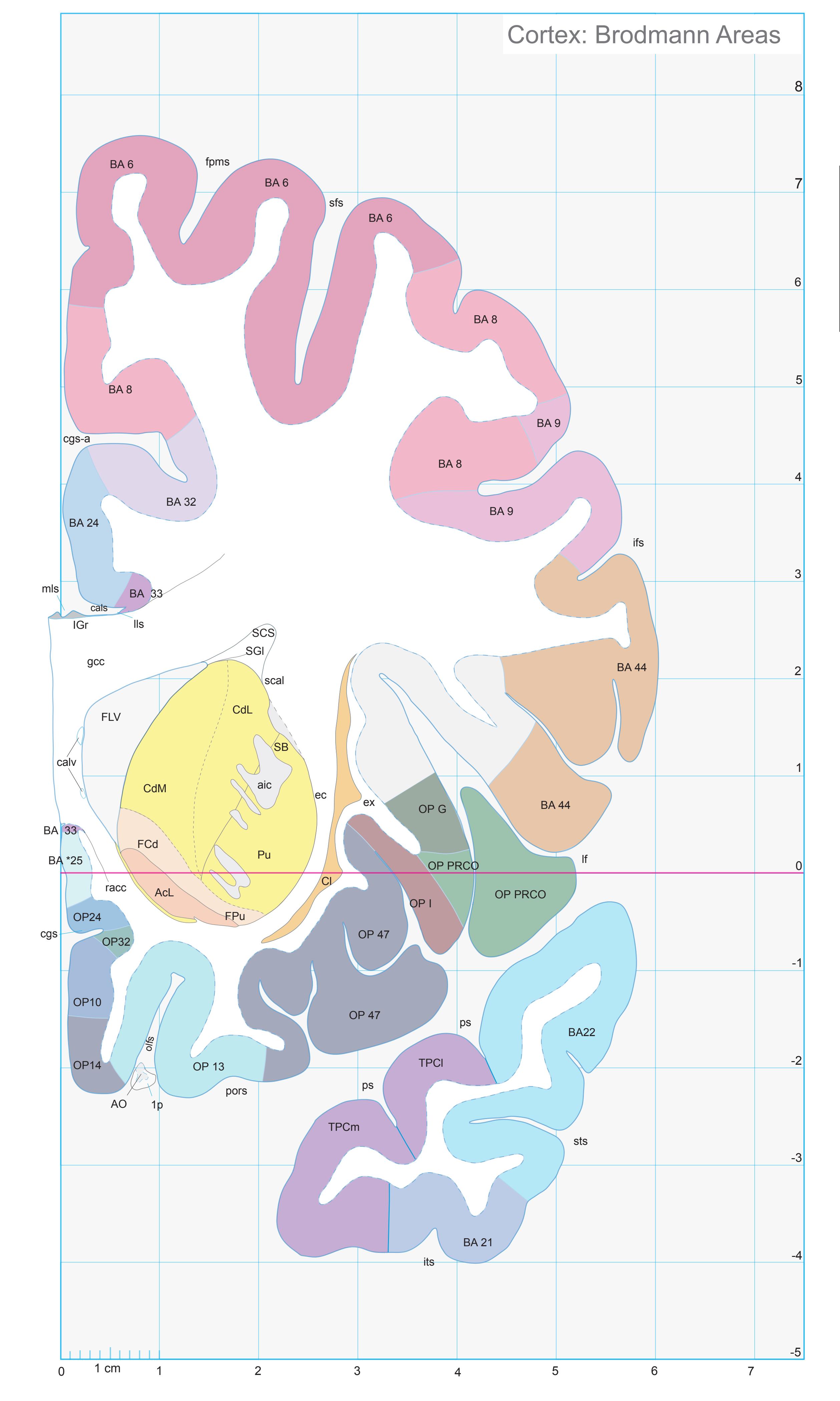
ICL: -16.24 MCP: -30.98 MNI: 17.06

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
\*BA25 see p. 101 1p olfactory peduncle AcL accumbens n., lateral p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region) cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs cingulate sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. Cl claustrum ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen gcc genu of corpus callosum ifs inferior frontal sulcus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,24,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus ps polas sulcus Pu putamen racc radiation of corpus callosum
SB striatal cell bridge scal subcallosal fc SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa sts superior temporal sulcus TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
**157**

MNI Position y = 17.03 mm AHB Position y = -16.21 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AOI Area orbitoinsularis CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus IP insular pole ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PCG precallosal gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis BA8 area frontalis intermedia BA9 area frontalis granularis BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA25 area subgenualis
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA44 area opercularis
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP24 area 24 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP32 area 32 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al.
2003) OP\_I agranular insular cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_PRCO precentral opercular area (by Öngür et al. 2003)
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension of areas OP10-47
## von Economo and Koskinas
FB agranular frontal area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area FDgamma+op triangular and opercular
granular frontal area
FF granular orbital area
FFalpha+phi agranular und pretriangular
orbital area
FH prefrontal area FHL parolfactory prefrontal area
FRL parolfactory
FL parolfactory ar
a33' anterior subregion of BA33
FL parolfactory area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
TA superior temporal area
TG temporo polar area
**158**
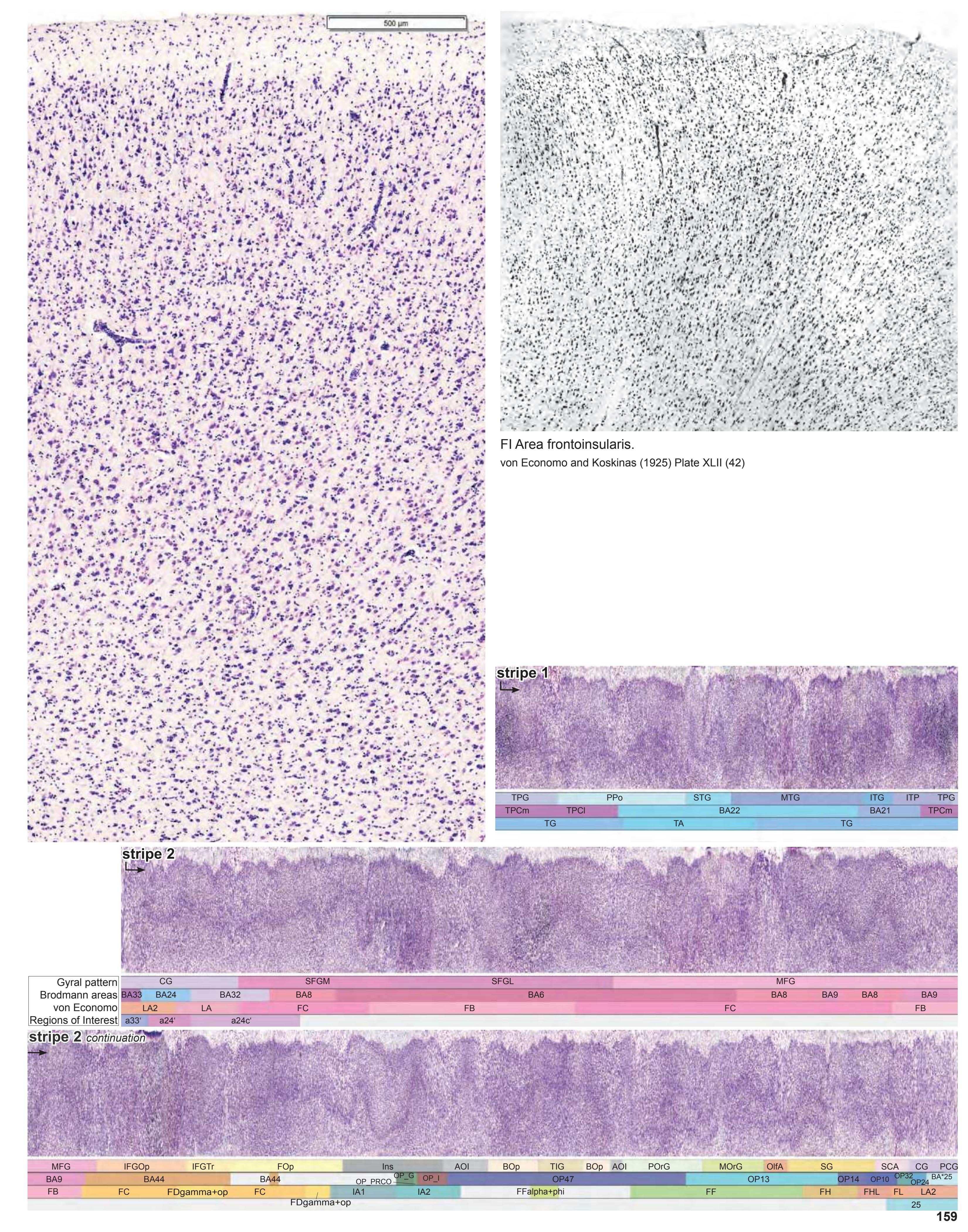
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci


MNI Position y = 15.82 mm AHB Position y = -15.06 mm
AOI Area orbitoinsularis CG cingulate gyrus BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IG insular gyrus IP insular pole ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cgs-i cingulate sulcus, inferior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus (f2) its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lf-v vertical ramus of lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors post. olfactory sulcus pors-m middle post. olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus
Fibers
Sulci
1p olfactory peduncle aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fxl fornix longus gcc genu of corpus callosum lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum rcc rostrum of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle sfs superior frontal sulcus
**160**

ICL: -15.06 MCP: -29.80 MNI: 15.82

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle AcL accumbens n., lateral p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region) cals callosal sulcus calv callosal vein CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus cis circular insular sulcus ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fmi forceps minor of corpus callosum fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen gcc genu of corpus callosum ifs inferior frontal sulcus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lls lateral longitudinal stria lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus mls medial longitudinal stria OlfA olfactory area olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,24,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP PRCO precentral opercular area (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus PPCl prepiriform claustrum ps polas sulcus
Pu putamen
scal subcallosal fc SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa sts superior temporal sulcus TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
racc radiation of corpus callosum
**161**
# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
Slice Nr. 1984
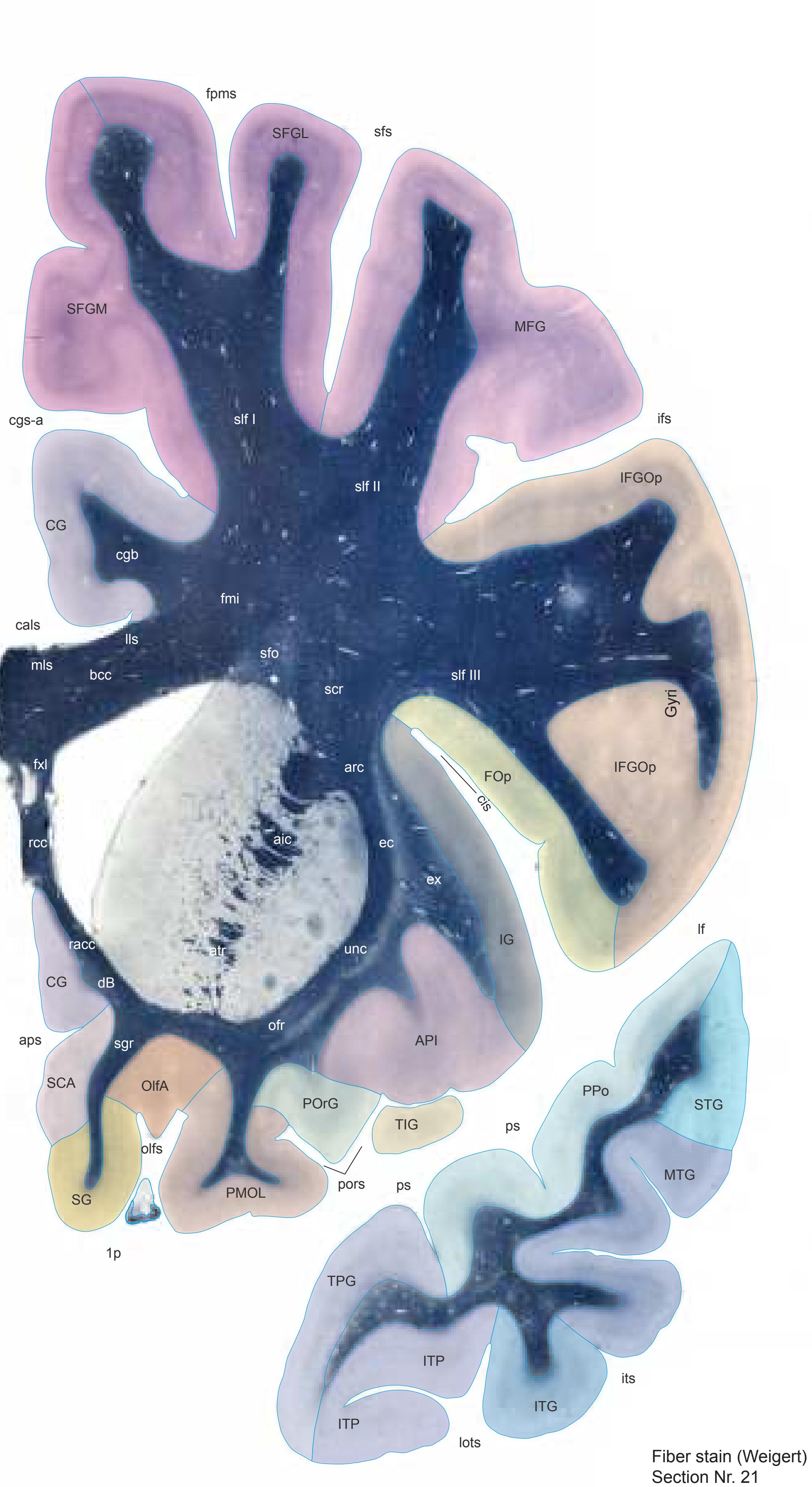
MNI Position y = 14.22 mm AHB Position y = -13.56 mm
API area piriformis insulae CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IG insular gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
aps anterior parolfactory sulcus cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus (f2) its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors transverse olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
1p olfactory peduncle aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fxl fornix longus lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum rcc rostrum of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**162**
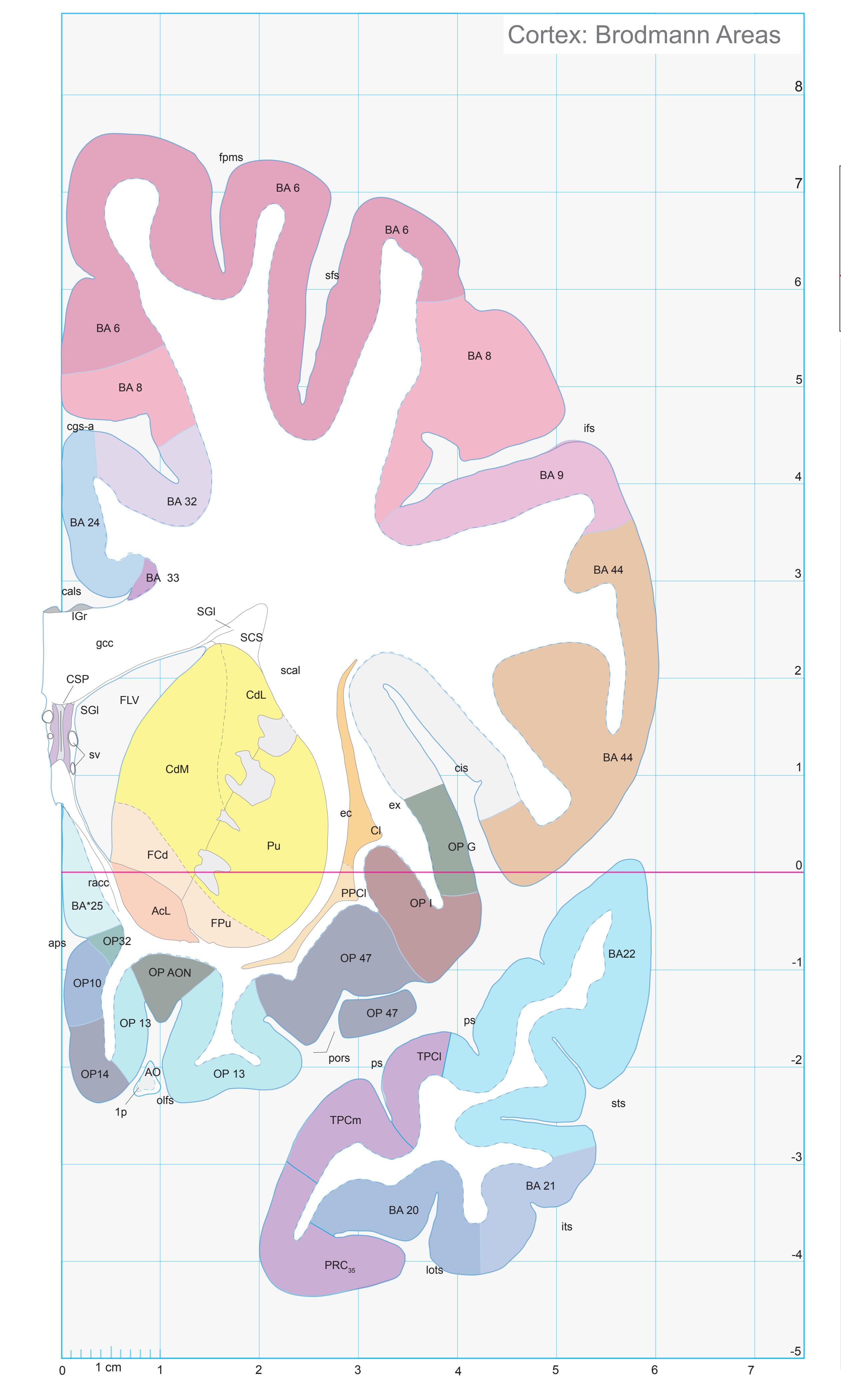
ICL: -13.56 MCP: -28.30 MNI: 14.22

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle
AcL accumbens n., lateral p.
AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region)
aps anterior parolfactory sulcus
cals callosal sulcus
CdL lateral caudate n.
CdM medial caudate n.
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p.
cis circular insular sulcus
Cl claustrum
CSP cavity of septum pellucidum
ec external capsule
ex extreme capsule
FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle
fpms frontal paramidline sulcus
FPu fundus region of putamen gcc genu of corpus callosum
ifs inferior frontal sulcus
IGr indusium griseum
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
olfs olfactory sulcus
OP10,13,14,32,47 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003)
OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped
from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et.
al. 2003)
OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from
Öngür et. al. 2003) pors posterior orbital sulcus
PPCl prepiriform claustrum
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
ps polas sulcus
Pu putamen racc radiation of corpus callosum
scal subcallosal fc
SCS subcallosal stratum
sfs superior frontal sulcus
SGl substantia gliosa
sts superior temporal sulcus
sv septal vein TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
The image provided is a blank, light gray rectangle. There is no text or discernible content within the image to transcribe into markdown.
**163**
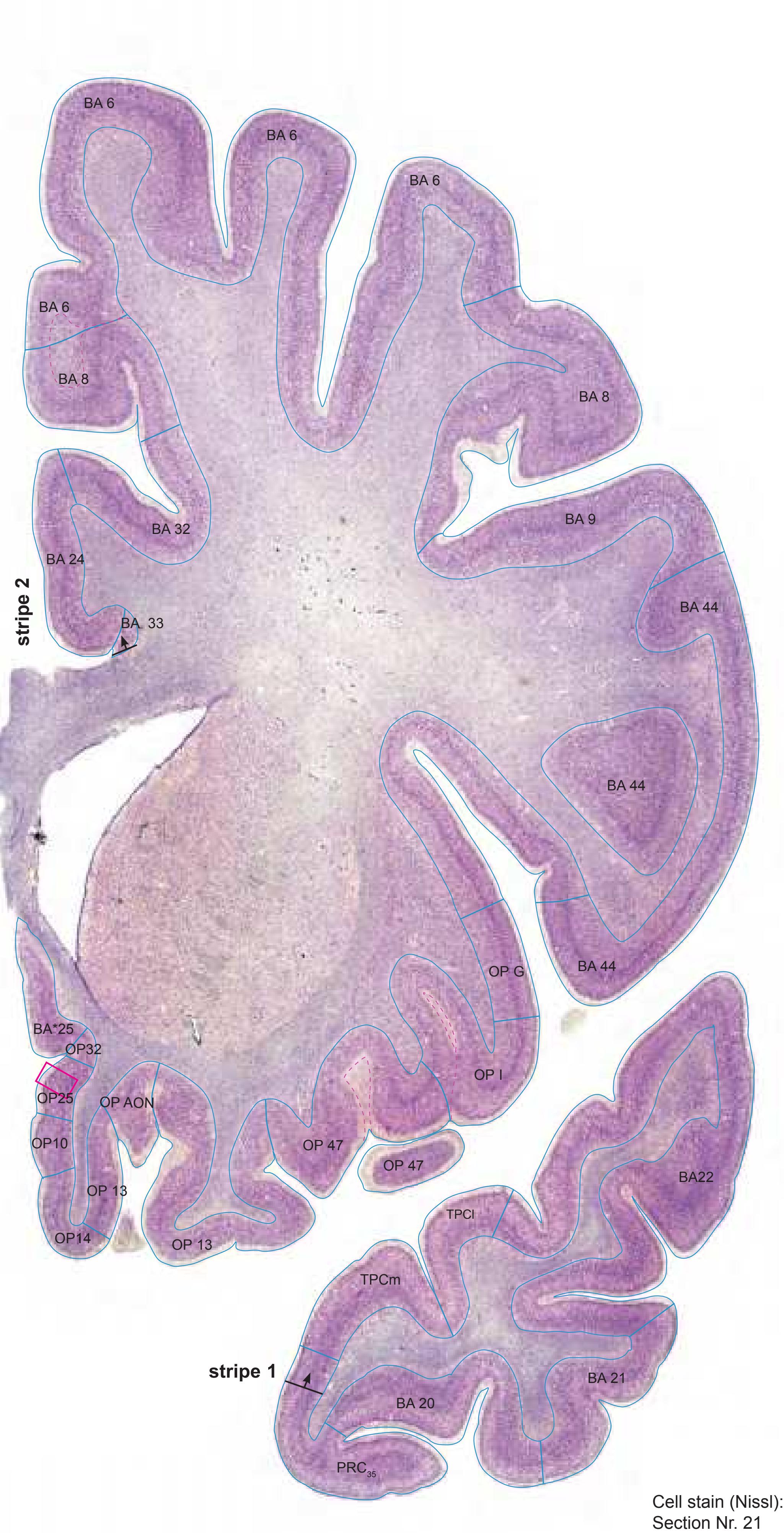
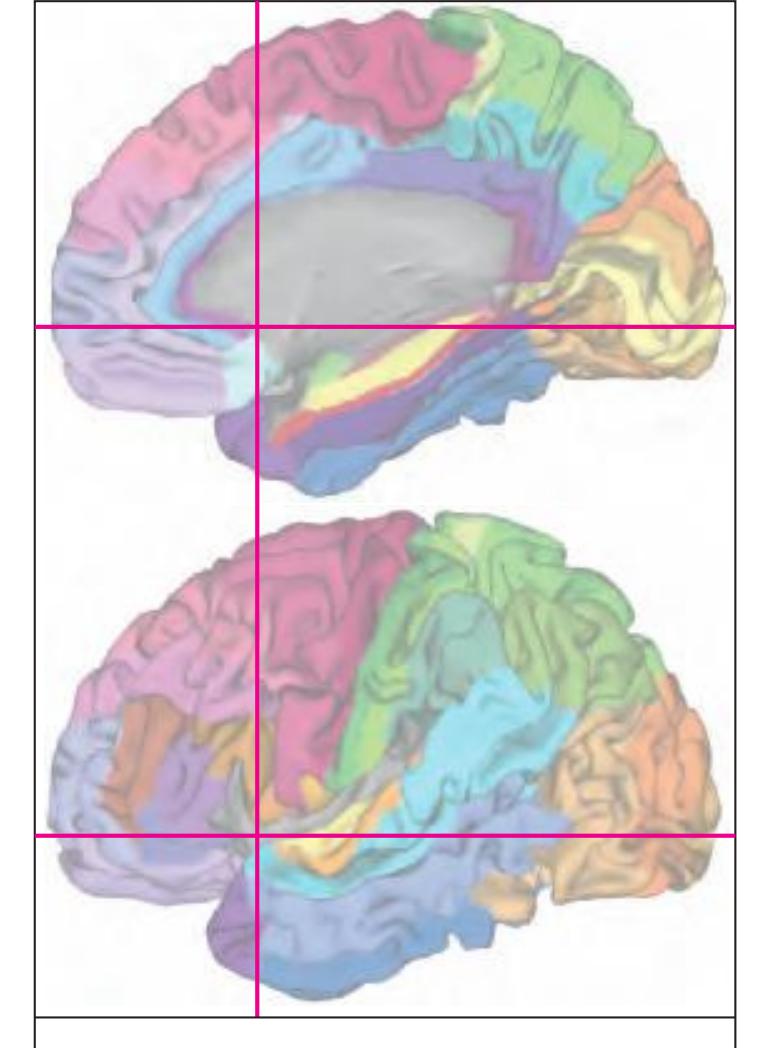
MNI Position y = 14.28 mm AHB Position y = -13.59 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
API area piriformis insulae CG cingulate gyrus FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IG insular gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
TIG transverse insular gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
- BA6 area frontalis agranularis
- BA8 area frontalis intermedia
- BA9 area frontalis granularis
- BA20 area temporalis inferior
- BA21 area temporalis media
- BA22 area temporalis superior BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
- BA25 area subgenualis
- BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
- BA33 area praegenualis
- BA44 area opercularis
- OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP32 area 32 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP47 area 47 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP\_AON anterior olfactory nucleus (by Öngür et al. 2003)
- OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al.
- 2003) OP\_I agranular insular cortex (by Öngür et
- al. 2003) PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
- TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
- TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
- BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
- of areas OP10-47
#### von Economo and Koskinas
- FB agranular frontal area
- FC intermediate frontal area
- FF granular orbital area
- FH prefrontal area
- FHL parolfactory prefrontal area FL parolfactory area
- IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
- IA2 ventral precentral insular area IAB insular transition area
- LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
- limbic area
- TA superior temporal area TE1 middle temporal area proper
- TE2 inferior temporal area proper
- TG temporo polar area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
Slice Nr. 1983
25 BA25
a24c' anterior division of BA24
a24' anterior division of BA24 a33' anterior subregion of BA33
**164**

Cortex: Gyri and Sulci

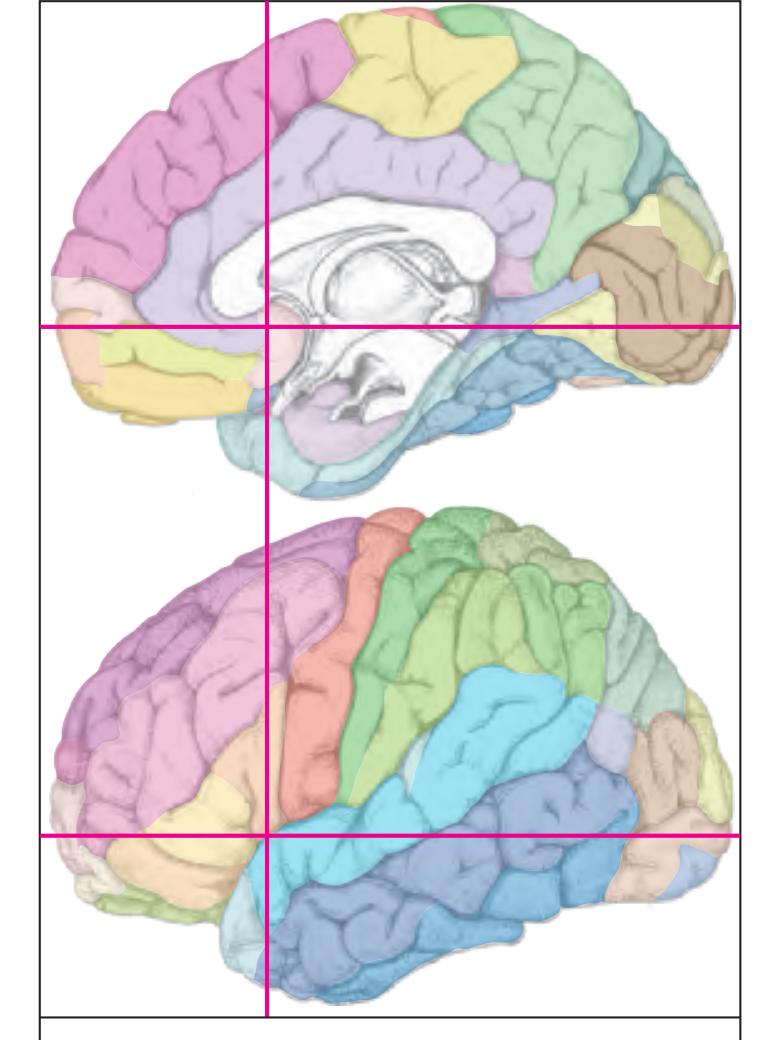
MNI Position y = 13.01 mm AHB Position y = -12.41 mm
API area piriformis insulae AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region) CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IG insular gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare SCA subcallosal area SCG cingulate gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, inf. branch apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, sup.branch cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus ifs inferior frontal sulcus (f2) its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors transverse olfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fxl fornix longus ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers rcc rostrum of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle sgr radiation of straight gyrus
1p olfactory peduncle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
Sulci
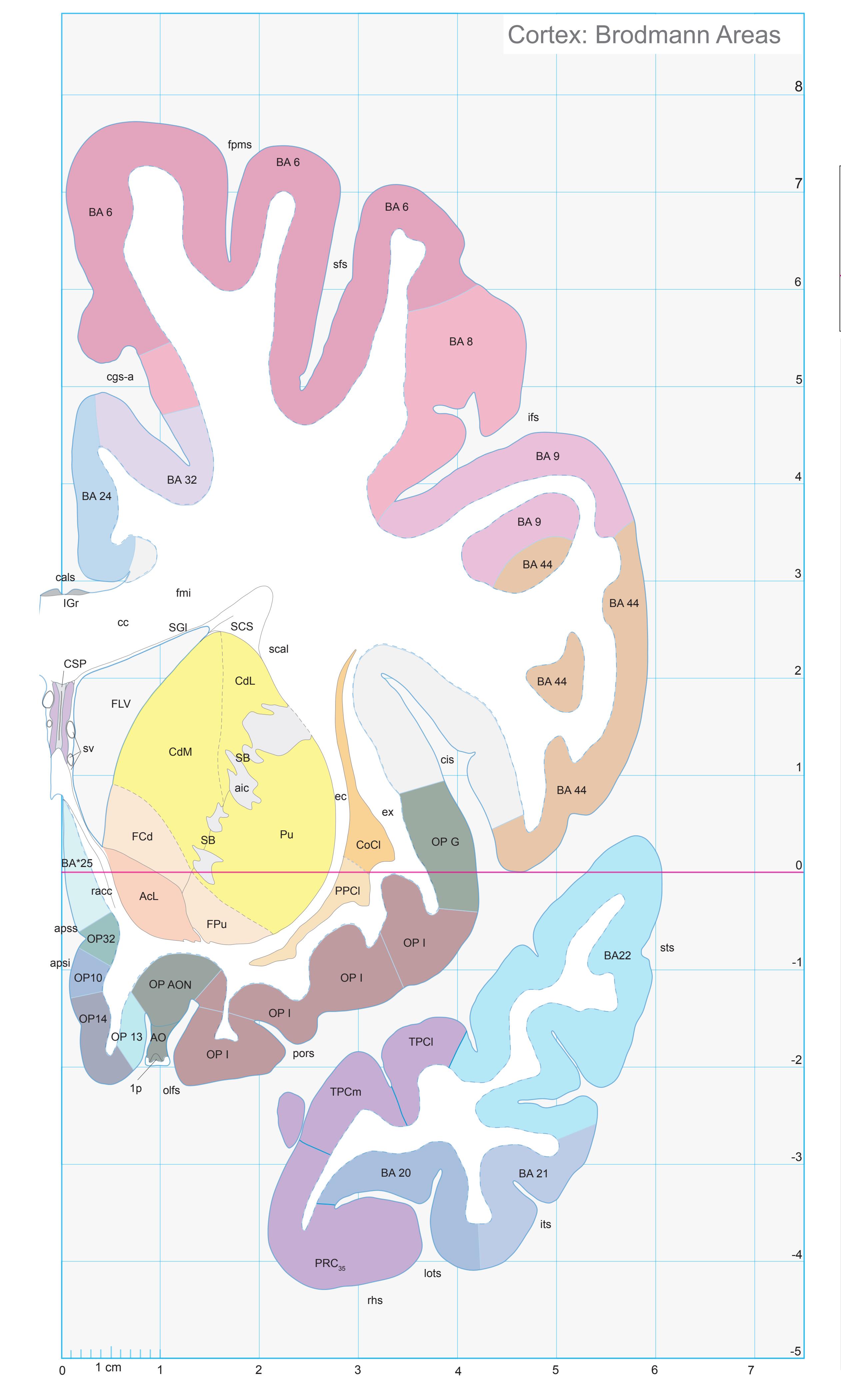
ICL: -12.41 MCP: -27.15 MNI: 13.01

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
1p olfactory peduncle AcL accumbens n., lateral p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AO anterior olfactory n. (retrobulbar region) apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, inf. branch apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, sup.branch cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum CSP cavity of septum pellucidum ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fmi forceps minor of corpus callosum fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen ifs inferior frontal sulcus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus OlfA olfactory area OP10,13,14,32 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) olfs olfactory sulcus PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule pors posterior orbital sulcus PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 Pu putamen racc radiation of corpus callosum rhs rhinal sulcus SB striatal cell bridge scal subcallosal fc SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex TPCm medial temporopolar cortex
**167**
Fibers

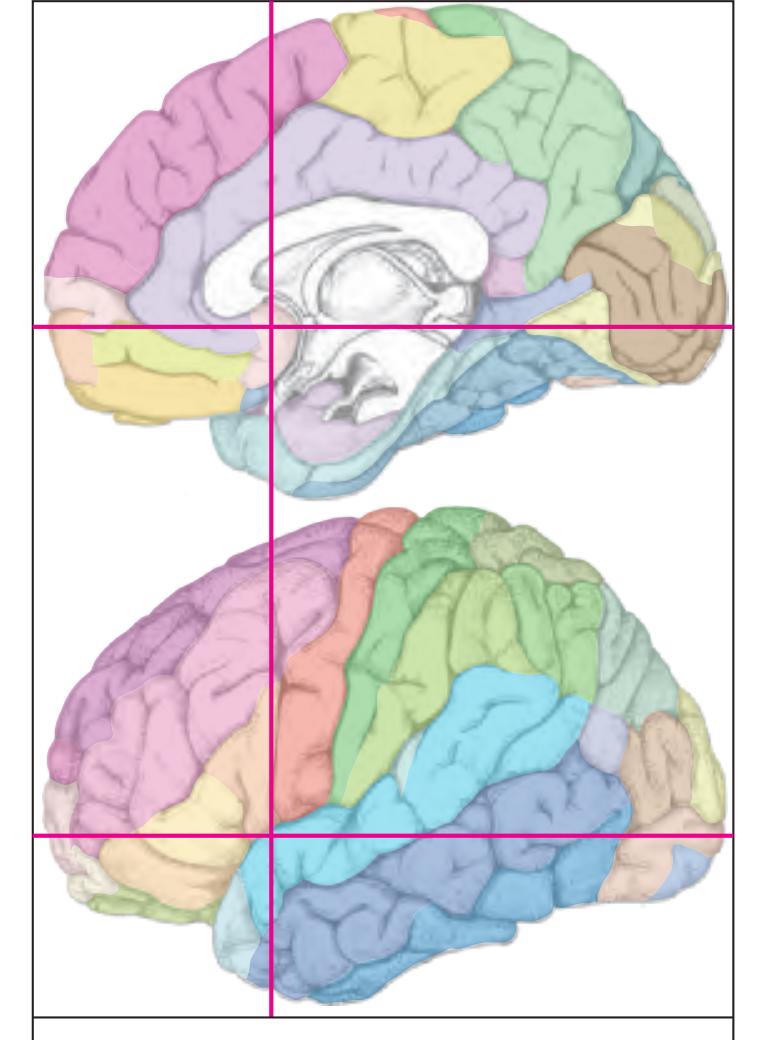
MNI Position y = 10.11 mm AHB Position y = -9.62 mm
API area piriformis insulae CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IG insular gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PTG paraterminal gyrus SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus
apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, inf. branch apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, sup.branch cals callosal sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olfs olfactory sulcus pors transverse olfactory sulcus pps posterior parolfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
Sulci
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fmi forceps minor of the corpus callosum fxl fornix longus ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers olfr olfactory radiation racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
**168**
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 -4 7 8 7 -5 Cortex: Brodmann Areas Pu sts its lots sfs AcC SSTI AcM AcL racc scal sfo SGl sv aic apss cc CdL CdM CoCl CSP ec ex FCd FPu IGr olf olfs PPCl pps ors fmi FLV apsi PRC35 PRC36 ps rhs irhs iprs fpms cgs-a cis iprs cals ifo Pir TPCl BA 6 BA 24 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 44 BA 8 OP G BA 32 BA22 BA 9 OP I OP I OP AON OP10 BA 20 BA 21 OP14 OP I BA22 OP32 OP 13 BA\*25
ICL: -9.62 MCP: -24.36 MNI: 10.11

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, inf. branch apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, sup.branch cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum CSP cavity of septum pellucidum ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fmi forceps minor of corpus callosum fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle IGr indusium griseum iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus olf olfactory peduncle olfs olfactory sulcus OP10,13,14,32 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) ors orbital sulcus Pir piriform cortex PPCl prepiriform claustrum pps posterior parolfactory sulcus PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 ps polas sulcus Pu putamen racc radiation of corpus callosum rhs rhinal sulcus scal subcallosal fc sfo superior fronto-occipital fc sfs superior frontal sulcus
SGl substantia gliosa SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
sv septal vein
1
0
3
2
4
5
6
**169**


MNI Position y = 10.14 mm AHB Position y = -9.65 mm
# Gyral Pattern
API area piriformis insulae
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex
FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
IG insular gyrus
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
ITP inferior temporopolar region
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
OlfA olfactory area
PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PTG paraterminal gyrus SCA subcallosal area
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SG straight gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
#### TPG tempopolar gyrus Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA25 area subgenualis
BA25 area subgenualis
BA32 area cingulari s anterior
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA44 area opercularis
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP13 area 13 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP14 area 14 (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP32 area 32 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP\_AON anterior olfactory nucleus (by
Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_I agranular insular cortex (by Öngür et
al. 2003) PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
Pir piriform cortex
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
of areas OP10-47
FB agranular frontal area von Economo and Koskinas
FC intermediate frontal area
FL parolfactory area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
La precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
La2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vo
B. Vogt: a24c' anterior division of BA24
a24' anterior division of BA24 a33' anterior subregion of BA33 p24c' anterior division of BA24
Slice Nr. 2130

**171**


MNI Position y = 7.18 mm AHB Position y = -6.91 mm
CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IG insular gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PCA precommissural archicortex PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PTG paraterminal gyrus SCA subcallosal area SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TPG tempopolar gyrus cals callosal sulcus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pps posterior parolfactory sulcus ps polar sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fxl fornix longus ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers olf olfactory peduncle olfr olfactory radiation racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle

ICL: -6.91 MCP: -21.65 MNI: 7.18

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
\*BA25 see p. 101 AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, sup.branch cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen IGr indusium griseum iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lls lateral longitudinal stria lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus mls medial longitudinal stria molf medial olfactory radiation olf olfactory peduncle olfr olfactory radiation OP10,14 areas defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) Pir piriform cortex PPCl prepiriform claustrum pps posterior parolfactory sulcus PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 ps polas sulcus Pu putamen racc radiation of corpus callosum rhs rhinal sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SptP septum pellucidum SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
unc uncinate fc
**173**


SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fxl fornix longus ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers


ICL: -5.36 MCP: -20.10 MNI: 5.63
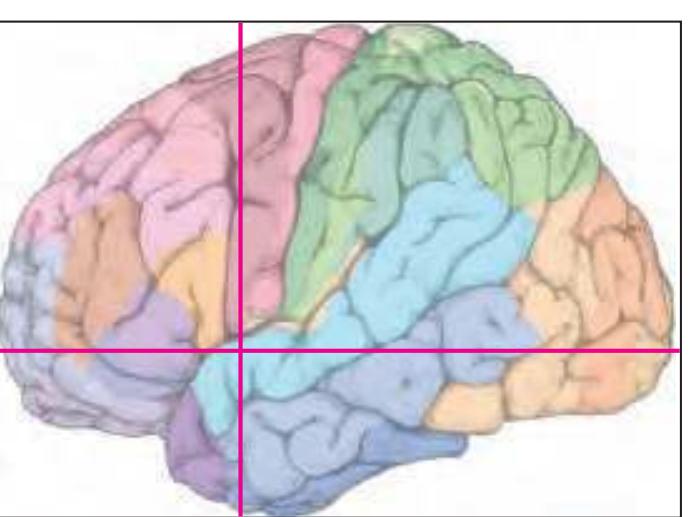
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) \*BA25 see p. 101
AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AOP anterior olfactory n., post. p. cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum dB diagonal band (Bandeletta diagonalis) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. molf medial olfactory radiation OP10 area defined by Öngür et.al. (2003) OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) Pir piriform cortex PPCl prepiriform claustrum pps posterior parolfactory sulcus PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 ps polas sulcus Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex Tu olfactory tubercle unc uncinate fc
VCl ventral claustrum
**175**


MNI Position y = 5.77 mm AHB Position y = -5.49 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex
FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
ITP inferior temporopolar region MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
OlfA olfactory area
PCA precommissural archicortex
PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PTG paraterminal gyrus SCA subcallosal area
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA25 area subgenualis BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA32 area cingularis an
BA32 area praegenualis
BA33 area praegenualis
BA44 area opercularis
OP10 area 10 (by Öngür et al. 2003) OP\_AON anterior olfactory nucleus (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
OP\_I agranular insular cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
Pir piriform cortex
TPCl lateral temporopolar cortex
BA\*1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 extension
of areas OP10-47
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
FL parolfactory area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
La precingulate agranular anterior limbic area La2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33 p24c' anterior division of BA24

**177**
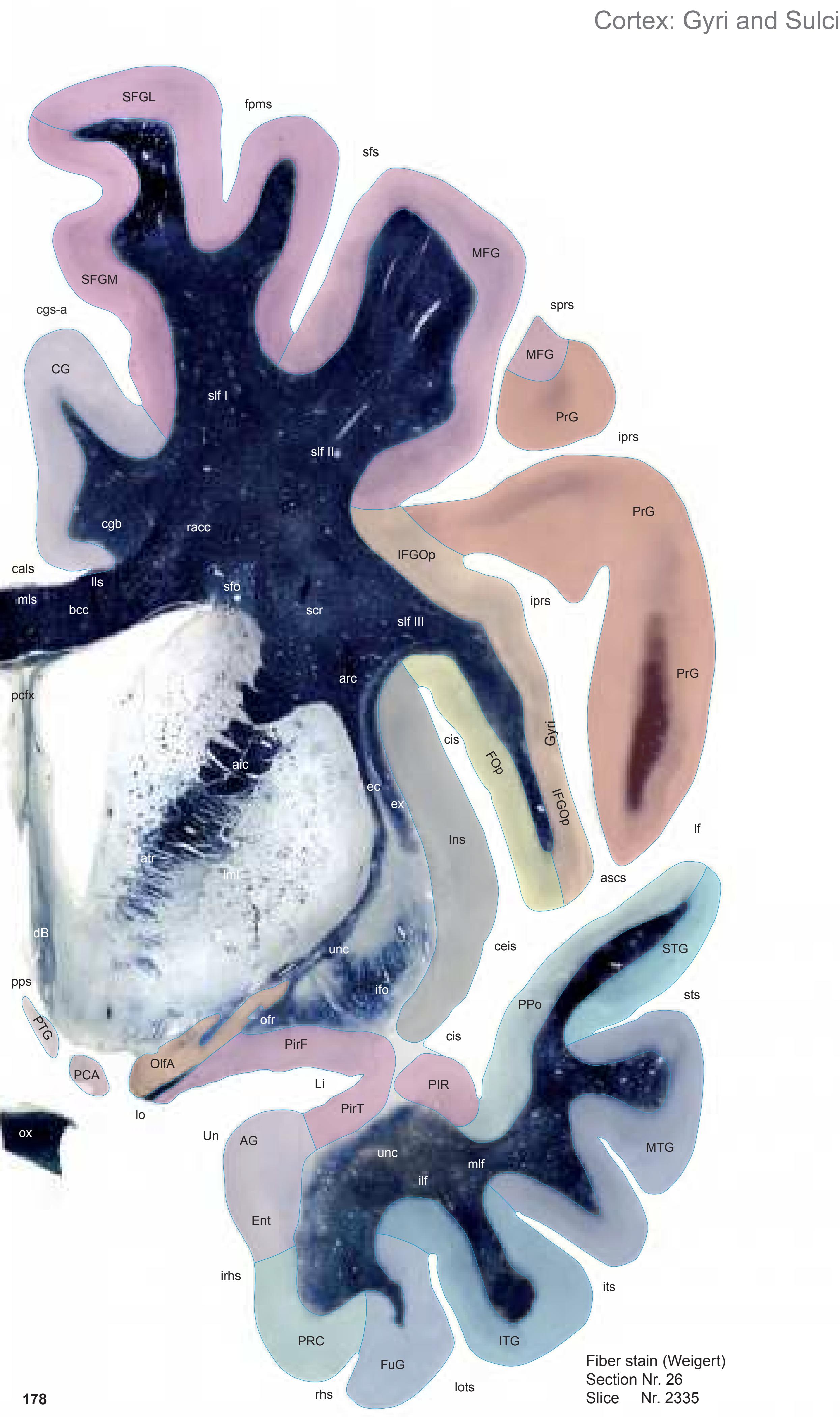

MNI Position y = 4.34 mm AHB Position y = -4.15 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus Li limen insulae MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PCA precommissural archicortex PIR parainsular region PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PTG paraterminal gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pps posterior parolfactory sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma pcfx precommissural fornix racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
unc uncinate fascicle
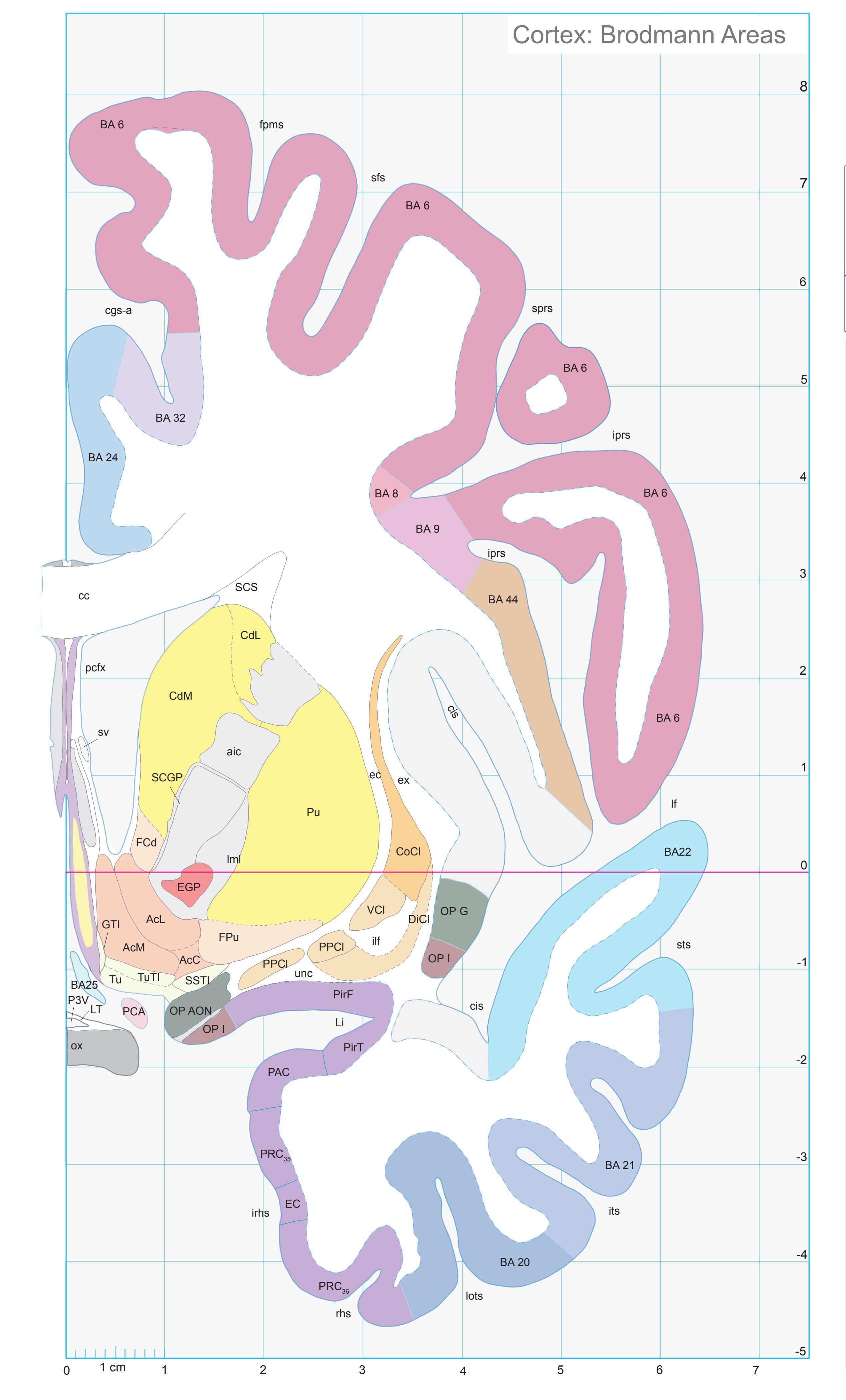
ICL: -4.15 MCP: -18.89 MNI: 4.34

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum ec external capsule EC entorhinal cortex EGP external globus pallidus ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen GTI great terminal island ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Li limen insulae lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LT lamina terminalis OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PAC periamygdaloid cortex PCA precommissural archicortex pcfx precommissural fornix PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SCA subcallosal area SCGP supracapsular part of globus pallidus SCS subcallosal stratum
sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus
sv septal vein Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
unc uncinate fc VCl ventral claustrum
**179**


MNI Position y = 3.12 mm AHB Position y = -2.81 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus Li limen insulae MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area PIR parainsular region PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PTG paraterminal gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pps posterior parolfactory sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma pcfx precommissural fornix racc radiation of corpus callosum
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle
scr superior corona radiata
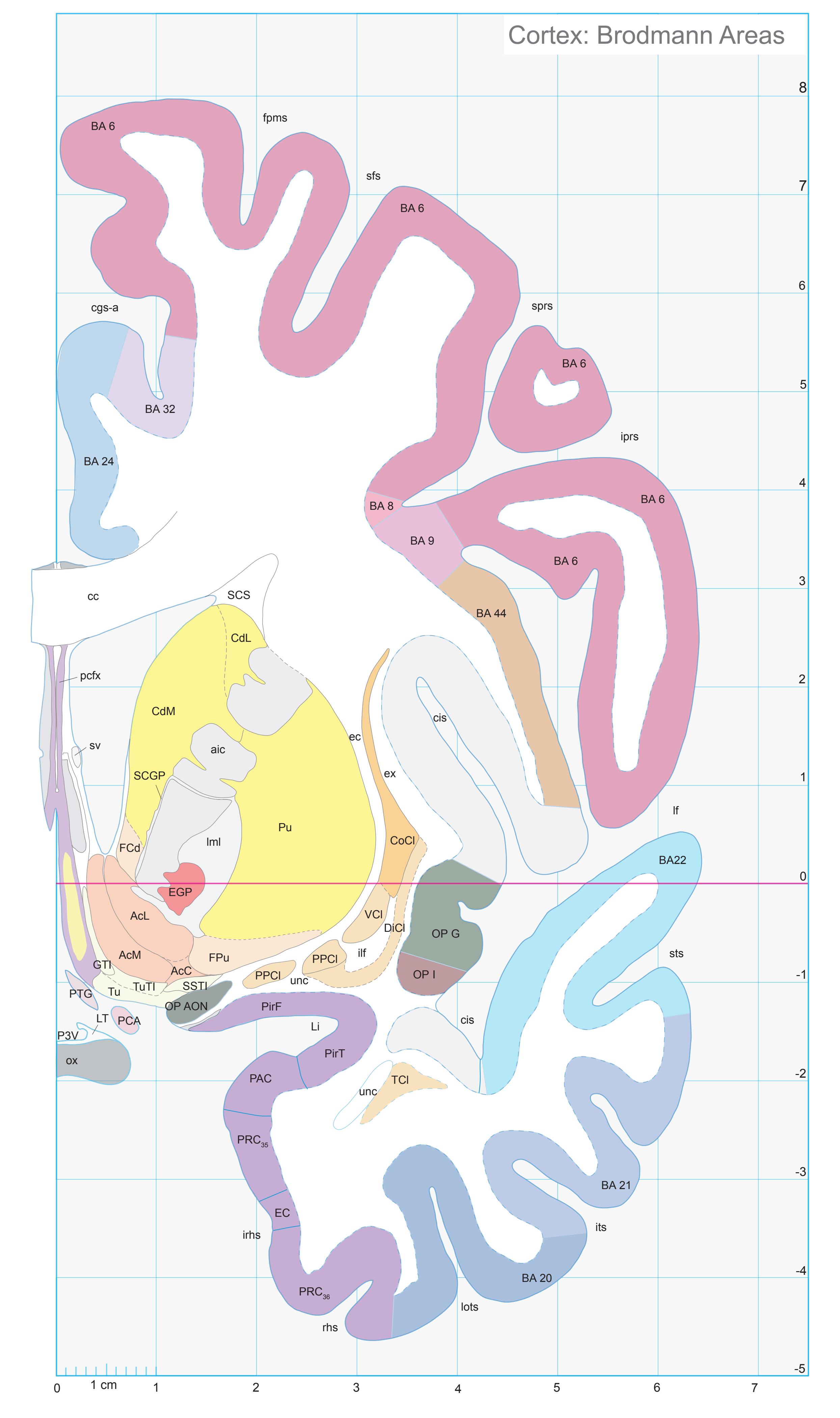
ICL: -2.81 MCP: -17.55 MNI: 3.12

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum ec external capsule EC entorhinal cortex EGP external globus pallidus ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen GTI great terminal island ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Li limen insulae lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LT lamina terminalis OlfA olfactory area OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP I agranular insular cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PAC periamygdaloid cortex PCA precommissural archicortex pcfx precommissural fornix PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PTG paraterminal gyrus Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SCA subcallosal area SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands unc uncinate fc VCl ventral claustrum
**181**

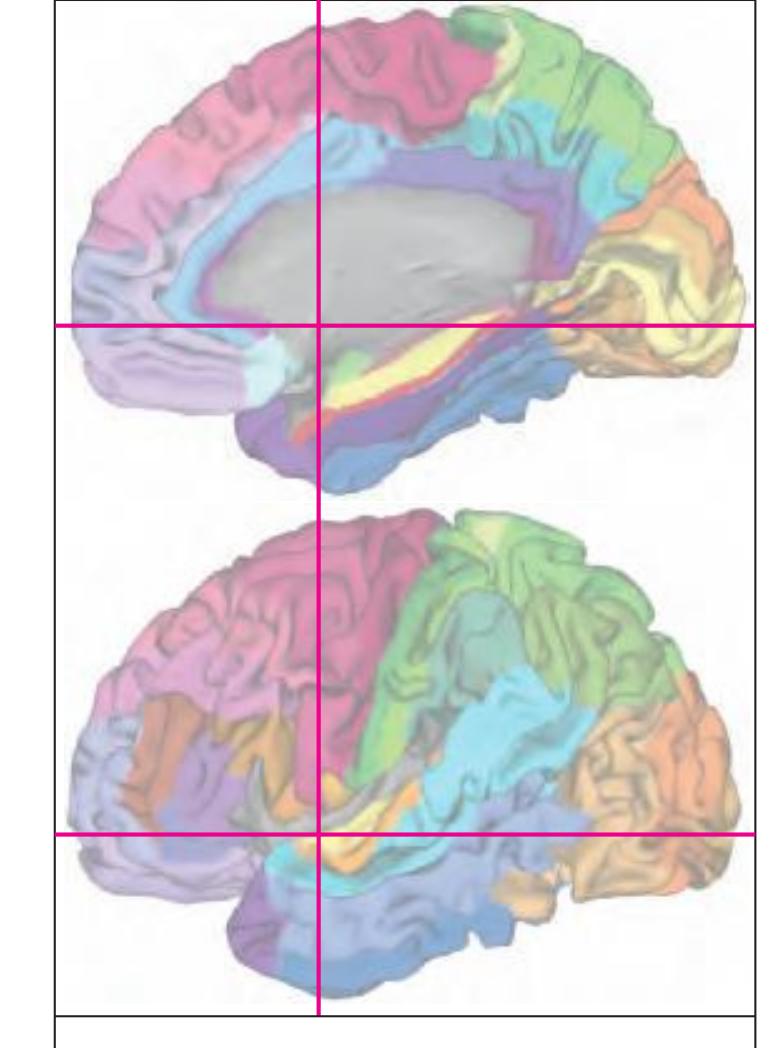
MNI Position y = 3.52 mm AHB Position y = -3.35 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum
FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
Li limen insulae
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
OlfA olfactory area
PIR parainsular region PirF piriform cortex, frontal part
PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PTG paraterminal gyrus
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
Un uncus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA9 area frontalis granularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA44 area opercularis
EC external capsule
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al.
2003)
OP\_I agranular insular cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
l. 2005)
PPC35, perirhinal cortex
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 Pir piriform cortex
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal
entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area
TA superior temporal area TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33 p24c' anterior division of BA24

# Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
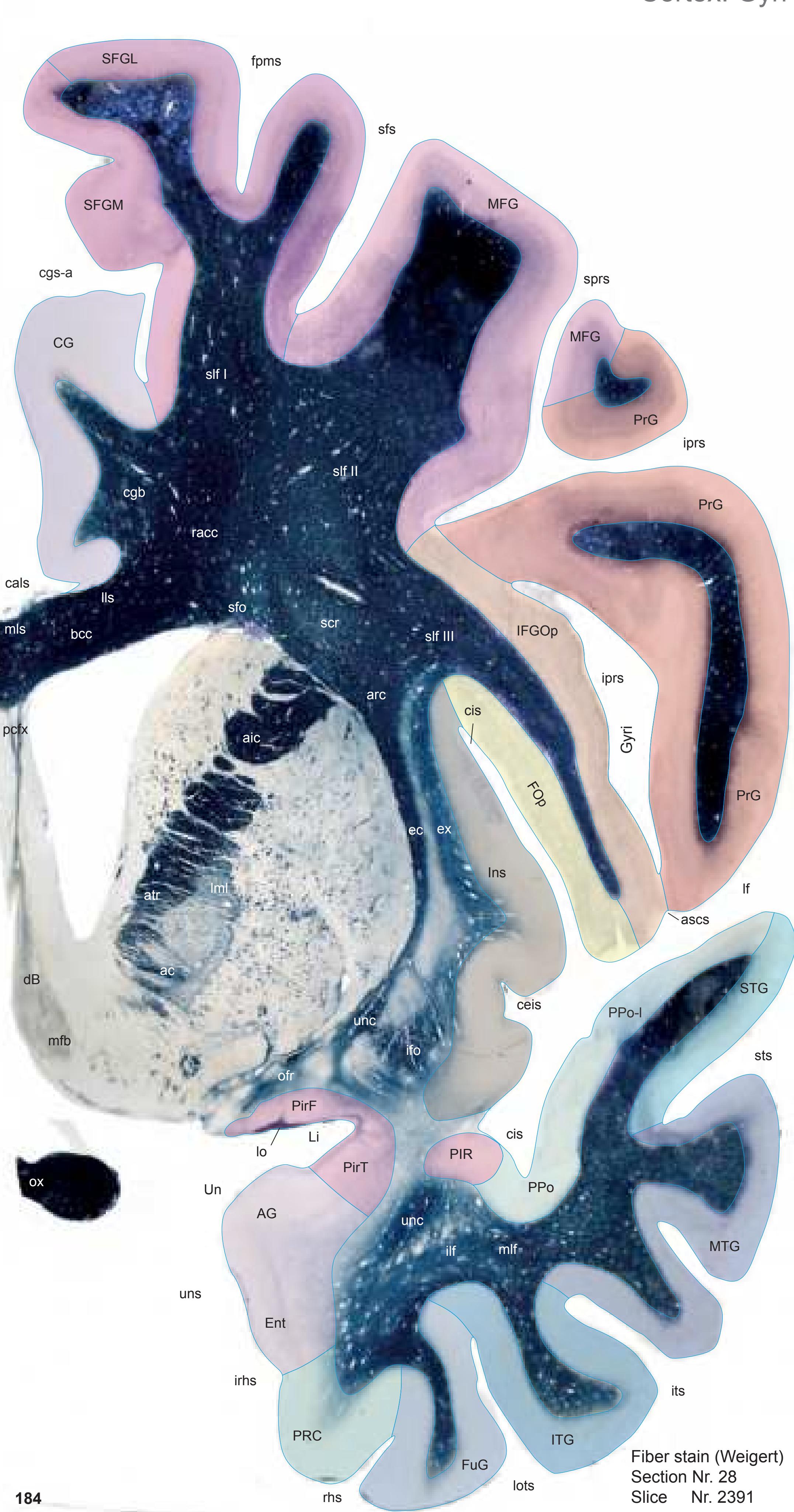

MNI Position y = 2.53 mm AHB Position y = -2.65 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus Li limen insulae MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PIR parainsular region PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
Fibers
Sulci
ac anterior commissure aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle dB diagonal band (Broca) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma pcfx precommissural fornix racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. unc uncinate fascicle

ICL: -2.65 MCP: -17.39 MNI: 2.53

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) ac anterior commissure AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aic anterior limb of the internal capsule BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central division BSTL bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral division cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum ec external capsule EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield ex extreme capsule FCd fundus region of caudate n. fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen GTI great terminal island IGr indusium griseum ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Li limen insulae lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. LT lamina terminalis mfb medial forbrain bundle mls medial longitudinal stria OlfA olfactory area OP AON anterior olfactory nucleus (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et. al. 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pcfx precommissural fornix PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum SCTI subcaudate terminal island SFi septofimbrial n. sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island
sts superior temporal sulcus
VDB vert. limb of the diagonal band
sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
unc uncinate fc VCl ventral claustrum
**185**
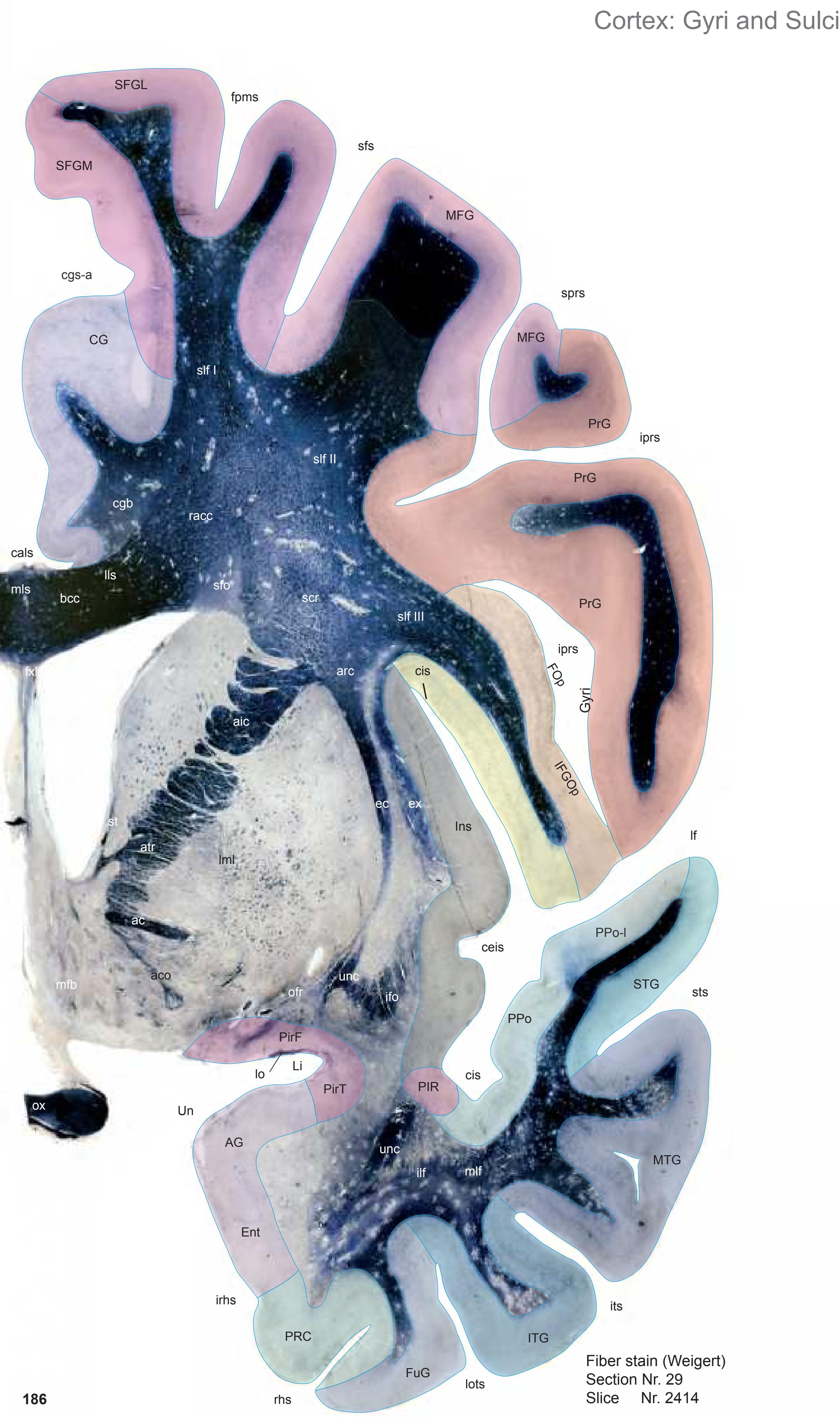


MNI Position y = 2.14 mm AHB Position y = -2.03 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus Li limen insulae MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PIR parainsular region PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
ac anterior commissure aco anterior commissure, anterior limb aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fxl fornix longus ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. st stria terminalis
unc uncinate fascicle

ICL: -2.03 MCP: -16.77 MNI: 2.14
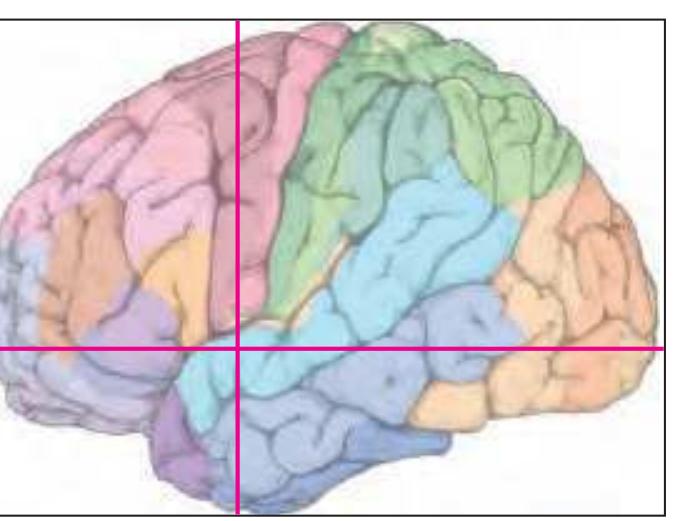
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) ac anterior commissure AcC accumbens n., central p. AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aco anterior commissure, anterior limb aic anterior limb of the internal capsule BA1-52 Brodman areas 1-52 ( see plate Nr. 1 ) BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central division BSTLJ bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral division, juxtacapsular p. BSTM bed n. of the stria terminalis, medial division cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum ec external capsule EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield ex extreme capsule FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen GTI great terminal island IGr indusium griseum ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Li limen insulae lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. LT lamina terminalis OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et.al., 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pcfx precommissural fornix PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SB striatal cell bridge scal subcallosal fc SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum SFi septofimbrial n. sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus
TCl temporal claustrum Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
VDB vert. limb of the diagonal band VGP ventral globus pallidus
Un uncus unc uncinate fc VCl ventral claustrum
**187**

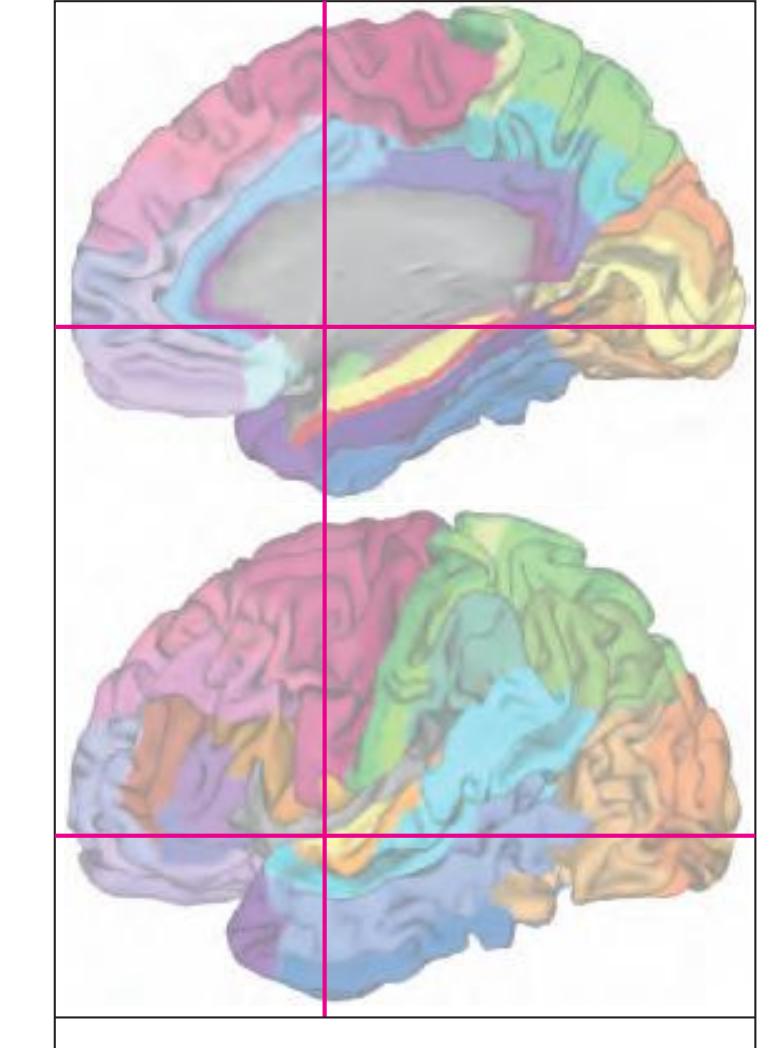
MNI Position y = 1.97 mm AHB Position y = -1.87 mm
### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum
FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
Li limen insulae
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PIR parainsular region
PirF piriform cortex, frontal part
PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
STG superior temporal gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA8 area frontalis intermedia
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA44 area opercularis
ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral
subfield
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### Pir piriform cortex
von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
entrance
precipul
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33
p24c' anterior division of BA24

**190** Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 30 Slice Nr. 2438 Cortex: Gyri and Sulci CG SFGL SFGM MFG PrG PrG PrG IFGOp FOp PPo STG MTG ITG FuG PRC Ent PirT AG uns lots Un sts cis cis sfs its cals rhs lf sprs fpms iprs irhs iprs cgs-a PirF PPo-l ceis pcis Ins unc bcc aco aic lml ifo ac mlf slf I ilf racc slf II slf III arc sfo mls cgb st lls ec ex scr pcfx pcfx mfb atr ofr lo ox unc

MNI Position y = 1.41 mm AHB Position y = -1.39 mm
Sulci
Gyri
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
ac anterior commissure aco anterior commissure, anterior limb aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma pcfx precommissural fornix racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. st stria terminalis unc uncinate fascicle
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 VGP Cortex: Brodmann Areas PAM MPOM sts PACl lo PirT pcfx PirF Pu SCh scal SCGP SCS SFi SO SSTI TS Tu TuTI VCl AVPe Un tsv TCl sv PPCl IGr PaAP ilf Li P3V ox LSD LSI LSV HDB GTI FPu FLV ex lml ec DiCl VDB CdM CdL BSTL cc EGP DPeH CoCl cis CdV BS TM BS TC aic ac AcM aco AcC PRC35 PRC36 lots PAC BA 20 BA 21 PRt rhs irhs lf iprs fpms sprs cgs-a sfs its cis ELR unc MPO BA 6 BA 43 BA 24 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 44 BA 6 BA 32 BA22 OP G
30
ICL: -1.39 MCP: -16.13 MNI: 1.41

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) ac anterior commissure AcC accumbens n., central p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aco anterior commissure, anterior limb aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AVPe anteroventral periventricular hypoth. n. BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, centra division BSTL bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral division BSTM bed n. of the stria terminalis, medial division cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DPeH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic n. ec external capsule EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield ex extreme capsule FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen GTI great terminal island HDB horizontal limb of the diagonal band IGr indusium griseum ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Li limen insulae lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. MPO medial preoptic n. MPO medial preoptic n., medial p. OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et.al., 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PaAP paraventricular hypothalamic n., anterior parvicellular p. PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum PAM periamygdaloid cortex pcfx precommissural fornix PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PPCl prepiriform claustrum PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus scal subcallosal fc SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum SFi septofimbrial n. sfs superior frontal sulcus SO supraoptic n. sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum TS triangular septal n. tsv thalamostriate vein Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands Un uncus unc uncinate fc VCl ventral claustrum VDB vertical limb of the diagonal band
VGP ventral globus palidus
**191**
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus MNI Position y = 0.68 mm AHB Position y = -0.67 mm

cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
Sulci
ac anterior commissure aco anterior commissure, anterior limb arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule ic internal capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma pcfx precommissural fornix racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sls sublenticular stria st stria terminalis unc uncinate fascicle

Fibers
**192**

ICL: -0.67 MCP: -15.41 MNI: 0.68

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) AB access. basal amygdaloid n. ac anterior commissure AcL accumbens n., lateral p. AcM accumbens n., medial p. aco anterior commissure, anterior limb ADB n. of the diagonal band, angular p. AG ambiens gyrus aic anterior limb of the internal capsule AVPe anteroventral periventricular hypothal. n. BC basal n., compact part BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTL bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral div. BSTM bed n. of the stria terminalis, medial div. cc corpus calosum CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DPeH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic n. ec external capsule EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield Eo entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield ex extreme capsule FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column and body) GTI great terminal island HDB horizontal limb of the diagonal band ilf inferior longitudinal fc iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus La lateral amygdaloid n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. mfb medial forbrain bundle MnPO median preoptic n. MPO medial preoptic n. OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et.al., 2003) ox optic chiasma P3V preoptic recess of third ventr. PaAP paraventricular hypothalamic n., ant. parvicellular p. PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus scal subcallosal fc SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum SFi septofimbrial n. sfs superior frontal sulcus SO supraoptic n. sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum
TS triangular septal n. tsv thalamostriate vein Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
unc uncinate fc unn uncal notch VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus palidus
**193**


MNI Position y = 0.51 mm AHB Position y = -0.48 mm
### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum
FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PAM periamygdaloid cortex
PirF piriform cortex, frontal part
PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
STG superior temporal gyrus
Un uncus
### Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA43 area subcentralis
BA44 area opercularis
DAT1 area operculum
Hi hippocampus
Hi hippocampus
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
# von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33
p24c' anterior division of BA24 p24' anterior division of BA24

**196** Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 32 Slice Nr. 2490 Cortex: Gyri and Sulci CG SFGL SFGM MFG PrG PrG IFGOp PrG FOp Ins PPo STG MTG ITG FuG PRC Ent PirT AG uns lots Un sts sfs its cals rhs lf PAM pcis pacs sprs fpms iprs irhs ceis cis cis ascs cgs-a PPo-l ac bcc aco unc unc aic lml ifo ac mlf slf I ilf racc slf II slf III arc mls sfo cgb st lls ec ex scr vaf fxl mfb atr sox ofr cfx lo ox

MNI Position y = 0.00 mm AHB Position y = 0.00 mm
Sulci
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression) ac anterior commissure aco anterior commissure, anterior limb aic anterior limb of the internal capsule arc arcuate fascicle
bcc body of corpus callosum cfx column of fornix cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule
atr anterior thalamic radiation
ex extreme capsule fxl fornix longus
cis circular sulcus
Gyri
lf lateral fissure
rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
pacs paracentral sulcus
fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
pcis posterior central insular sulcus
ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract
mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
ofr orbito-frontal fibers ox optic chiasma
racc radiation of corpus callosum
scr superior corona radiata
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sls sublenticular stria
sox supraoptic commissure
st stria terminalis
unc uncinate fascicle
vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 unc uncinate fc Unn uncinate nucleus VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus palidus IGr Cortex: Brodmann Areas SCS Unn LH MPO PaD lo db DPeH mfb ac mml ox FPu TuTI VCl VGP SSTI sv SxD TCl TS tsv Tu InfS 3V BM ac ic BSTC BSTM CdM CoCl EGP FLV fx ilf LSD LSV MS PACl PaMC Pu BSTL BSTV CdL CdV DiCl lml GTI La LSI BLVM scal SCGP SCh SO AG ER PRC35 PRC36 irhs ELR unn Eo PAC lots sts lf iprs MPOL opt LiCl PRt fpms sprs cgs-a sfs BC pacs its rhs PirF PirT PACl unc unc SGl BA 6 BA 43 BA 24 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 44 BA 6 OP G BA 21 BA 22 BA 21 BA 20
ICL: 0.00 MCP: -14.74 MNI: 0.00

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) 3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure AG ambiens gyrus BC basal n., compact part BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTL bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral div. BSTM bed n. of the stria terminalis, medial div. BSTV bed n. of the stria terminalis, ventral div. CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. CoCl compact insular claustrum db diagonal band (Bandeletta diagonalis) DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DPeH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic n. EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield Eo entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column and body) GTI great terminal island ic internal capsule IGr indusium griseum ilf inferior longitudinal fc InfS infundibular stalk iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus La lateral amygdaloid n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum lml lateral medullary lamina of the glob. pallidus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. mfb medial forbrain bundle mml medial medullary lamina of glob. pallidus MPO medial preoptic n. MPOL medial preoptic nucleus, lateral p. MS medial septal n. OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür et.al., 2003) opt optic tract ox optic chiasma PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p. PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p. PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus scal subcallosal fc SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa SO supraoptic n. sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein SxD sexual dimorphic n. TCl temporal claustrum TS triangular septal n. tsv thalamostriate vein Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
**197**
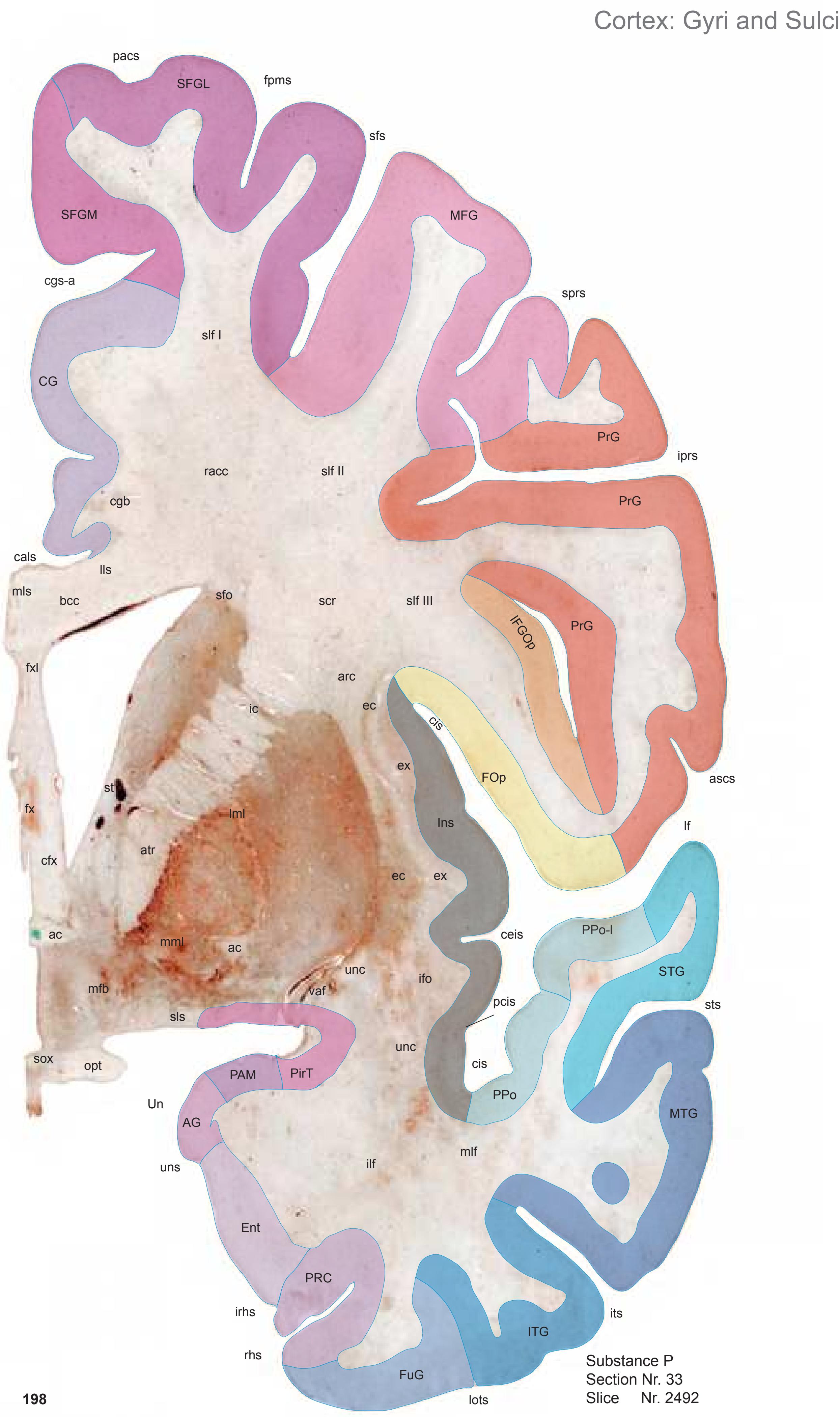
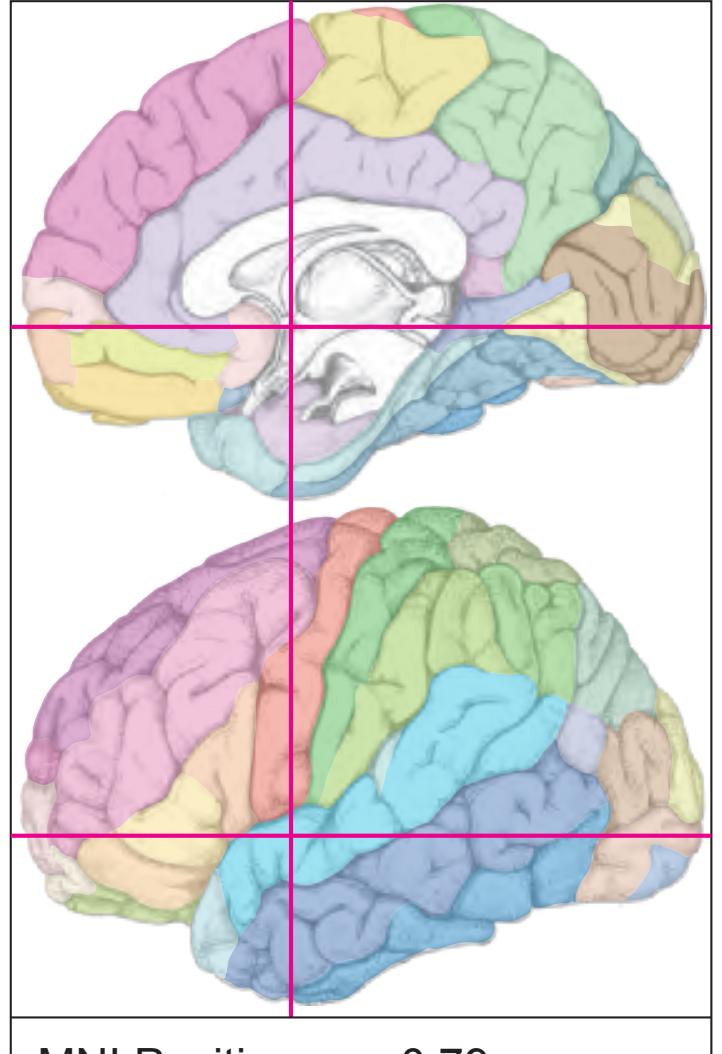
MNI Position y = -0.79 mm AHB Position y = 0.70 mm
Sulci
Gyri
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
ac anterior commissure arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cfx column of fornix cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column and body) fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus opt optic tract racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sls sublenticular stria sox supraoptic commissure st stria terminalis
unc uncinate fascicle
vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 pallidus pallidus et.al., 2003) PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SCS subcallosal stratum sfs superior frontal sulcus SO supraoptic n. sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island st stria terminalis sv septal vein tsv thalamostriate vein unc uncinate fc unn uncal notch VCl ventral claustrum Cortex: Brodmann Areas SCS LH Unn MPO PaD lo db DPeH mfb ac mml ox FPu TuTI VCl VGP SSTI sv SxD TCl TS tsv Tu InfS 3V BM ac ic BSTM BSTC CdM CoCl EGP FLV fx ilf LSD LSV MS PACl PaMC Pu BSTL BSTV CdL CdV DiCl lml GTI La LSI BLVM SCGP SCh SO st PRt ER PRC35 PRC36 rhs ELR unn Eo lots irhs its PirF PirT lf iprs cgs-a sfs cis PAC BC sts sprs pacs fpms BA 21 unc unc IGr AG BA 6 BA 43 BA42 BA 24 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 44 BA 6 BA 6 OP G BA 22 BA 21 BA 20 BA 22
ICL: 0.70 MCP: -14.04 MNI: -0.79
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) 3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure AG ambiens gyrus BC basal n., compact part BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTL bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral div. BSTM bed n. of the stria terminalis, medial div. BSTV bed n. of the stria terminalis, ventral div. CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum db diagonal band (Bandeletta diagonalis) DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DPeH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic n. EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield Eo entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield FLV frontal horn of lat. ventricle fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column and body) GTI great terminal island ic internal capsule IGr indusium griseum ilf inferior longitudinal fc InfS infundibular stalk iprs inferior precentral sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus La lateral amygdaloid n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus lo lateral olfactory tract lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. mfb medial forbrain bundle mml medial medullary lamina of the globus MPO medial preoptic n. MS medial septal n. OP G gustatory cortex (mapped from Öngür ox optic chiasma PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p. PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p. PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
sts superior temporal sulcus
SxD sexual dimorphic n.
TCl temporal claustrum TS triangular septal n.
Tu olfactory tubercle TuTI tubercular terminal islands
Unn uncinate nucleusv
VGP ventral globus palidus
**199**
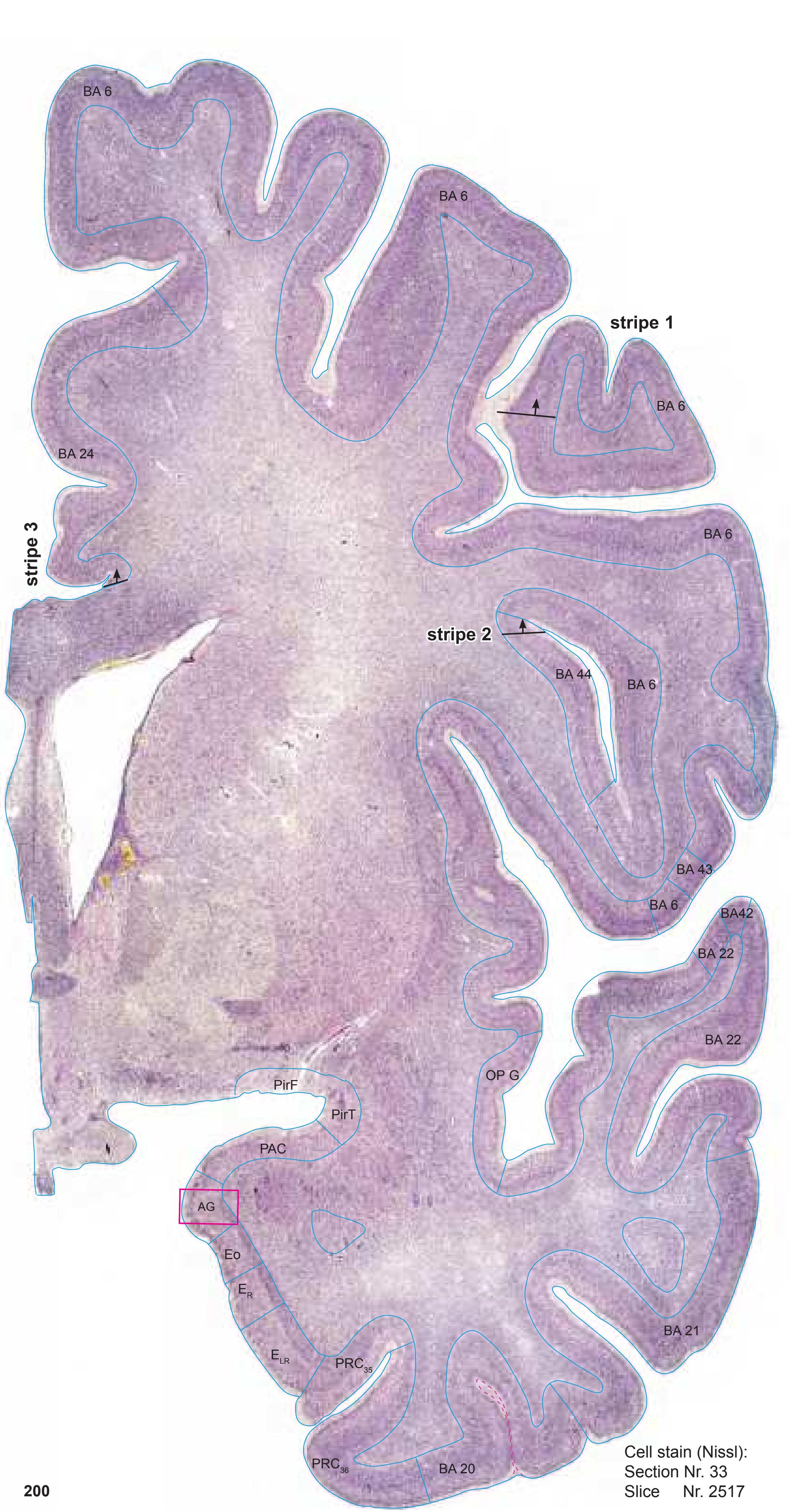
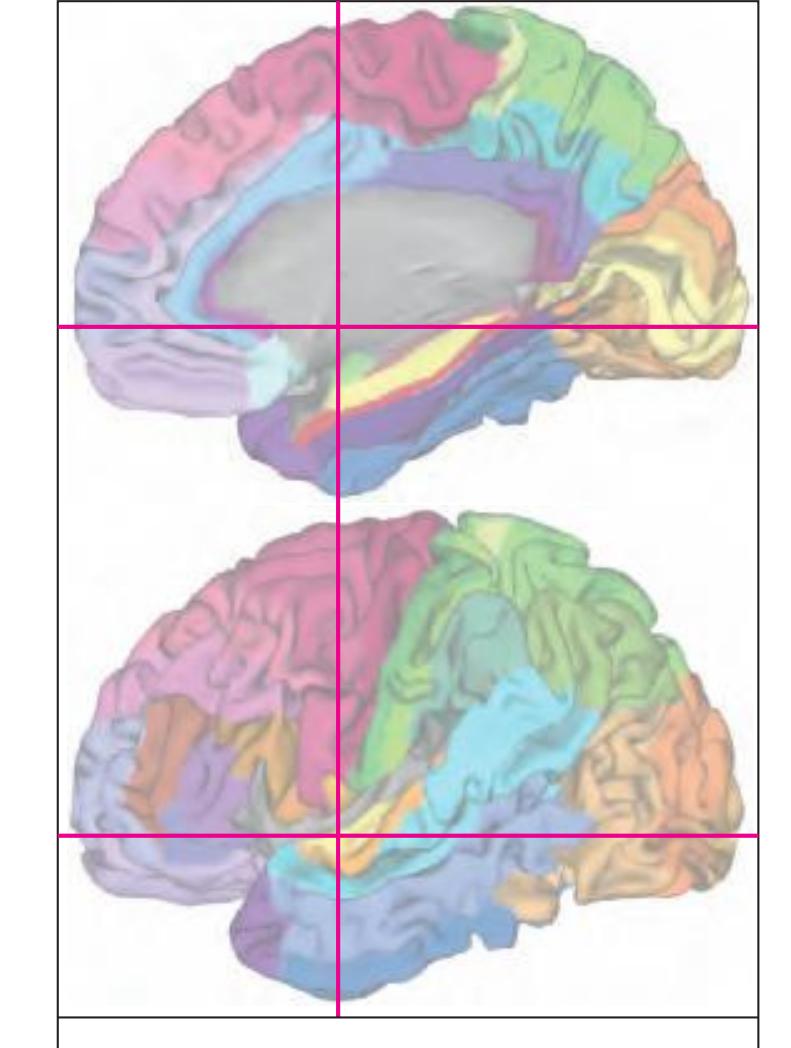
MNI Position y = -0.76 mm AHB Position y = 0.73 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex
FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
PAC periamygdaloid cortex PirF piriform cortex, frontal part
PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
BA44 area opercularis
Hi hippocampus
OP\_G gustatory cortex (by Öngür et al. 2003)
PRC35, perirhinal c
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33
p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24

**201**
Cortex: Gyri and Sulci
Fibers


MNI Position y = -1.35 mm AHB Position y = 1.26 mm
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression) mts middle temporal sulcus
Sulci
ac anterior commissure arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum
cfx column of fornix cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sls sublenticular stria sox supraoptic commissure
st stria terminalis unc uncinate fascicle
opt optic tract
vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
racc radiation of corpus callosum
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 Cortex: Brodmann Areas MPO PAM PaMC sts sfs 3V 3V CxA VGP ACo ac BL BM BLVM BSTC BSTLJ BSTP BSTV CdL CdV CdM CoCl DiCl DoH EGP lml FPu ic InfS fx IGr mml La LiCl LH LSD LSV LSI LV mfb MS PaPC Tu opt PACl PaFo SCGP SO SSTI TCl tsv Un VCl Pu SCS sox sv PirT ER BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 rhs ELR unn Eo PAC GSL lots DCl its SFO PaD AH SCh cgs-a iprs PirF CSP EA PRt LiCl BC sprs pacs fpms BD unc LH AG BA 6 BA 43 BA42 BA 24 BA 4 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 43
ICL: 1.26 MCP: -13.48 MNI: -1.35

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus AH anterior hypothalamic area BC basal n., compact part BD basal n., diffuse part BL basolateral amygdaloid n.
BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. BM basomedial amygdaloid n.
BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTLJ bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral division, juxtacapsular p.
BSTP bed n. of the stria terminalis, posterior div. BSTV bed n. of the stria terminalis, ventral div. CdL lateral caudate n.
CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n.
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. CoCl compact insular claustrum
CSP cavity of septum pellucidum CxA cortico-amygdaloid transition area
DCl dorsal claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DoH dorsal hypothalamic n.
EA extended amygdala
EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield
Eo entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield fpms frontal paramidline sulcus
FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column)
GSL gyrus semilunaris IGr indusium griseum InfS infundibular stalk
iprs inferior precentral sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus La lateral amygdaloid n.
LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum
lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p.
LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p.
LSV lateral septal n., ventral p. LV lateral ventricle
mfb medial forbrain bundle
mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus MPO medial preoptic n.
MS medial septal n. opt optic tract
PAC periamygdaloid cortex
PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus
PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p.
PaFo paraventricular n., fornical p.
PAM periamygdaloid cortex
PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p.
PaPC paraventricular n., parvicellular p. PirF piriform cortex, frontal p.
PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone
Pu putamen
rhs rhinal sulcus
SCGP supracapsular part of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n.
SCS subcallosal stratum
SFO subfornical organ sfs superior frontal sulcus
SO supraoptic n.
sox supraoptic commissure
sprs superior precentral sulcus
SSTI substriatal terminal island
sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum
tsv thalamostriate vein Tu olfactory tubercle
Tu
Jn uncus
Un uncus
unc uncinate fc
unn uncal notch
VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus palidus
**203**
Gyri **204** Fiber stain Section Nr. 35 Slice Nr. 2567 Cortex: Gyri and Sulci CG SFGL SFGM MFG PrG PrG PrG IFGOp FOp Ins PPo STG MTG ITG FuG PRC Ent PHA AG uns Un sts cis cis sfs its cals rhs lf sas pcis pacs sprs fpms ceis lots PirT cgs-a iprs ACo PPo-l mlf slf I ilf racc slf II slf III arc mls sfo cgb st lls ec ex scr lml cfx vaf fxl atr st eml bcc unc ic ifo fx ac opt

MNI Position y = -2.25 mm AHB Position y = 2.07 mm
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
Un uncus
Sulci
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
ac anterior commissure arc arcuate fascicle
atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cfx column of fornix (pars tecta) cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column)
ifo inferior fronto-occipital fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria
mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
opt optic tract
fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule
racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
sls sublenticular stria st stria terminalis
unc uncinate fascicle
vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
Fibers
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) 3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus AH anterior hypothalamic area BC basal n., compact p. BD basal n., diffuse p. BL basolateral amygdaloid n. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTLJ bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral division, juxtacapsular p. BSTP bed n. of the stria terminalis, posterior div. BSTV bed n. of the stria terminalis, ventral div. CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum CxA cortico-amygdaloid transition area DCl dorsal claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DoH dorsal hypothalamic n. EA extended amygdala EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield Eo entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield fpms frontal paramidline sulcus FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column) GSL gyrus semilunaris ic internal capsule InfS infundibular stalk iprs inferior precentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus La lateral amygdaloid n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum lml lateral medullary lamina of the glob. pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LV lateral ventricle mfb medial forbrain bundle mml medial medullary lamina of the glob.pallidus MPO medial preoptic n. MS medial septal n. opt optic tract PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p. PaFo paraventricular n., fornical p. PAM periamygdaloid cortex PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p. PaPC paraventricular n., parvicellular p. PirF piriform cortex, frontal p. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SCh suprachiasmatic n. SFO subfornical organ sfs superior frontal sulcus SO supraoptic n. sox supraoptic commissure sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum tsv thalamostriate vein Tu olfactory tubercle unc uncinate fc unn uncal notch 35 ICL: 2.07 MCP: -12.67 MNI: -2.25

0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6
**205**
7
-5
VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus palidus


MNI Position y = -2.11 mm AHB Position y = 2.01 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n.
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex
FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus
IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area
PirF piriform cortex, temporal part
PirT piriform cortex, temporal part
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
STG superior temporal gyrus Un uncus
- unos
#### Brodmann Areas
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
BA44 area opercularis
Hi hippocampus
HI hippocampus
PRC35, perirhinal cortex
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area
TA superior temporal area TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
Roger
B. Vog
B. Vogt: a24' anterior division of BA24
a33' anterior subregion of BA33
p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24
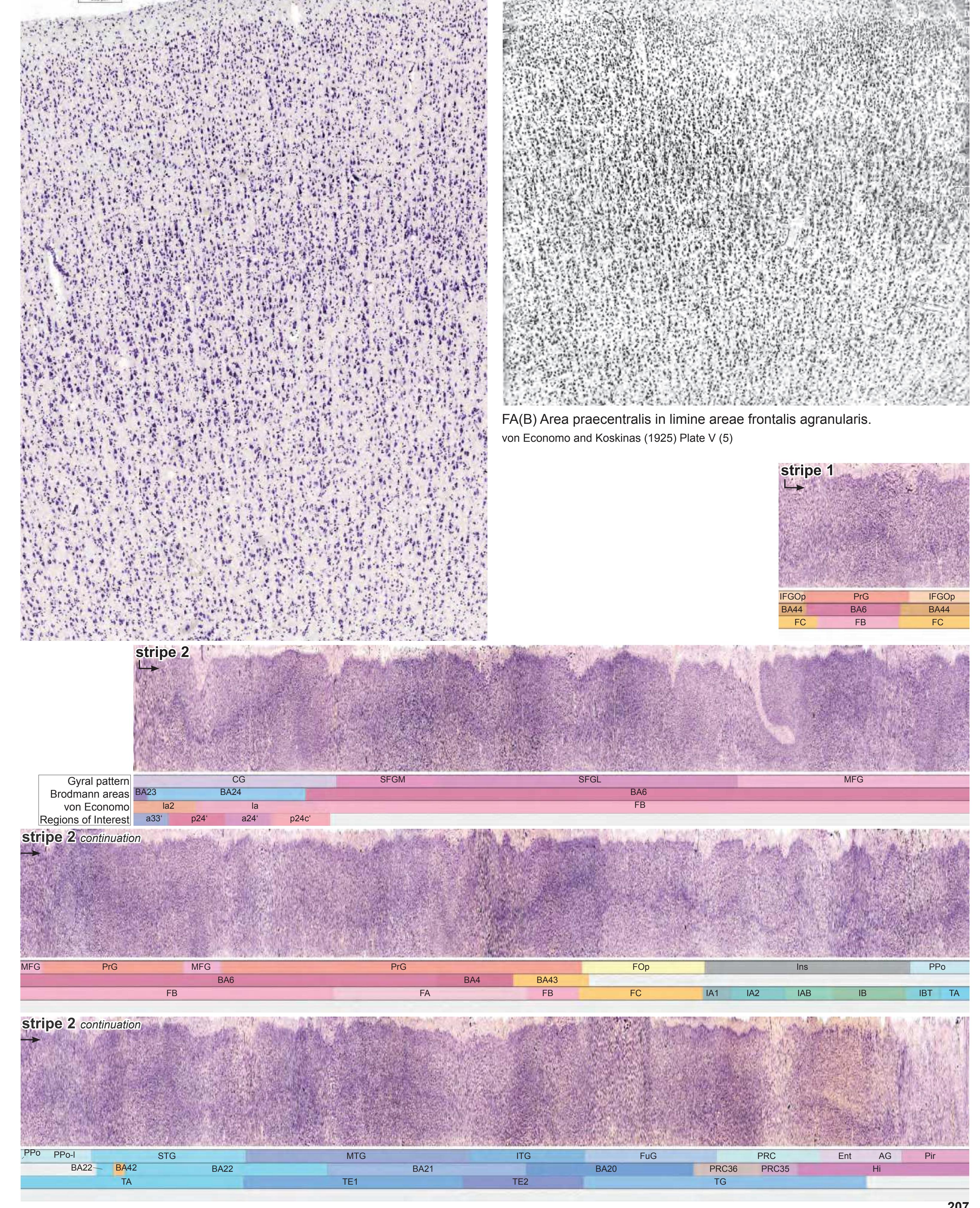
**207**
Fibers
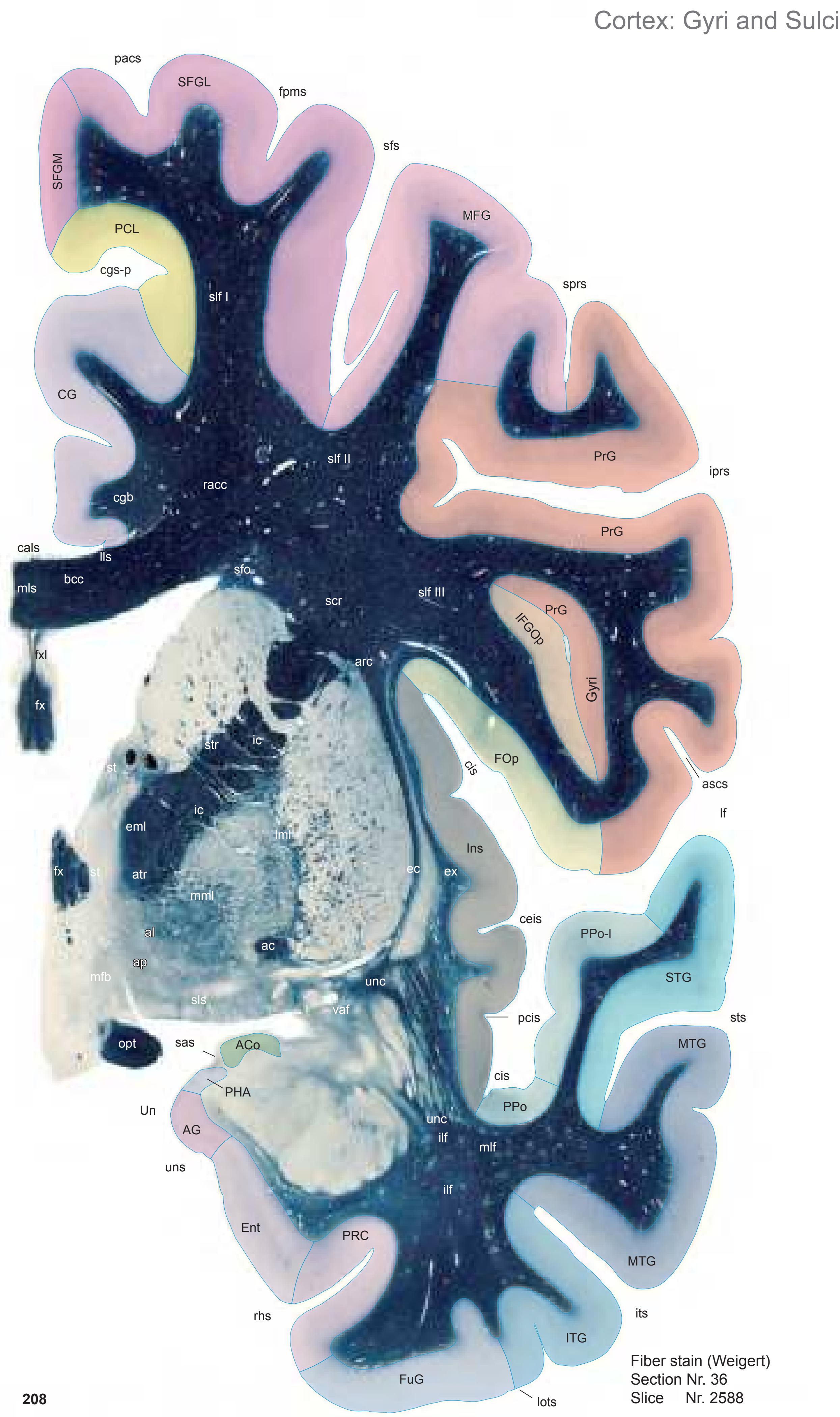

MNI Position y = -2.73 mm AHB Position y = 2.63 mm
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus
Un uncus
Sulci
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus iprs inferior precentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis ap ansa peduncularis arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation
bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column)
ic internal capsule
fxl fornix longus
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
mfb medial forbrain bundle
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
opt optic tract
racc radiation of corpus callosum
scr superior corona radiata
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
sls sublenticular stria
st stria terminalis
str superior thalamic stria
unc uncinate fascicle vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway

ICL: 2.63 MCP: -12.11 MNI: -2.73

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) AAA anterior amygdaloid area ac anterior commissure ACoD anterior cortical amygdaloid n., dorsal p. ACoV anterior cortical amygdaloid n., ventral p. AH anterior hypothalamic area AI amygdaloid island aic anterior lim of the internal capsule ap ansa peduncularis Arc arcuate n. BC basal n., compact part BD basal n., diffuse part BL basolateral amygdaloid n. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. BSTC bed n. of the stria terminalis, central div. BSTCV ventral extension of BSTC BSTLJ bed n. of the stria terminalis, lateral div. BSTP bed n. of the stria terminalis, posterior div. CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. CdV ventral caudate n. cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum CSP cavity of septum pellucidum DCl dorsal claustrum DH dorsal hypothalamic area DiCl diffuse insular claustrum EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial im. subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (colum) GSL gyrus semilunaris IGP internal globus pallidus iprs inferior precentral sulcus IVF interventricular foramen La lateral amygdaloid n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum lml lateral medullary lamina of the glob. pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LV lateral ventricle mfb medial forbrain bundle mml medial medullary lamina of the glob.pallidus MS medial septal n. opt optic tract PAC periamygdaloid cortex PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p. PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p. PaPC paraventricular n., parvicellular p. Pe periventricular n. PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition a. PirT piriform cortex, temporal p. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus SFO subfornical organ sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa SODL supraoptic n., dorsolat. p. SOVM supraoptic n., ventromed. p. sox supraoptic commissure sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum tsv thalamostriate vein unn uncal notch
**209**
opt optic tract Ins insula Un uncus Sulci
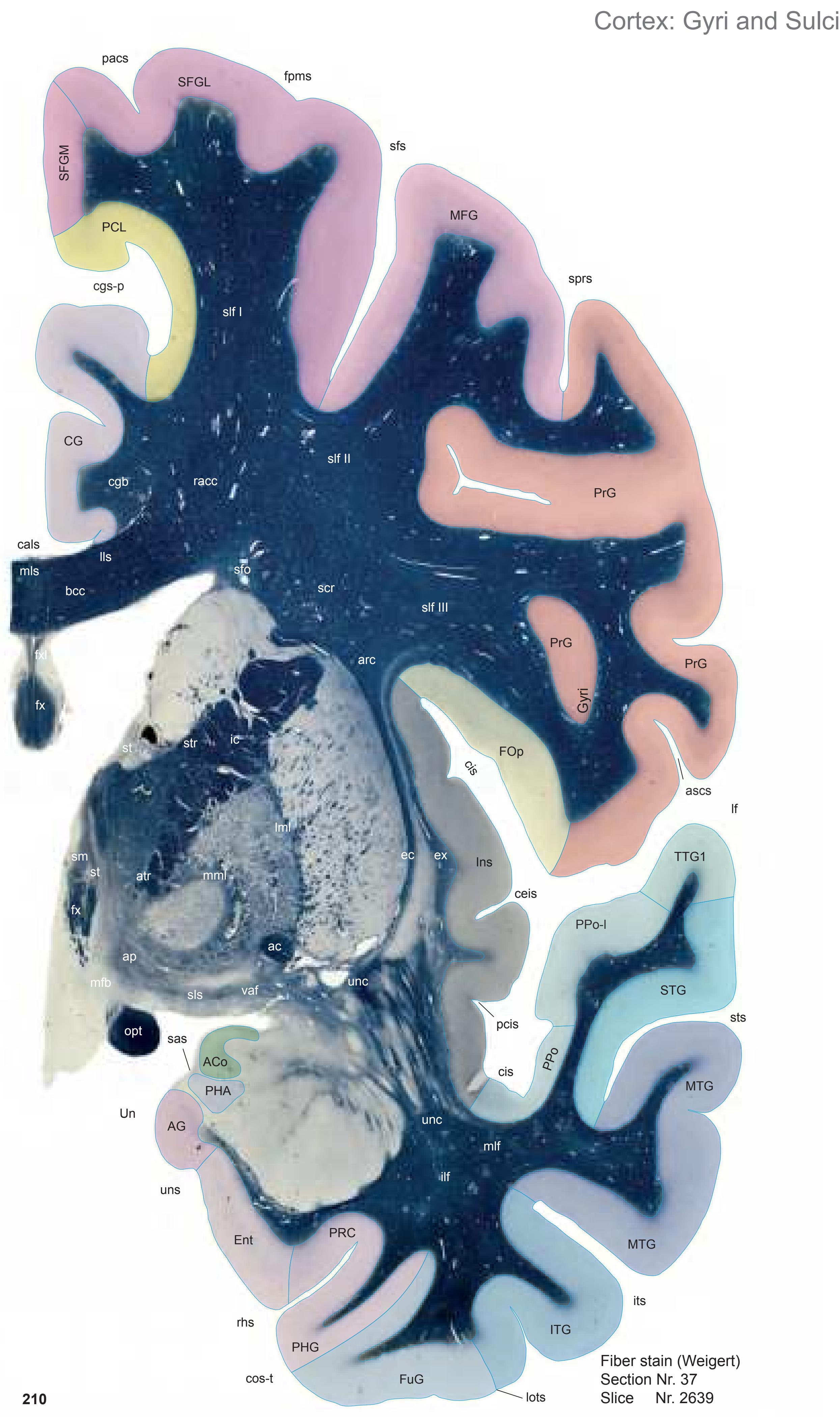
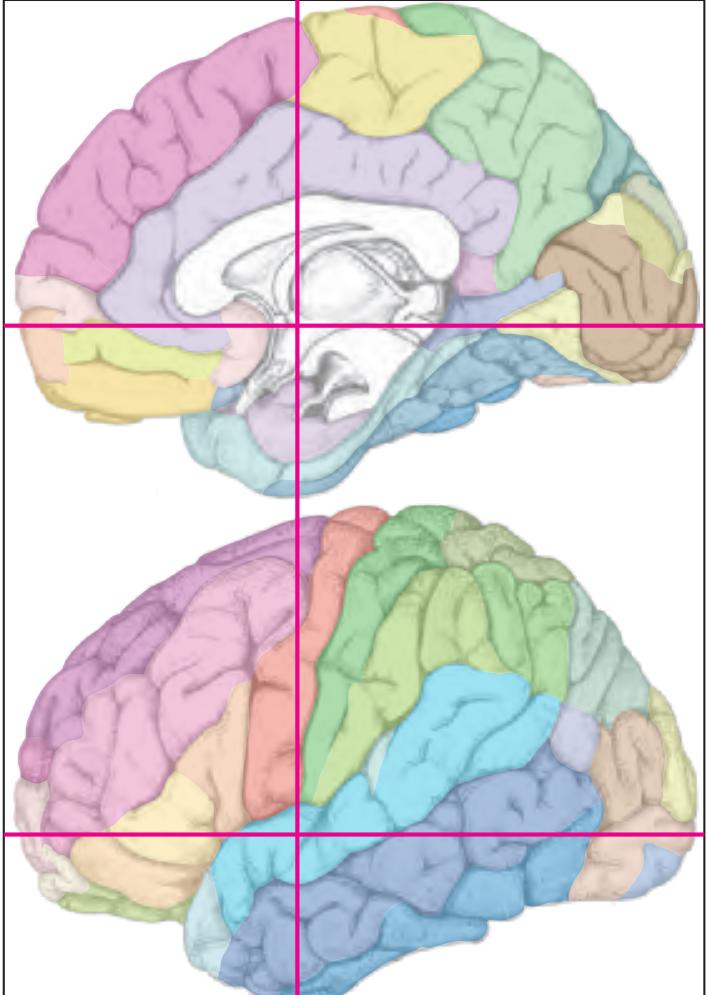
MNI Position y = -4.17 mm AHB Position y = 4.00 mm
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area PHG parahippocampal gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
Fibers
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus fpms frontal paramidline sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
ac anterior commissure ap ansa peduncularis arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column) fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sls sublenticular stria sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria unc uncinate fascicle vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) 3V third ventricle ac anterior commissure AG ambiens gyrus AH anterior hypothalamic area AI amygdaloid island al ansa lenticularis ap ansa peduncularis Arc arcuate n. ASt amygdalostriatal transition area BD basal n., diffuse part BL basolateral amygdaloid n. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. CdL lateral caudate n. CdM medial caudate n. Ce central amygdaloid n. cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. cis circular insular sulcus CoCl compact insular claustrum DCl dorsal claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DMH dorsomed. hypothalamic n. EGP external globus pallidus ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial im.subfield ER entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield FPu fundus region of putamen fx fornix (column and body) GSL gyrus semilunaris IGP internal globus pallidus IGr indusium griseum ithp inferior thalamic peduncle its inferior temporal sulcus IVF interventricular foramen La lateral amygdaloid n. LaDL lateral amygdaloid n., dorsolateral p. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LV lateral ventricle MeA medial amygdaloid n., ant. p. mfb medial forbrain bundle MS medial septal n. opt optic tract PACl preamygdalar claustrum pacs paracentral sulcus PaD paraventricular n., dorsal p. PaMC paraventricular n., magnocellular p. PaPC paraventricular n., parvicellular p. Pe periventricular n. PeF perifornical n. PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone Pu putamen rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus SCS subcallosal stratum SEpS subependymal stratum SFO subfornical organ sfs superior frontal sulcus SGl substantia gliosa sm stria medullaris of thalamus SODL supraoptic n., dorsolat. p. SOVM supraoptic n., ventromed. p. sox supraoptic commissure sprs superior precentral sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus sv septal vein TCl temporal claustrum tsv thalamostriate vein unn uncal notch vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway VCl ventral claustrum VMHDM ventromedial hypoth. n., dorsomedial p. VMHVL ventromedial hypoth. n., ventrolateral p. 37 MCP: -10.74 MNI: -4.17 Cortex: Brodmann Areas Arc Pe PaPo DMH PaD PaMC PaPC PeF SEpS ASt PACl LaDL 3V sas BLVM ACoD ACoV PHA st opt MS Pu PRt SGl sm SOVM TCl vaf tsv sv SODL SFO VCl fx ac AI MeA BM BL CdM CdL Ce cis CoCl fx DiCl IGP EGP IGr lml mml IVF La LH LiCl LSD LSI LV mfb sox ithp ER PRC35 PRC36 rhs ELR unn EMI FPu GSL lots its VMHDM VMHVL DCl AH sts cis lf sprs sfs cgs-p pacs SCS BD al ap AG BA 23 BA 6 BA 43 BA42 BA 1 BA 24 BA 4 BA 6 BA 6 BA 4 BA 6 BA 6 BA 6 BA 22 BA 21 BA 20
37
ICL: 4.00

ACoD anterior cortical amygdaloid n., dorsal p. ACoV anterior cortical amygdaloid n., ventral p. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus PaPo paraventricular hypothalamic n., post. p. PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transit. area
**211**
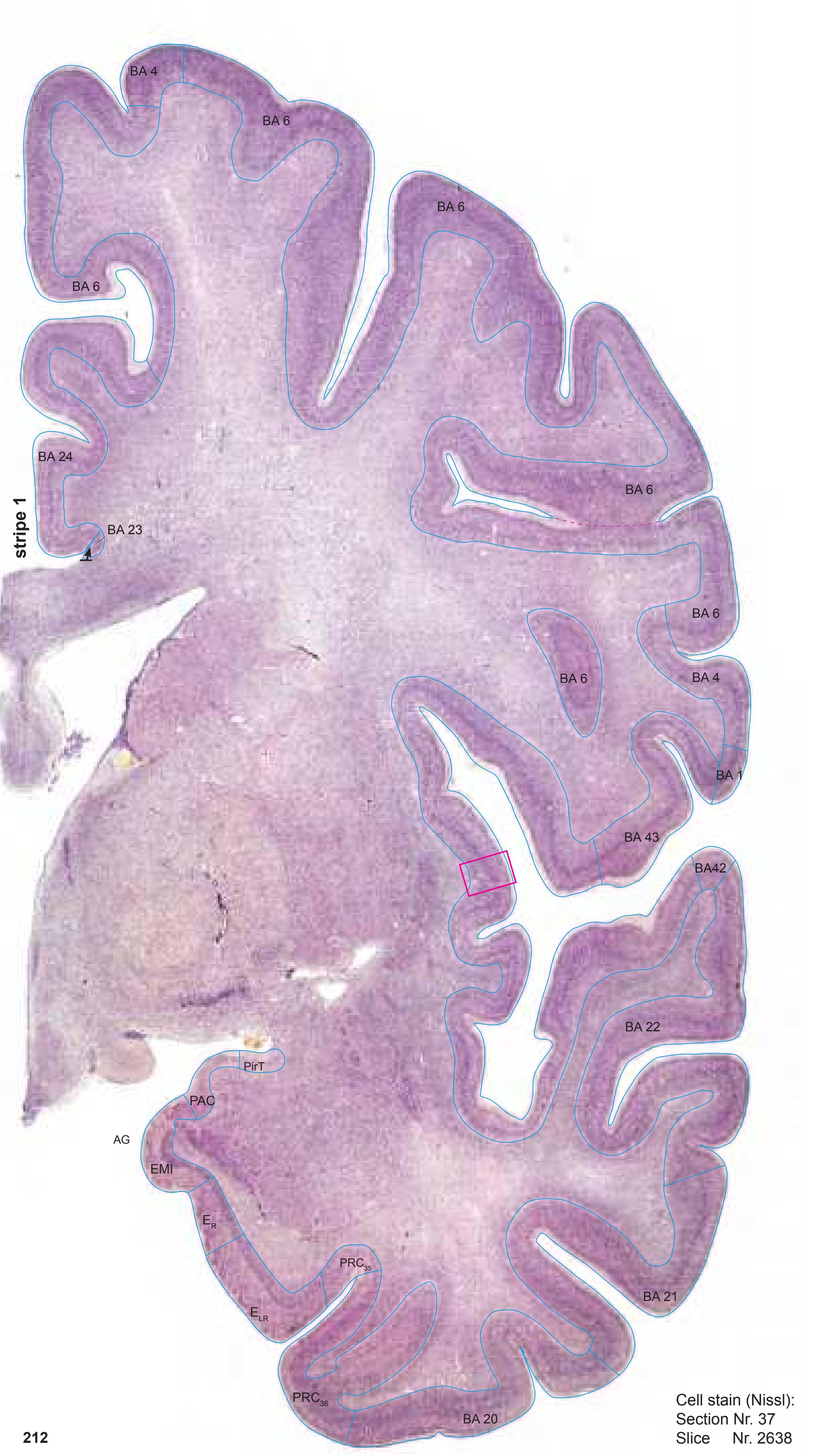

MNI Position y = -4.16 mm AHB Position y = 3.97 mm
# Gyral Pattern
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n.
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex
FOp frontal operculum
FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
PCL paracentral lobule
PAC periamygdaloid cortex
PHG parahippocampal gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
# Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area LA2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
a24' anterior division of BA24
p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
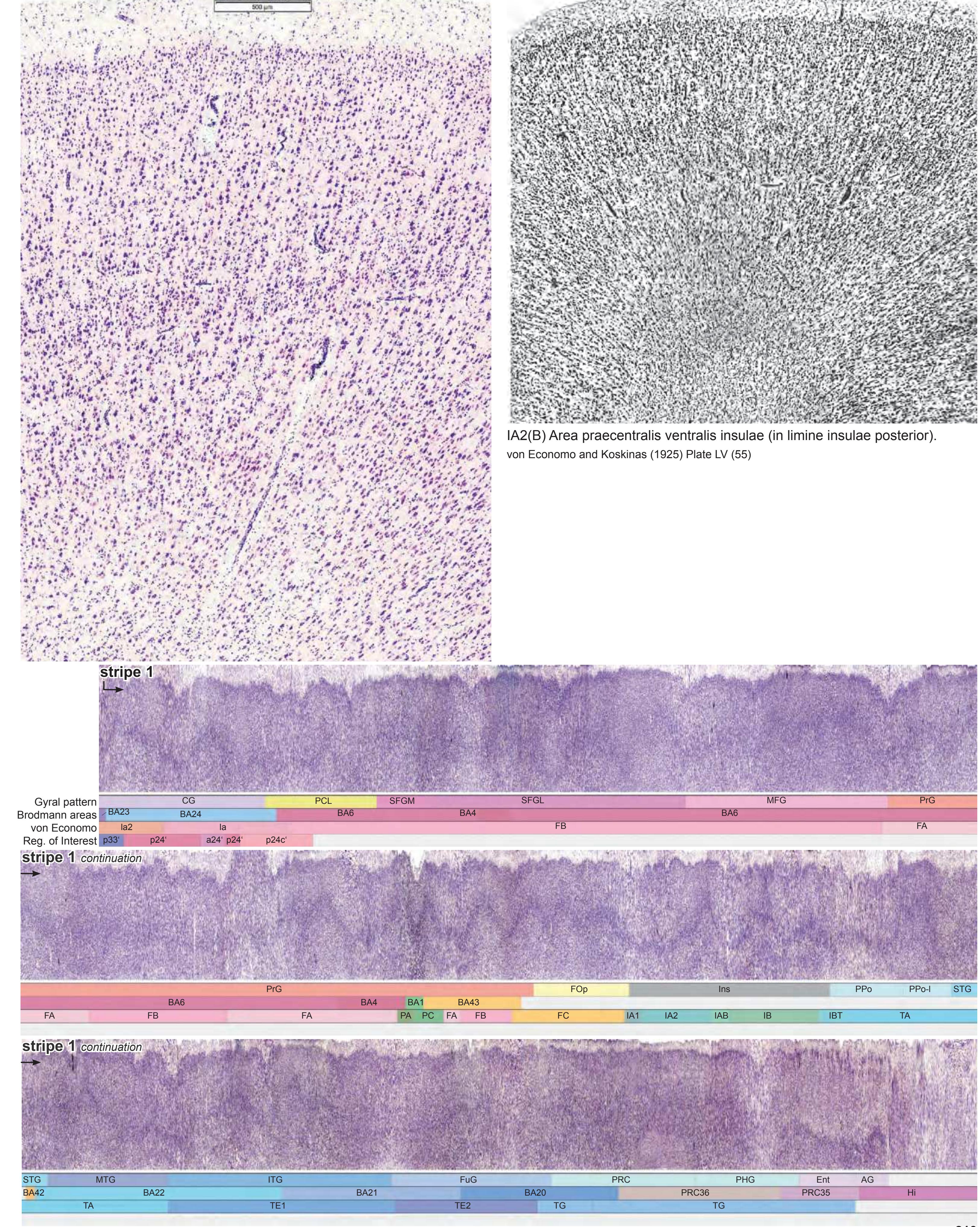
**213**
Fibers


MNI Position y = -5.66 mm AHB Position y = 5.58 mm
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid n. AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area PHG parahippocampal gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
acs acusticus sulcus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression)
Sulci
ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis arc arcuate fascicle atr anterior thalamic radiation bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column) fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule icml incomplete medullary lamina of the globus pallidus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus opt optic tract racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria unc uncinate fascicle
vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway
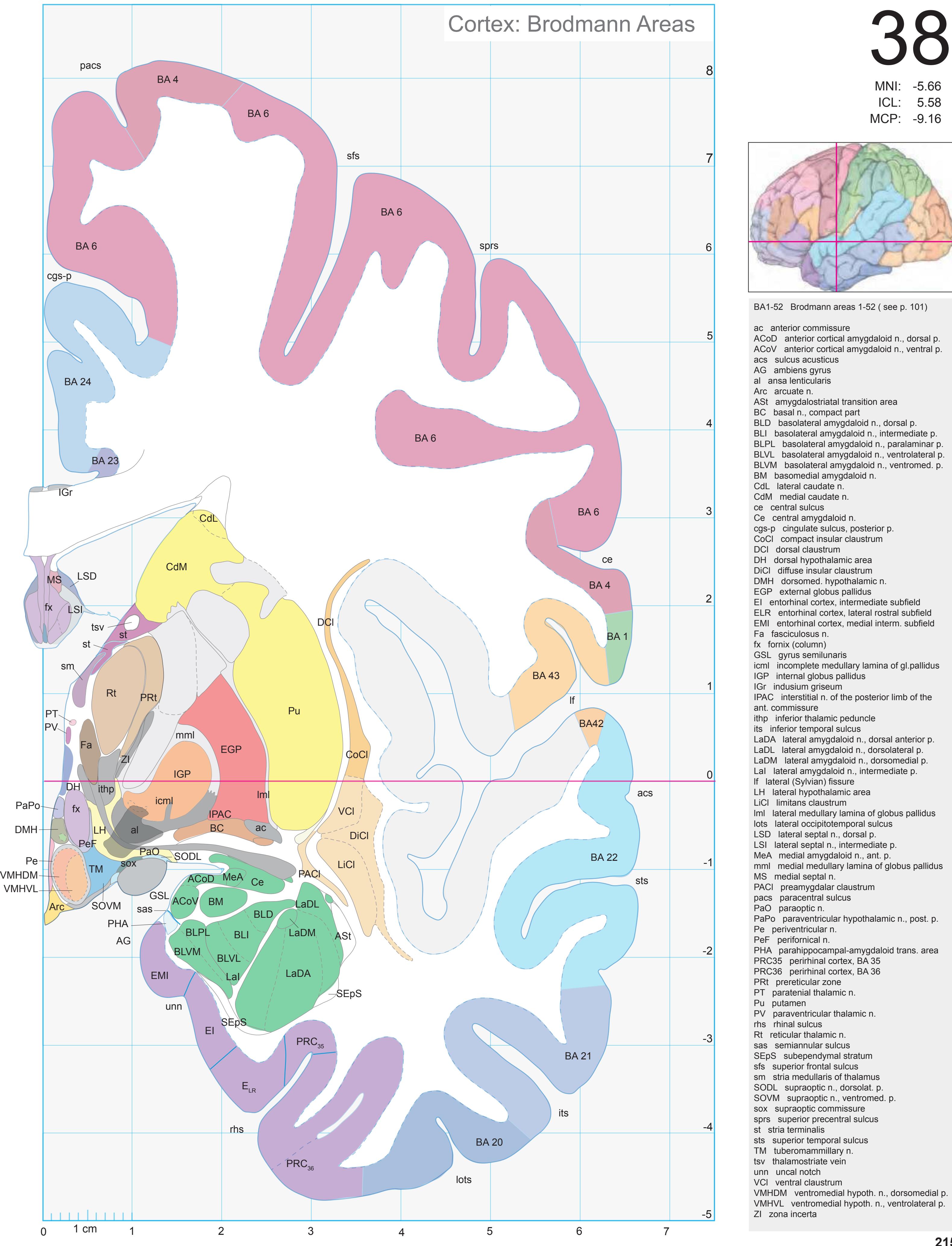
38
ICL: 5.58 MNI: -5.66

ACoD anterior cortical amygdaloid n., dorsal p. ACoV anterior cortical amygdaloid n., ventral p. BLI basolateral amygdaloid n., intermediate p. BLPL basolateral amygdaloid n., paralaminar p. BLVL basolateral amygdaloid n., ventrolateral p. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. ELR entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial interm. subfield icml incomplete medullary lamina of gl.pallidus IPAC interstitial n. of the posterior limb of the LaDA lateral amygdaloid n., dorsal anterior p. LaDM lateral amygdaloid n., dorsomedial p. lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus PaPo paraventricular hypothalamic n., post. p. PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid trans. area
**215**
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus ap ansa peduncularis arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column and body) fxl fornix longus ic internal capsule icml incomplete medullary lamina of glob. pallidus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ithp inferior thalamic peduncle liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus opt optic tract racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle vaf ventral amygdalofugal pathway AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area PHG parahippocampal gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus acs acusticus sulcus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus uns uncal sulcus (impression) Sulci Fibers MNI Position y = -7.04 mm AHB Position y = 6.68 mm
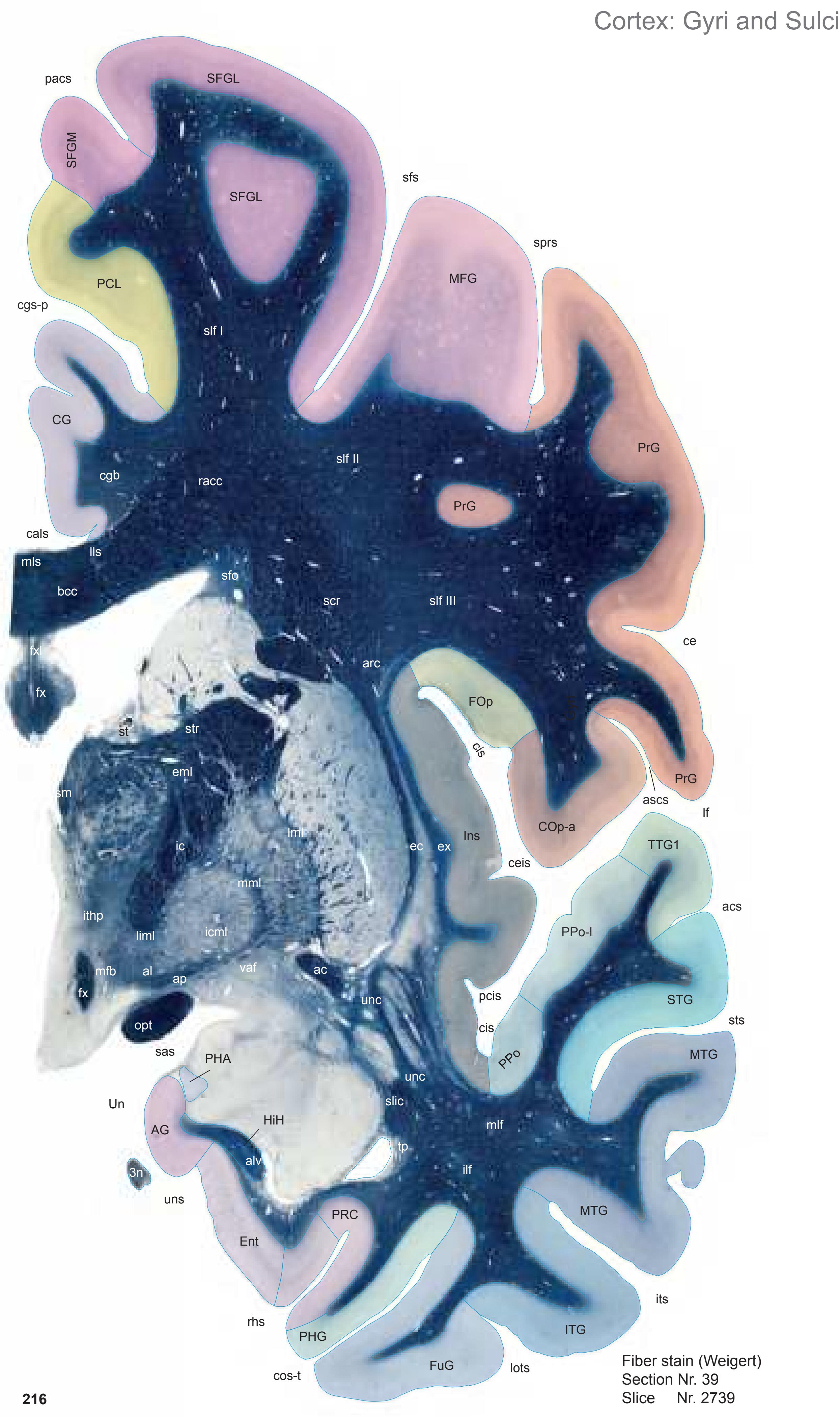

ICL: 6.68 MCP: -8.06 MNI: -7.04

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve
ac anterior commissure AD anterodorsal thalamic n.
AG ambiens gyrus
al ansa lenticularis
ap ansa peduncularis
Arc arcuate n. ASt amygdalostriatal transition area
AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part
BL basolateral amygdaloid n.
BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p.
BM basomedial amygdaloid n.
CdM medial caudate n.
ce central sulcus
Ce central amygdaloid n.
cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p.
CoCl compact insular claustrum
cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus
DCl dorsal claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum
DMH dorsomed. hypothalamic n.
DMHC dorsomedial hypothalamic n., compact p.
EGP external globus pallidus
EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield
ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial intermed. subfield
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
Fa fasciculosus n. fx fornix (column)
HiH hippocampal head
icml incomplete medullary lamina of gl. pallidus
IGP internal globus pallidus
IGr indusium griseum irs intrarhinal sulcus
ithp inferior thalamic peduncle
its inferior temporal sulcus
LaDA lateral amygdaloid n., dorsal anterior p. LaDL lateral amygdaloid n., dorsolateral p.
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
If lateral (Sylvian) fissure
LH lateral hypothalamic a
LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum
liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p.
LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p.
LTu lateral tuberal n.
ME median eminence MeA medial amygdaloid n., ant. p.
mfb medial forbrain bundle
MS medial septal n.
opt optic tract
pacs paracentral sulcus PaPo paraventricular hypothalamic n., post. p.
PCo post. cortical amygdaloid n.
Pe periventricular n.
PeF perifornical n.
PHA parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition a.
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PRt prereticular zone
PT paratenial thalamic n.
Pu putamen PuV ventral putamen
PV paraventricular thalamic n.
rhs rhinal sulcus
Rt reticular thalamic n. sas semiannular sulcus
SCGP supracapsular p. of globus pallidus
SFO subfornical organ sfs superior frontal sulcus
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
sprs superior precentral sulcus SSTI substriatal terminal island
sts superior temporal sulcus
tfx tenia of fornix
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
TM tuberomammillary n. tsc tenia semicircularis
tsv thalamostriate vein
tt tenia of thalamus
VA ventroanterior n. (ventral anterior n.)
VCl ventral claustrum VMHDM ventromedial hypoth. n., dorsomedial p. VMHVL ventromedial hypoth. n., ventrolateral p.
ZI zona incerta
**217**

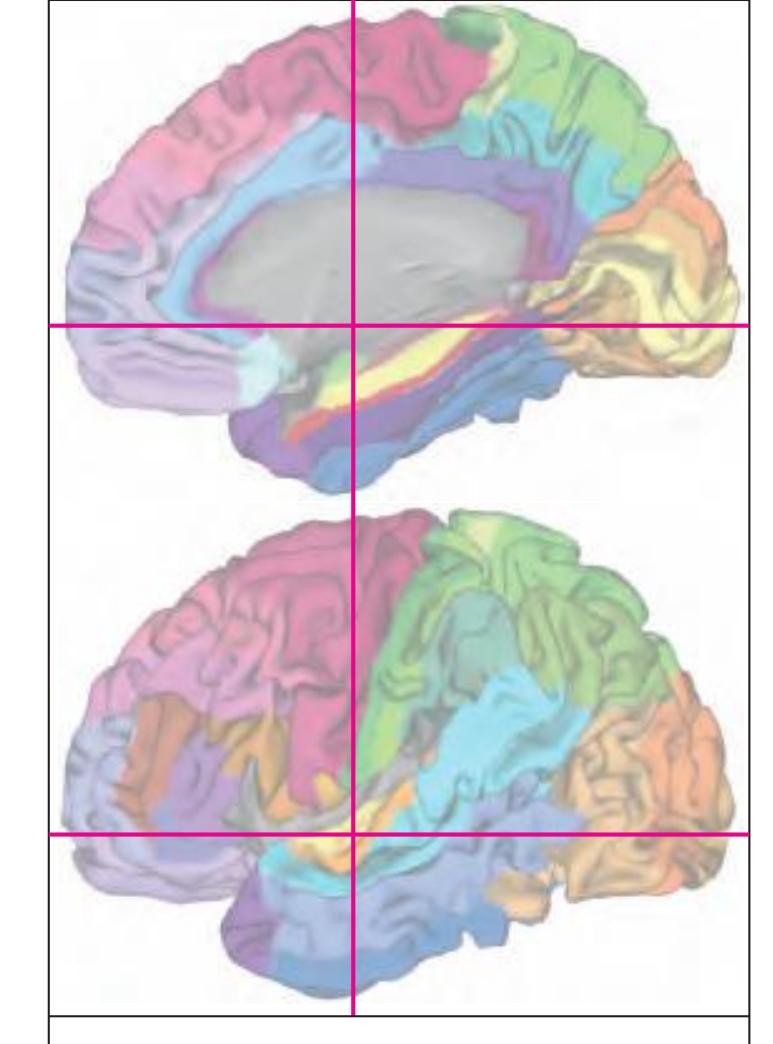
MNI Position y = -7.03 mm AHB Position y = 6.70 mm
# Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PAC periamygdaloid cortex PHG parahippocampal gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part
STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA1 dorsal precentral insular area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
La precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
La2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior
limbic area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TG temporo polar area
# Regions of Interest
Reg
B. Yor
B. Vogt: p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33

Gyri **220** Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 40 Slice Nr. 2788 Cortex: Gyri and Sulci CG SFGL SFGM MFG PrG PrG FOp Ins PPo STG MTG ITG FuG PRC Ent AG unn Un sts cis cis sfs its cals rhs lf MTG PCL ceis TTG1 ce PCL PHG PoG sas pcis pacs sprs lots COp-a cgs-p ascs acus cos-ph PPo-l HiH du sox iml eml ithp al unc ic ac bcc mlf slf I ilf racc slf II slf III slic tp arc sfo sm mls cgb str lenf st 3n lls palhy ec ex unc liml h2 scr icml mml lml fx mfb alv opt fx

MNI Position y = -8.36 mm AHB Position y = 7.99 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
acus sulcus acusticus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus du diverticulum unci its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus unn uncal notch
Sulci
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column and body) h2 lenticular fascicle ic internal capsule icml incomplete medullary lamina of the globus pallidus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus opt optic tract
palhy pallidohypothalamic fibers racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus
sox supraoptic commissure st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria
tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle Fibers
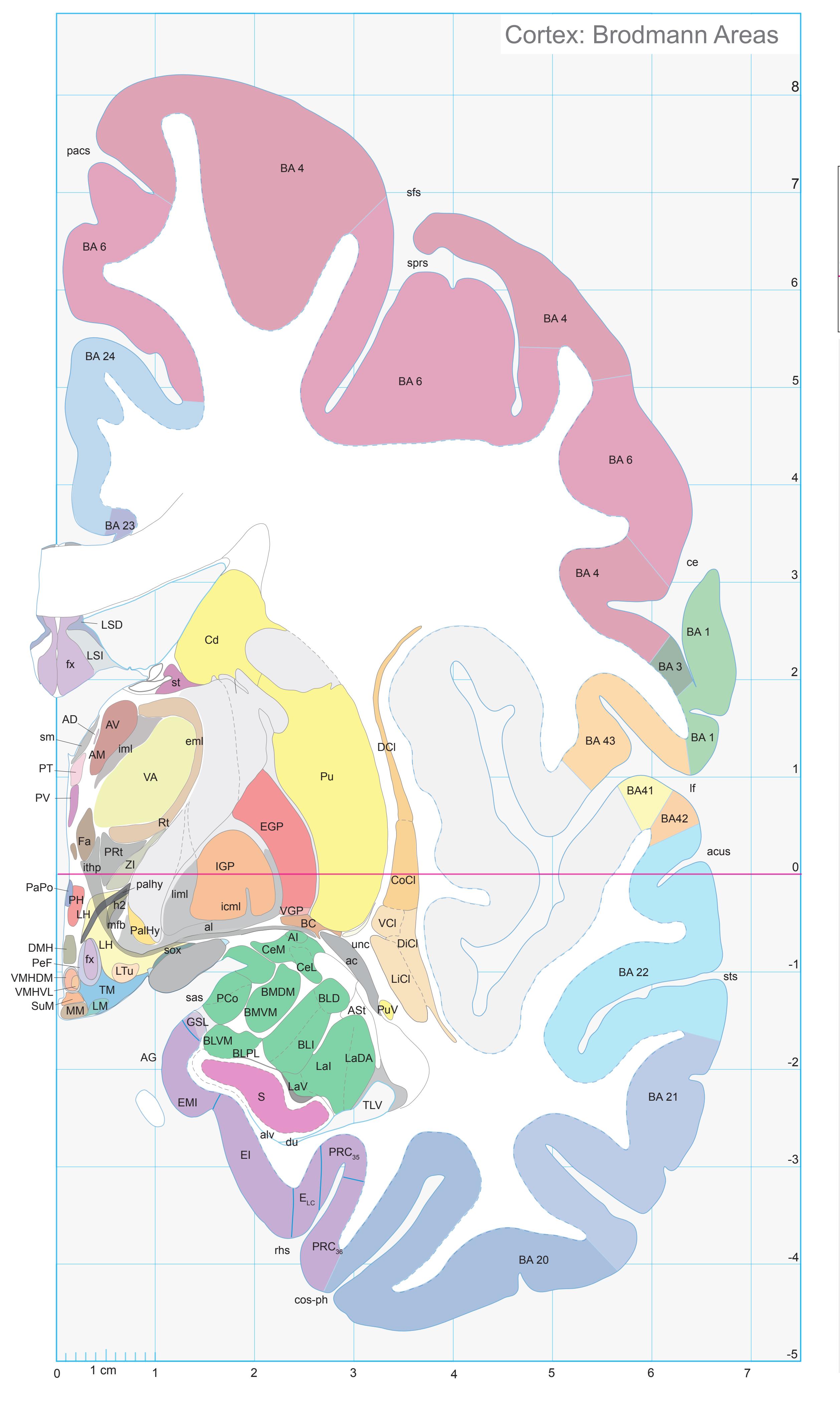
ICL: 7.99 MCP: -6.75 MNI: -8.36

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) ac anterior commissure acus sulcus acusticus AD anterodorsal thalamic n. AG ambiens gyrus AI amygdaloid island al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus AM anteromedial thalamic n. ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part BLD basolateral amygd. n., dorsal (magnoc.) p. BLI basolateral amygdaloid n., intermediate p. BLPL basolateral amygdaloid n., paralaminar p. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromedi. p. BMDM basomedial amygdaloid n., dorsomed. p. BMVM basomedial amygdaloid n., ventromed. p. Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus CeL central amygdaloid n, lat. p. CeM central amygdaloid n, med. p. CoCl compact insular claustrum cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. DCl dorsal claustrum DiCl diffuse insular claustrum DMH dorsomed. hypothalamic n. du diverticulum unci EGP external globus pallidus EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial intermed. subfield eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus Fa fasciculosus n. fx fornix (column) GSL gyrus semilunaris h2 lenticular fascicle icml incomplete medullary lamina of gl. pallidus IGP internal globus pallidus iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle LaDA lateral amygdaloid n., dorsal anterior p. LaI lateral amygdaloid n., intermediate p. LaV lateral amygdaloid n., ventral p. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus LM lateral mammillary n. LSD lateral septal n., dorsal p. LSI lateral septal n., intermediate p. LTu lateral tuberal n. mfb medial forbrain bundle MM medial mammillary n., med. p. pacs paracentral sulcus PalHy pallidohypothalamic n. palhy pallidohypothalamic fibers PaPo paraventricular hypoth. n., posterior p. PCo post. cortical amygdaloid n. PeF perifornical n. PH posterior hypothalamic area PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRt prereticular zone PT paratenial thalamic n. Pu putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus sm stria medullaris of thalamus sox supraoptic commissure sprs superior precentral sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus
SuM supramammillary n.
TM tuberomammillary n. unc uncinate fc
VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus pallidus
ZI zona incerta
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
VA ventroanterior n. (ventral anterior n.)
VMHDM ventromedial hypoth. n., dorsomedial p. VMHVL ventromedial hypoth. n., ventrolateral p.
**221**
Fibers


MNI Position y = -9.66 mm AHB Position y = 9.22 mm
CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PPo planum polare PPo-l planum polare, lat. part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus acus sulcus acusticus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus unn uncal notch
Sulci
comb comb system ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fx fornix (column and body) gic genu of internal capsule h2 lenticular fascicle ic internal capsule icml incomplete medullary lamina of glob. pallidus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus lls lateral longitudinal stria lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mfb medial forbrain bundle
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus
mp mammillary peduncle opt optic tract
arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum cgb cingulum bundle
cgh cingulum (hippocampal part)
racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria
tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle

ICL: 9.22 MCP: -5.52 MNI: -9.66

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure AD anterodorsal thalamic n.
AG ambiens gyrus
al ansa lenticularis AM anteromedial thalamic n.
ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n.
BC basal n., compact part
bfx body of fornix
BLD basolateral amygdaloid n., dorsal p.
BLI basolateral amygdaloid n., intermediate p. BLPL basolateral amygdaloid n., paralaminar p.
BLVL basolateral amygdaloid n., ventrolateral p. BLVM basolateral amygdaloid n., ventromed. p.
BM basomedial amygdaloid n.
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
Cd caudate n.
ce central sulcus
CeL central amygdaloid n, lat. p.
CeM central amygdaloid n, med. p. CeMe central medial thalamic n.
cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p.
CoCl compact insular claustrum
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r.
DCl dorsal claustrum
DiCl diffuse insular claustrum EGP external globus pallidus
EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield
ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield EMI entorhinal cortex, medial intermed. subfield
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
EP entopeduncular n.
Fa fasciculosus n.
fx fornix
h2 lenticular fascicle
icml incomplete medullary lamina of gl. pallidus IGP internal globus pallidus
IGr indusium griseum
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
l internal medullary lamin
ThA interthalamic adhesion
IThA interthalamic adhesion its inferior temporal sulcus
La lateral amygdaloid n.
lenf lenticular fasciculus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
LH lateral hypothalamic area
LiCl limitans claustrum
LM lateral mammillary n. lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
mfb medial forbrain bundle
ML medial mammillary n., lat. p.
MM medial mammillary n., med. p. mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus
PAC periamygdaloid cortex pacs paracentral sulcus
PalHy pallidohypothalamic n.
PCo post. cortical amygdaloid n.
PedL peduncle of lentiform n. PH posterior hypothalamic area
pm principal mammillary fasciculus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PT paratenial thalamic n.
Pu putamen
PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n.
Re reuniens thalamic n.
rhs rhinal sulcus
Rt reticular thalamic n.
S subiculum
sas semiannular sulcus sfs superior frontal sulcus
sm stria medullaris of thalamus sprs superior precentral sulcus
st stria terminalis
sts superior temporal sulcus
SuM supramammillary n. TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
TM tuberomammillary n.
tsv thalamostriate vein
unn uncal notch
VA ventroanterior n. (ventral anterior n.)
VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents)
VGP ventral pallidum ZI zona incerta
**223**
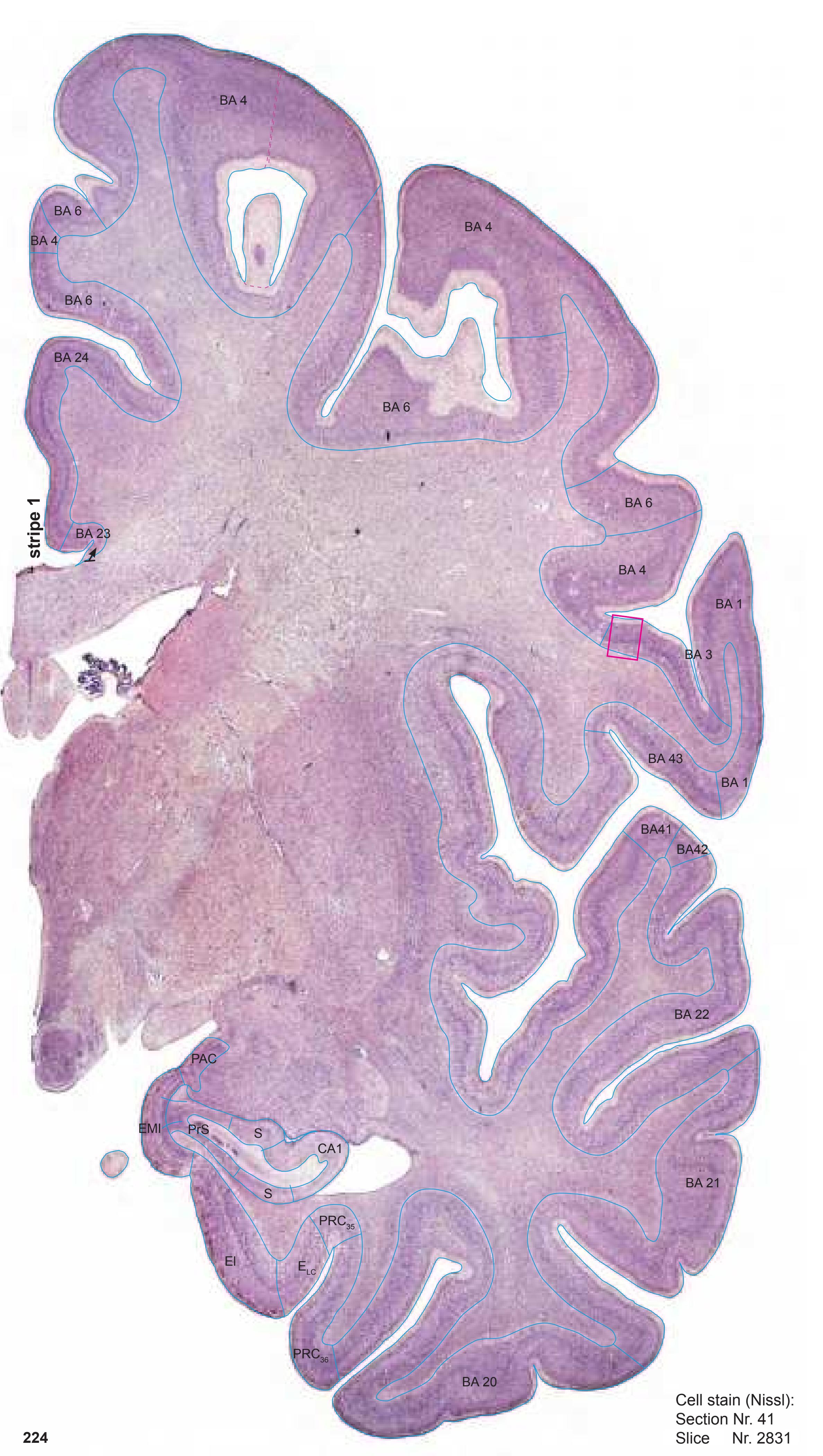

MNI Position y = -9.60 mm AHB Position y = 9.14 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus
COp-a anterior central operculum
Ent entorhinal cortex FOp frontal operculum
FuG fusiform gyrus
HiH hippocampal head
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PCI postcentral insular cortex
PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PPo planum polare
PPo-l planum polare, lat. part
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial part SLG semilunar gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
Un uncus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior) BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
(posterior)
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
FC intermediate frontal area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
La precingulate agranular anterior limbic area La2 anterior cingulate agranular anterior limbic
area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TG temporo polar area
B. Vogt: Regions of Interest
p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33

von Economo and Koskinas (1925) Plate LIX (59)
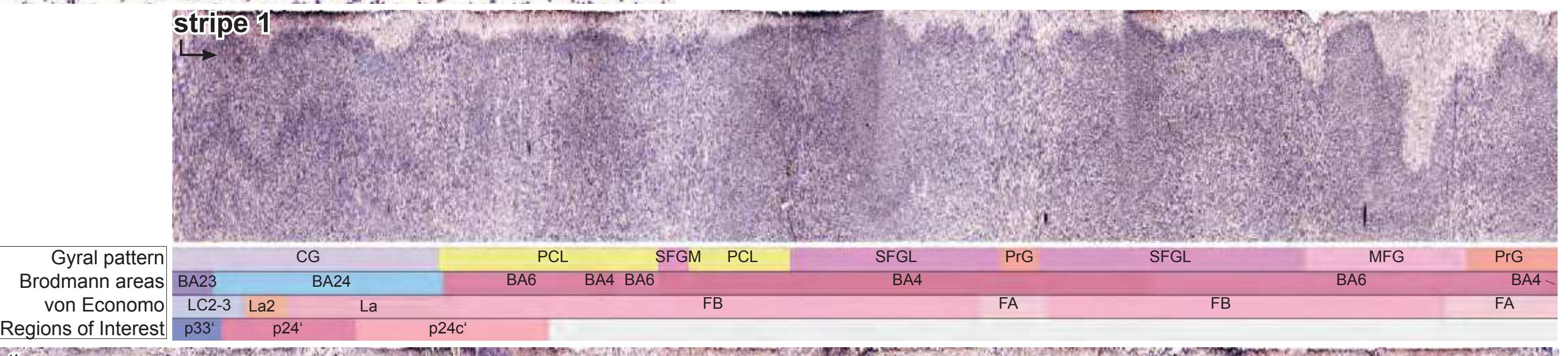


**225**
Fibers


MNI Position y = -10.95 mm AHB Position y = 10.56 mm
CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum PPo planum polare SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SLG semilunar gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
acus sulcus acusticus ascs anterior subcentral sulcus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus unn uncal notch
Sulci
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule gic genu of internal capsule h2 lenticular fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus lls lateral longitudinal stria mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mp mammillary peduncle mtg mammillotegmental tract opt optic tract racc radiation of corpus callosum scr superior corona radiata sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis
str superior thalamic stria
tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle
-3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 -5 BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) ac anterior commissure AD anterodorsal thalamic n. AHi amygdalohippocampal area ASt amygdalostriatal transition area al ansa lenticularis AM anteromedial thalamic n. AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part bfx body of fornix BLD basolateral amygdaloid n., dorsal p. BLI basolateral amygdaloid n., intermediate p. BLPL basolateral amygdaloid n., paralaminar p. BLVL basolateral amygdaloid n., ventrolateral p. BMCM basomedial amygd. n., centromedial p. BMDL basomedial amygd. n., dorsolateral p. BMDM basomedial amygd. n., dorsomedial p. BMVM basomedial amygd. n., ventromedial p. CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus CeL central amygdaloid n, lat. p. CeM central amygdaloid n, med. p. CoCl compact insular claustrum comb comb system cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. cp cerebral peduncle DiCl diffuse insular claustrum dPrS dorsal presubiculum du diverticulum unci EGP external globus pallidus EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus EP entopeduncular n. Fa fasciculosus n. h2 lenticular fascicle HATA hippocampo amygdaloid transitional area IGP internal globus pallidus iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus IThA interthalamic adhesion ithp inferior thalamic peduncle La lateral amygdaloid n. lenf lenticular fasciculus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum liml limiting medullary lamina of globus pallidus LM lateral mammillary n. lml lateral medullary lamina of . globus pallidus maprs marginal precentral sulcus Me medial amygdaloid n. mfb medial forbrain bundle ML medial mammillary n., lat. p. MM medial mammillary n., med. p. mml medial medullary lamina of . globus pallidus mt mammillothalamic tract PalHy pallidohypothalamic n. PCo post. cortical amygdaloid n. PedL peduncle of lentiform n. PH posterior hypothalamic area PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 prf principal fc PrS presubiculum PT paratenial thalamic n. PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SB striatal cell bridge sm stria medullaris of thalamus sprs superior precentral sulcus st stria terminalis SuM supramammillary n. TM tuberomammillary n. tsv thalamostriate vein tt tenia of thalamus unc uncinate fc VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents) VAM medial ventroanterior n. (nigral afferents) VAMC magnocellular ventroanterior n. VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus pallidus ZI zona incerta 42 ICL: 10.56 MCP: -4.18 MNI: -10.95 Cortex: Brodmann Areas ASt ce lf st S CeM PuV unc VCl PCo Pu PedL Rt ac al BLPL -VM CA1 CeL CoCl DiCl EGP eml EP IGP La LiCl liml S AHi BLD BLI BLVL -CM -DM Cd BM-SB PrS lenf lml Me mml -DL VAL mt dPrS HATA BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 rhs cos-ph ELC VGP BC sprs maprs EI du BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 1 BA 2 BA 4 BA 6 BA 3 BA 1
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6
SuM
prf
Re
tt
sm
PH
ML
LM
LH
mfb
Fa
MM
PV
IThA
PT
bfx
AV
AM
BA 23
BA 24
BA 6
iml
VAM
AD
cp
comb
ZI
PalHy
TM
h2
VAMC
st
tsv
BA 4
VAM
**227**
Fibers


MNI Position y = -12.67 mm AHB Position y = 12.09 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SLG semilunar gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, post. part cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus pscs posterior subcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus unn uncal notch
Sulci
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus h2 lenticular fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus lls lateral longitudinal stria mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria mp mammillary peduncle mt mammillothalamic tract mtg mammillotegmental tract opt optic tract pic posterior limb of the internal capsule prf principal fc racc radiation of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria
tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 prf 3n oculomotor nerve 3V third ventricle al ansa lenticularis bfx body of fornix Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus Co commissural n. comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle Cuc cucullaris n. DCl dorsal claustrum DG dentate gyrus DiCl diffuse insular claustrum EGP external globus pallidus EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield GU gyrus uncinate h2 lenticular fascicle LH lateral hypothalamic area LV lateral ventricle opt optic tract PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 prf principal fc PrS presubiculum PT paratenial thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum st stria terminalis unn uncal notch VAMC magnocellular ventroanterior n. VL ventrolateral n. VP ventral pallidum ZI zona incerta Cortex: Brodmann Areas Pu DCl Co CeMe ce lf its sts BC PuV LH st VA 3V al ASt bfx BM Cd CeM comb Cuc EGP eml ithp gic iml lml LV MM mml mt opt PCo PT Re S TLV AHi AV BL CA1 CeL cp DiCl st h2 IGP mfb LiCl SCS SNR Me MD mtg PH PedL Rt sm TCd DG tsv GU unn VA VAMC ZI VCl 3n PV iml HATA hf EI BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 rhs cos-ph ELC CA1 S CA3 VGP SEpS pacs cgs-p sprs maprs PrS VAL BA 23 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 1 BA 2 BA 24 BA 6 BA 4 BA 6
ICL: 12.09 MCP: -2.65 MNI: -12.67
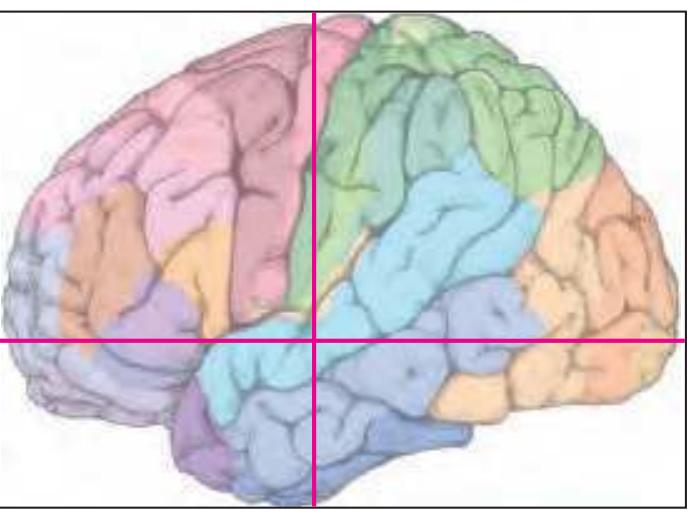
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
AHi amygdalohippocampal area ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact p. BL basolateral amygdaloid n. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus CeL central amygdaloid n, lat. p. CeM central amygdaloid n, med. p. CeMe central medial thalamic n. cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r.
ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus gic genu of corpus callosum
HATA hippocampo amygdaloid transitional area hf hippocampal fissure
IGP internal globus pallidus iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
ithp inferior thalamic peduncle its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
LiCl limitans claustrum lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus
maprs marginal precentral sulcus MD medial dorsal thalamic n.
Me medial amygdaloid n. mfb medial forbrain bundle MM medial mammillary n., med. p.
mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus mt mammillothalamic tract
mtg mammillo-tegmental tract pacs paracentral sulcus
PCo post. cortical amygdaloid n. PedL peduncle of lentiform n. PH posterior hypothalamic area
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n.
SCS subcallosal stratum SEpS subependymal stratum sm stria medullaris of thalamus
SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata sprs superior precentral sulcus
sts superior temporal sulcus
TCd tail of caudate n.
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsv thalamostriate vein
VA ventroanterior n. (ventral anterior n.) VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents)
VCl ventral claustrum
**229**

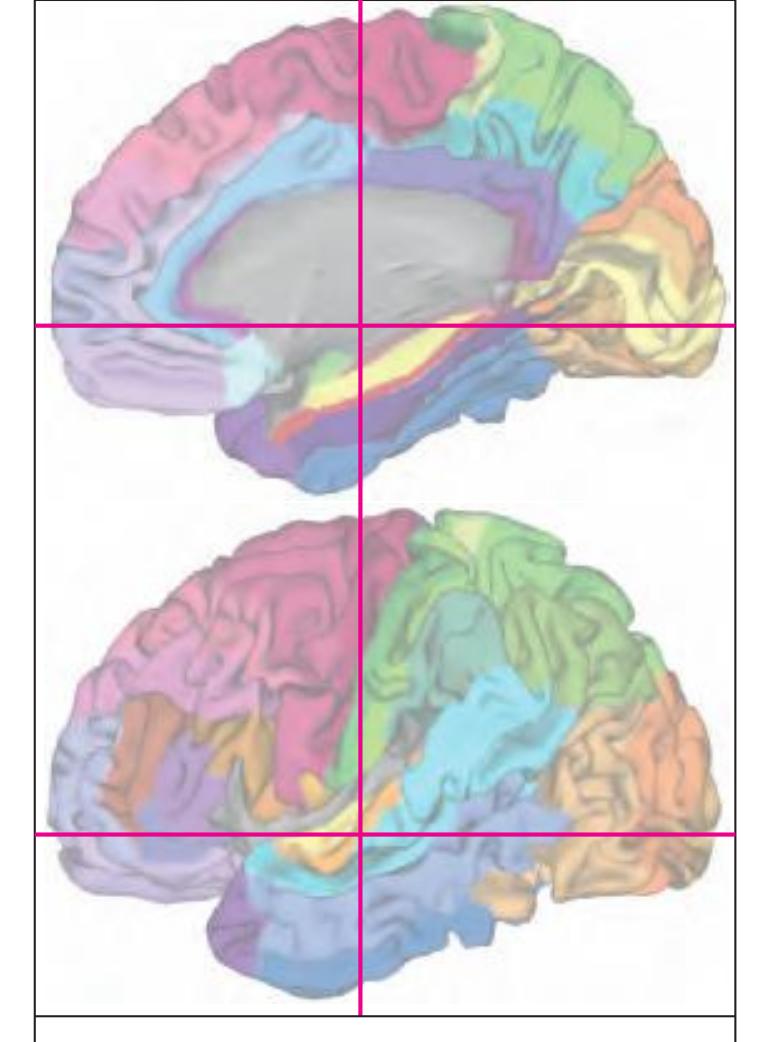
MNI Position y = -12.52 mm AHB Position y = 11.93 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
COp-a anterior central operculum
COp-p posterior central operculum
Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus
HiH hippocampal head
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum
PPo planum polare
PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SLG semilunar gyrus
SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
## Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior) BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior) BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area H hippocampal area
IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal
entrance LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area PC intermediate postcentral area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vo
B. Vogt: p24c' anterior division of BA24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
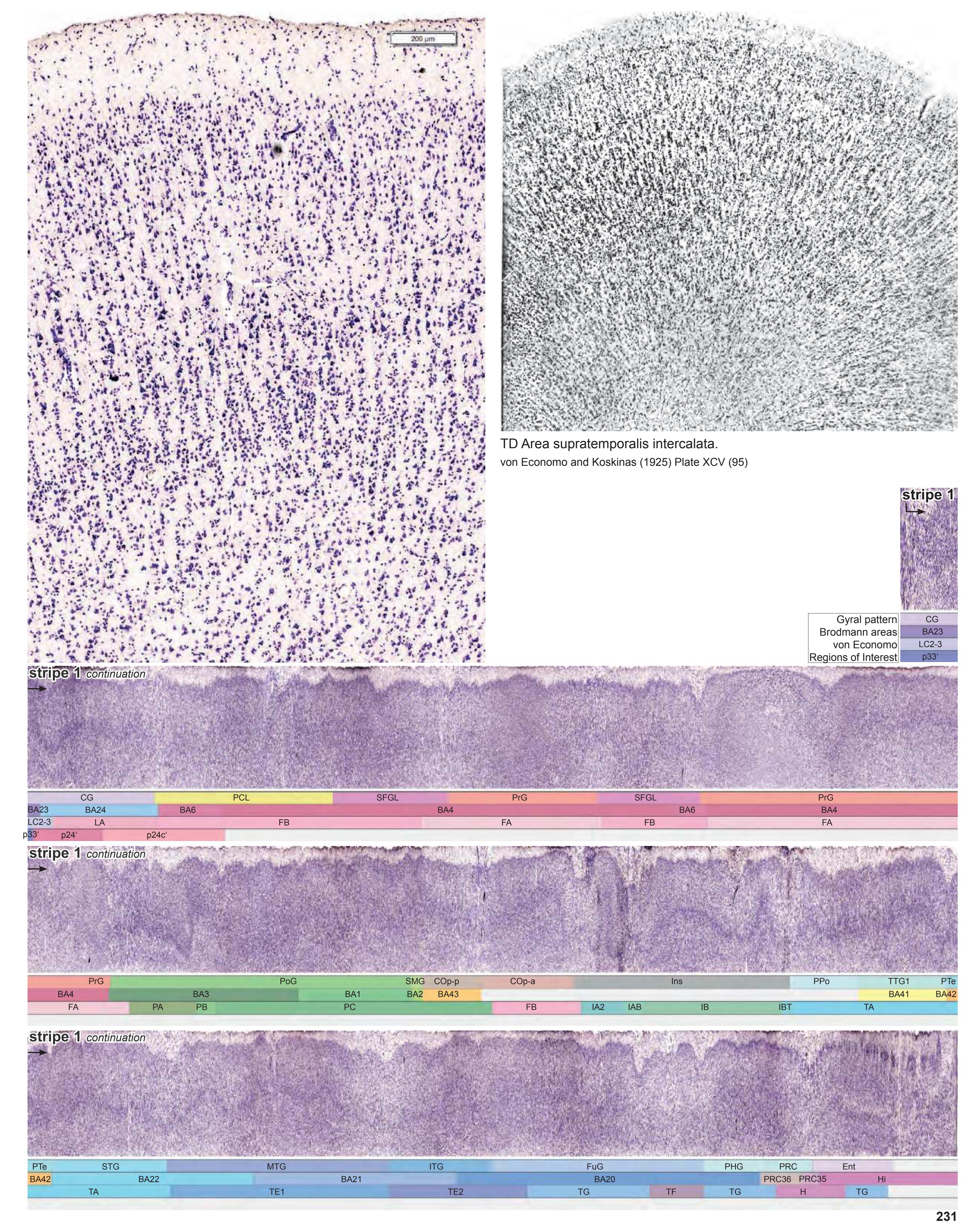
Gyri **232** Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 44 Slice Nr. 2988 Cortex: Gyri and Sulci CG SFGL PrG Ins PPo STG MTG ITG FuG Ent PRC unn Un sts cis cis its cals cgs lf PCL TTG1 ce PHG PoG PrG sas PrG AG SLG S PTe HiH rhs SFGL PrS COp-p pacs COp-a sprs maprs ceis SMG pcis sH hf cos-ph ipocs PCI pscs mlf slf I ilf racc slf II slf III cgh pic slic st tp arc sfo sm cgb comb str lenf rmx st cp mfb 3n ithp mtg ac unc iml sz mt bfx h2 h1 eml al bcc alv opt mt

MNI Position y = -13.99 mm AHB Position y = 13.35 mm
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus HiH hippocampal head Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SLG semilunar gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
Fibers
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus ceis central insular sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus pscs posterior subcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sas semiannular sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus unn uncal notch
Sulci
3n oculomotor nerve ac anterior commissure al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus h1 thalamic fascicle h2 lenticular fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus mfb medial forbrain bundle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mt mammillothalamic tract mtg mammillotegmental tract opt optic tract pic posterior limb of the internal capsule racc radiation of corpus callosum rmx retromammillary commissure sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis
str superior thalamic stria sz stratum zonale tp tapetum unc uncinate fascicle
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) 3V third ventricle AD anterodorsal thalamic n. al ansa lenticularis ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part bfx body of fornix BL basolateral amygdaloid n. BM basomedial amygdaloid n. CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus CeL central amygdaloid n, lat. p. CeM central amygdaloid n, med. p. CeMe central medial thalamic n. cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. Co commissural n. comb comb system cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. cp cerebral peduncle Cuc cucullaris n. DCl dorsal claustrum DG dentate gyrus DiCl diffuse insular claustrum EGP external globus pallidus EI entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield H H-field of Forel h1 thalamic fascicle h2 lenticular fascicle hf hippocampal fissure IGP internal globus pallidus irs intrarhinal sulcus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle its inferior temporal sulcus lenf lenticular fasciculus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LH lateral hypothalamic area LiCl limitans claustrum LV lateral ventricle maprs marginal precentral sulcus MD medial dorsal thalamic n. Me medial amygdaloid n. MM medial mammillary n., med. p. mt mammillothalamic tract mtg mammillo-tegmental tract pacs paracentral sulcus PedL peduncle of lentiform n. PH posterior hypothalamic area PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 prf principal fc PrS presubiculum PT paratenial thalamic n. Pu putamen PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus rmx retromammillary commissure Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SCS subcallosal stratum sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata sprs superior precentral sulcus st stria terminalis STh subthalamic n. sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsv thalamostriate vein VAb basal ventroanterior n. VAMC magnocellular ventroanterior n. VGP ventral globus pallidus ZI zona incerta 44 MCP: -1.39 Cortex: Brodmann Areas CeMe Co ce lf its sts PrS st VAM lenf ithp rmx SNC PuV h1 mt sm SNR st STh TCd TLV tsv VAM VAMC DCl ZI VAL AD al bfx BM CA1 comb cp DiCl EGP eml h2 LiCl lml MD MM mml mtg PH Pu PV Re Rt 3V AV CeM CeL DG BL iml IGP S LV Me mt PedL S SCS Cd PT LH Cuc HATA hf EI BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 rhs cos-ph ELC irs CA3 CA1 VLA VAb VGP BC prf H pacs cgs-p sprs maprs ASt BA 23 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 1 BA 2 BA 24 BA 6 BA 4
## 44
ICL: 13.35 MNI: -13.99

ELC entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus HATA hippocampo amygdaloid transitional area iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents) VAM medial ventroanterior n. (nigral afferents) VLA anterior ventrolateral n. (medial oral div.)
**233**
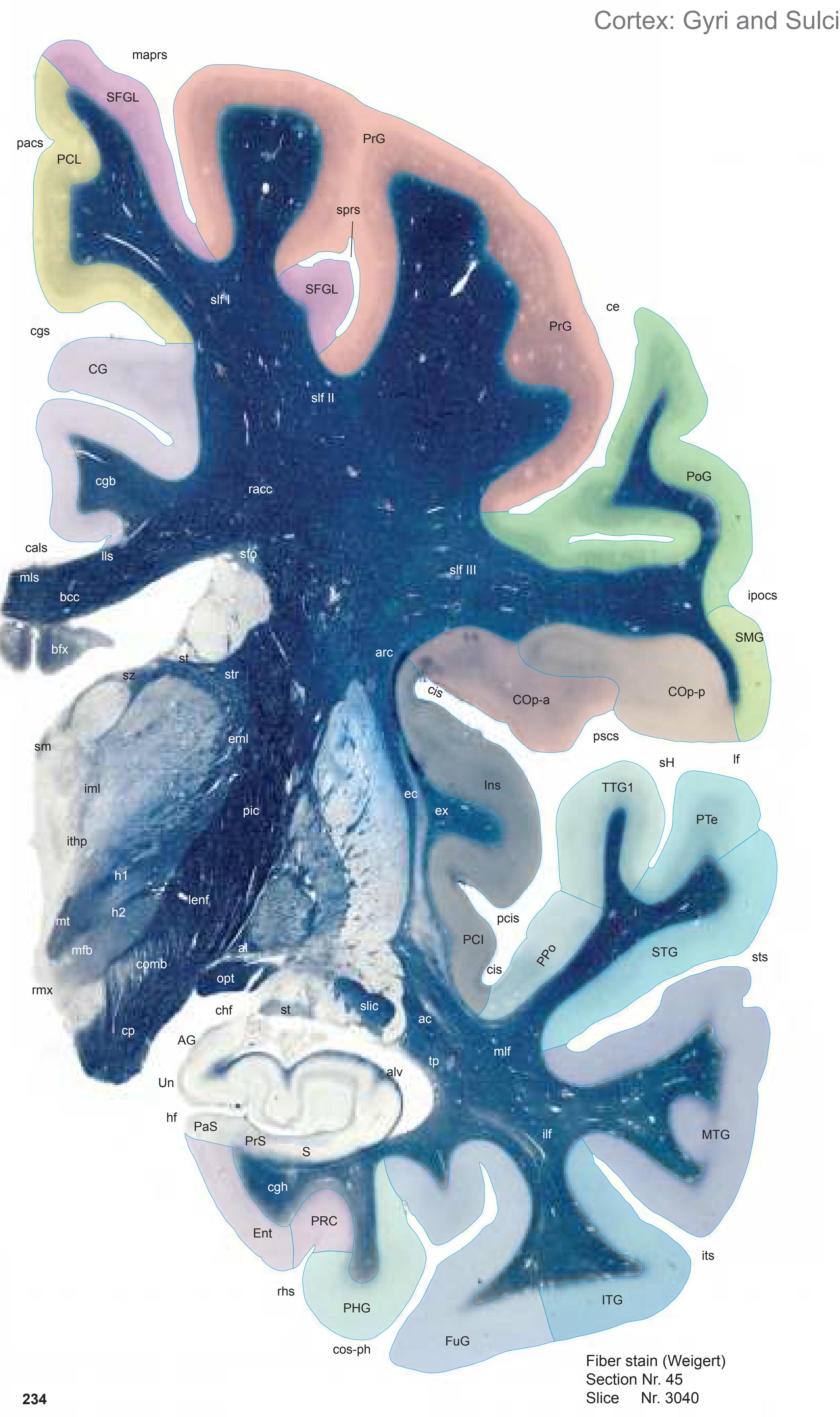

MNI Position y = -15.51 mm AHB Position y = 14.74 mm
AG ambiens gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus pscs posterior subcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sprs superior precentral sulcus
ac anterior commissure sts superior temporal sulcus
alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle
al ansa lenticularis
Sulci
Fibers Gyri
bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule h1 thalamic fascicle h2 lenticular fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ithp inferior thalamic peduncle lenf lenticular fasciculus lls lateral longitudinal stria mfb medial forbrain bundle
mls medial longitudinal stria mt mammillothalamic tract opt optic tract pic posterior limb of the internal capsule racc radiation of corpus callosum
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
rmx retromammillary commissure sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis str superior thalamic stria sz stratum zonale
tp tapetum
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocell. p. mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents) VLA anterior ventrolateral n. (medial oral div.) 45 ICL: 14.74 MCP: 0.00 MNI: -15.51

0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6
**235**
7
-5
VTA ventral tegmental area
ZI zona incerta


MNI Position y = -15.53 mm AHB Position y = 14.77 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
AG ambiens gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum
Ent entorhinal cortex
FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum S subiculum
PPo planum polare
PTe planum temporale S subiculum
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
(unlabeled)
BA42 area
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area IA2 ventral precentral insular area
IAB insular transition area
IB postcentral insular area
IBT postcentral insular area at temporal entrance
LA precingulate agranular anterior limbic area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
TG temporo polar area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24d subregion of BA 24 p24c' anterior division of BA24 p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
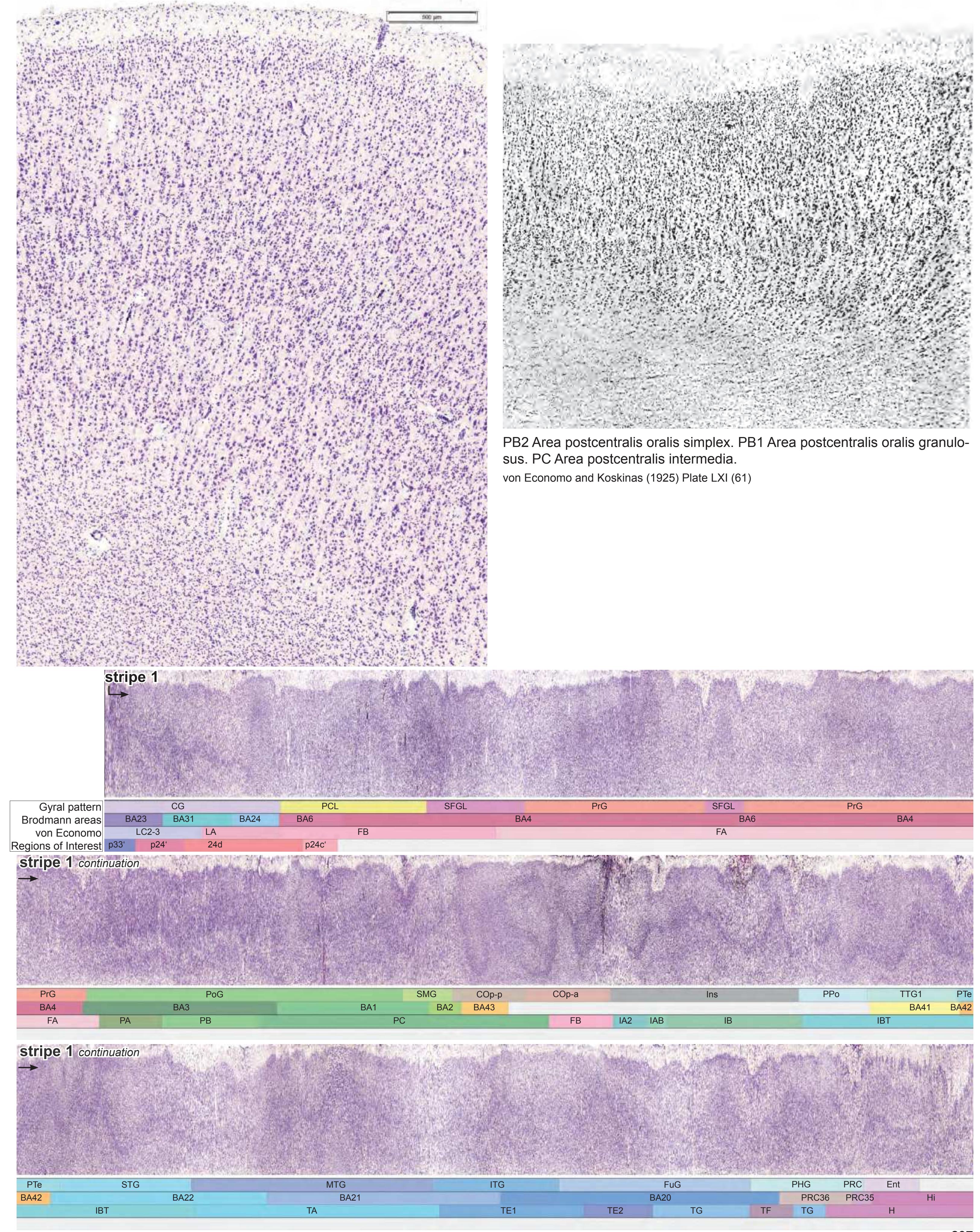
**237**

MNI Position y = -16.83 mm AHB Position y = 16.11 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure maprs marginal precentral sulcus pacs paracentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-
3n oculomotor nerve
Sulci
Fibers Gyri
ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
ex extreme capsule fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-
interpeduncularis)
h1 thalamic fascicle
thalamic tract)
h2 lenticular fascicle
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
lenf lenticular fasciculus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
mls medial longitudinal stria
opt optic tract
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
pons pontine fibers
racc radiation of corpus callosum
Tacc radiation of corpus callosum
rmx retromamillary con
rmx retromammillary commissure sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis
str superior thalamic stria
sz stratum zonale tp tapetum
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 Cortex: Brodmann Areas tt CeMe lf its ce sts 3n VTA VAb st SNR CA1 hf VCl VAL VLA VGP tsv tsc tfi rmx st ZI 3V AD al Amg AV cc bG S CA3 comb Cuc ec bfx CA1 Cd cp DG EGP eml ex h1 h2 IGP LV MDPC MDMC opt pic PT PuV Re lml mml Pons PV Pu sm Rt SNC STh TCd tfx TLV iml ithp PV mtg cr PrS Ec BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 DG DG CA3 S VLPE pacs cgs maprs cals ipocs rhs cos-ph SB ASt tsc mls SEpS BC BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA41 BA42 BA 4 BA 1 BA 2 BA 24 BA 6 BA 4
ICL: 16.11 MCP: 1.37 MNI: -16.83
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve 3V third ventricle AD anterodorsal thalamic n.
al ansa lenticularis Amg amygdala
ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n.
BC basal n., compact part
bfx body of fornix bG band of Giacomini
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus
cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum
Cd caudate n.
ce central sulcus
CeMe central medial thalamic n.
cgs cingulate sulcus comb comb system
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r.
cp cerebral peduncle
cr capsule of the red n.
Cuc cucullaris n.
DG dentate gyrus
Ec entorhinal cortex, caudal subfield
ec external capsule
EGP external globus pallidus
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
ex extreme capsule h1 thalamic fascicle
h2 lenticular fascicle
hf hippocampal fissure
IGP internal globus pallidus
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus
ithp inferior thalamic peduncle
its inferior temporal sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus
If lateral (Sylvian) fissure
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus
LV lateral ventricle
maprs marginal precentral sulcus
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocell. p.
MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p.
mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus
mtg mammillo-tegmental tract
opt optic tract
pacs paracentral sulcus pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
Pons pons PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PrS presubiculum
PT paratenial thalamic n. Pu putamen
PuV ventral putamen
PV paraventricular thalamic n.
Re reuniens thalamic n.
rhs rhinal sulcus
rmx retromammillary commissure
x retromamillary
Diastolic the last
Rt reticular thalamic n.
S subiculum SB striatal cell bridge
SEpS subependymal stria
sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta
SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata
st stria terminalis STh subthalamic n.
sts superior temporal sulcus
TCd tail of caudate n.
tfi tenia of fimbria
tfx tenia of fornix
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsc tenia semicircularis
tsv thalamostriate vein
tt tenia of thalamus
us uncal sulcus
VAb basal ventroanterior n.
VAL lateral ventroanterior n. (pallidal afferents) VCl ventral claustrum
VGP ventral globus pallidus
VLA anterior ventrolateral n. (medial oral div.) VLPE posterior ventrolateral n., external p.
VTA ventral tegmental area
ZI zona incerta
**239**

cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus h2 lenticular fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lenf lenticular fasciculus lls lateral longitudinal stria mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria pic posterior limb of the internal capsule ptpt parieto-temporopontine tract py pyramidal tract racc radiation of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule st stria terminalis

MNI Position y = -18.30 mm AHB Position y = 17.45 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus cals callosal sulcus Fibers
ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure maprs marginal precentral sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus pcs postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
Sulci
3n oculomotor nerve al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle
bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix
bG band of Giacomini cgb cingulum bundle
comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle
ec external capsule
ec external capsule
eml external medullary lamina
ex extreme capsule
fmt frontopontine tra
ex extreme capsule
fpt frontopontine tract fr fasciculus retroflexus
h1 thalamic fascicle
h2 lenticular fascicle
ilf inferior longitudinal
iml internal medullary lamina o
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
Icm
lls lateral longitudinal stri
lls lateral longitudin
mlf middle longitudin
in middle longitu
mls medial longitu
is medial longit
opt optic tract
opt optic tract
pic posterior limb of th
pons pontine fibers
ptpt parieto-temp
nv pyramidal trac
pyramidal tract
racc radiation of corpus callosum
Tract Radiation of corpus callosum
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
str superior thalamic stria
sz stratum zonale tp tapetum
The following are the results of the experiment:
| Labels | Values |
|-------------------------|-------------------------|
| Experiment ID | 12345 |
| Date | 2023-10-27 |
| Temperature | 25.5 °C |
| Pressure | 101.3 kPa |
| Humidity | 60% |
Additional notes:
- The experiment was conducted under controlled conditions.
- All measurements were recorded accurately.
- Further analysis will be performed on the collected data.
If you have any questions, please contact the research team.
$E = mc^2$
$$\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-x^2} dx = \frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{2}$$
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 Cortex: Brodmann Areas Co VLb its lf sts ce DG SNR st ZID ZIV SCS sm SNC SNR STh tsv VLPI VGP st TCd VCl us VLPE 3n 3V AD al Amg AV cc bfx CA1 bG CA3 Cd comb cp cr crt ec EGP eml ex h1 IGP VTA DSF lml MDPC MDMC mml mtg Pons PrS Pu PV Re Rt S TLV iml LV mls opt pic PT PuV IGr DCl fi CA3 DG CA2 CA1 bG ECL BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 CA3 DG IPF cos-ph rhs cgs pcs Un VAb PV ASt cis sH BC BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA41 BA42 BA 4 BA 3 BA 1 BA 2 BA 24 BA 6 BA 4
ICL: 17.45 MCP: 2.71 MNI: -18.30

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve 3V third ventricle AD anterodorsal thalamic n. al ansa lenticularis Amg amygdala
ASt amygdalostriatal transition area
AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part
bfx body of fornix bG band of Giacomini
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cc corpus calosum
Cd caudate n.
ce central sulcus
cgs cingulate sulcus cis circular sulcus
Co commissural n.
comb comb system cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r.
cp cerebral peduncle
cr capsule of the red n.
crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers
(dentato-thalamic tract)
DCl dorsal claustrum
DG dentate gyrus
DSF dorsal superficial n. ec external capsule
ECL entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield
EGP external globus pallidus eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
ex extreme capsule
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
h1 thalamic fascicle
IGP internal globus pallidus
IGr indusium griseum iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
IPF interpeduncular fossa
its inferior temporal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus
LV lateral ventricle
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocell. p. MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p. mls medial longitudinal stria
mml medial medullary lamina of globus pallidus
mtg mammillo-tegmental tract opt optic tract
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
pcs postcentral sulcus
Pons pons PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
PrS presubiculum
PT paratenial thalamic n.
Pu putamen
PuV ventral putamen
PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n.
rhs rhinal sulcus
Rt reticular thalamic n.
S subiculum
SCS subcallosal stratum
sH Heschl sulcus
sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta
SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata
st stria terminalis
STh subthalamic n. sts superior temporal sulcus
TCd tail of caudate n.
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tsv thalamostriate vein
Un uncus
us uncal sulcus
VAb basal ventroanterior n.
VCI ventral claustrum
VGP ventral globus p
VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus pallidus
VLb basal (inferior) ventrolateral n. [VPI] (entry zone of the cerebellar fibers)
VLPE posterior ventrolateral n., external p.
VLPI posterior ventrolateral n., internal p. VTA ventral tegmental area
VTA ventral tegmental area
ZID zona incerta, dorsal n
ZID zona incerta, dorsal p. ZIV zona incerta, ventral p.
**241**

This is a blank image. There is no text or any other content to extract.
This is a sample text.
## Brain Atlas
This image displays a sagittal view of the human brain, segmented into different functional regions. The brain is shown in two separate views, one above the other, with a pink grid overlaying both to indicate spatial divisions.
Each region is color-coded, suggesting a parcellation scheme based on anatomical or functional characteristics. The gyri and sulci are clearly visible, highlighting the complex folding of the cerebral cortex.
**Top View:**
- Shows the lateral and medial aspects of the brain.
- The grid divides the brain into four quadrants, facilitating localization.
**Bottom View:**
- Presents a similar view, possibly from a slightly different angle or with a different emphasis on specific structures.
- The color-coding is consistent with the top view, allowing for comparison.
This type of visualization is crucial in neuroscience for understanding brain organization, connectivity, and the effects of neurological conditions or interventions.
MNI Position y = -19.14 mm AHB Position y = 18.23 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
DG dentate gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
COp-a anterior central operculum
COp-p posterior central operculum
Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata
FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex
PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum
PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum
S subiculum
PPo planum polare
PTe planum temporale S subiculum
SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part
SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
Un uncus
# Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA6 area frontalis agranularis
BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA24 area cingularis anterior ventralis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior) BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior) BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area PD caudal postcentral area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
**242**


Slice Nr. 3189

MNI Position y = -19.65 mm AHB Position y = 18.74 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PCI postcentral insular cortex PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure
Sulci
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus maprs marginal precentral sulcus
Fibers
pcis posterior central insular sulcus pcs postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus
3n oculomotor nerve sts superior temporal sulcus
sH Heschl sulcus
al ansa lenticularis alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of forn*ix* cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-
thalamic tract) ec external capsule
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
ex extreme capsule
fcl fasciculus circumligatus (Ziehen)
fpt frontopontine tract
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis)
h1 thalamic fascicle
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
half middle longit
nt optic tract
opt optic tract
pcr posterior corona radiata
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
ptpt parieto-temporopontine tract
py pyramidal tract sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis
str superior thalamic stria sz stratum zonale
tp tapetum
**244**
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 Cortex: Brodmann Areas SCS IGr ec ce lf sts its PF fi chf FD st CA3 DG VGP ZI al Amg AV ASt cc bfx CA1 CA2 CA1 Cd CM comb cp cr crt DCl DG EGP eml ex TLV bG FD h1 us iml VCl DSF MDPC MDMC opt PaS PV Pons PrS Pu R pic VLPI PuV S Rt Re sm SNC SNR st STh TCd lml LV ECL BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 lots CA3 SPF VPMPC VLPE PT cos-ph rhs cgs fr VLb pcs RLi PN VTA BC PBP tfp BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 2 BA 1 BA 2 BA 6 BA 4
ICL: 18.74 MCP: 4.00 MNI: -19.65

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) al ansa lenticularis Amg amygdala ASt amygdalostriatal transition area AV anteroventral thalamic n. BC basal n., compact part bfx body of fornix bG band of Giacomini CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroidal fissure CM centromedian thalamic n. comb comb system cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus cp cerebral peduncle cr capsule of the red n. crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-thalamic tract) DCl dorsal claustrum DG dentate gyrus DSF dorsal superficial n. ec external capsule ECL entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield EGP external globus pallidus eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule FD fascia dentata fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo interpeduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle IGr indusium griseum iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lml lateral medullary lamina of globus pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LV lateral ventricle MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular p. MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p. opt optic tract PaS parasubiculum PBP parabrachial pigmented n. of the VTA PF parafascicular thalamic n. pic posterior limb of the internal capsule PN paranigral n. of ventral tegmental area pcs postcentral sulcus Pons pons PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PrS presubiculum PT paratenial thalamic n. Pu putamen PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. R red n. Re reuniens thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus RLi rostral linear n. Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SCS subcallosal stratum sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SPF subparafascicular thalamic n. st stria terminalis STh subthalamic n. sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. tfp transverse fibers of the pons TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle us uncal sulcus VCl ventral claustrum VGP ventral globus pallidus VLb basal (inferior) ventrolateral n. VLPE posterior ventrolateral n., external p. VLPI posterior ventrolateral n., internal p.
**245**
VPMPC medial ventroposterior n., parvicellular p.
VTA ventral tegmental area
ZI zona incerta

Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 49 Slice Nr. 3239

MNI Position y = -21.14 mm AHB Position y = 20.08 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus COp-p posterior central operculum Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PPo planum polare PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
3n oculomotor nerve Un uncus cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcis posterior central insular sulcus pcs postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) comb comb system cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract) ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fcl fasciculus circumligatus (Ziehen) fpt frontopontine tract
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus
l medial lemniscus
mlf middle longitudinal fasc
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
al ansa lenticularis
Sulci
alv alveus of the hippocampus
opt optic tract
pcr posterior corona radiata
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
ptpt parieto-temporopontine tract
py pyramidal tract
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
**246**
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 al ansa lenticularis Amg amygdala bfx body of fornix cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus Cl claustrum cp cerebral peduncle DG dentate gyrus ec external capsule ex extreme capsule FD fascia dentata interpeduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle IGr indusium griseum pallidus LV lateral ventricle opt optic tract PaS parasubiculum Pons pons PrS presubiculum PuV ventral putamen rhs rhinal sulcus S subiculum SB striatal cell bridge st stria terminalis STh subthalamic n. TCd tail of caudate n. tfi tenia of fimbria Un uncus us uncal sulcus VLPI posterior ventrolateral n., internal p. VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n. VPMPC medial ventroposterior n., parvicellular p. VTA ventral tegmental area ZI zona incerta Cortex: Brodmann Areas VPL MDMC ce cr DG crt tsc tsv Un us VLPI ZI al Amg cc CA1 bfx CA2 CA3 Cd Cl cp mtg eml ec ex IGr lml MDPC PaS pic Pons Pu PuV PV Re Rt S SCS sm SNC SNR st STh TCd tclv tfi TLV CM DG EGP FD fi iml DSF LV opt PF alv PT PrS RPC SB ECL BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 PRC35 PRC36 fr VPMPC VLb cos-ph lots h1 lf sts rhs its cgs SPF VLPE pcs PBP ASt VTA VGP BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 1 BA 3 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 2 BA 3 BA 1 BA 2 BA 4
ICL: 20.08 MCP: 5.34 MNI: -21.14

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) alv alveus of the hippocampus ASt amygdalostriatal transition area CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus CM centromedian thalamic n. cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. cr capsule of the red n. crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-thalamic tract) DSF dorsal superficial n. ECL entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield EGP external globus pallidus eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocell. p. MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p. mtg mammillo-tegmental tract PBP parabrachial pigmented n. of the VTA PF parafascicular thalamic n. pic posterior limb of the internal capsule pcs postcentral sulcus PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PT paratenial thalamic n. PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n. RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p. Rt reticular thalamic n. SCS subcallosal stratum sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SPF subparafascicular thalamic n. sts superior temporal sulcus tclv tela choroidea of the lateral ventricle TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsc tenia semicircularis tsv thalamostriate vein VGP ventral globus pallidus VLb basal (inferior) ventrolateral n. [VPI] (entry zone of the cerebellar fibers) VLPE posterior ventrolateral n., external p.
**247**

Section Nr. 49 Slice Nr. 3241

MNI Position y = -21.14 mm AHB Position y = 20.13 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
DG dentate gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
COp-p posterior central operculum
Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata
FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum
PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum
PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum
S subiculum PPo planum polare
PTe planum temporale
S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
Un uncus
# Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area H hippocampal area
IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PD caudal postcentral area
PF supramarginal area TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
# Regions of Interest
# Reg
B. Vo
B. Vogt: 24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24
p33' posterior subregion of BA33
**248**

Fibers
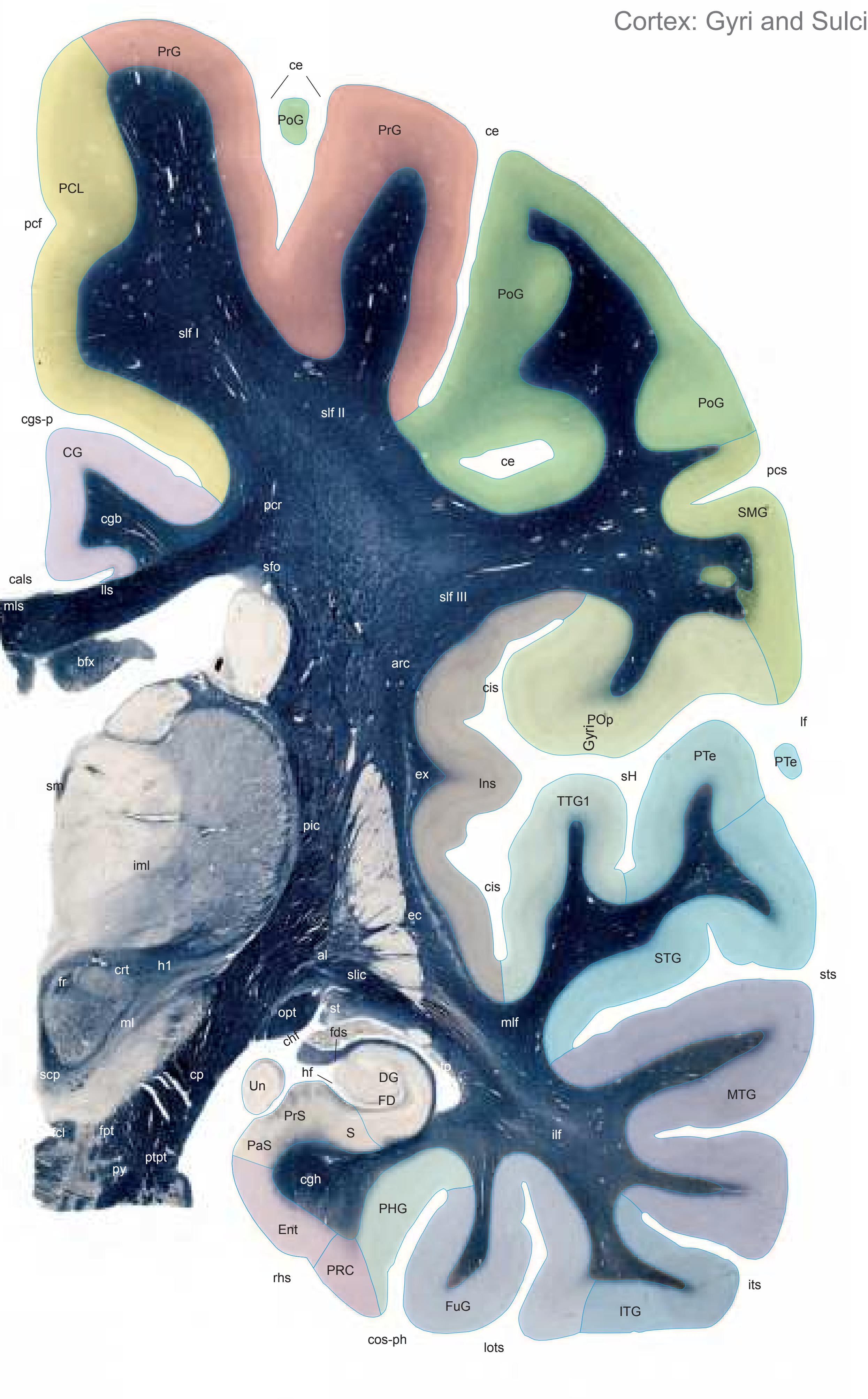


MNI Position y = -22.49 mm AHB Position y = 21.47 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus Un uncus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus fds fimbriodentate sulcus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa pcs postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
al ansa lenticularis
Sulci
arc arcuate fascicle bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract) ec external capsule ex extreme capsule fcl fasciculus circumligatus (Ziehen) fpt frontopontine tract fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo interpeduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria opt optic tract pcr posterior corona radiata
lls lateral longitudinal stria ml medial lemniscus
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule ptpt parieto-temporopontine tract py pyramidal tract scp superior cerebellar peduncle sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 50 Slice Nr. 3291
**250**
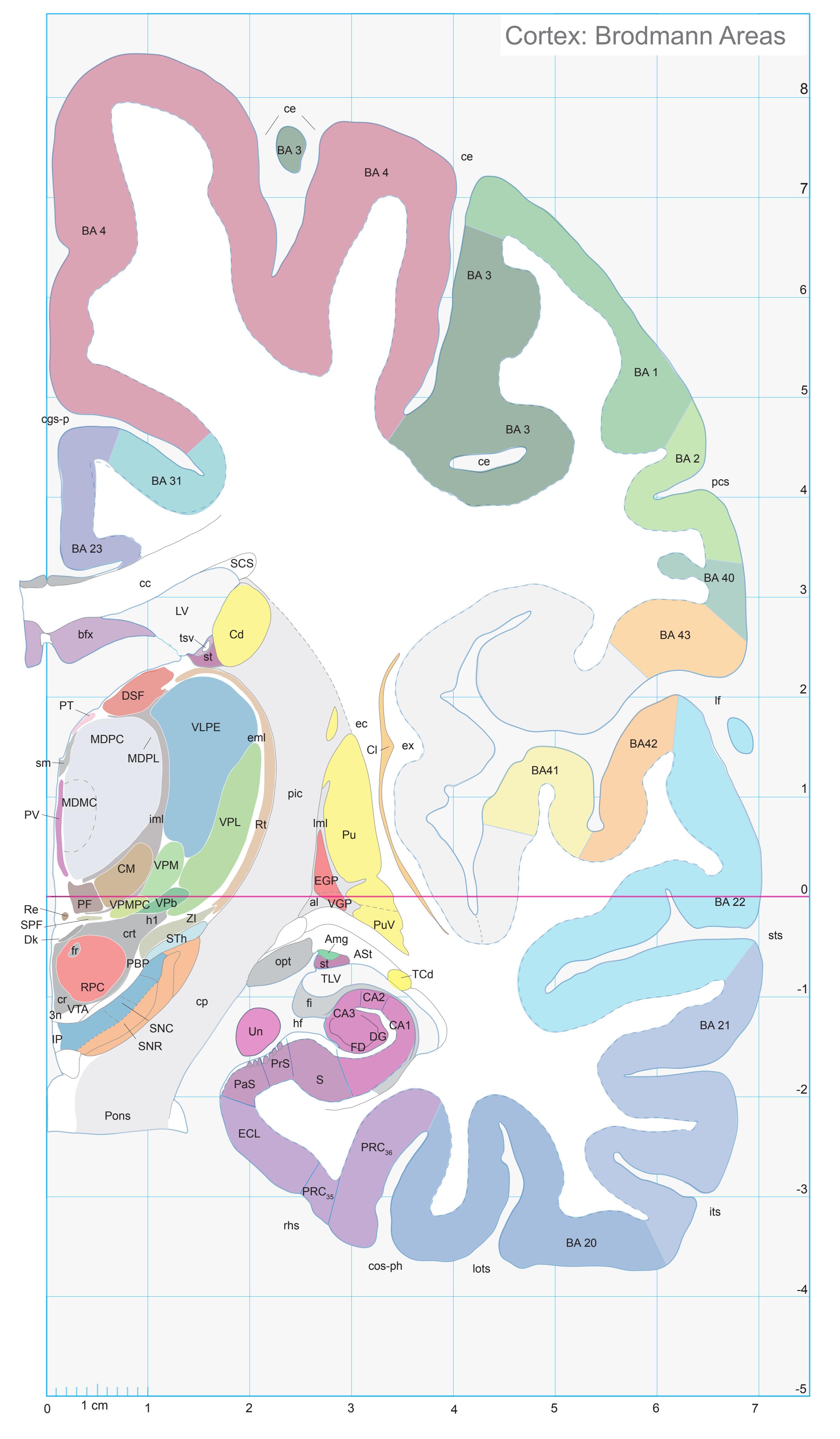
ICL: 21.47 MCP: 6.73 MNI: -22.49

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve al ansa lenticularis Amg amygdala ASt amygdalostriatal transition area bfx body of fornix CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. Cl claustrum CM centromedian thalamic n.
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus
cp cerebral peduncle cr capsule of the red n. crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract) DG dentate gyrus
Dk nucleus of Darkschewitsch DSF dorsal superficial n. ec external capsule
ECL entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield EGP external globus pallidus eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
ex extreme capsule FD fascia dentata
fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-
interpeduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle
hf hippocampal fissure iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
IP interpeduncular n. its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LV lateral ventricle
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular
part MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p. MDPL mediodorsal thalamic n., paralaminar p. opt optic tract
PaS parasubiculum PBP parabrachial pigmented n. PF parafascicular thalamic n.
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule pcs postcentral sulcus Pons pons
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PrS presubiculum
PT paratenial thalamic n. Pu putamen
PuV ventral putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n.
Re reuniens thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus
RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p. Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum
SCS subcallosal stratum sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta
SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SPF subparafascicular thalamic n.
st stria terminalis STh subthalamic n.
sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n.
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsv thalamostriate vein
Un uncus VGP ventral globus palidus
VLPE posterior ventrolateral n., external p. VPb basal ventroposterior n. [VMpo] (entry zone of sensory afferents)
VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n. VPM medial thalamic ventroposterior n. VPMPC medial ventroposterior n., parvicell. p. VTA ventral tegmental area
ZI zona incerta
**251**
Fibers


MNI Position y = -24.35 mm AHB Position y = 22.76 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus fds fimbriodentate sulcus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa pcs postcentral sulcus rhs rhinal sulcus sH Heschl sulcus
Sulci
al ansa lenticularis arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentatothalamic tract) ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fcl fasciculus circumligatus (Ziehen) fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis) h1 thalamic fascicle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle opt optic tract or optic radiation pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule pons pontine fibers sts superior temporal sulcus
scp superior cerebellar peduncle sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
st stria terminalis tp tapetum
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sm stria medullaris of thalamus
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 51 Slice Nr. 3339
**252**

ICL: 22.76 MCP: 8.02 MNI: -24.35
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) al ansa lenticularis bfx body of fornix ASt amygdalostriatal transition area CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. Cl claustrum CM centromedian thalamic n. cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal r. cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract) DG dentate gyrus DSF dorsal superficial n. ec external capsule ECL entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo interpeduncularis) hf hippocampal fissure IF interfascicular n. iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus IP interpeduncular n. IPF interpeduncular fossa its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LG lateral geniculate n. lml lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LV lateral ventricle MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular p. MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p. MDPL mediodorsal thalamic n., paralaminar p. mtg mammillo-tegmental tract PaS parasubiculum PBP parabrachial pigmented n. pcf paracentral fossa PF parafascicular thalamic n. pic posterior limb of the internal capsule pcs postcentral sulcus Pons pons PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PrS presubiculum Pu putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. Re reuniens thalamic n. rhs rhinal sulcus RLi rostral linear n. RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p. Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SB striatal cell bridge scp superior cerebellar peduncle SCS subcallosal stratum sH Heschl sulcus sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SPF subparafascicular thalamic n. st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF tfi tenia of fimbria tfx tenia of fornix TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
**253**
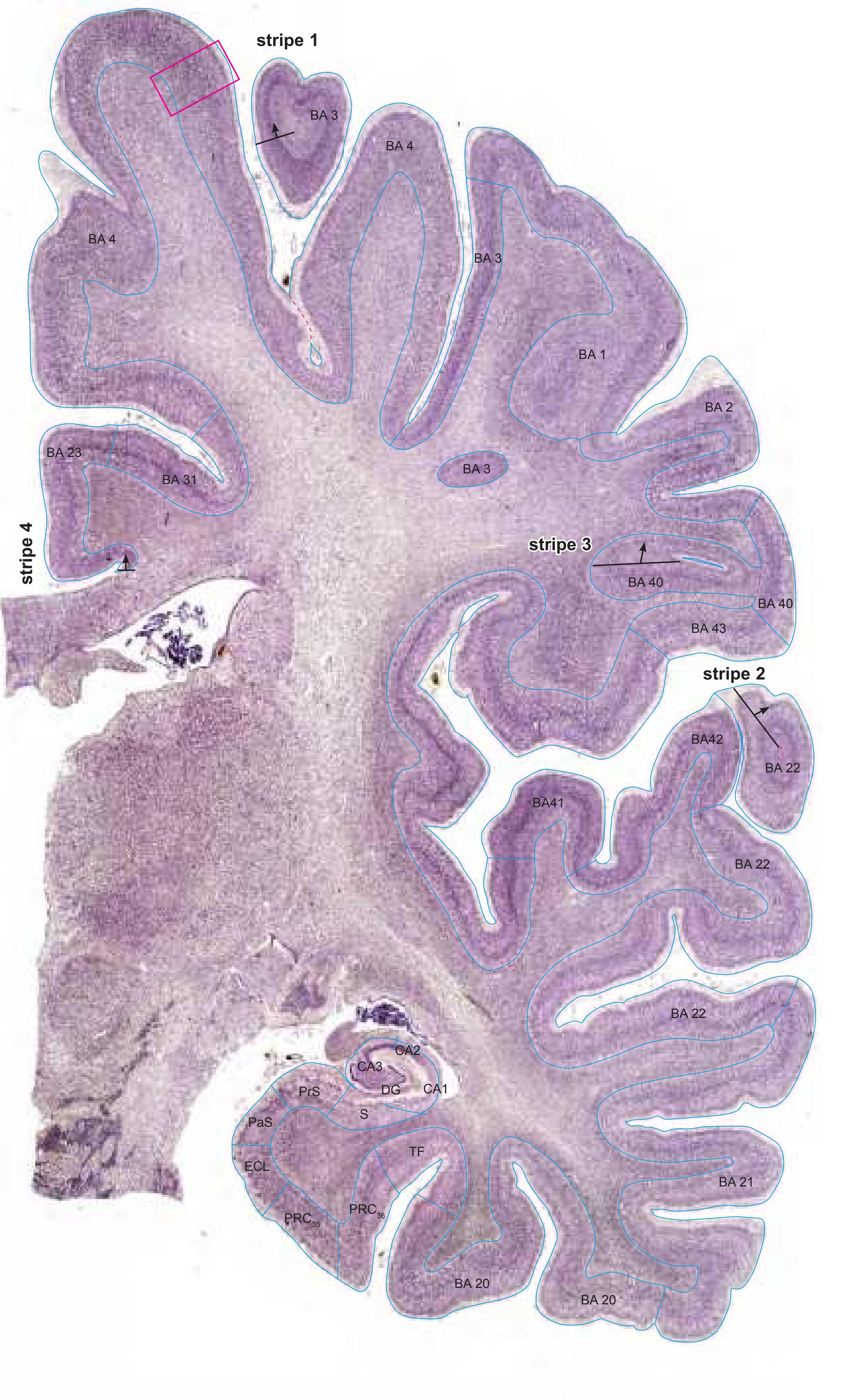
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 51
MNI Position y = -24.77 mm AHB Position y = 23.59 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
DG dentate gyrus
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex
FD fascia dentata FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex
PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum
S subiculum PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
# Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior) BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
PRC35 perirhinal cortex, BA 35
PRC36 perirhinal cortex, BA 36
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PD caudal postcentral area PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
Slice Nr. 3370
**254**
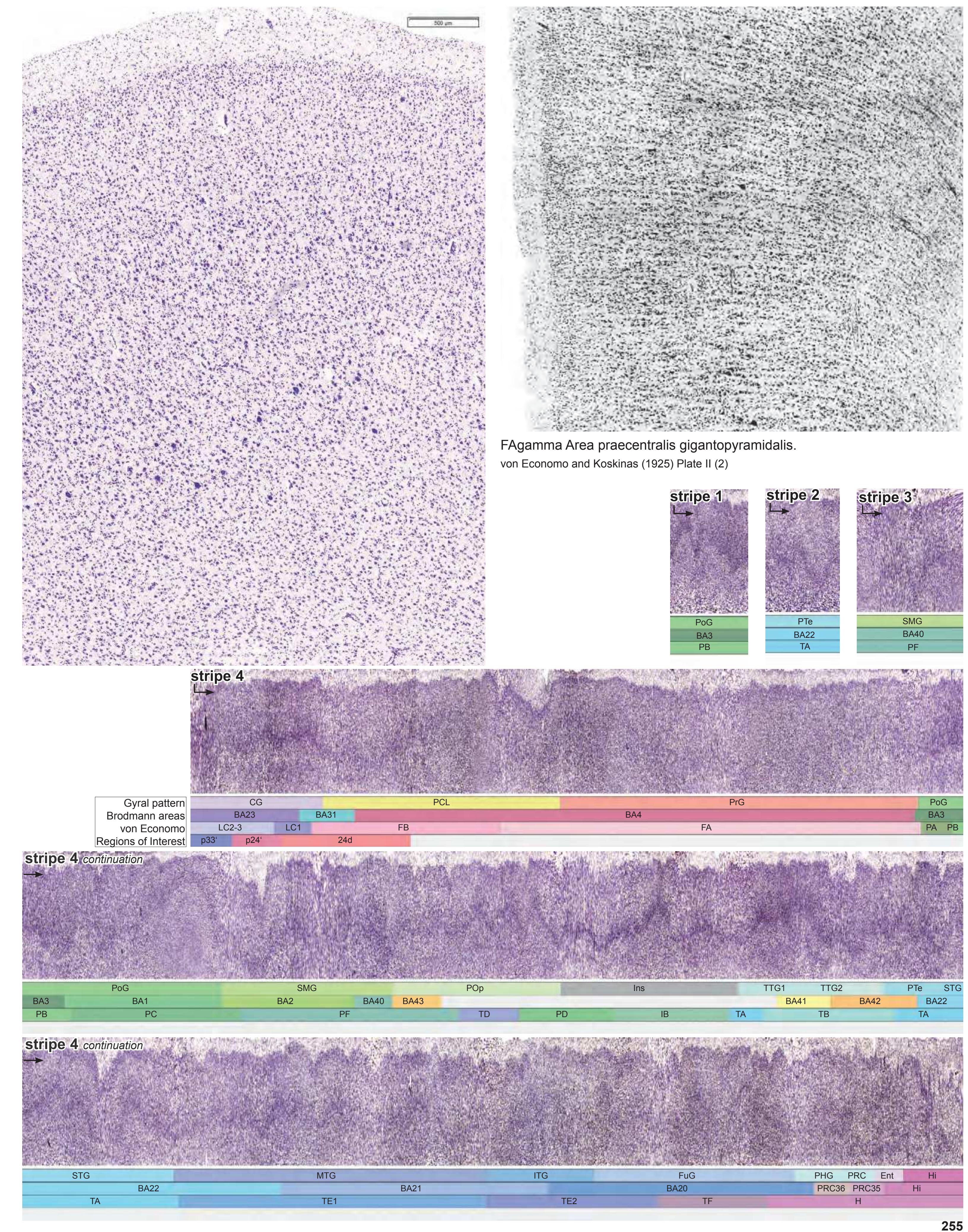
**255**

MNI Position y = -25.31 mm AHB Position y = 24.01 mm
DG dentate gyrus CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
3n oculomotor nerve cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa pcs postcentral sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tvt transverse temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle
cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle
crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract)
al ansa lenticularis
ec external capsule eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus ex extreme capsule
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
or optic radiation
pcr posterior corona radiata
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
vtx ventral tegmental decussation
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 52 Slice Nr. 3386
**256**
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 VPMPC medial ventroposterior n., parvicellular Cortex: Brodmann Areas APul ce ce pcs lf lots its sts st VTA ZI VPL SPF TCd TLV tsv MD PL PaS PBP pic PrS Pu PV Re RPC Rt S scp SCS SGe sm SNC SNR st Pons PF PT cc bfx CA1 CA2 CA3 Cd Cl CM cos-ph cp ec eml ex fr fi crt hf IGr iml IP DSF LG LV MDPC MD MC VPMPC VPM VPb TH TF BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 DG ADPul mtg cgs-p pcf EW RLi IF ASt tvt PPA ce BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 3 BA 1 BA 3 BA 40 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 4 BA 2
ICL: 24.01 MCP: 9.27 MNI: -25.31

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus) APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus ASt amygdalostriatal transition area bfx body of fornix CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus
cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus
cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p.
Cl claustrum CM centromedian thalamic n.
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal
ramus cp cerebral peduncle
crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-
thalamic tract)
DG dentate gyrus DSF dorsal superficial n.
ec external capsule
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
EW Edinger-Westphal n. ex extreme capsule
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-interpe duncularis)
hf hippocampal fissure IF interfascicular n.
IF interascicular II.
I Gr. indusium griseu
IGr indusium griseum iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
IP interpeduncular n.
its inferior temporal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LG lateral geniculate n.
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
LV lateral ventricle
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular part
MDPC mediodorsal thalamic n., parvicellular p.
MDPL mediodorsal thalamic n., paralaminar p. mtg mammillo-tegmental tract
PaS parasubiculum
PBP parabrachial pigmented n.
pcf paracentral fossa
PF parafascicular thalamic n. pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
pcs postcentral sulcus
Pons pons PrS presubiculum
PPA peripeduncular area
PT paratenial thalamic n.
Pu putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n.
Re reuniens thalamic n.
RLi rostral linear n.
RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p.
Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
SCS subcallosal stratum
SGe suprageniculate n.
sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta
SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata
SPF subparafascicular thalamic n.
st stria terminalis
sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n.
TF parahippocampal area TF
TH parahippocampal area TH
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsv thalamostriate vein
tsv thalamostriate vein
tvt transverse temporal su
tvt transverse temporal sulcus VPb basal ventroposterior n. [VMpo] (entry zone
of sensory afferents)
VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n.
VPM medial thalamic ventroposterior n.
part
VTA ventral tegmental area ZI zona incerta
**257**
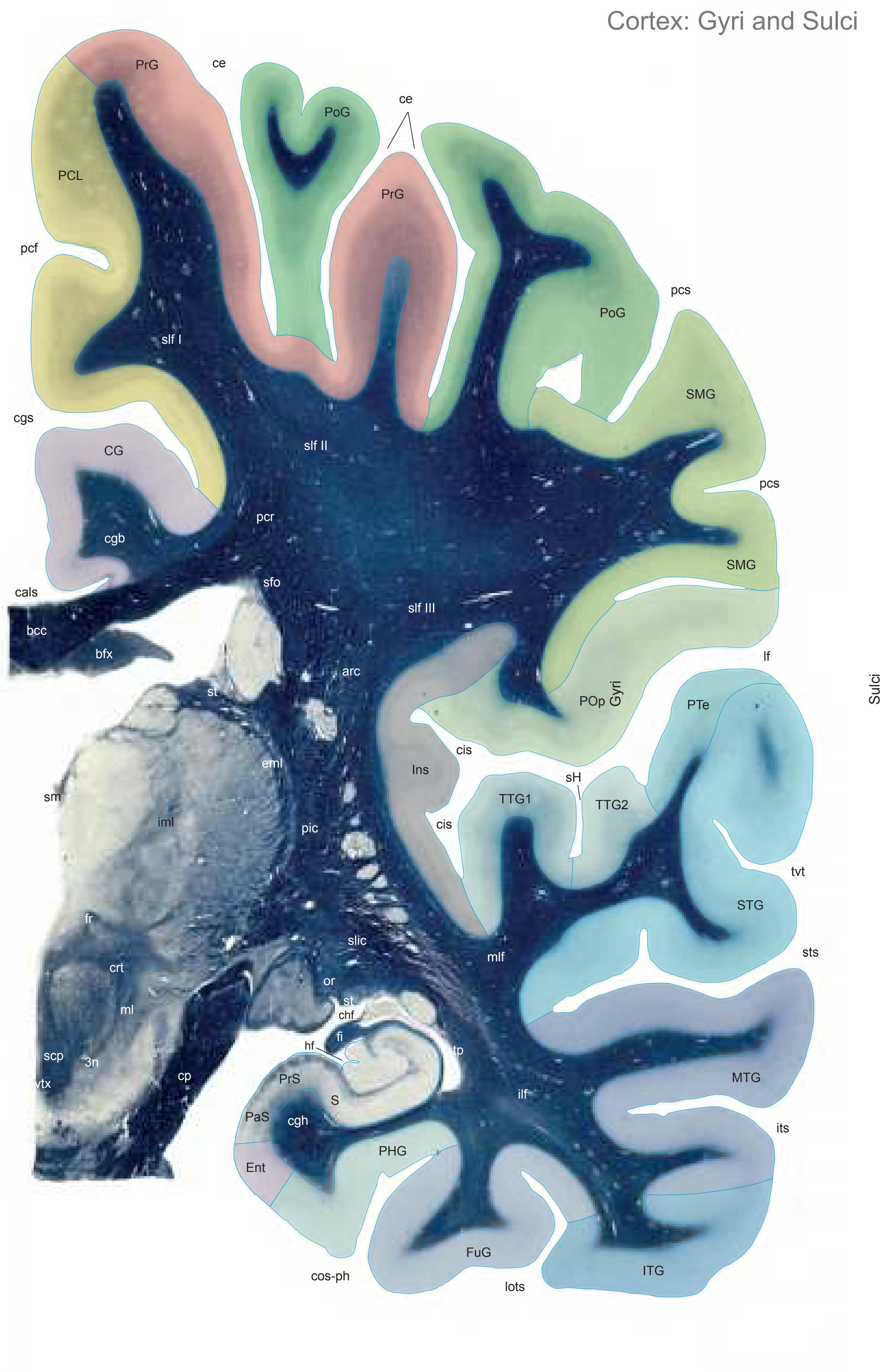

MNI Position y = -26.74 mm AHB Position y = 25.49 mm
CG cingulate gyrus Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa pcs postcentral sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tvt transverse temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract)
3n oculomotor nerve
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter-
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
or optic radiation
peduncularis)
pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
vtx ventral tegmental decussation
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 53 Slice Nr. 3441
**258**
0 1 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 -3 -2 -1 1 3 4 5 6 0 -4 2 7 8 7 -5 posterior nucleus) alv alveus of the hippocampus APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus nucleus) bfx body of fornix CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cals callosal sulcus cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus CM centromedian thalamic n. ramus cp cerebral peduncle thalamic tract) DG dentate gyrus DSF dorsal superficial n. eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus EW Edinger-Westphal n. fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis) hf hippocampal fissure IF interfascicular n. iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus IP interpeduncular n. its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LG lateral geniculate n. lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle MD medial dorsal thalamic n. part ml medial lemniscus mtg mammillo-tegmental tract PaS parasubiculum PBP parabrachial pigmented n. pcf paracentral fossa PF parafascicular thalamic n. pic posterior limb of the internal capsule pcs postcentral sulcus Pons pons PP peripeduncular n. PPA peripeduncular area PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum Pu putamen PV paraventricular thalamic n. RLi rostral linear n. RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p. Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum scp superior cerebellar peduncle SCS subcallosal stratum sfms superficial medullary stratum sH Heschl sulcus sm stria medullaris of thalamus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tvt transverse temporal sulcus VPb basal ventroposterior n. VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n. VPM medial thalamic ventroposterior n. part VTA ventral tegmental area ZI zona incerta Cortex: Brodmann Areas cos-ph lots its ce pcs lf PPA cc PP PBP Pons Pu IP LG LV MD MC MD fr crt CA1 CA2 Cd VTA ZI VPMPC VPL SNC SNR st TLV TCd Rt S scp SCS sm PrG PaS PF pic PrS RPC PV DSF MDPL cp eml fi iml hf alv bfx CA3 CM VPM LPul APul VPb mtg ml DG TH TF BA 20 BA 21 BA 22 AV IF sH pcs pcf cgs cals sts ce ADPul EW RLi tvt sfms BA 23 BA 31 BA 4 BA 3 BA 1 BA 3 BA 2 BA 40 BA 43 BA42 BA41 BA 1 BA 4 BA 2
ICL: 25.49 MCP: 10.75 MNI: -26.74

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral AV anteroventral nucleus (anteroprincipal cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter-
peduncularis)
hf hippocampal fissure
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular
MDPL mediodorsal thalamic n., paralaminar p.
VPMPC medial ventroposterior n., parvicellular
**259**

Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 53
MNI Position y = -26.74 mm AHB Position y = 25.46 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus
Ent entorhinal cortex FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
PaS parasubiculum
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum
PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum
S subiculum PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA40 area supramarginalis
BA10 area supramarginale
BA41 area temporalis transversa
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
BA43 area subcentralis
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
# von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area PD caudal postcentral area
PF supramarginal ar
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
Slice Nr. 3440
**260**

**261**


MNI Position y = -28.01 mm AHB Position y = 26.64 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum S subiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
3n oculomotor nerve cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa pcs postcentral sulcus sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tvt transverse temporal sulcus Fibers
bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato thalamic tract)
arc arcuate fascicle
dtx dorsal tegmental decussation eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis) ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus lls lateral longitudinal stria ml medial lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
mls medial longitudinal stria or optic radiation
pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
scp superior cerebellar peduncle scs subcallosal fascicle
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
sm stria medullaris of thalamus st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 54 Slice Nr. 3484
**262**

ICL: 26.64 MCP: 11.90 MNI: -28.01

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3N oculomotor n.
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus)
alv alveus of the hippocampus
APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus
AV anteroventral nucleus (anteroprincipal nucleus)
bfx body of fornix
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus
cals callosal sulcus
cc corpus calosum
Cd caudate n.
ce central sulcus
cgs cingulate sulcus CLi caudal linear n.
CM centromedian thalamic n.
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus
cp cerebral peduncle
DG dentate gyrus
DSF dorsal superficial n.
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
EW Edinger-Westphal n.
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter-
peduncularis)
hf hippocampal fissure
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus IP interpeduncular n.
its inferior temporal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LG lateral geniculate n.
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus
LV lateral ventricle
MD medial dorsal thalamic n.
MDMC mediodorsal thalamic n., magnocellular part
part
pl mediodorsal thala
MDPL mediodorsal thalamic n., paralaminar p.
MG medial geniculate n.
ml medial lemniscus
or optic radiation
PaS parasubiculum pcf paracentral fossa
PF parafascicular thalamic n.
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
PN paranigral n. pcs postcentral sulcus
Pons pons
PPA peripeduncular area PrS presubiculum
Pu putamen
RPC red nucleus, parvicellular p.
Rt reticular thalamic n.
S subiculum
subiculum
scp superior cer
scp superior cerebellar peduncle SCS subcallosal stratum
sfms superficial medullary stratum
sH Heschl sulcus
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata
st stria terminalis
sts superior temporal sulcus
TCd tail of caudate n.
TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tsv thalamostriate vein
tvt transverse temporal sulcus
VPb basal ventroposterior n. [VMpo] (entry zone
of sensory afferents) VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n.
xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar
peduncle
**263**
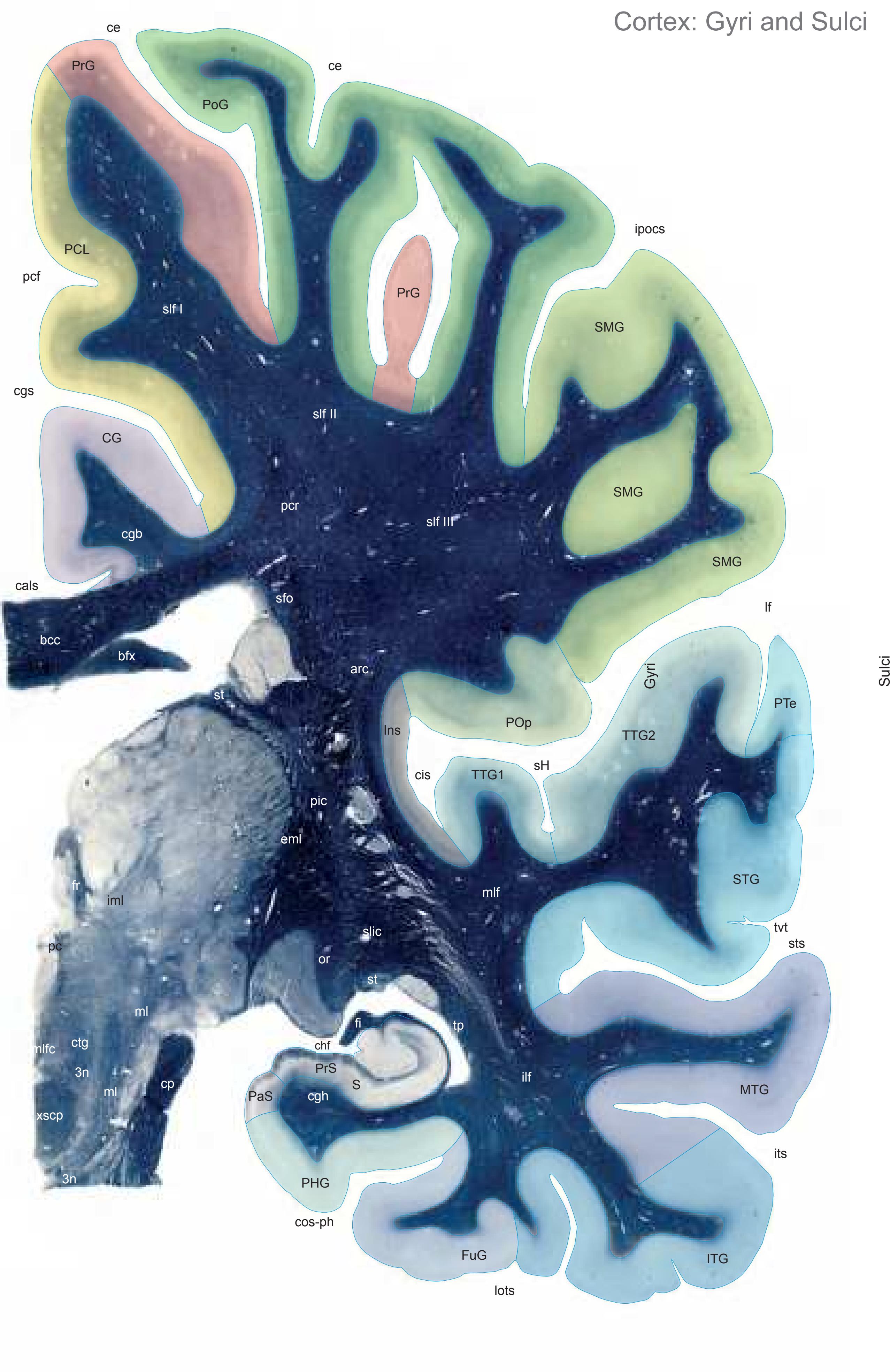

MNI Position y = -29.53 mm AHB Position y = 28.20 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos-ph collateral sulcus, phip. ramus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pc posterior commissure pcf paracentral fossa sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tvt transverse temporal sulcus Fibers
3n oculomotor nerve arc arcuate fascicle
bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle ctg central tegmental tract eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus or optic radiation pc posterior commissure
pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp.
slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
st stria terminalis tp tapetum
xscp commissure of the superior cerebellar peduncle
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 55 Slice Nr. 3542
**264**
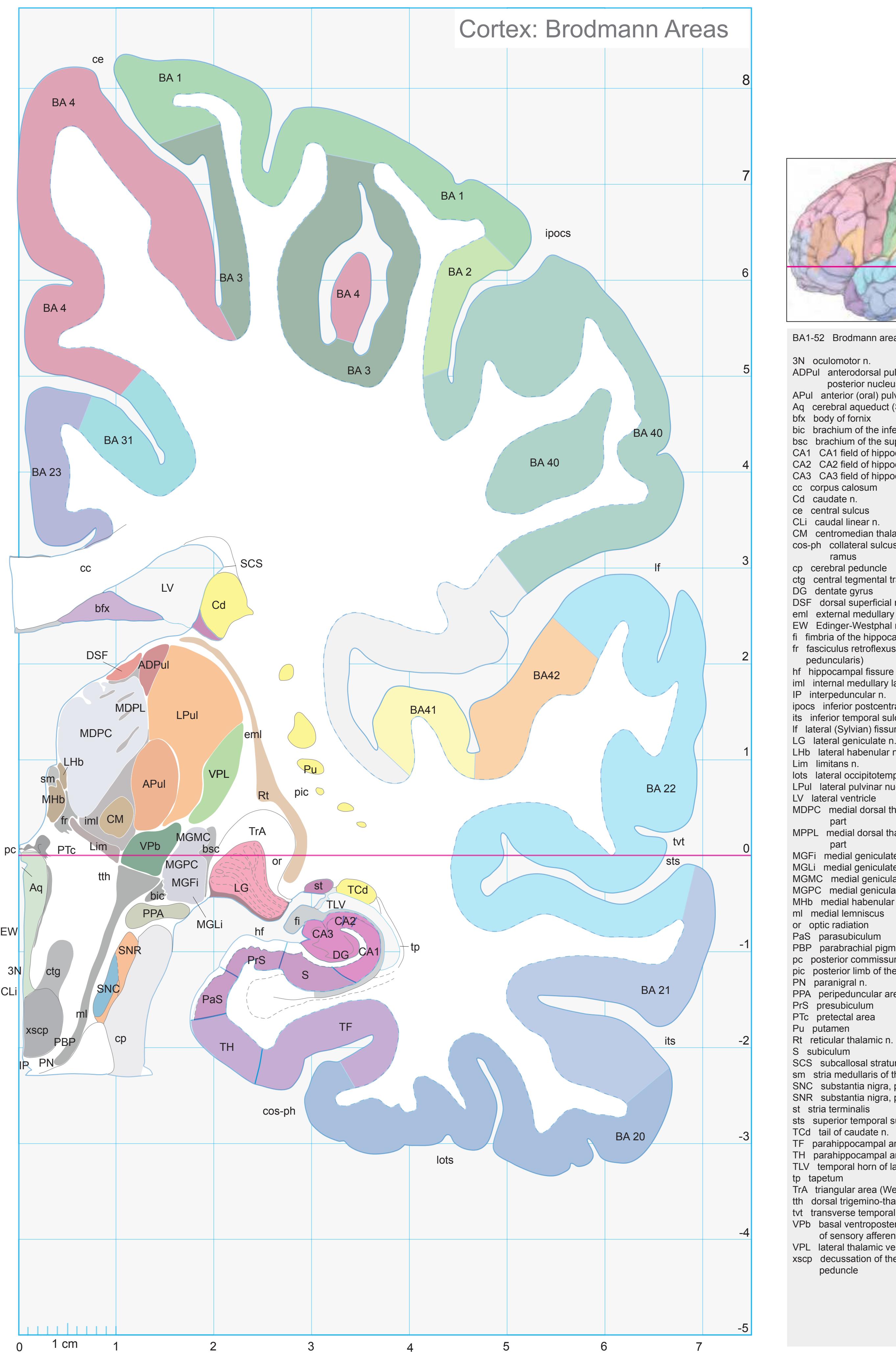
ICL: 28.20 MCP: 13.46 MNI: -29.53

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3N oculomotor n.
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus)
APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus
Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius)
bfx body of fornix
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus
CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus
cc corpus calosum
Cu caudate n.
as control sulc
ce central sulcus
CLi caudal linear n.
CM centromedian thalamic n.
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal
cp cerebral peduncle
ctg central tegmental tract
DG dentate gyrus
DSF dorsal superficial n.
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus EW Edinger-Westphal n.
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter-
peduncularis)
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus
IP interpeduncular n.
ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
LG lateral geniculate n.
LHb lateral habenular n.
Lim limitans n.
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus
LV lateral ventricle
MDPC medial dorsal thalamic n.. parvicellular part
MPPL medial dorsal thalamic n.. paralaminar
MGFi medial geniculate n., fibrosus p.
MGLi medial geniculate n., limitans p.
MGMC medial geniculate n., magnocellular p. MGPC medial geniculate n., parvicellular p.
MHb medial habenular n.
ml medial lemniscus
or optic radiation
PBP parabrachial pigmented n.
pc posterior commissure
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule
PN paranigral n.
PPA peripeduncular area
PrS presubiculum
PTc pretectal area
Pu putamen
Rt reticular th
S subiculum
SCS subcallosal stratum
sm stria medullaris of thalamus
SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata
st stria terminalis
sts superior temporal sulcus
TCd tail of caudate n.
TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tp tapetum
TrA triangular area (Wernicke)
tth dorsal trigemino-thalamic tract tvt transverse temporal sulcus
VPb basal ventroposterior n. [VMpo] (entry zone
of sensory afferents) VPL lateral thalamic ventroposterior n.
xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
**265**

MNI Position y = -29.58 mm AHB Position y = 28.17 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus
FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
PaS parasubiculum
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum
PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis BA41 area temporalis transversa interna
(anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PD caudal postcentral area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex TD intercalated supratemporal area
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TF1 middle temporal area proper
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23
24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 55 Slice Nr. 3541
**266**

**267**
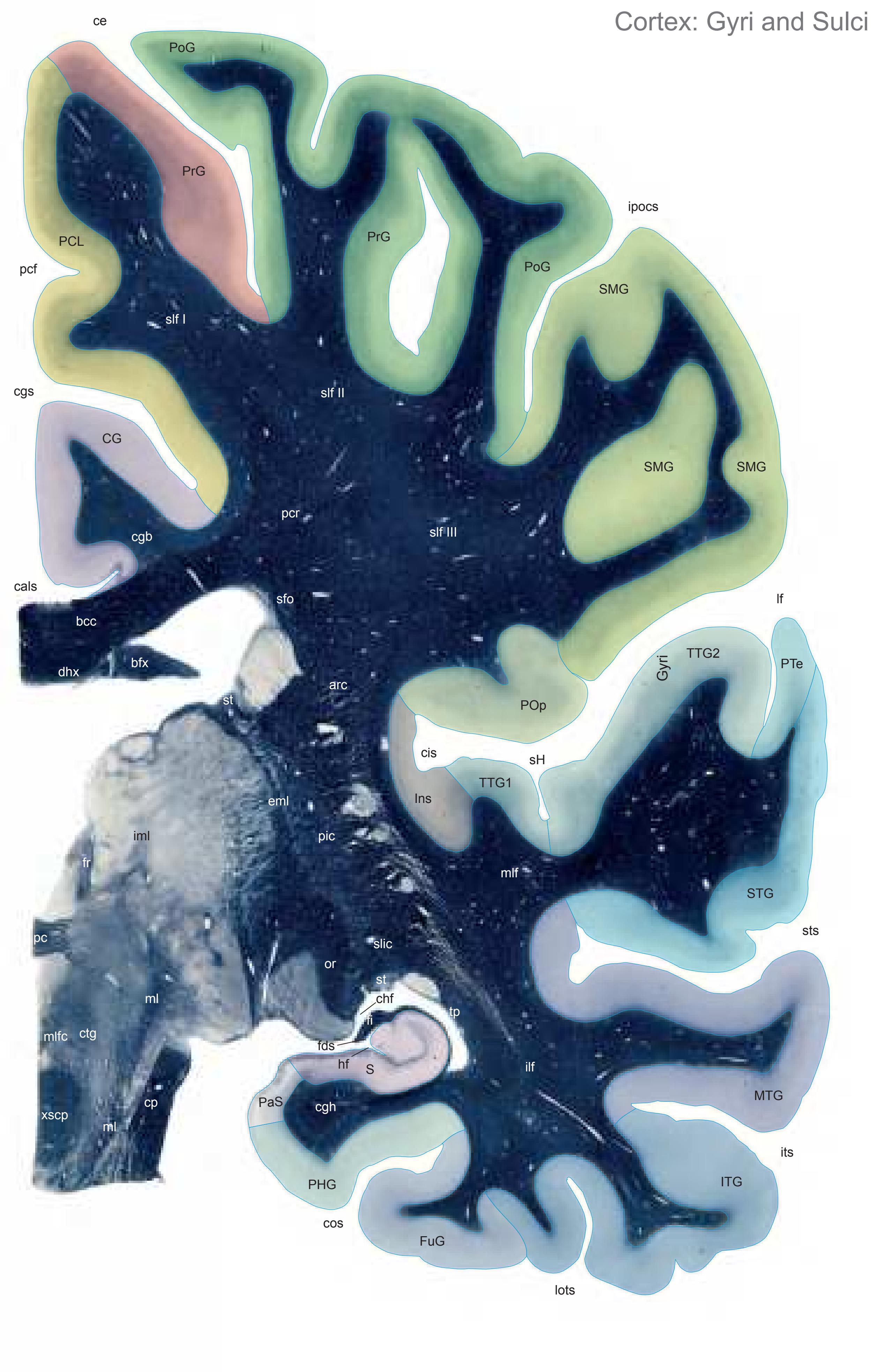

MNI Position y = -30.18 mm AHB Position y = 28.73 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
arc arcuate fascicle cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus fds fimbriodentate sulcus hf hippocampal fissure ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
bcc body of corpus callosum bfx body of fornix cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cp cerebral peduncle ctg central tegmental tract dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter peduncularis) ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ml medial lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus or optic radiation pc posterior commissure pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule st stria terminalis tp tapetum xscp decussation of the superior cereb. peduncles
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 56 Slice Nr. 3562
**268**
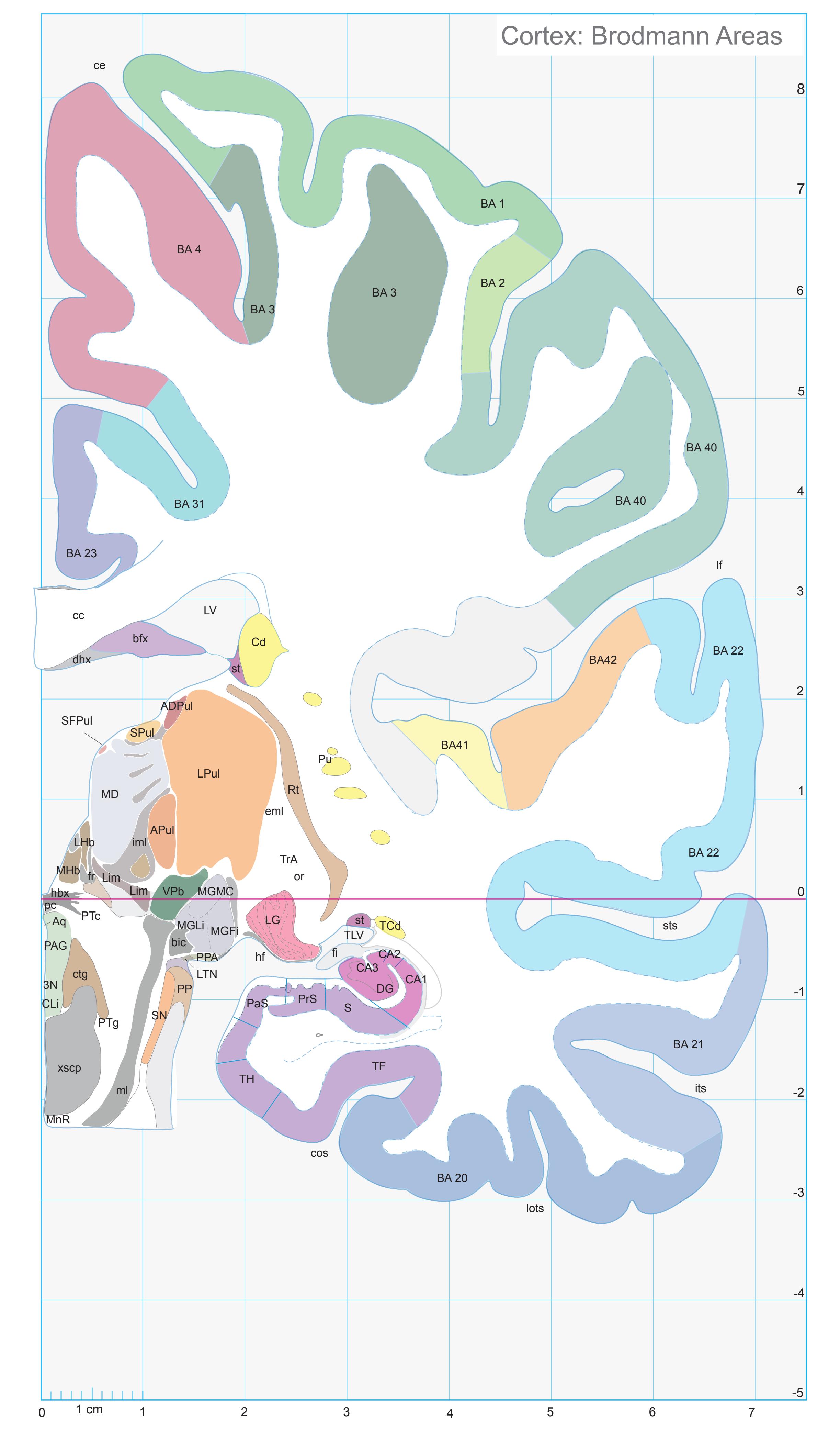
ICL: 28.73 MCP: 13.99 MNI: -30.18

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3N oculomotor n.
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus)
APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus
Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius)
bfx body of fornix
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus
cc corpus calosum
Cd caudate n.
ce central sulcus CLi caudal linear n.
cos collateral sulcus
ctg central tegmental tract
dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure
DG dentate gyrus eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus
fi fimbria of the hippocampus
fr fasciculus retroflexus (fc. habenulo-inter-
peduncularis)
hbx habenular commissure
hf hippocampal fissure
iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus its inferior temporal sulcus
lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure
LG lateral geniculate n. LHb lateral habenular n.
Lim limitans n.
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus
LTN lateral terminal n. of the accessory optic
system
LV lateral ventricle
MD medial dorsal thalamic n.
MGFi medial geniculate n., fibrosus p. MGLi medial geniculate n., limitans p.
MGMC medial geniculate n., magnocellular p.
MHb medial habenular n.
ml medial lemniscus
MnR median raphe n. or optic radiation
PAG periaqueductal gray
PaS parasubiculum pc posterior commissure
c posterior commissure
P peripeduncular n
PP peripeduncular n.
PPA peripeduncular area
PrS presubiculum
PTc pretectal area PTG pedunculotegmental n.
Pu putamen
Rt reticular thalamic n.
S subiculum
SFPul superficial pulvinar n. SN substantia nigra
SPul superior pulvinar nucleus
SPul superior pulv
et stria terminalis
st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus
sts superior tempora
TOI: tail of caudate
TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF
TH parahippocampal area TH
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
TrA triangular area (Wernicke) VPb basal ventroposterior n. [VMpo] (entry zone
of sensory afferents) xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar
peduncle
**269**


MNI Position y = -32.37 mm AHB Position y = 30.80 mm
CG cingulate gyrus
FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
arc arcuate fascicle cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus, cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa sH Heschl sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
bsc brachium of the superior colliculus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part)
crfx crus of fornix ctg central tegmental tract
ml medial lemniscus
dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ll lateral lemniscus
mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus or optic radiation
pc posterior commissure pcr posterior corona radiata
pic posterior limb of the internal capsule scc splenium of corpus callosum
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
spth spinothalamic tract st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
xscp decussation of the superior cereb. peduncles
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 57 Slice Nr. 3639
**270**

ICL: 30.80 MCP: 16.06 MNI: -32.37
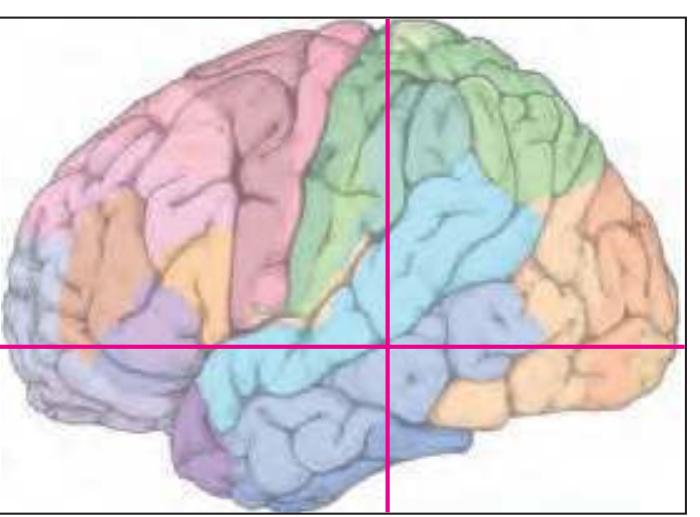
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
3n oculomotor nerve 3N oculomotor n. APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius) bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cc corpus calosum Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus CLi caudal linear n. cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix csc commissure of the superior colliculi ctg central tegmental tract DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus IGPul intergeniculatus pulvinar nucleus iml internal medullary lamina of the thalamus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LG lateral geniculate n. LHb lateral habenular n. Lim limitans n. LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle MD medial dorsal thalamic n. MDe margo denticulatus MGDP medial geniculate n., dorsal posterior p. MGFi medial geniculate n., fibrosus p. MGLi medial geniculate n., limitans p. mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus MnR median raphe n. MPul medial pulvinar nucleus or optic radiation PAG periaqueductal gray PaS parasubiculum pc posterior commissure Pi pineal gland pic posterior limb of the internal capsule PrS presubiculum PTc pretectal area PTg pedunculotegmental n. Pu putamen Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scal subcallosal fc SFPul superficial pulvinar n. SGe suprageniculate n. sfms superficial medullary stratum slic sublenticular p. of internal capsule spth spino-thalamic tract SPul superior pulvinar nucleus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
**271**


MNI Position y = -32.37 mm AHB Position y = 30.82 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum
PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum
PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SMG supramarginal gyrus
STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior) Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
IB postcentral insular area LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PD caudal postcentral area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TC supratemporal area granulosa
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
# Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23
23d dorsal division of BA 23
24d subregion of BA 24
p24' anterior division of BA24 p33' posterior subregion of BA33
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 57 Slice Nr. 3640
**272**

**273**
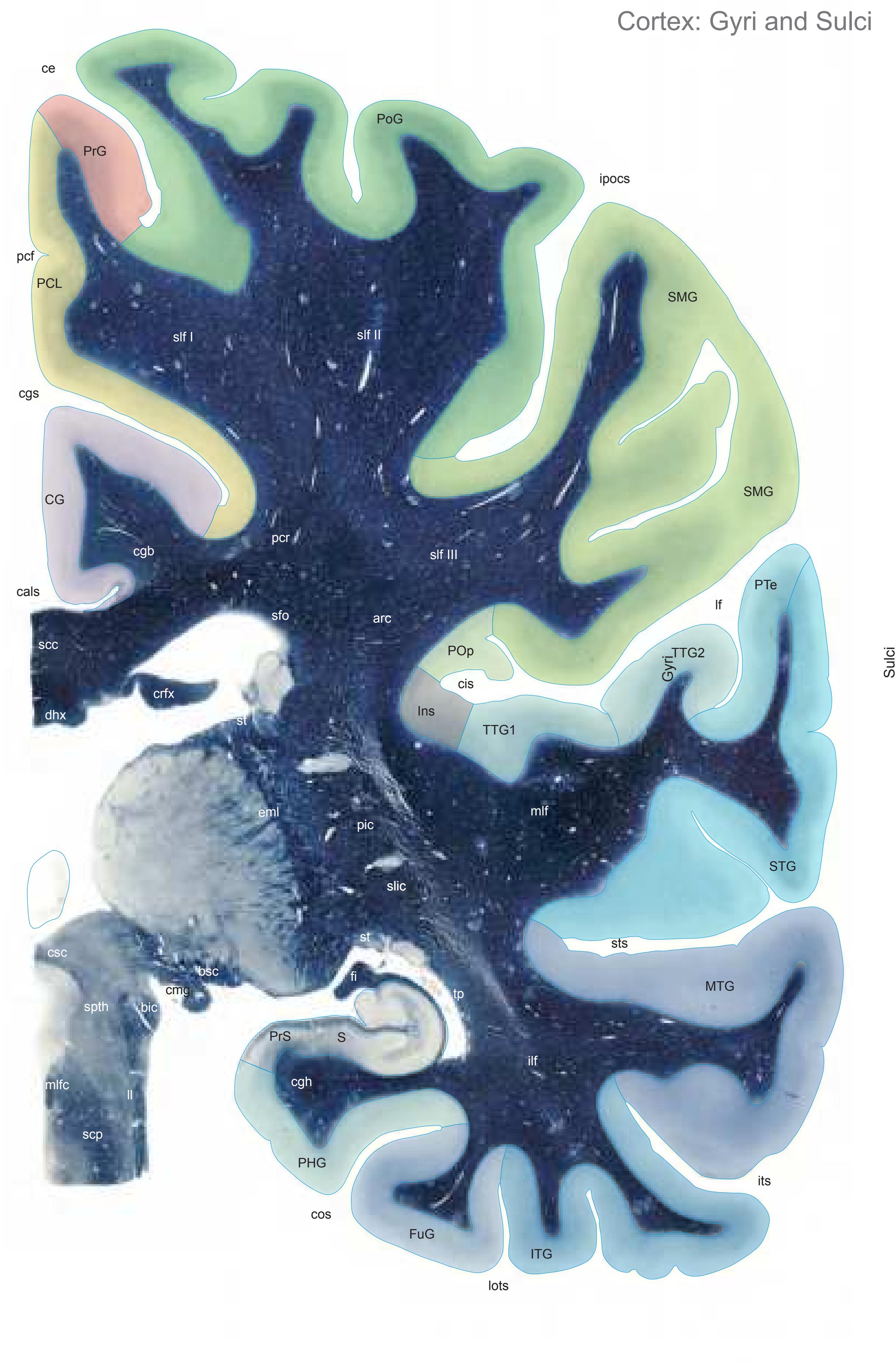

MNI Position y = -33.78 mm AHB Position y = 32.11 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus, cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus
cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part)
cmg capsule of the medial geniculate n. crfx crus of fornix csc commissure of the superior colliculi dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure
eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ll lateral lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle
pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule scc splenium of corpus callosum scp superior cerebellar peduncle
mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule spth spinothalamic tract
st stria terminalis tp tapetum
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 58 Slice Nr. 3688
**274**
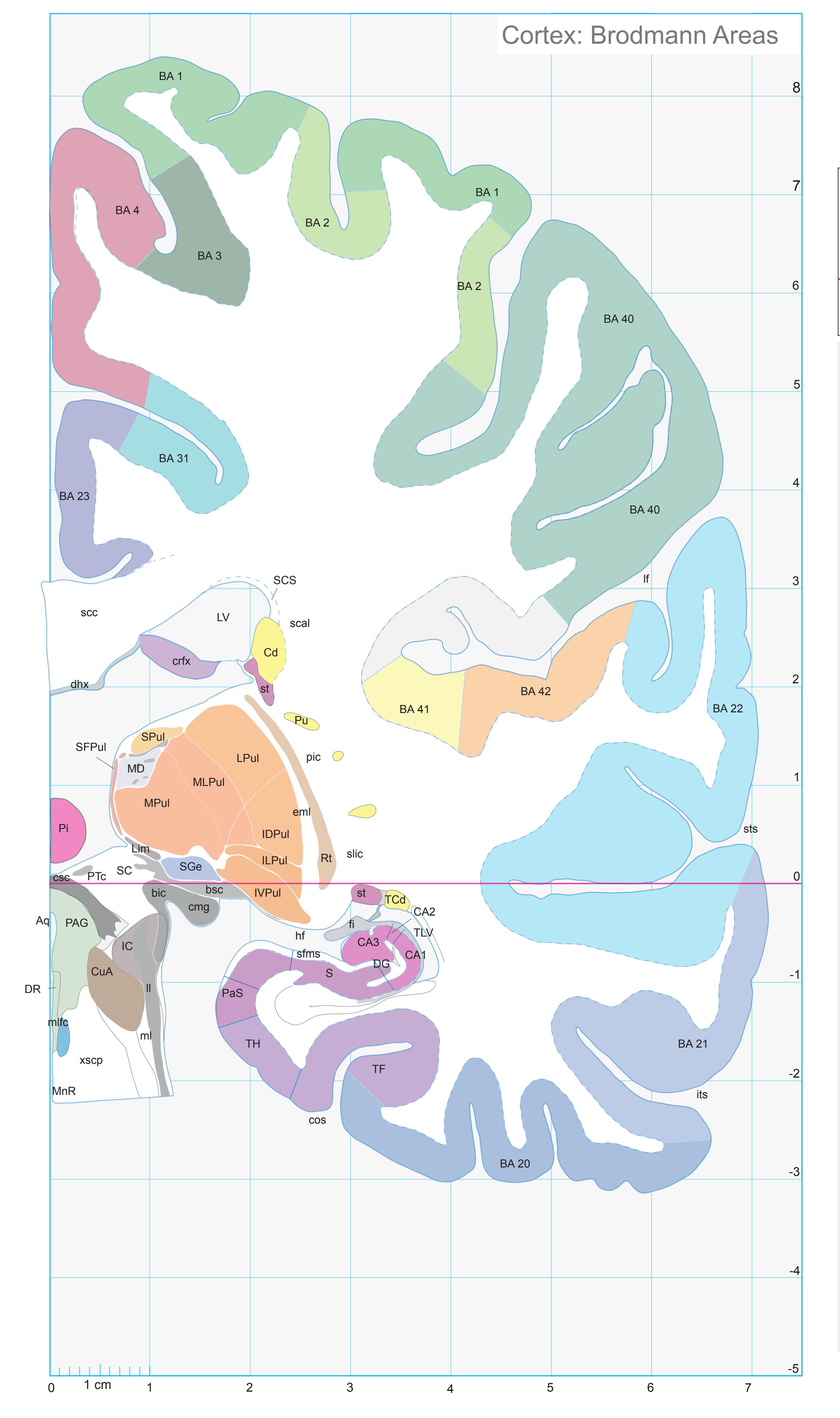
ICL: 32.11 MCP: 17.37 MNI: -33.78

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius) bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. cmg capsule of the medial geniculate n. cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix csc commissure of the superior colliculi CuA cuneiform area DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure DR dorsal raphe n. eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus hf hippocampal fissure IC inferior colliculus IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal p. ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate p. its inferior temporal sulcus IVPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, ventral p. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure Lim limitans n. ll lateral lemniscus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle MD medial dorsal thalamic n. ml medial lemniscus mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MnR median raphe n. MPul medial pulvinar nucleus PAG periaqueductal gray PaS parasubiculum Pi pineal gland pic posterior limb of the internal capsule PTc pretectal area Pu putamen
SCS subcallosal stratum sfms superficial medullary stratum SFPul superficial pulvinar n. SGe suprageniculate n.
scc splenium of corpus callosum
slic sublenticular p. of internal capsule SPul superior pulvinar nucleus st stria terminalis
sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n.
Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scal subcallosal fc
TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH
TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle xscp decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
**275**


MNI Position y = -35.08 mm AHB Position y = 33.42 mm
CG cingulate gyrus
Sulci
FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PaS parasubiculum PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus PrS presubiculum PTe planum temporale S subiculum SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus, cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcf paracentral fossa ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus
cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix
csc commissure of the superior colliculi dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus
ll lateral lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus pcr posterior corona radiata pic posterior limb of the internal capsule scc splenium of corpus callosum
scp superior cerebellar peduncle
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule
spth spinothalamic tract st stria terminalis tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 59 Slice Nr. 3737
**276**

ICL: 33.42 MCP: 18.68 MNI: -35.08
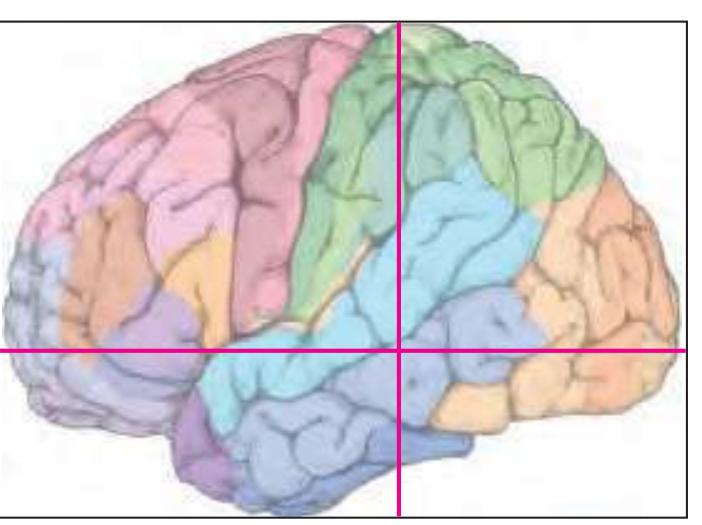
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101) Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius) bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix csc commissure of the superior colliculi CuF cuneiform n. DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus hf hippocampal fissure IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal p. IGr indusium griseum ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate p. ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus IPul inferior pulvinar nucleus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle MiTg microcellular tegmental n. ml medial lemniscus mlfc medial longitudinal fasciculus MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MPul medial pulvinar nucleus PAG periaqueductal gray PaS parasubiculum pcf paracentral fossa Pi pineal gland ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrCuF precuneiform area PrS presubiculum PTg pedunculotegmental n. Pu putamen RSC retrosplenial cortex Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scc splenium of corpus callosum SFPul superficial pulvinar n.
sms spramarginal sulcus SPul superior pulvinar nucleus
TH parahippocampal area TH TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tsc tenia semicircularis
st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF
tfx tenia of fornix
**277**

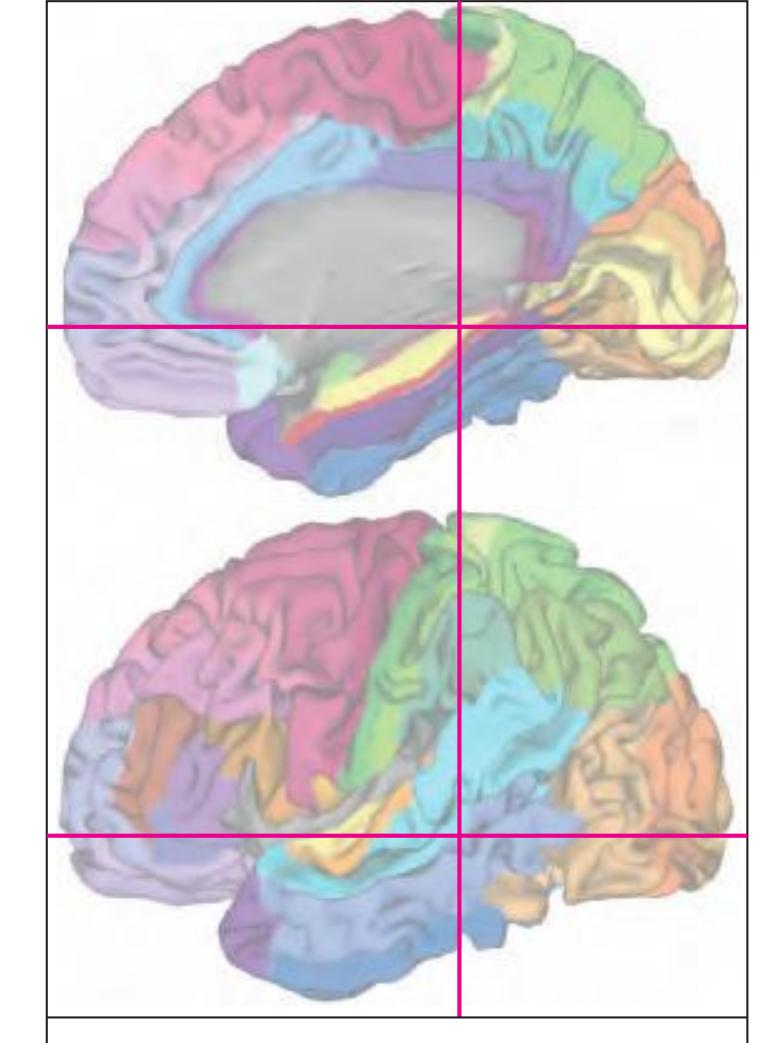
MNI Position y = -35.13 mm AHB Position y = 33.45 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
PCL paracentral lobule
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus
PrS presubiculum
PTe planum temporale
S subiculum
SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus
TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA41 area temporalis transversa interna (anterior)
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area IB postcentral insular area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area PC intermediate postcentral area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TC supratemporal area granulosa
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23
23d dorsal division of BA 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 59 Slice Nr. 3738
**278**

**279**


MNI Position y = -36.57 mm AHB Position y = 34.82 mm
CG cingulate gyrus
Sulci
FuG fusiform gyrus IC inferior colliculus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PSR perisplenial region PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior part cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
4n trochlear nerve arc arcuate fascicle bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cic commissure of the inferior colliculi crfx crus of fornix dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ll lateral lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle pcr posterior corona radiata scc splenium of corpus callosum scp superior cerebellar peduncle sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sms superficial medullary stratum spth spinothalamic tract st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 60 Slice Nr. 3789
**280**


ICL: 34.82 MCP: 20.08 MNI: -36.57

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix CuF cuneiform n. DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure DTg dorsal tegmental n. eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus hf hippocampal fissure IC inferior colliculus IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal p. ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus LDTg laterodordal tegmental n. lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle Me5 mesencephalic trigeminal n. MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MPul medial pulvinar nucleus PAG periaqueductal gray pcf paracentral fossa Pi pineal gland ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrS presubiculum PSR perisplenial region Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scc splenium of corpus callosum scp superior cerebellar peduncle SFPul superficial pulvinar n. sms spramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF
TH parahippocampal area TH TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
**281**


MNI Position y = -37.13 mm AHB Position y = 35.16 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PSR perisplenial region PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior part chf choroid fissure cis circular sulcus cos collateral sulcus ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
4n trochlear nerve
tp tapetum
arc arcuate fascicle bic brachium of the inferior colliculus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cic commissure of the inferior colliculi crfx crus of fornix dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ll lateral lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle pcr posterior corona radiata scc splenium of corpus callosum scp superior cerebellar peduncle sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sms superficial medullary stratum st stria terminalis
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 61 Slice Nr. 3802
**282**

ICL: 35.16 MCP: 20.42 MNI: -37.13
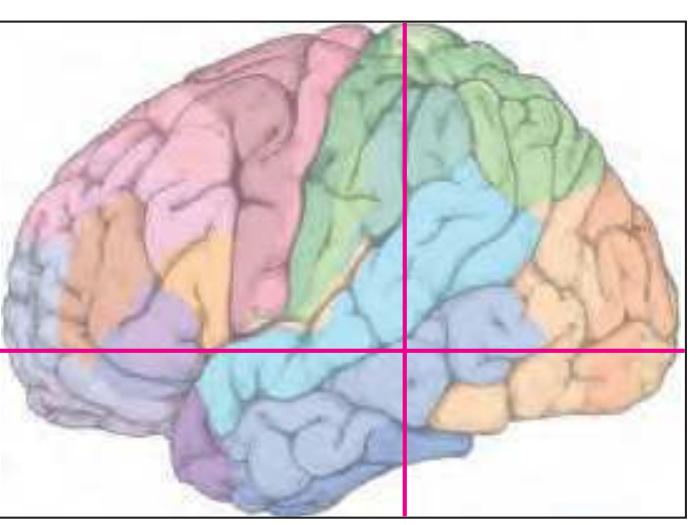
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus bsc brachium of the superior colliculus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus Cd caudate n. ce central sulcus cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior p. cis circular insular sulcus cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix CuF cuneiform n. DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure DTg dorsal tegmental n. eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus hf hippocampal fissure IC inferior colliculus IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal p. ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate p. ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus IPul inferior pulvinar nucleus its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure LDTg laterodordal tegmental n. lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle Me5 mesencephalic trigeminal n. MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MPul medial pulvinar nucleus PAG periaqueductal gray Pi pineal gland ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrS presubiculum PSR perisplenial region Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scc splenium of corpus callosum scp superior cerebellar peduncle SFPul superficial pulvinar n. sms spramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF TH parahippocampal area TH TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle tsv thalamostriate vein
**283**
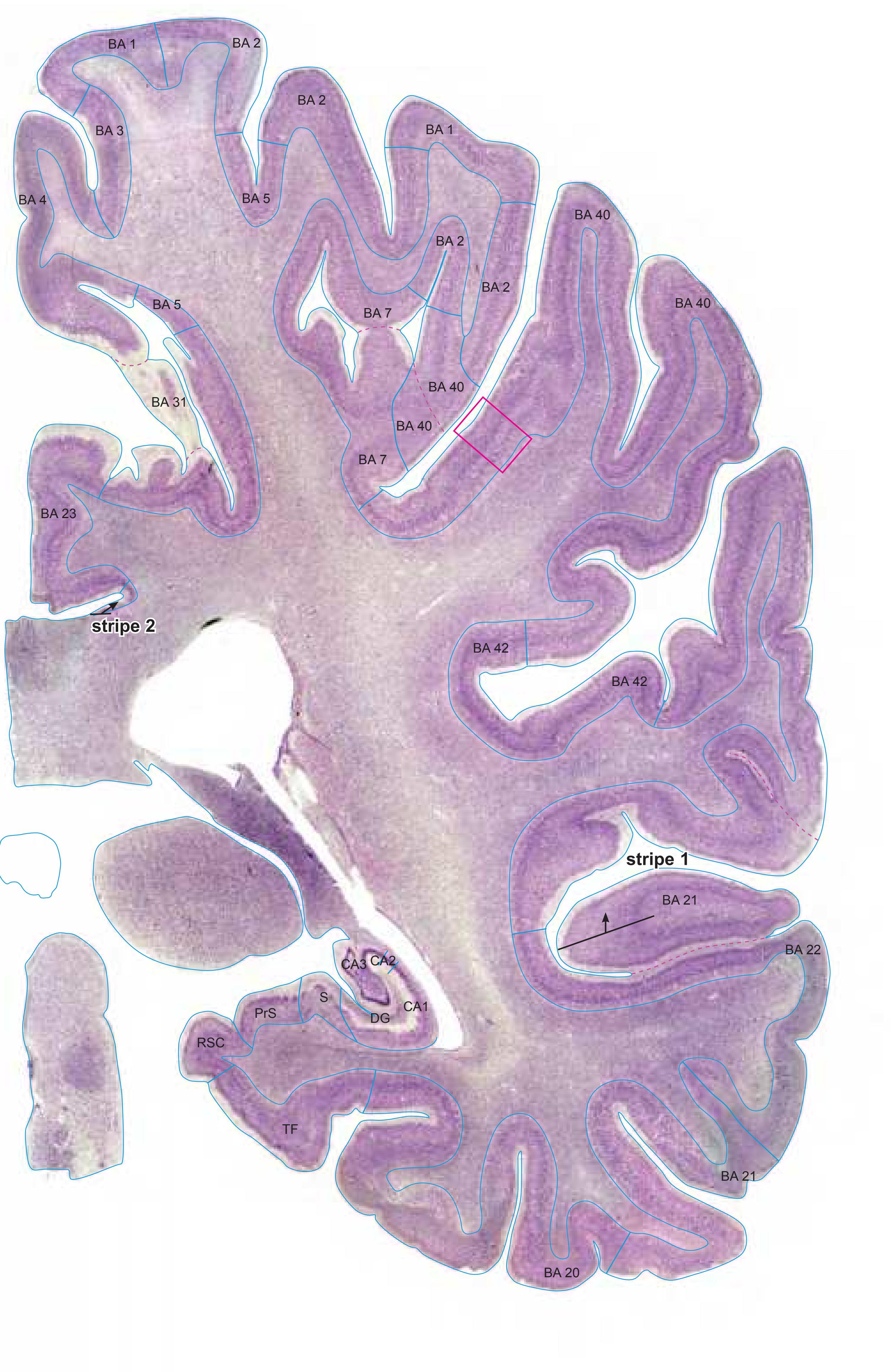

MNI Position y = -37.44 mm AHB Position y = 35.65 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus IC inferior colliculus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum
PrS presubiculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
TTG1 ant. transverse temp. gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
Brodmann Areas BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis BA5 area praeparietalis
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TC supratemporal area granulosa
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23 23d dorsal division of BA 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 61 Slice Nr. 3820
**284**

**285**
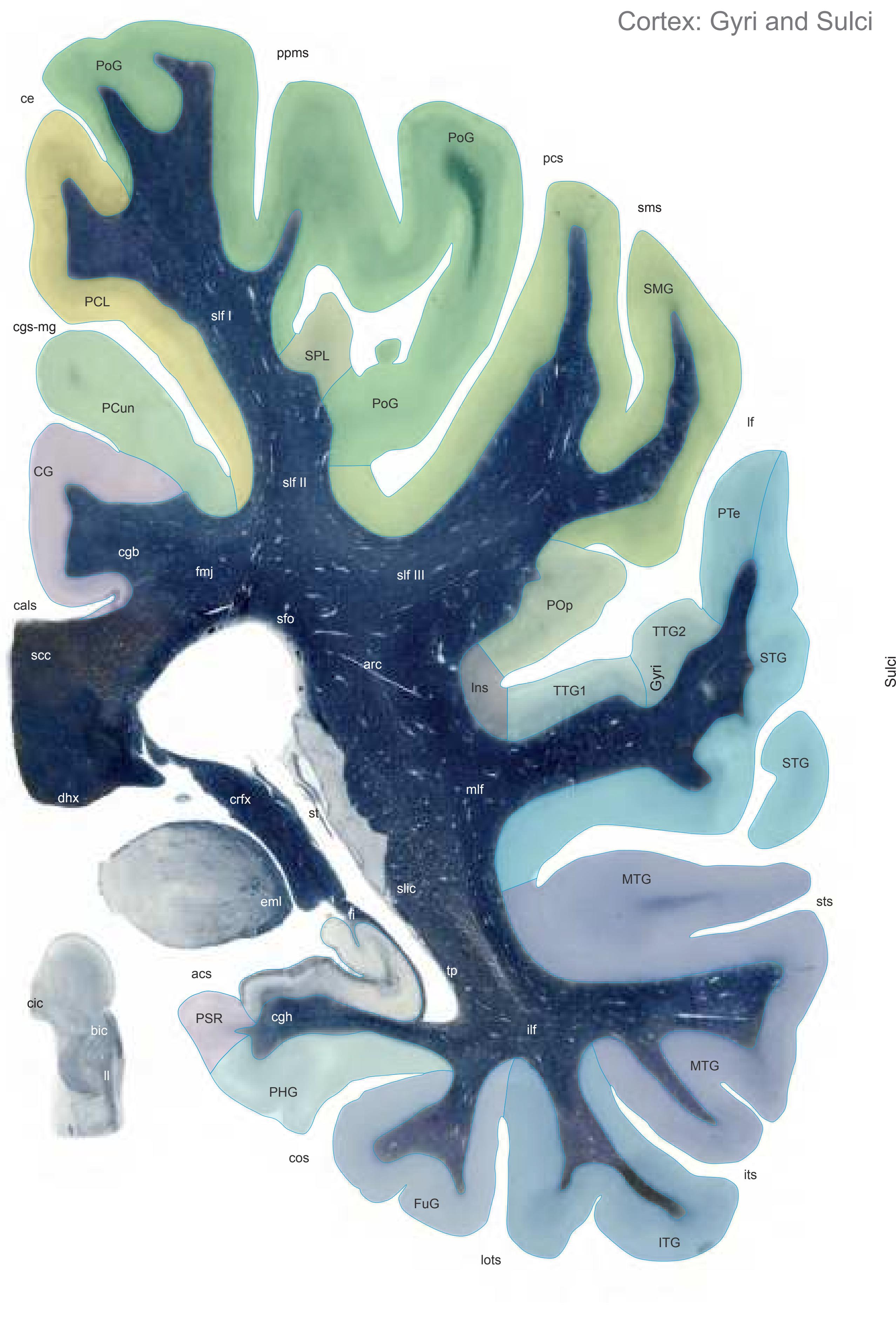

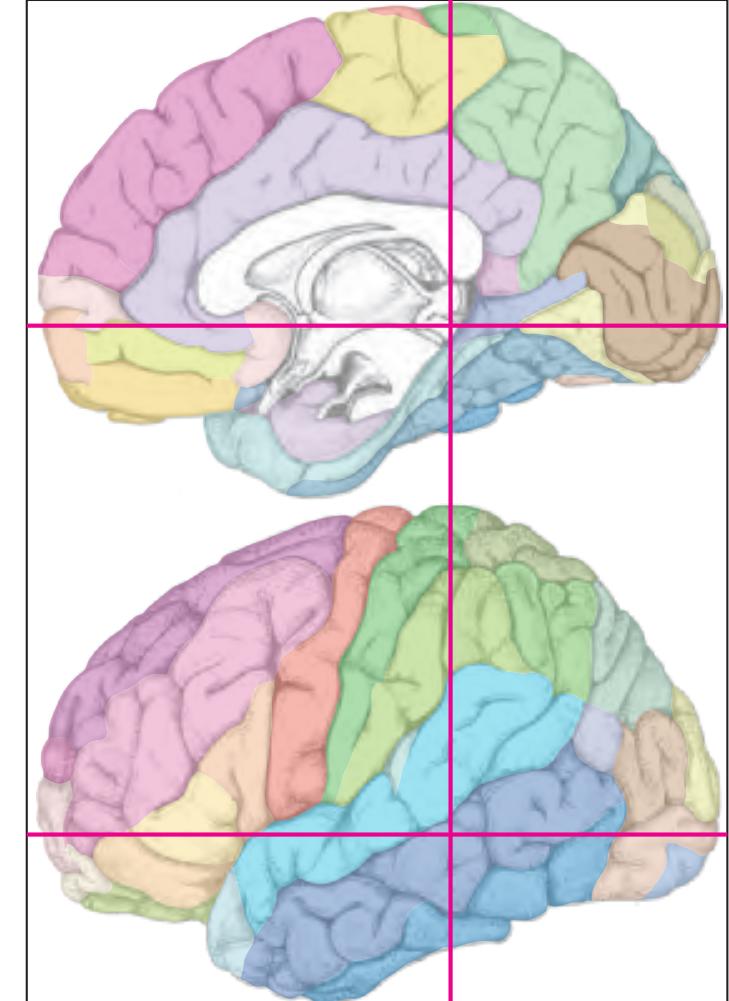
MNI Position y = -37.95 mm AHB Position y = 36.21 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus IC inferior colliculus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PSR perisplenial region PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cals callosal sulcus Fibers
ce central sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pcs postcentral sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus
arc arcuate fascicle bic brachium of the inferior colliculus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) cic commissure of the inferior colliculi crfx crus of fornix dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus fi fimbria of the hippocampus fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle ll lateral lemniscus mlf middle longitudinal fascicle scc splenium of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sms superficial medullary stratum st stria terminalis
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 62 Slice Nr. 3841
**286**

ICL: 36.21 MCP: 21.47 MNI: -37.95
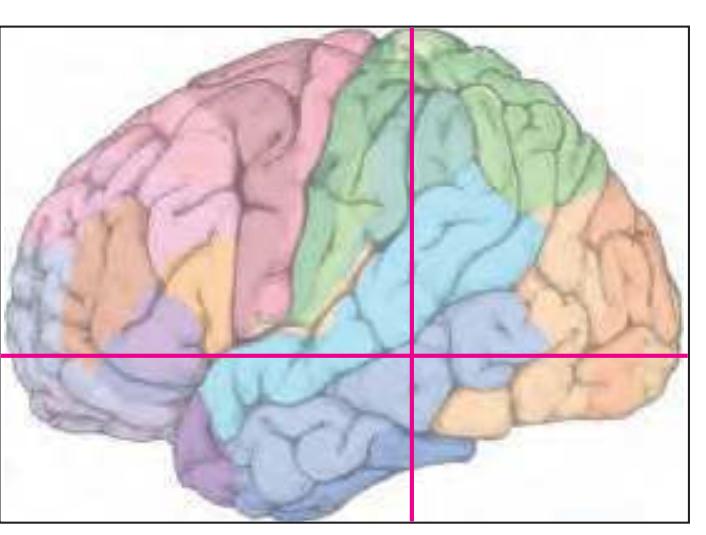
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cic commissure of the inferior colliculi cis circular insular sulcus cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix DG dentate gyrus dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure eml external medullary lamina of the thalamus IC inferior colliculus ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate p. ipocs inferior postcentral sulcus IPul inferior pulvinar nucleus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus LV lateral ventricle MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MPul medial pulvinar nucleus PAG periaqueductal gray PBG parabigeminal n. ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrS presubiculum PSR perisplenial region Rt reticular thalamic n. S subiculum SC superior colliculus scc splenium of corpus callosum SFPul superficial pulvinar n. sms spramarginal sulcus st stria terminalis sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n.
TF parahippocampal area TF TLV temporal horn of lateral ventricle
tsv thalamostriate vein
**287**


MNI Position y = -42.31 mm AHB Position y = 40.28 mm
CG cingulate gyrus
Sulci
DG dentate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fds fimbriodentate sulcus hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure fi fimbria of the hippocampus fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle mlf middle longitudinal fascicle scc splenium of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. slic sublenticular part of internal capsule sms superficial medullary stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 63 Slice Nr. 3993
**288**

ICL: 40.28 MCP: 25.54 MNI: -42.31
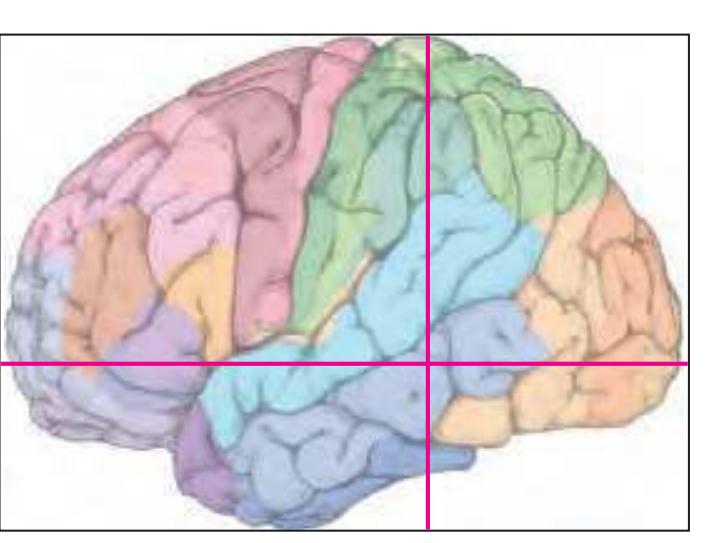
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus ARG Andreas Retzii gyrus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus crfx crus of fornix dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure DG dentate gyrus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lf lateral (Sylvian) fissure lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrS presubiculum PSR perisplenial region S subiculum scc splenium of corpus callosum sms spramarginal sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus TCd tail of caudate n. TF parahippocampal area TF
TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
**289**
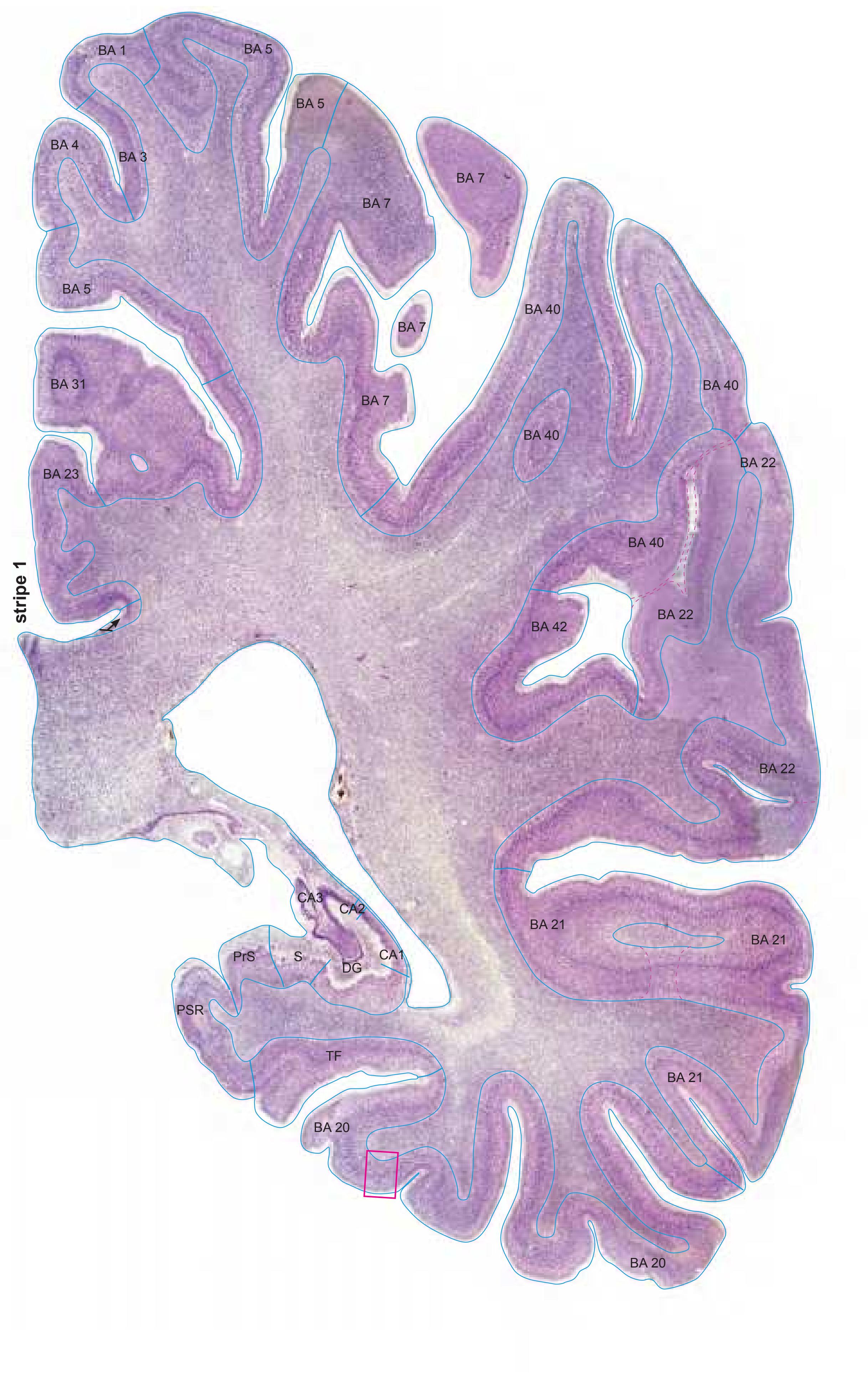

MNI Position y = -42.79 mm AHB Position y = 40.74 mm
#### Gyral Pattern
CG cingulate gyrus DG dentate gyrus
FG fasciolar gyrus
FuG fusiform gyrus
Ins insula
ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5)
MTG middle temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyrus
PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus
PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum
PTe planum temporale
SMG supramarginal gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus
#### Brodmann Areas
BA1 area postcentralis intermedia
BA3 area postcentralis oralis
BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA5 area praeparietalis
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa
(posterior)
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
#### von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex TC supratemporal area granulosa
TC supratemporal area granulosa
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area TH hippocampotemporal area
#### Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23 23d dorsal division of BA 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 63 Slice Nr. 4010
**290**


MNI Position y = -43.66 mm AHB Position y = 41.57 mm
ARG Andreas Retzii gyrus CG cingulate gyrus DG dentate gyrus FG fasciolar gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Ins insula ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv hf hippocampal fissure its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus sms supramarginal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix fi fimbria of the hippocampus fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mlf middle longitudinal fascicle scc splenium of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sms superficial medullary stratum
tp tapetum
Sulci
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 64 Slice Nr. 4041
**292**
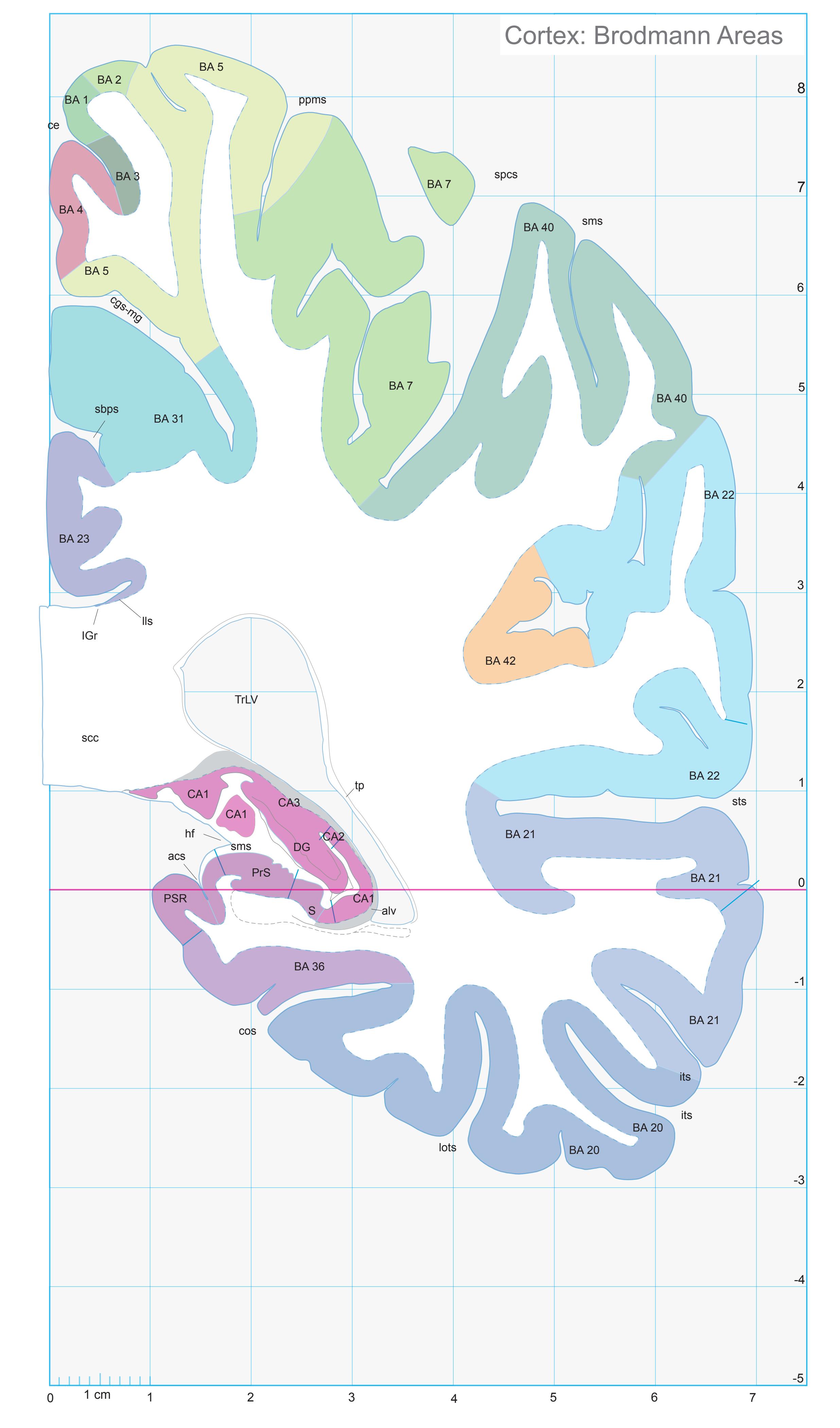
ICL: 41.57 MCP: 26.83 MNI: -43.66

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus alv alveus of the hippocampus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus DG dentate gyrus hf hippocampal fissure IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lls lateral longitudinal stria lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PrS presubiculum PSR perisplenial region S subiculum sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum sms spramarginal sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tp tapetum TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
**293**


MNI Position y = -45.04 mm AHB Position y = 42.88 mm
ARG Andreas Retzii gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
alv alveus of the hippocampus arc arcuate fascicle cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mlf middle longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria scc splenium of corpus callosum sfo superior fronto-occipital fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 65 Slice Nr. 4090
**294**

ICL: 42.88 MCP: 28.14 MNI: -45.04

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus alv alveus of the hippocampus ARG Andreas Retzii gyrus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lls lateral longitudinal stria lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PSR perisplenial region S subiculum sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum sms spramarginal sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tp tapetum TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
**295**
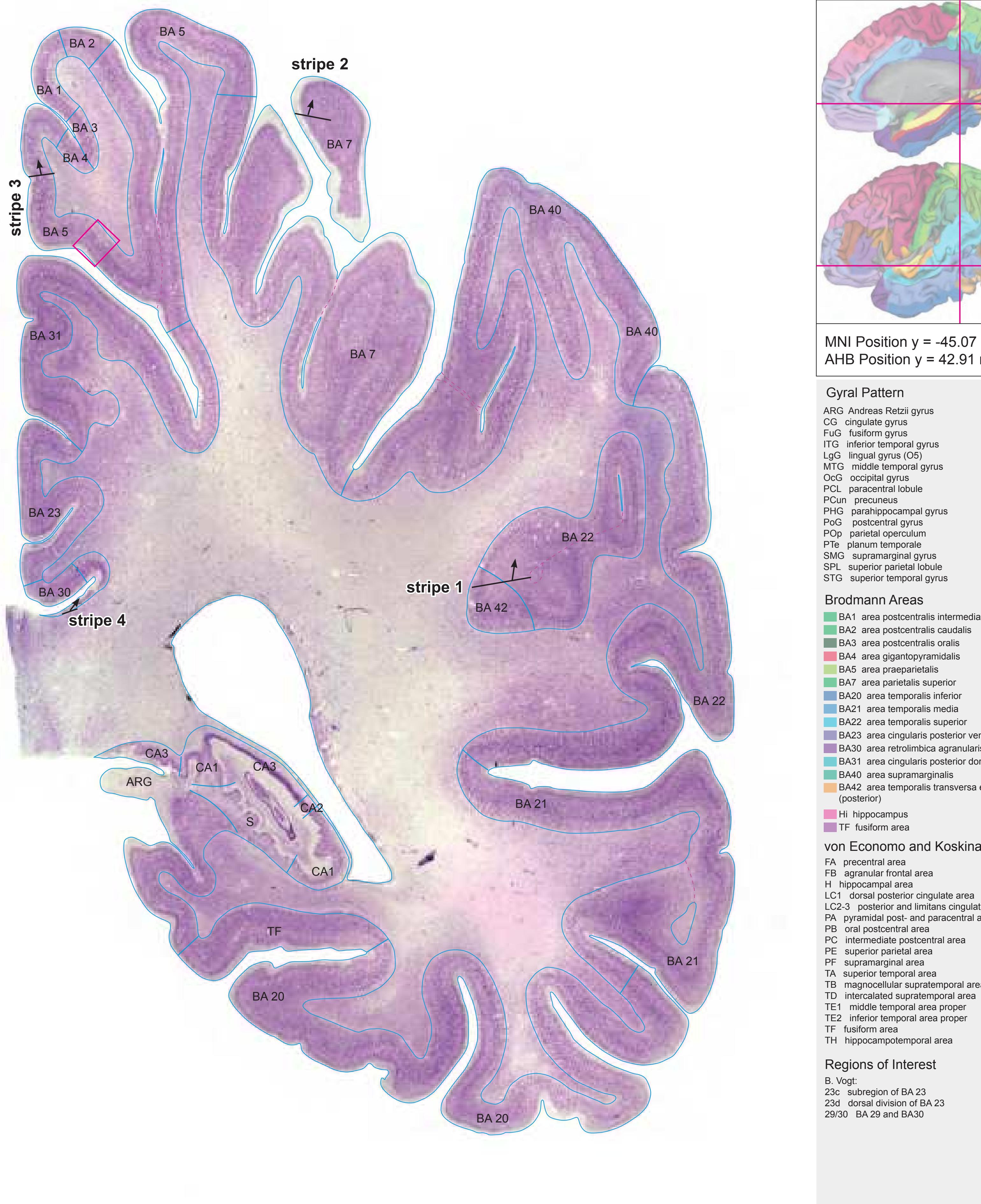
MNI Position y = -45.07 mm AHB Position y = 42.91 mm
## Gyral Pattern
ARG Andreas Retzii gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus
POp parietal operculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas

BA2 area postcentralis caudalis
BA3 area postcentralis oralis BA4 area gigantopyramidalis
BA5 area praeparietalis
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA20 area temporalis inferior
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA31 area cingularis posterior
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA40 area supramarginalis
BA42 area temporalis transversa externa (posterior)
Hi hippocampus
TF fusiform area
## von Economo and Koskinas
FA precentral area
FB agranular frontal area
H hippocampal area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area
TA superior temporal area
TB magnocellular supratemporal area simplex
TD intercalated supratemporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TE2 Inferior temporal area
TF fusiform area
TF fusiform area TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23c subregion of BA 23 23d dorsal division of BA 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 65 Slice Nr. 4091
**296**
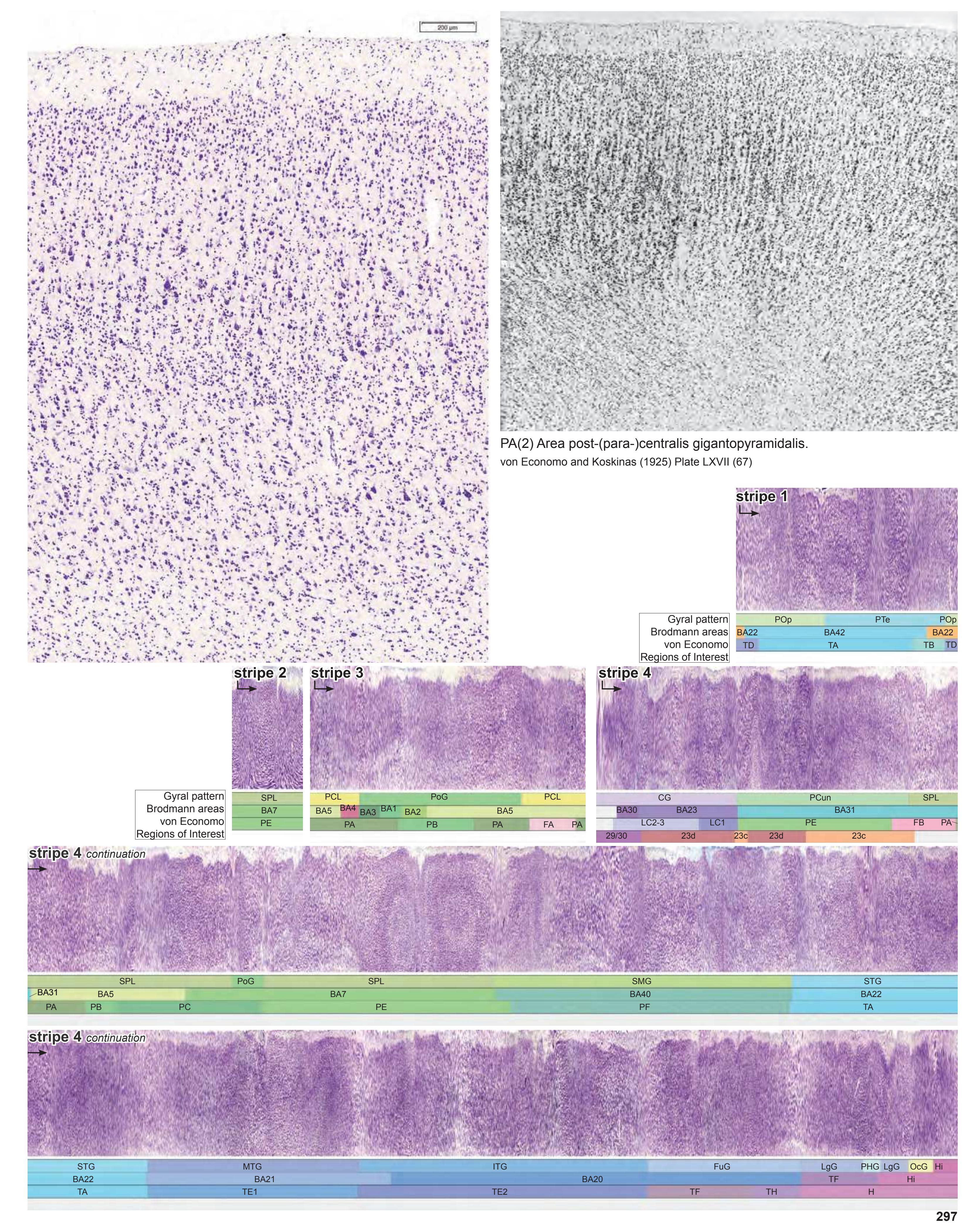
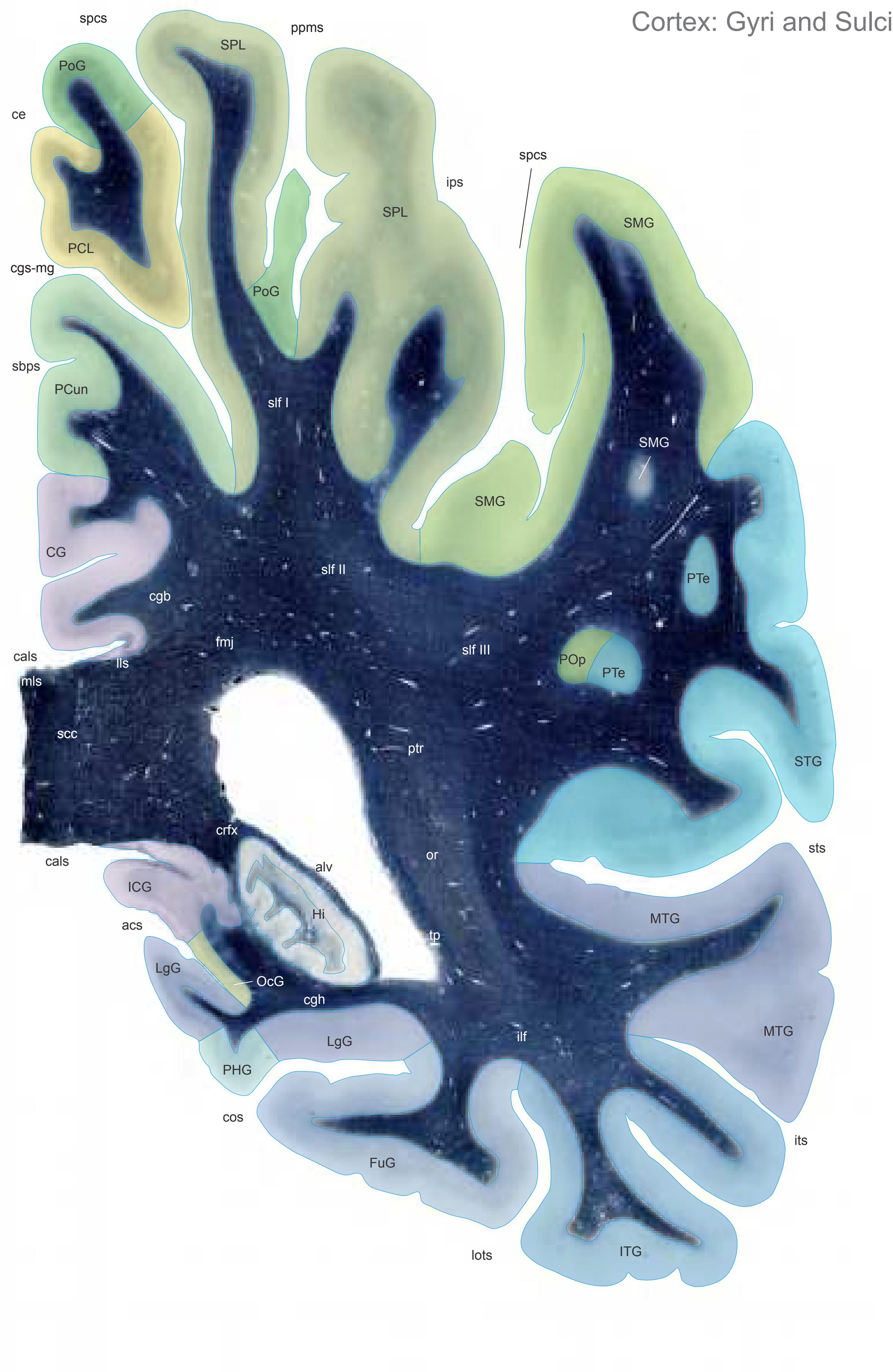
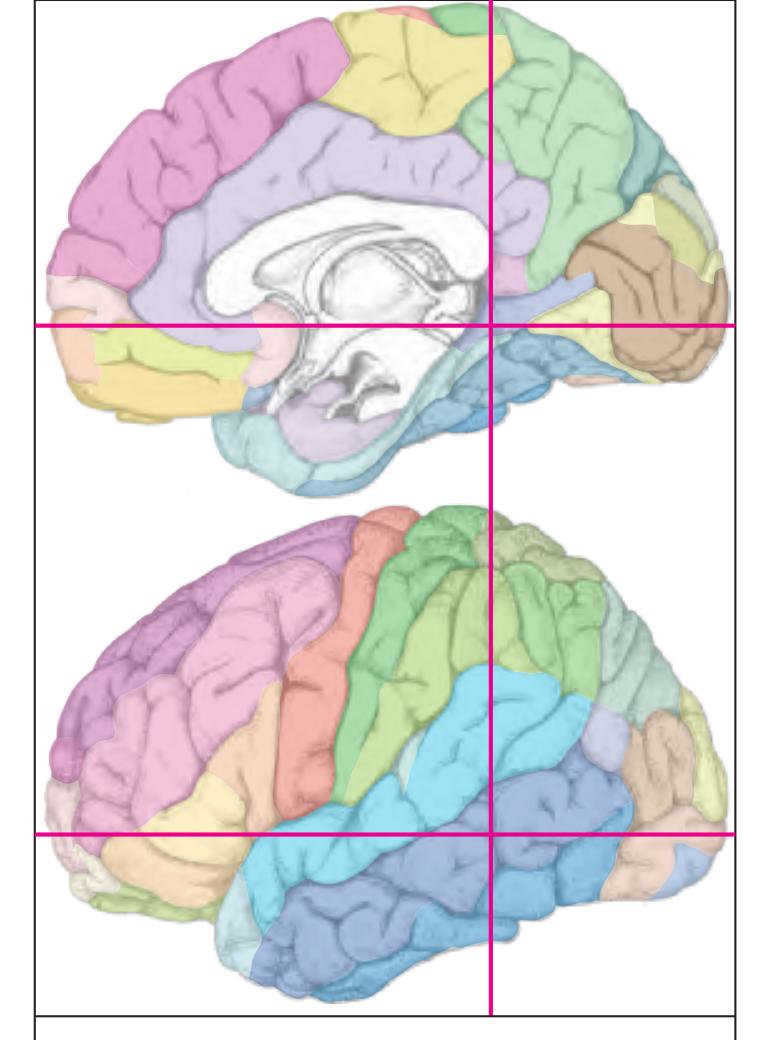
MNI Position y = -46.42 mm AHB Position y = 44.20 mm
CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cals callosal sulcus ce central sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus Fibers
Sulci
alv alveus of the hippocampus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria or optic radiation ptr posterior thalamic radiation scc splenium of corpus callosum slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 66 Slice Nr. 4139
**298**
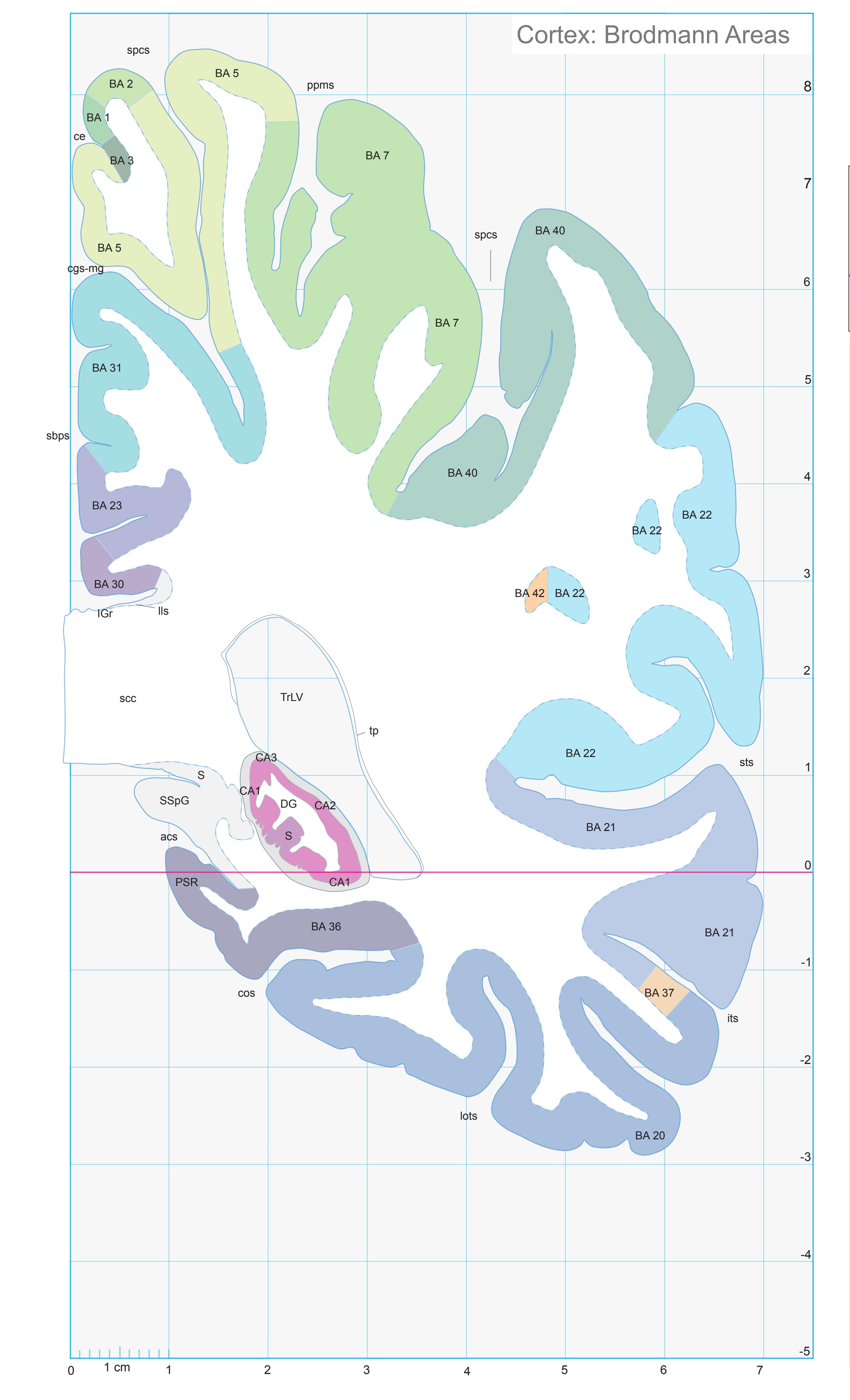
ICL: 44.20 MCP: 29.46 MNI: -46.42

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus ce central sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus DG dentate gyrus IGr indusium griseum its inferior temporal sulcus lls lateral longitudinal stria lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus PSR perisplenial region S subiculum sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum spcs superior postcentral sulcus SSpG subsplenial gyrus sts superior temporal sulcus tp tapetum TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
**299**


MNI Position y = -47.89 mm AHB Position y = 45.59 mm
AAnG anterior angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule SSpG subsplenial gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal part its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus Fibers
alv alveus of the hippocampus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) crfx crus of fornix fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle lls lateral longitudinal stria mls medial longitudinal stria or optic radiation ptr posterior thalamic radiation scc splenium of corpus callosum slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
tp tapetum
Sulci
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 67 Slice Nr. 4191
**300**
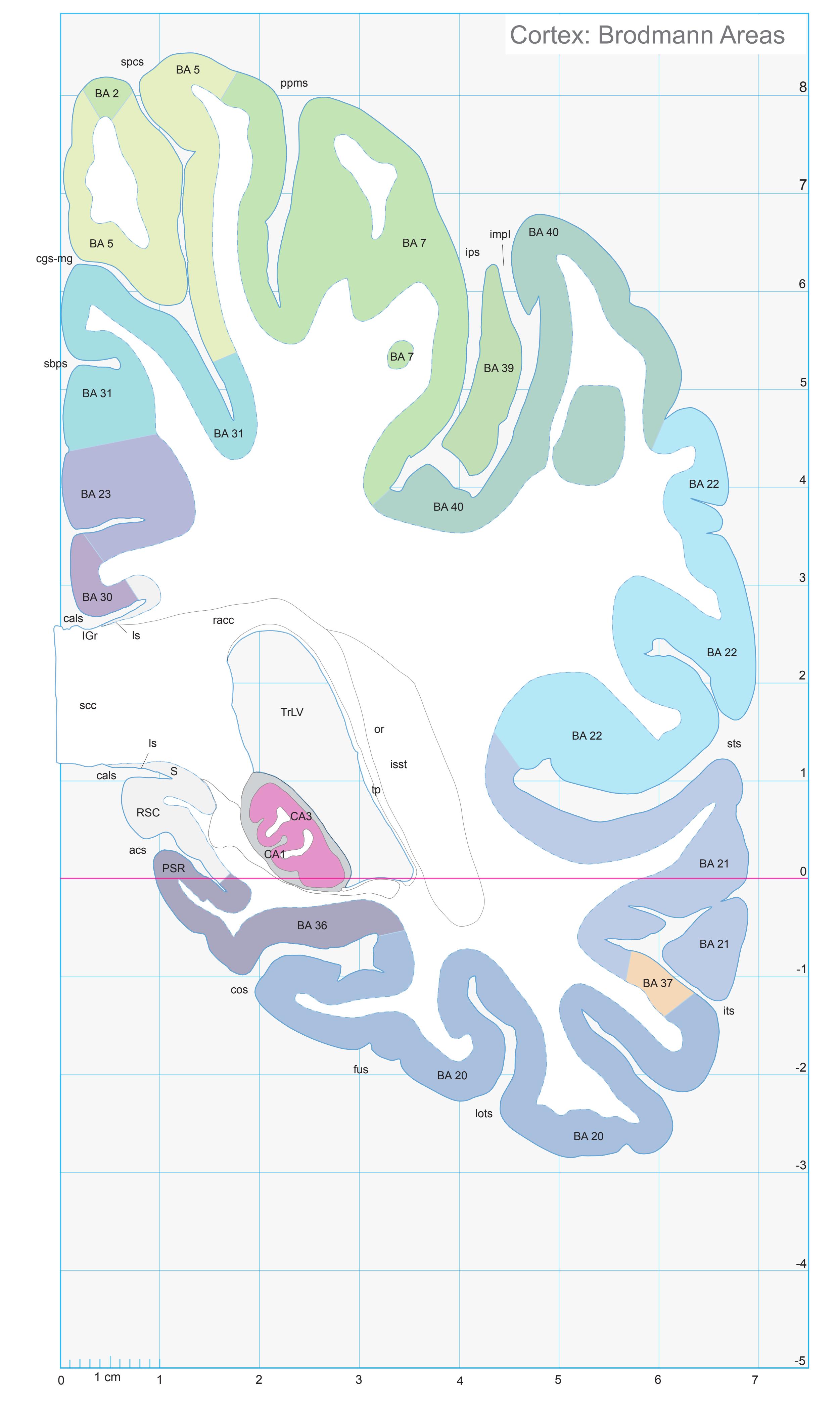
ICL: 45.59 MCP: 30.85 MNI: -47.89

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus fus midfusiform sulcus IGr indusium griseum impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen ips intraparietal sulcus isst internal sagittal stratum its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ls longitudinal stria or optic radiation ppms posterior paramidline sulcus
PSR perisplenial region RSC retrosplenial cortex S subiculum sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
racc radiation of corpus callosum
TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
tp tapetum
**301**
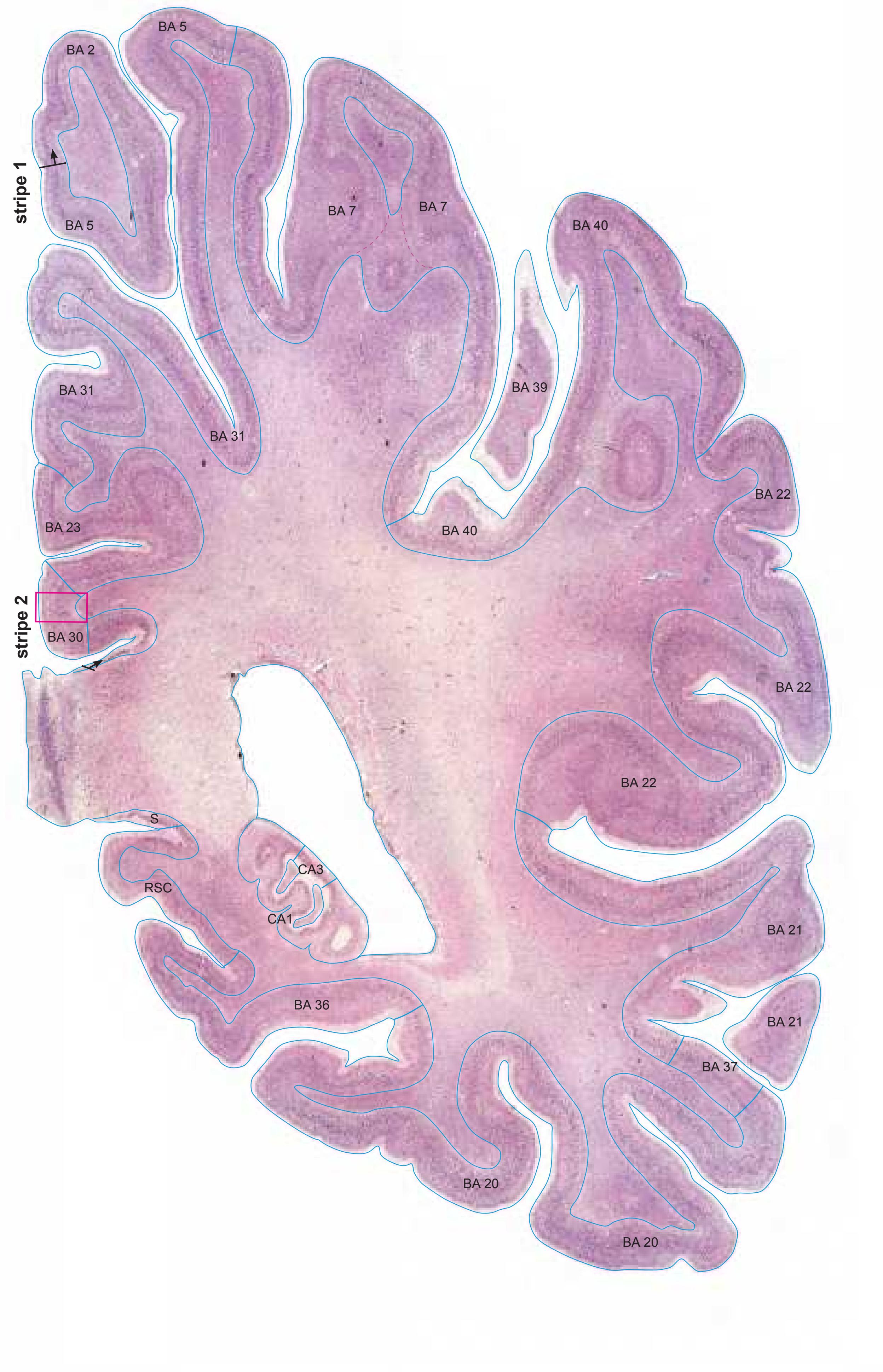
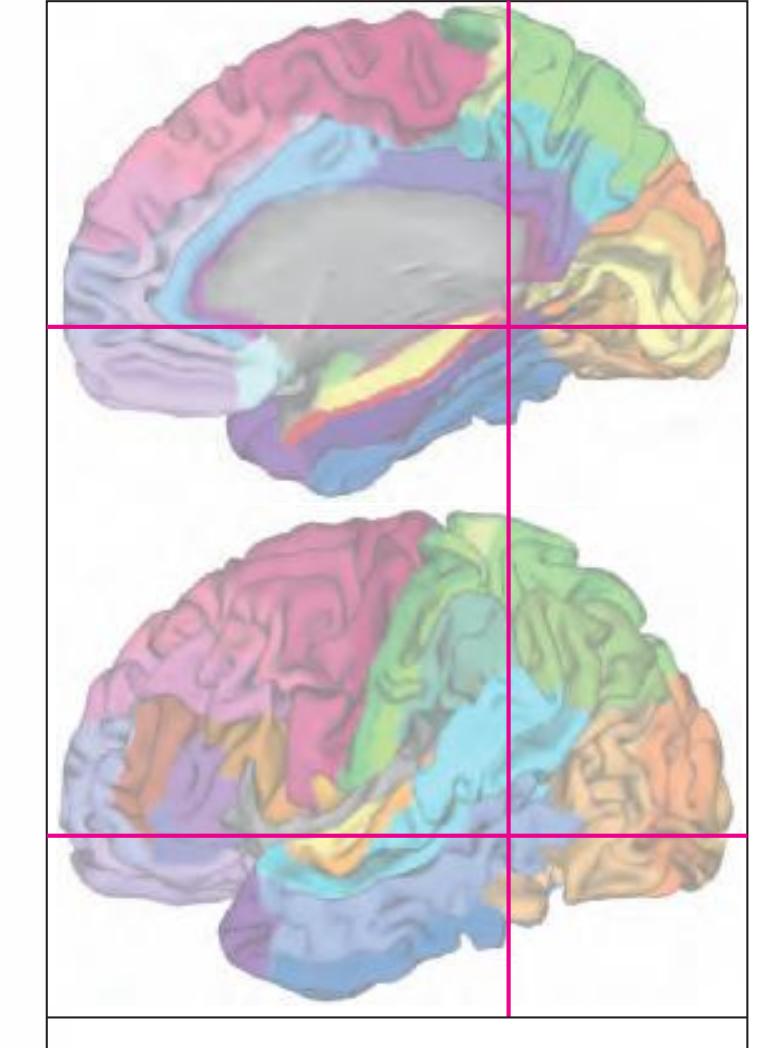
MNI Position y = -47.91 mm AHB Position y = 45.62 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG anterior angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule SSpG subsplenial gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas
- BA2 area postcentralis caudalis BA5 area praeparietalis BA7 area parietalis superior
- BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media
- BA22 area temporalis superior BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis
- BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA37 area occipito-temporalis
- BA40 area supramarginalis
- Hi hippocampus
## von Economo and Koskinas
FB agranular frontal area H hippocampal area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PB oral postcentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PE superior parietal area PF supramarginal area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23d dorsal division of BA 23 23v ventral division of 23
29/30 BA 29 and BA30 d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 67 Slice Nr. 4192
**302**
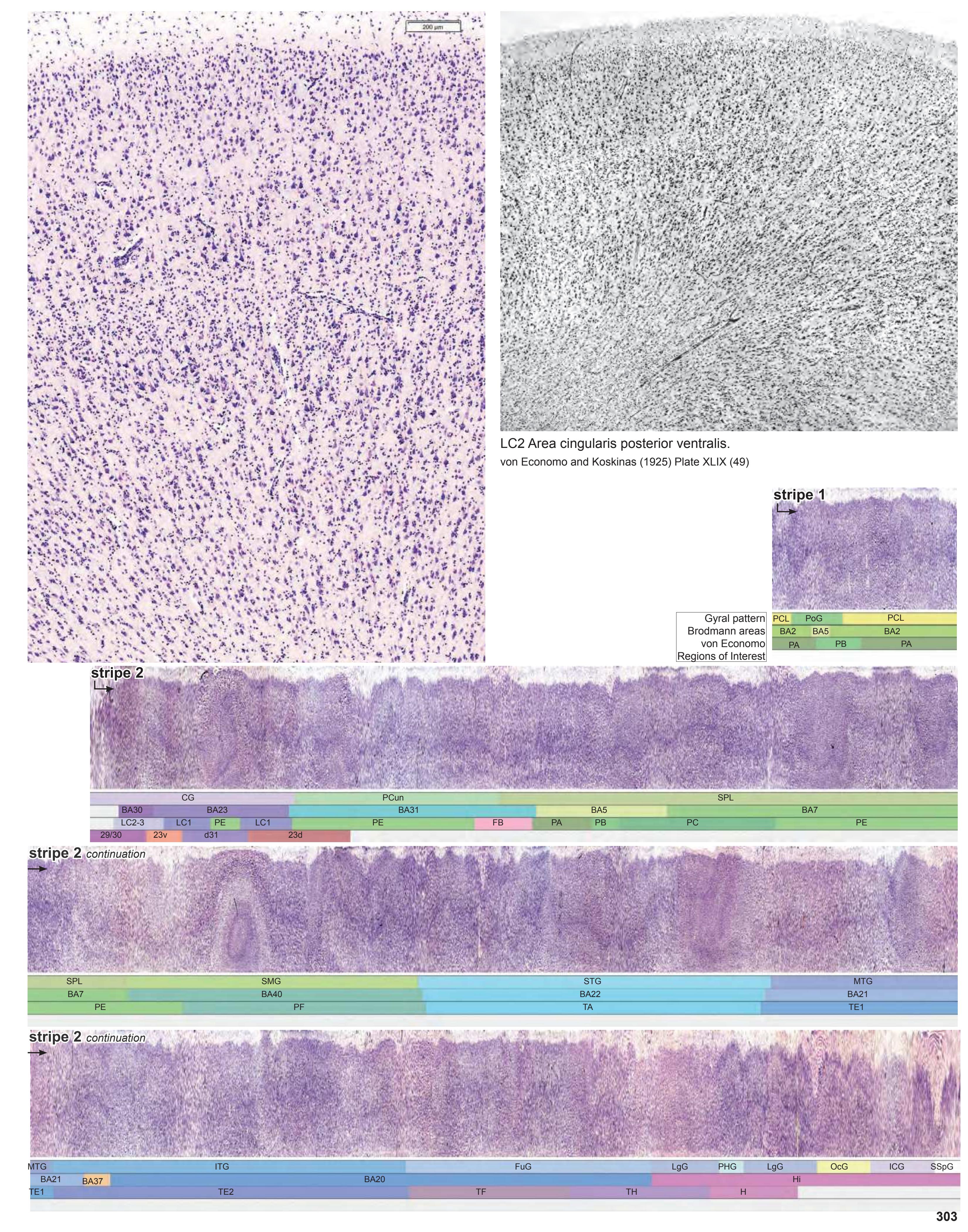
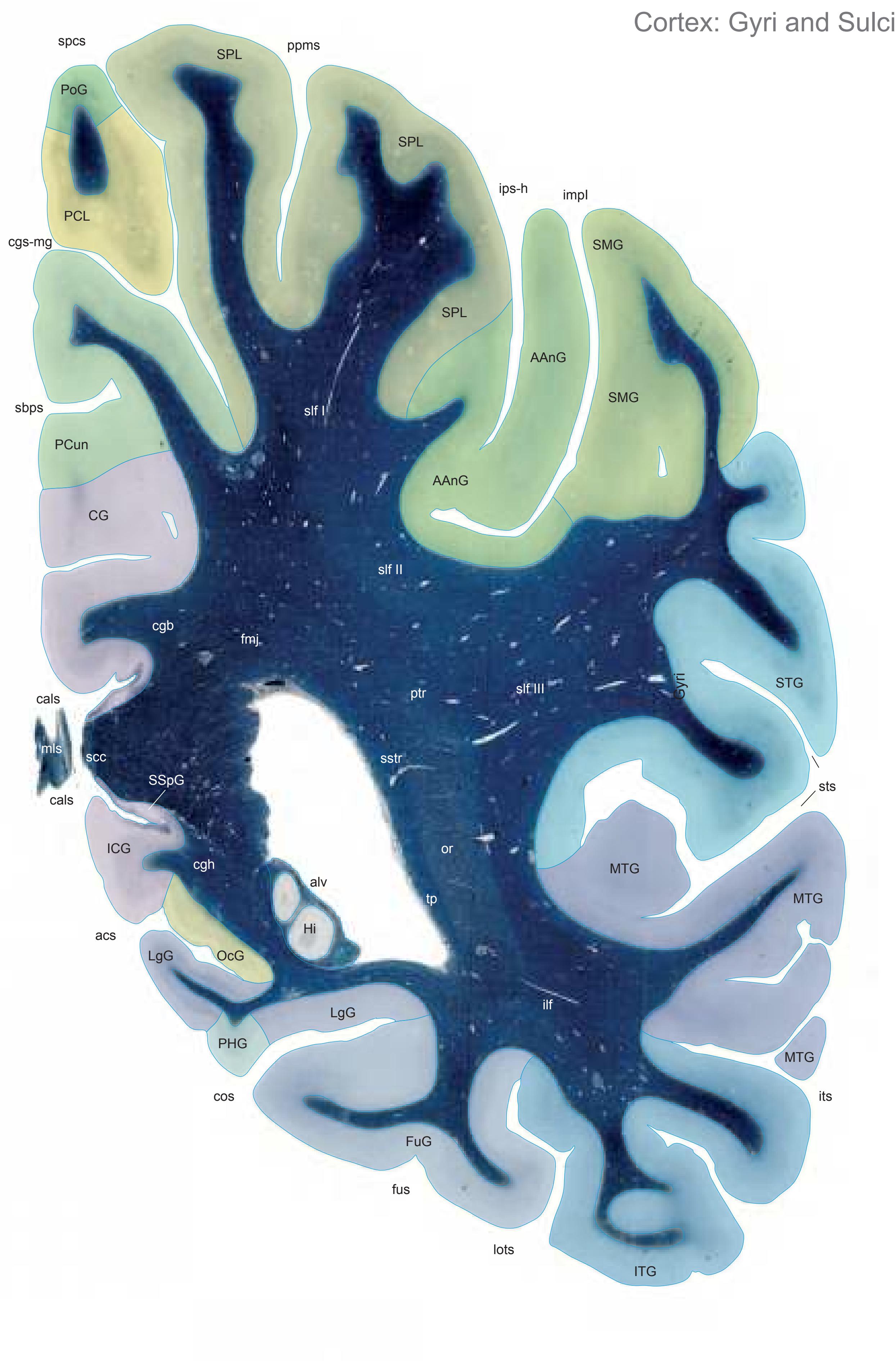

MNI Position y = -49.29 mm AHB Position y = 46.93 mm
AAnG anterior angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule SSpG subsplenial gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal part Fibers
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
alv alveus of the hippocampus cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle mls medial longitudinal stria or optic radiation ptr posterior thalamic radiation scc splenium of corpus callosum slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum
tp tapetum
Sulci
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 68 Slice Nr. 4241
**304**

ICL: 46.93 MCP: 32.19 MNI: -49.29

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment isst internal sagittal stratum its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus mfs midfusiform sulcus or optic radiation racc radiation of corpus callosum PSR perisplenial region
sts superior temporal sulcus tp tapetum TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum spcs superior postcentral sulcus SSpG subsplenial gyrus
**305**
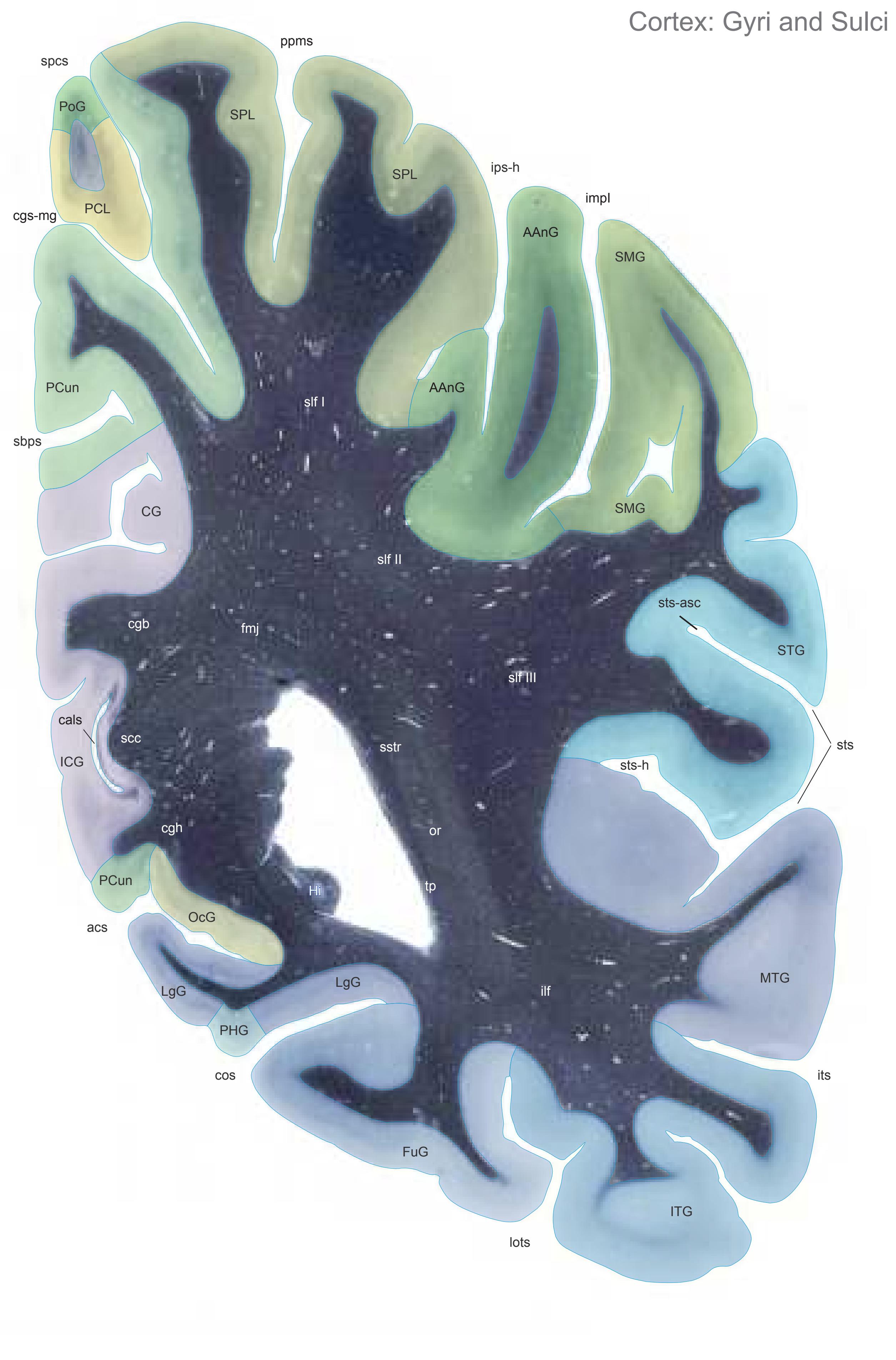

MNI Position y = -50.70 mm AHB Position y = 48.27 mm
AAnG angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal part its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
## Fibers
segment (sts-2)
cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation scc splenium of corpus callosum slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 69 Slice Nr. 4291
**306**
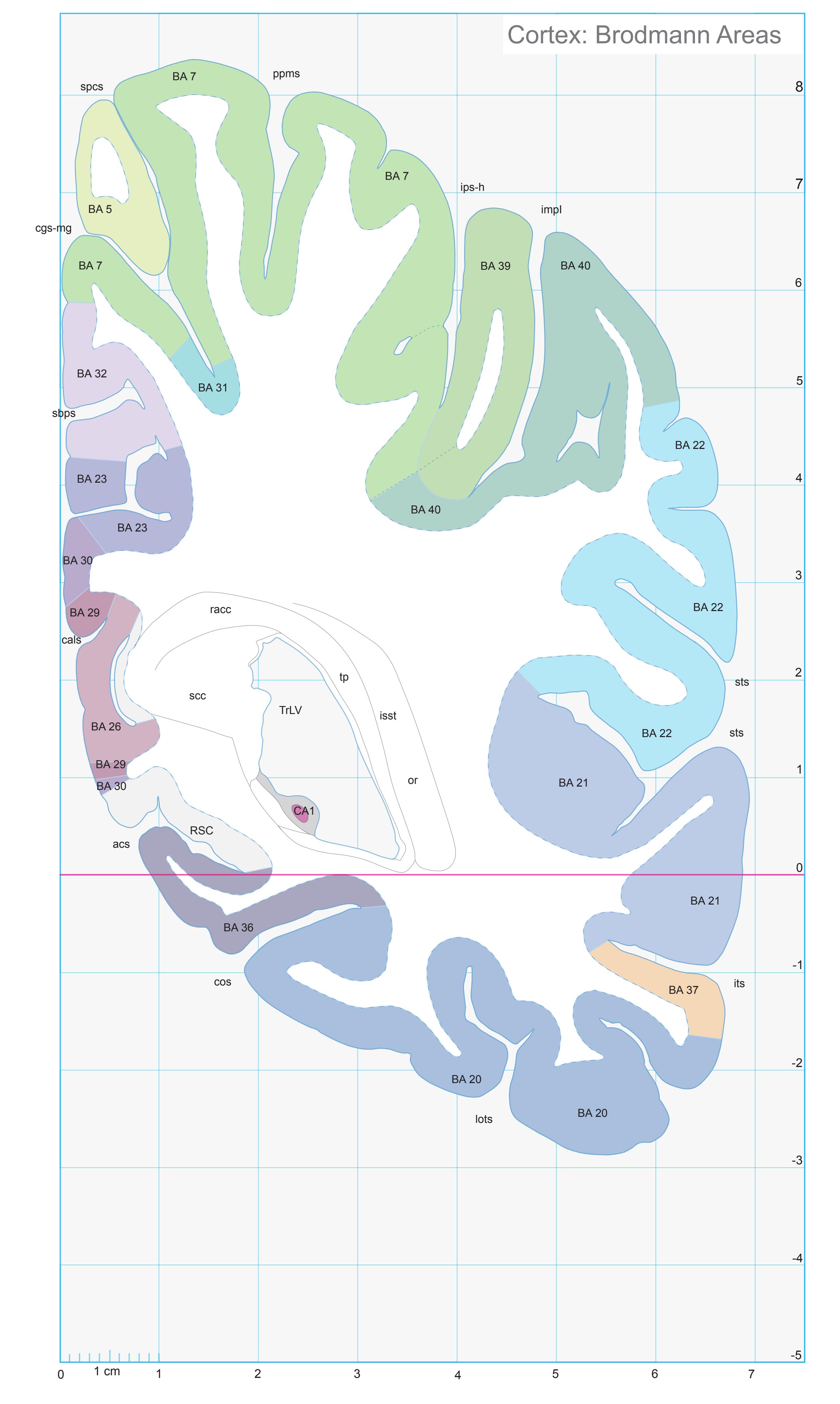

ICL: 48.27 MCP: 33.53 MNI: -50.70
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment isst internal sagittal stratum
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus or optic radiation ppms posterior paramidline sulcus racc radiation of corpus callosum RSC retrosplenial cortex
its inferior temporal sulcus
S subiculum sbps subparietal sulcus scc splenium of corpus callosum spcs superior postcentral sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus tp tapetum
TrLV trigone of lateral ventricle
**307**
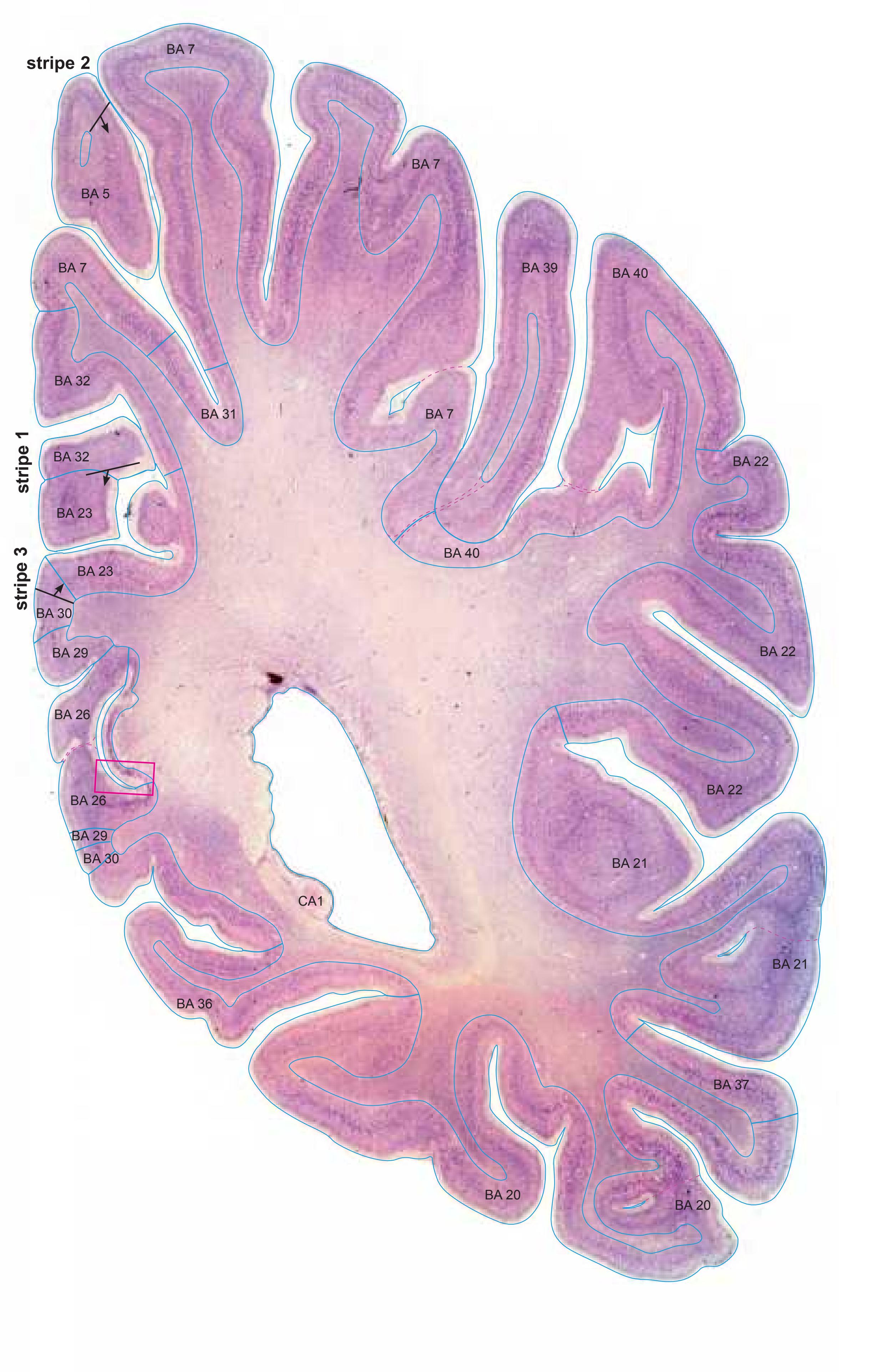

MNI Position y = -50.67 mm AHB Position y = 48.24 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus
PoG postcentral gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
BA5 area praeparietalis
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA26 area ectosplenialis BA29 area retrolimbica granularis
BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA32 area cingularis anterior dorsalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis BA39 area angularis BA40 area supramarginalis
## von Economo and Koskinas
H hippocampal area LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
FB agranular frontal area
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PB oral postcentral area PC intermediate postcentral area
PE superior parietal area PF supramarginal area PG angular area
TA superior temporal area TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23v ventral division of 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 69 Slice Nr. 4290
**308**
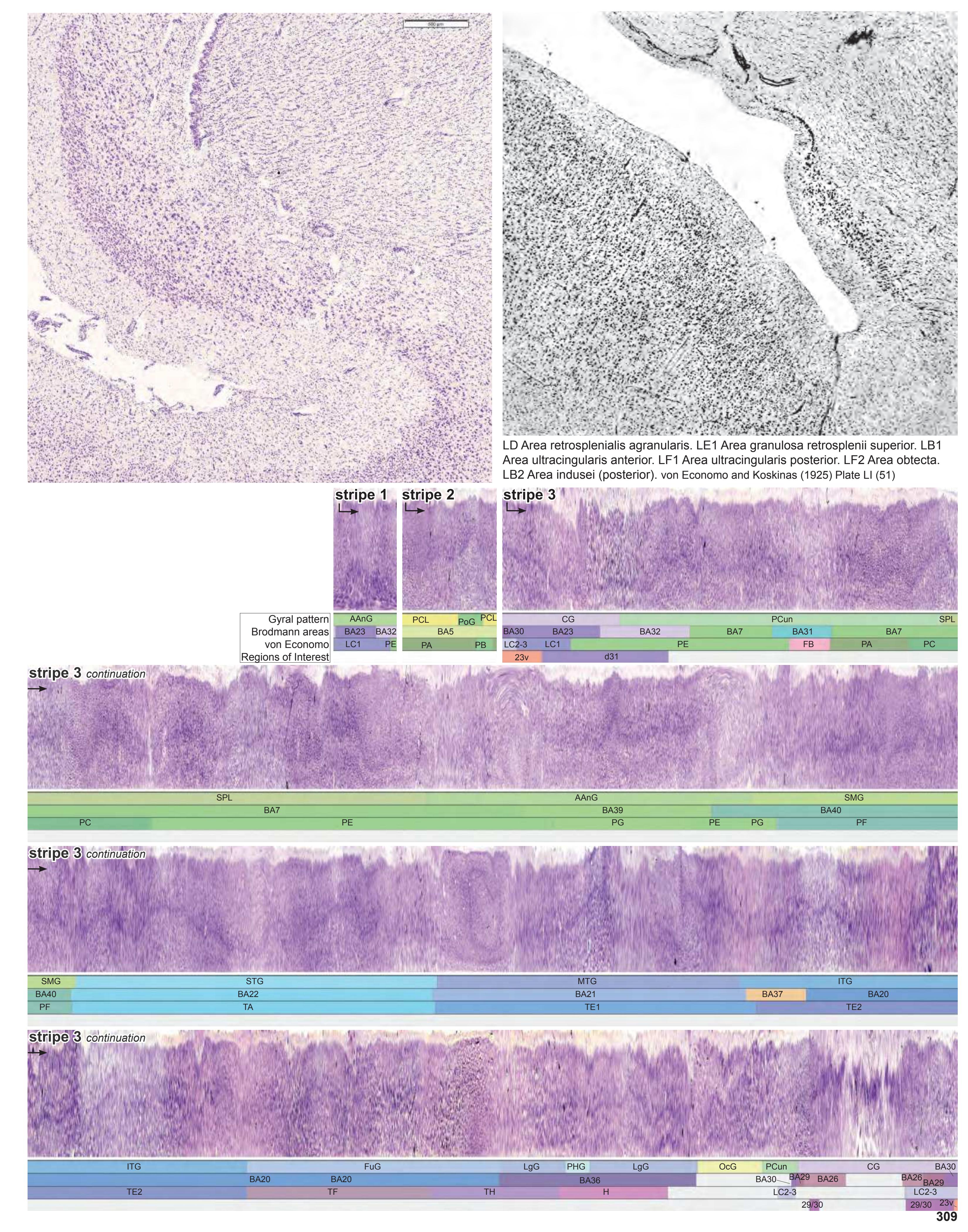

MNI Position y = -52.05 mm AHB Position y = 49.56 mm
AAnG angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal part its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal Sulci
## Fibers
segment (sts-2)
cgb cingulum bundle cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation scc splenium of corpus callosum slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 70 Slice Nr. 4339
**310**

ICL: 49.56 MCP: 34.82 MNI: -52.05

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
cals callosal sulcus cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus
cos collateral sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of
Jensen ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**311**

MNI Position y = -53.52 mm AHB Position y = 50.95 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus
sbps subpavrietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
cgb cingulum bundle
cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 71 Slice Nr. 4391
**312**

ICL: 50.95 MCP: 36.21 MNI: -53.52
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cal calcar avis
cals callosal sulcus
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of
Jensen ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
ppms posterior paramidline sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
posterior segment sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**313**
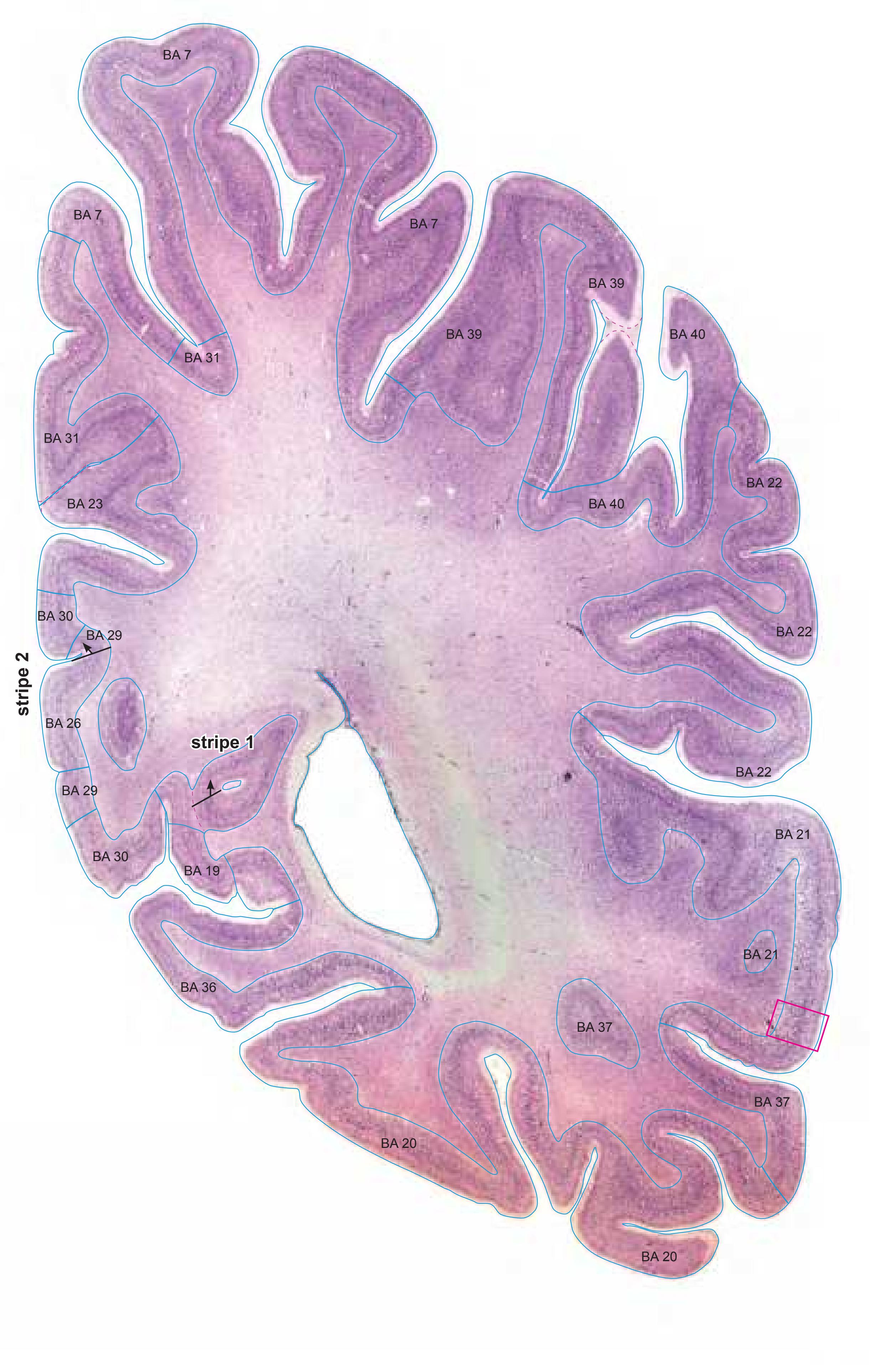
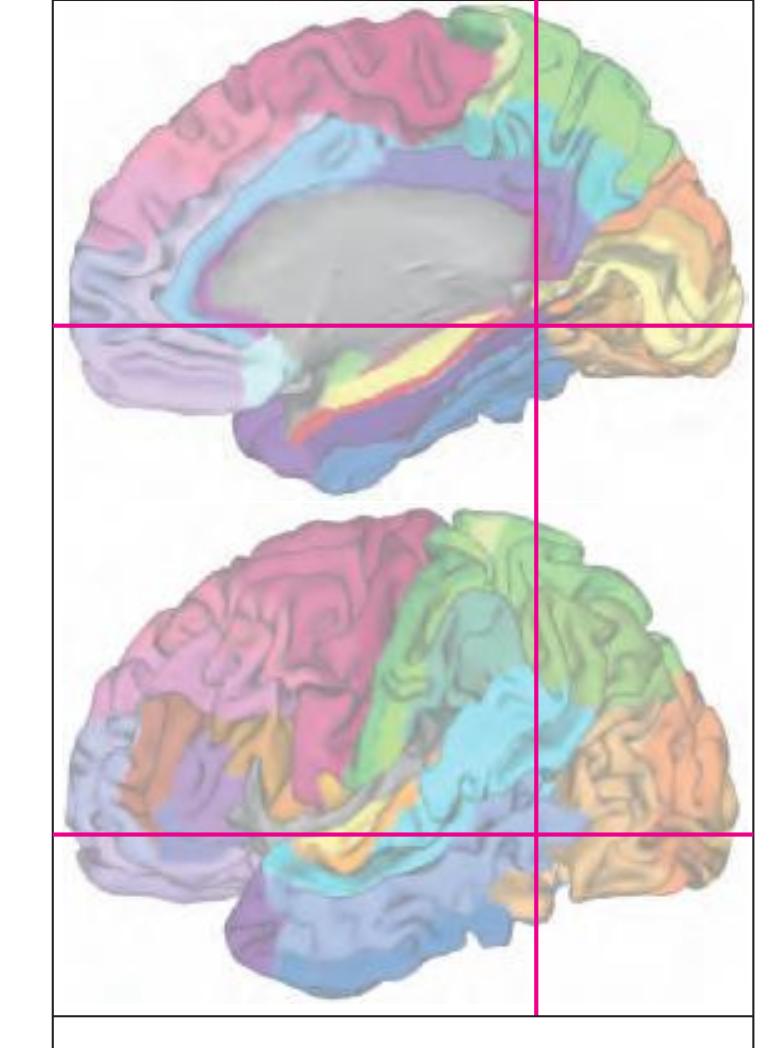
MNI Position y = -53.54 mm AHB Position y = 50.98 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus
## STG superior temporal gyrus Brodmann Areas
SPL superior parietal lobule
- BA7 area parietalis superior BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
- BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA26 area ectosplenialis
- BA29 area retrolimbica granularis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis
- BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA37 area occipito-temporalis
- BA39 area angularis BA40 area supramarginalis
## von Economo and Koskinas
H hippocampal area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area
PC intermediate postcentral area
PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area
PG angular area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23v ventral division of 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 71 Slice Nr. 4392
**314**
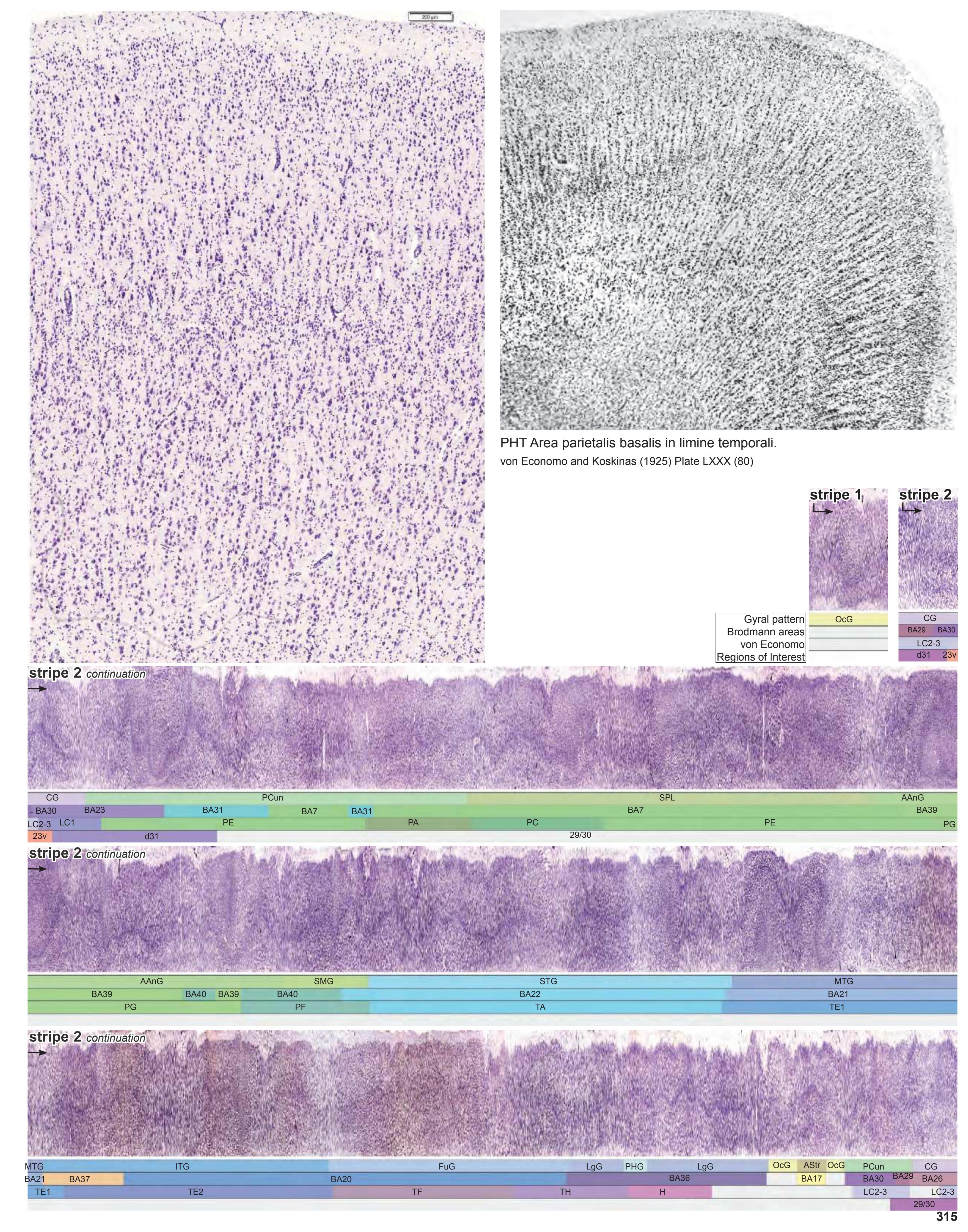
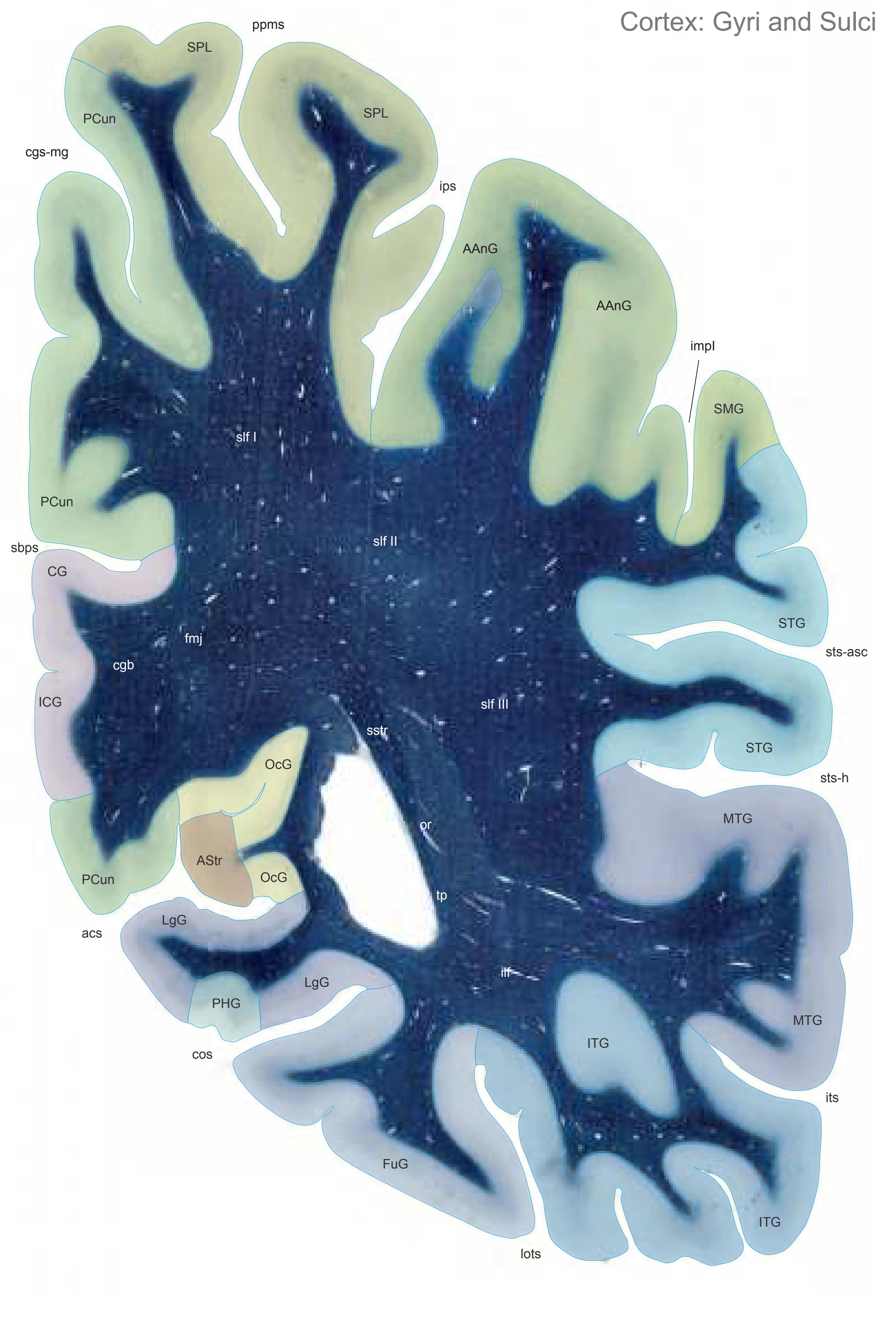

MNI Position y = -54.92 mm AHB Position y = 52.29 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
## Fibers
segment (sts-2)
cgb cingulum bundle fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 72 Slice Nr. 4441
**316**
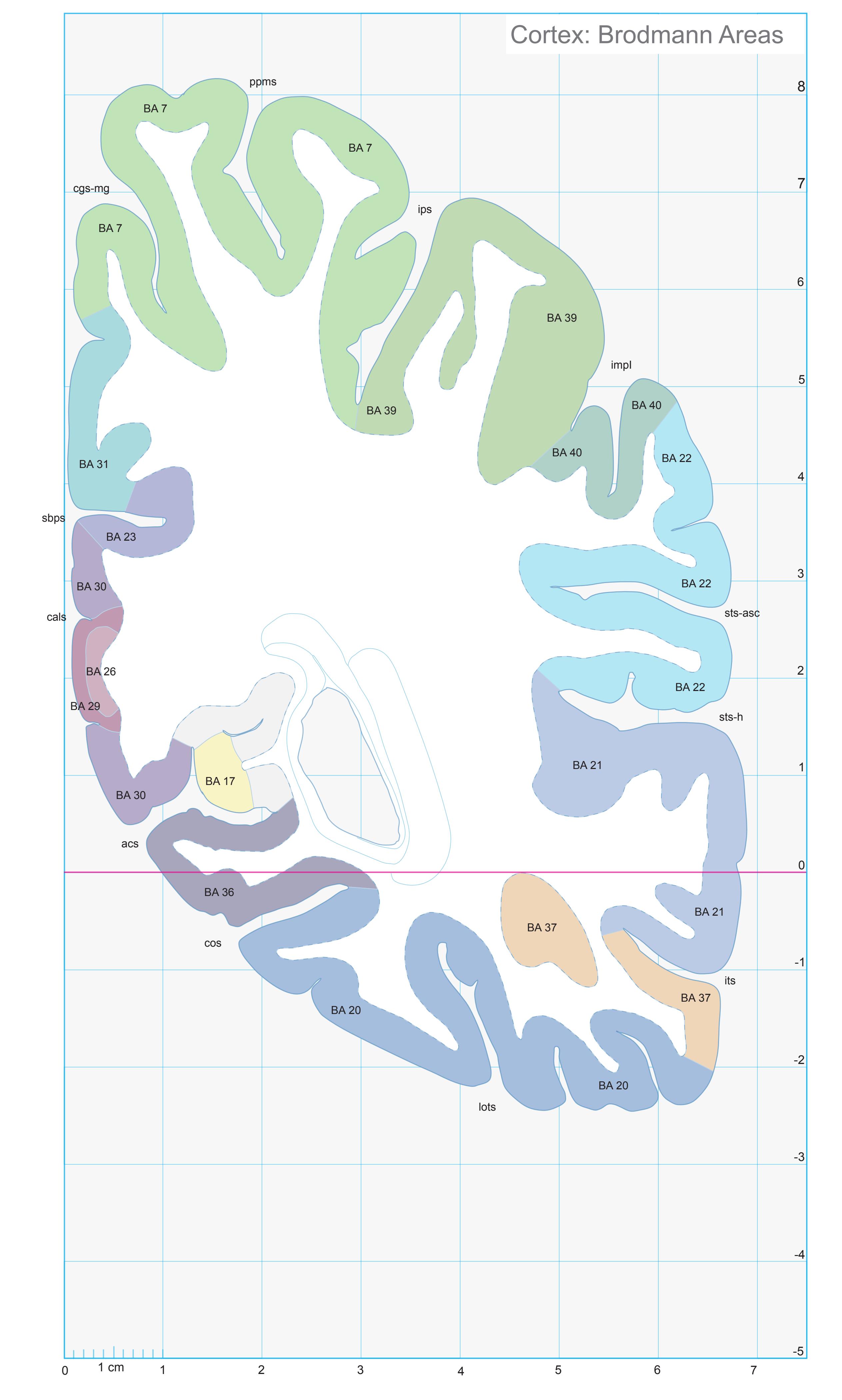
ICL: 52.29 MCP: 37.55 MNI: -54.92
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
cals callosal sulcus
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cos collateral sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
ips intraparietal sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
ppms posterior paramidline sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
posterior segment
ts-asc superior temporal s
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
**317**


MNI Position y = -56.36 mm AHB Position y = 53.66 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
cgb cingulum bundle
fmj forceps major of the corpus callosum ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 73 Slice Nr. 4492
**318**
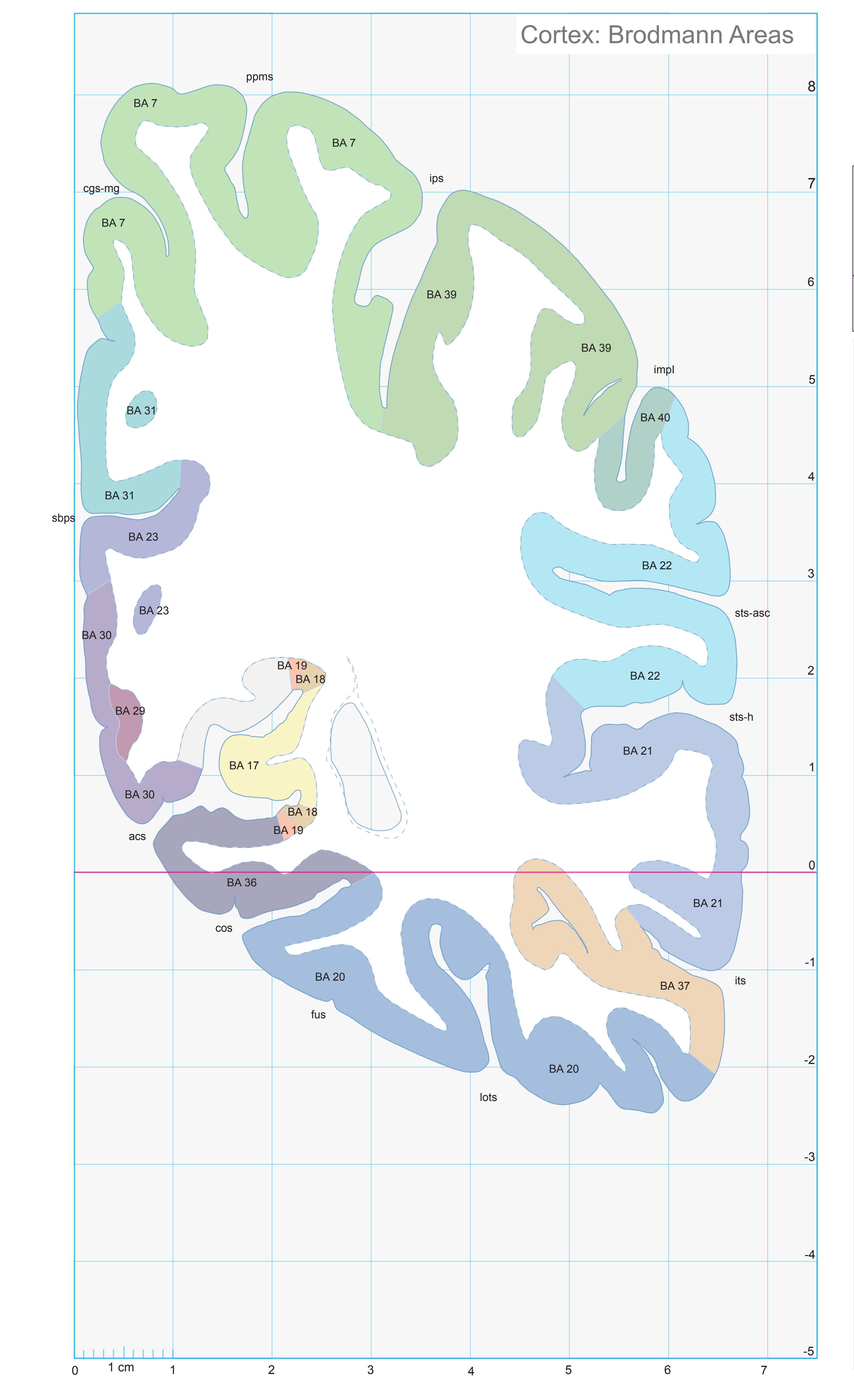
ICL: 53.66 MCP: 38.92 MNI: -56.36
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus
cos collateral sulcus fus midfusiform sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**319**

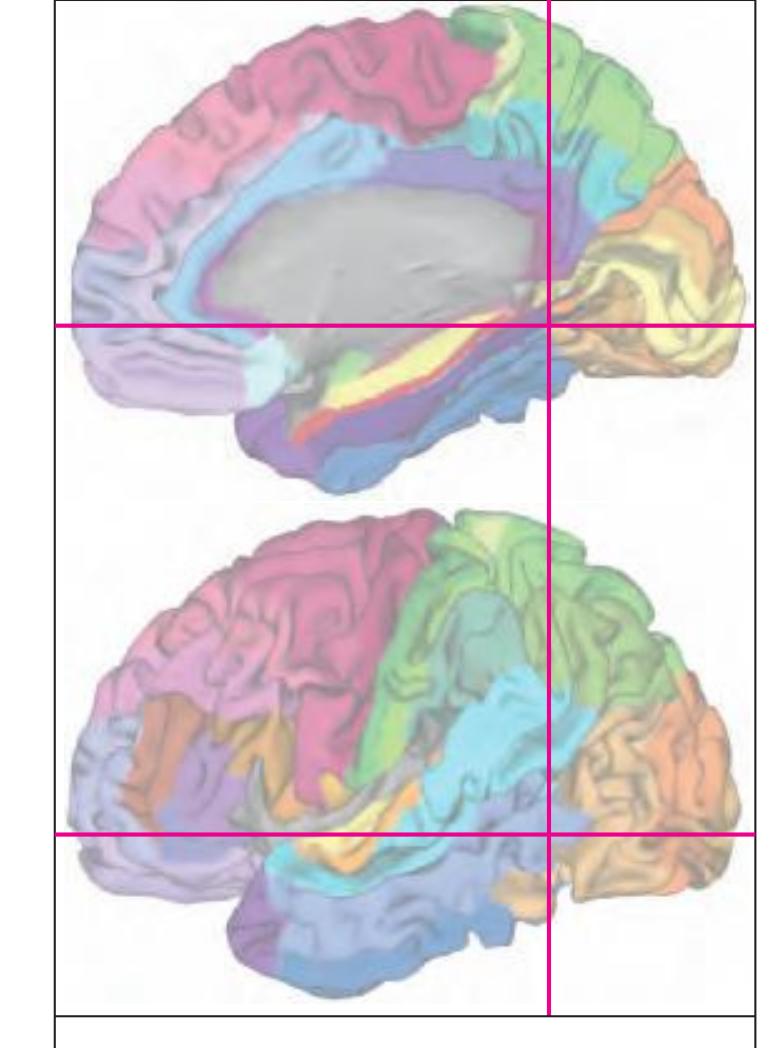
MNI Position y = -56.33 mm AHB Position y = 53.63 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus PStr parastriate area SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA29 area retrolimbica granularis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA36 area ectorhinalis BA37 area occipito-temporalis BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
BA40 area supramarginalis
H hippocampal area LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PC intermediate postcentral area PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area PG angular area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
Regions of Interest
## B. Vogt:
23v ventral division of 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30 d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 73 Slice Nr. 4491
**320**



MNI Position y = -57.65 mm AHB Position y = 55.02 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area CG cingulate gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
## Fibers
segment (sts-2)
cgb cingulum bundle ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 74 Slice Nr. 4543
**322**

ICL: 55.02 MCP: 40.28 MNI: -57.65

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus
cos collateral sulcus fus midfusiform sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of
Jensen ips intraparietal sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus
spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**323**


MNI Position y = -59.12 mm AHB Position y = 56.28 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneusv SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
## Sulci
cgs-mg cingulate sulcus, marginal part cos collateral sulcusv fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 75 Slice Nr. 4590
**324**
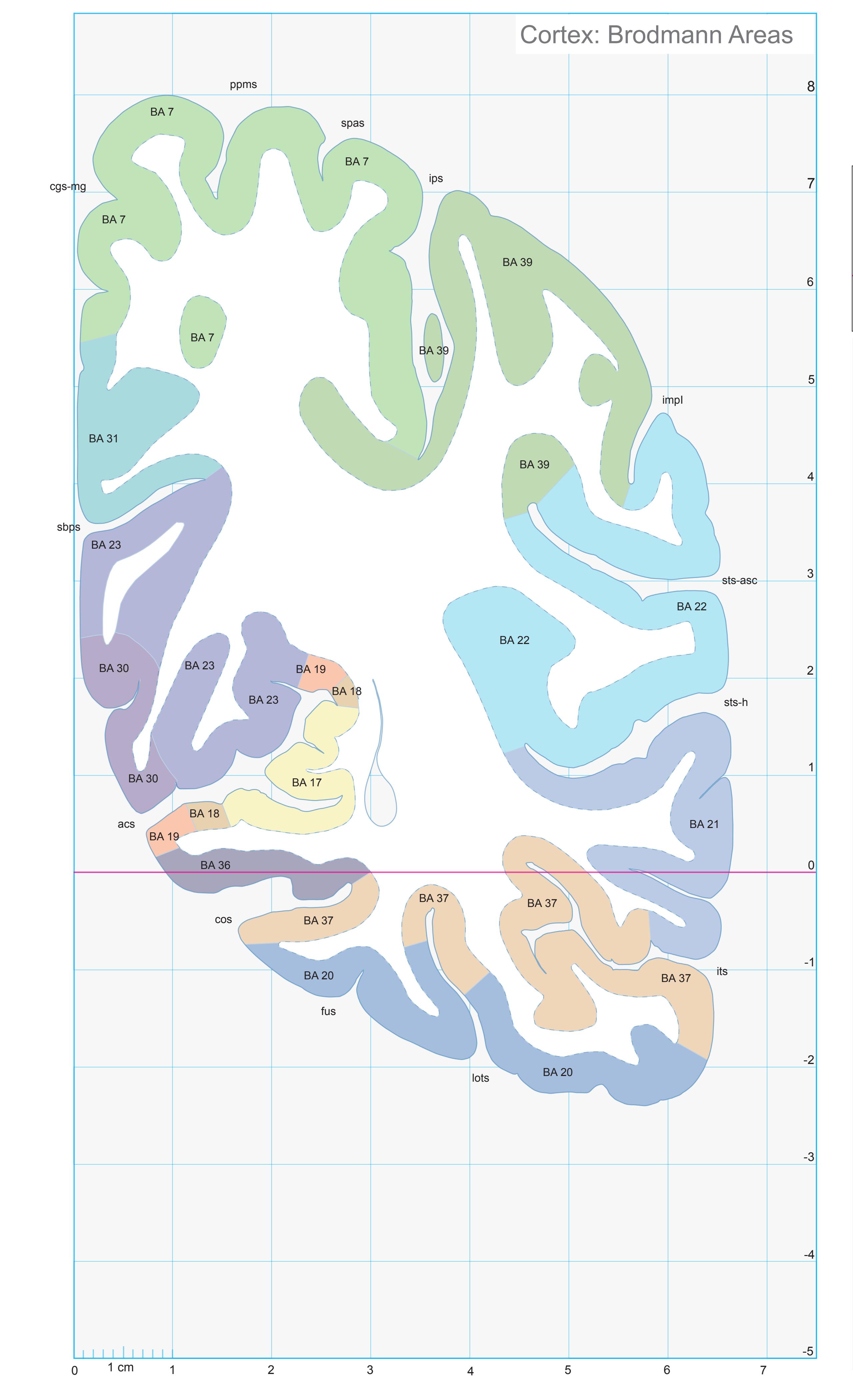
ICL: 56.28 MCP: 41.54 MNI: -59.12
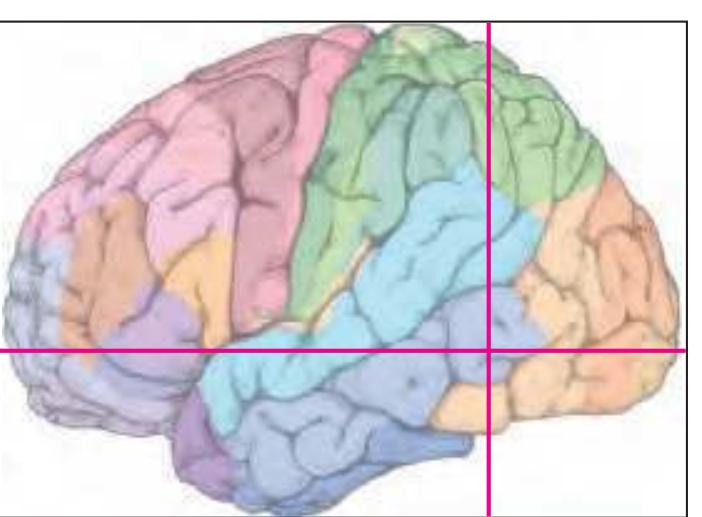
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus
cos collateral sulcus
fus midfusiform sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of
Jensen
ips intraparietal sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
ppms posterior paramidline sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**325**

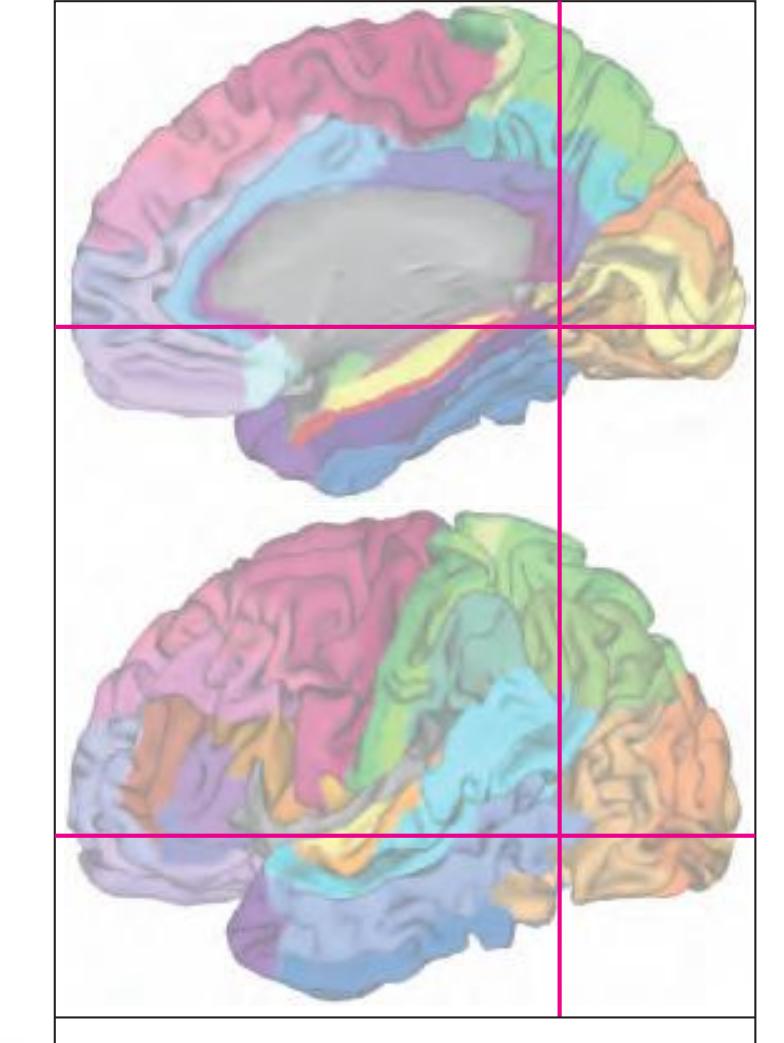
MNI Position y = -59.09 mm AHB Position y = 56.26 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus LgG lingual gyrus (O5) MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneusv PStr parastriate area SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA36 area ectorhinalis BA37 area occipito-temporalis
## von Economo and Koskinas
H hippocampal area LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area OC striate area (granulosa) PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PE superior parietal area
BA39 area angularis
PF supramarginal area PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper TF fusiform area TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23v ventral division of 23 29/30 BA 29 and BA30 d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31 v23 subregion of BA 23
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 75 Slice Nr. 4589
**326**

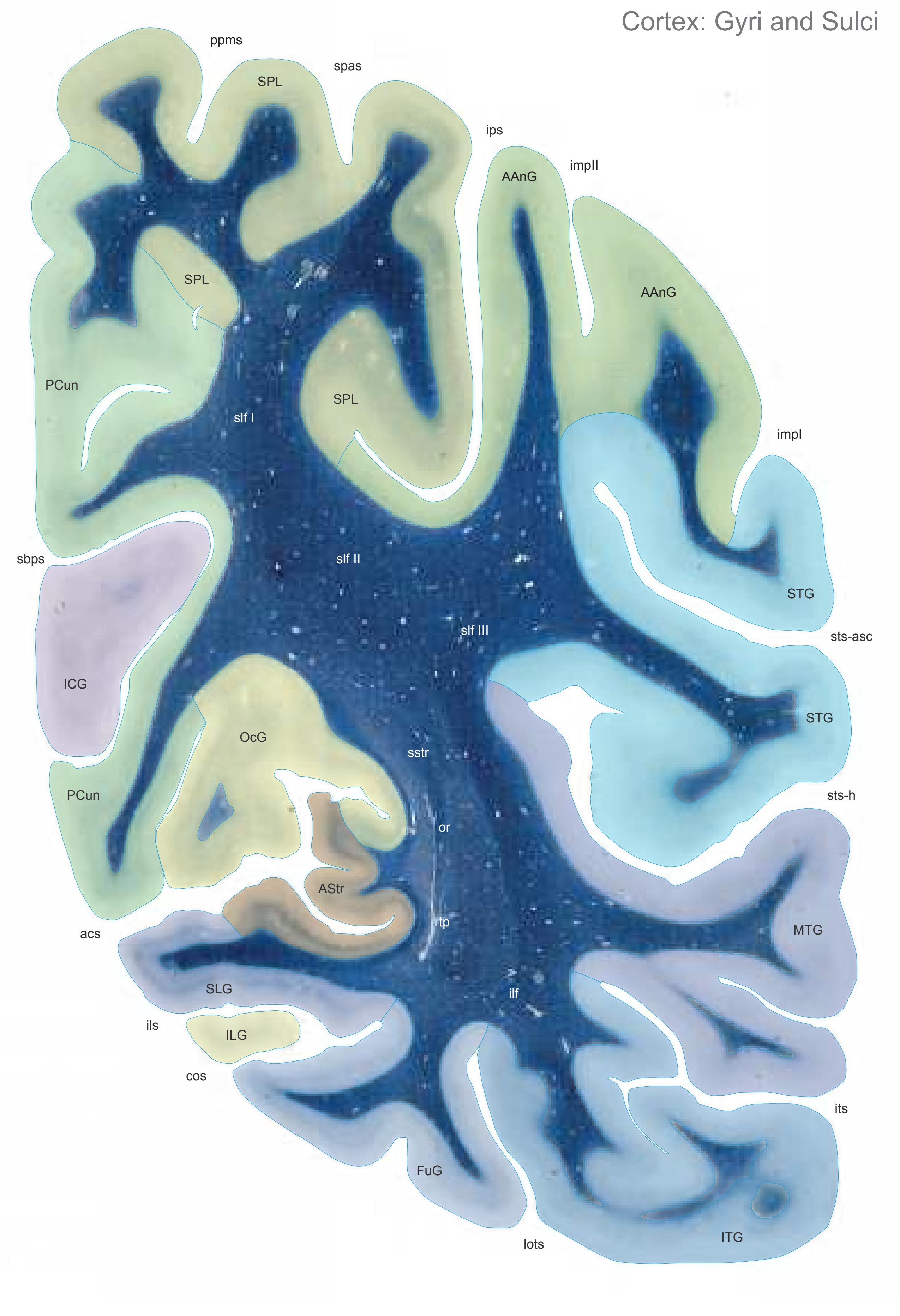

MNI Position y = -60.55 mm AHB Position y = 57.65 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
segment (sts-2)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
## Fibers
or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 76 Slice Nr. 4641
**328**

ICL: 57.65 MCP: 42.91 MNI: -60.55
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus fus midfusiform sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**329**


MNI Position y = -61.88 mm AHB Position y = 58.91 mm
AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cos collateral sulcus
AAnG angular gyrus
## Sulci
ils intralingual sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus prcus precuneal sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 77 Slice Nr. 4688
**330**
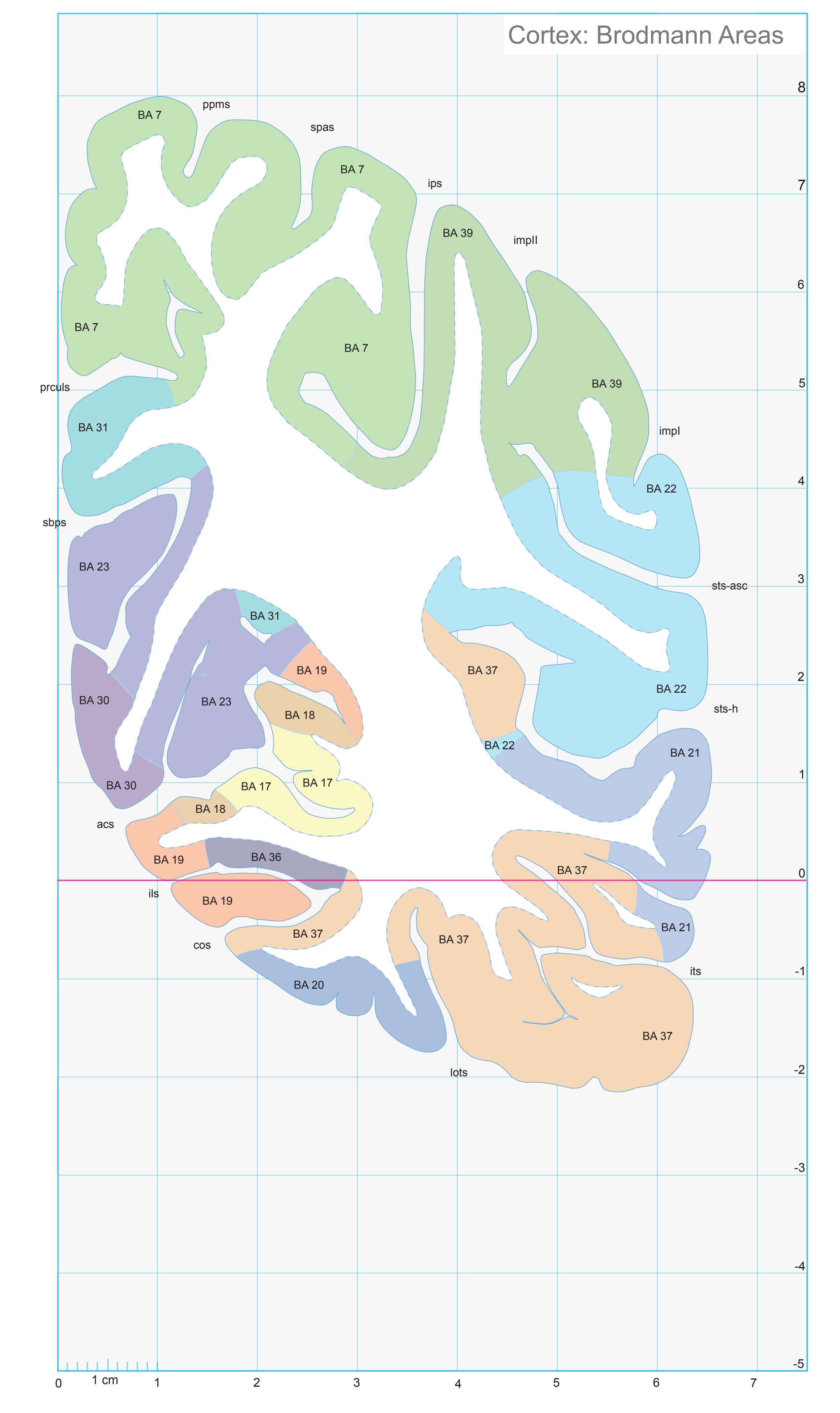
ICL: 58.91 MCP: 44.17 MNI: -61.88

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
Jensen
impl second inter
impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus
sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**331**


MNI Position y = -61.96 mm AHB Position y = 58.99 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
FuG fusiform gyrus ICG isthmus of cingulate gyrus
ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri
PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
PStr parastriate area SLG superior lingual gyrus
SLG superior lingual gyrus
SPI superior parietal lobule
SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA17 area striata
BA18 area occipitalis
BA19 area praeoccipitalis
BA20 area temporalis inferior BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA30 area retrolimbica agranularis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA36 area ectorhinalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis
BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
H hippocampal area
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa)
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
TA superior temporal area TE1 middle temporal area proper
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
23v ventral division of 23
29/30 BA 29 and BA30
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31 v23 subregion of BA 23
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 77 Slice Nr. 4691
**332**

**333**


MNI Position y = -63.34 mm AHB Position y = 60.30 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms parietal paramidline sulcus
prcus precuneal sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
branch sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp.
slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 78 Slice Nr. 4740
**334**

ICL: 60.30 MCP: 45.56 MNI: -63.34

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen
Jensen
mpll second
impII second intermediate parietal sulcus
ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ppms posterior paramidline sulcus
prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
posterior segment sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**335**
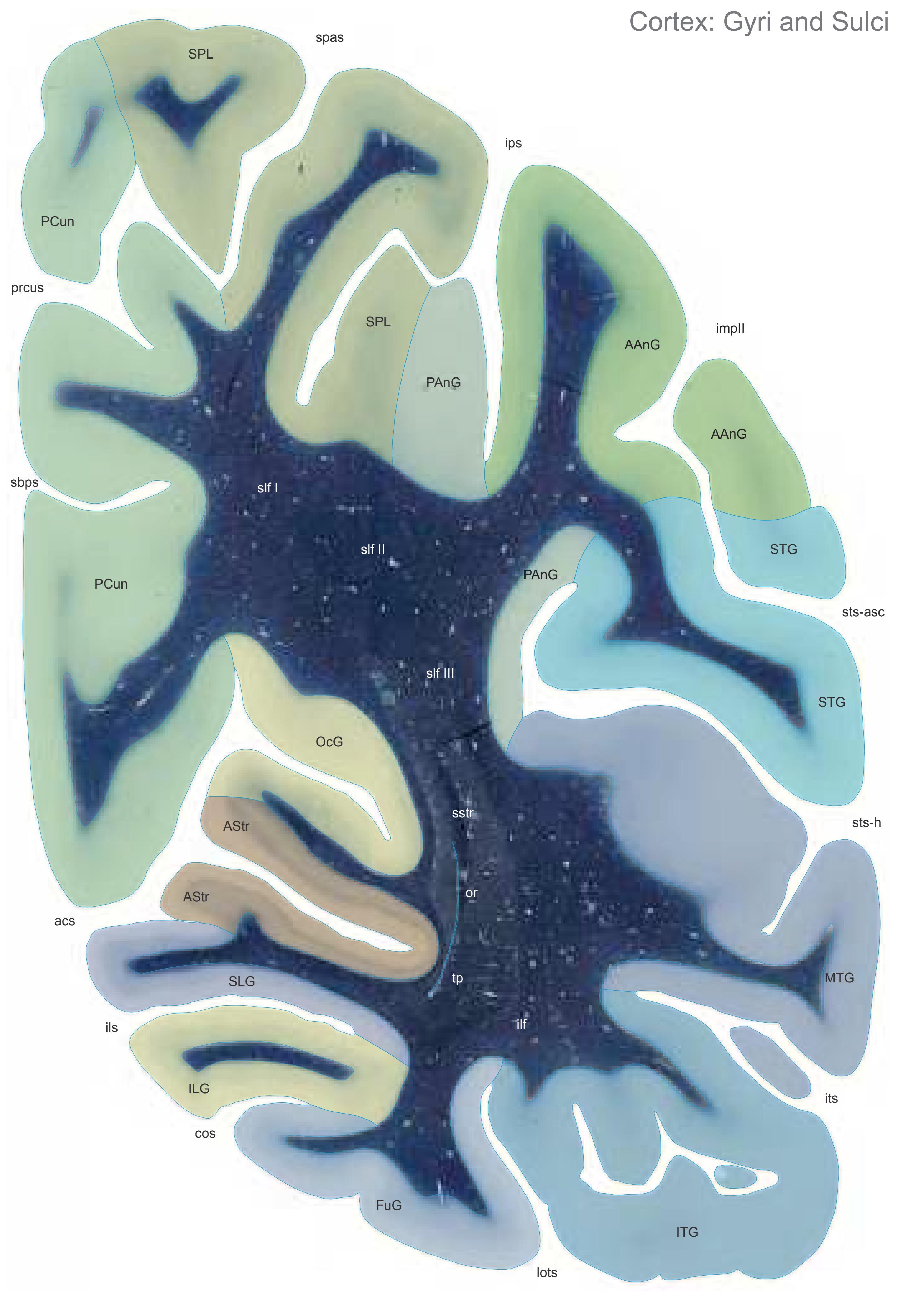

MNI Position y = -64.78 mm AHB Position y = 61.62 mm
AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
AAnG angular gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus prcus precuneal sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending branch
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum Fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 79 Slice Nr. 4789
**336**

ICL: 61.62 MCP: 46.88 MNI: -64.78

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
posterior segment sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**337**


MNI Position y = -64.83 mm AHB Position y = 61.72 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri
PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus
SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Brodmann Areas
- BA7 area parietalis superior
- BA17 area striata
- BA18 area occipitalis
- BA19 area praeoccipitalis
- BA20 area temporalis inferior
- BA21 area temporalis media BA22 area temporalis superior
- BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
- BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA36 area ectorhinalis
- BA37 area occipito-temporalis
- BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
LC2-3 posterior and limitans cingulate area
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa)
PA pyramidal post- and paracentral area PE superior parietal area
PF supramarginal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
TA superior temporal area
TE1 middle temporal area proper TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
## TH hippocampotemporal area Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v23 subregion of BA 23
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 79 Slice Nr. 4793
**338**
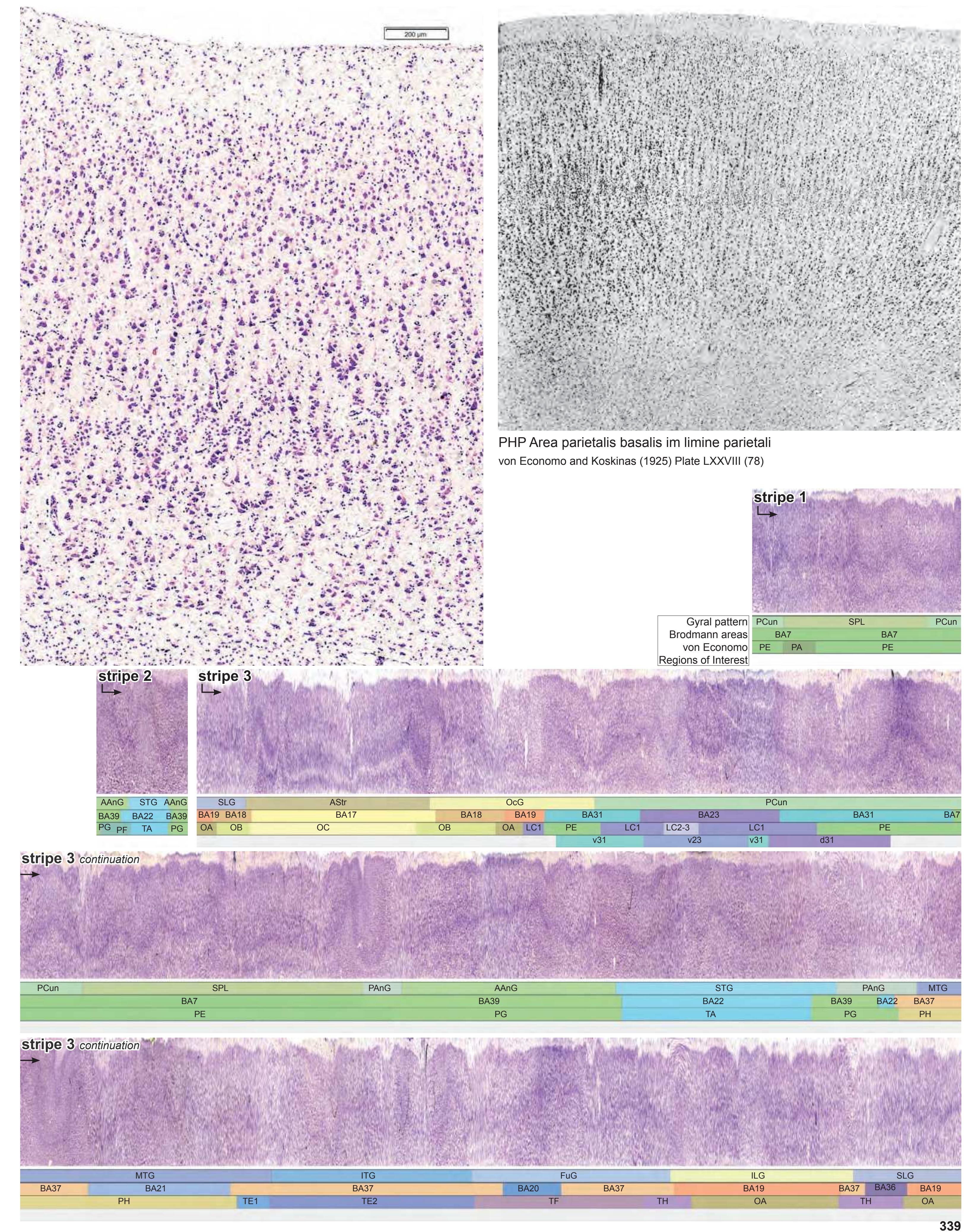
**339**
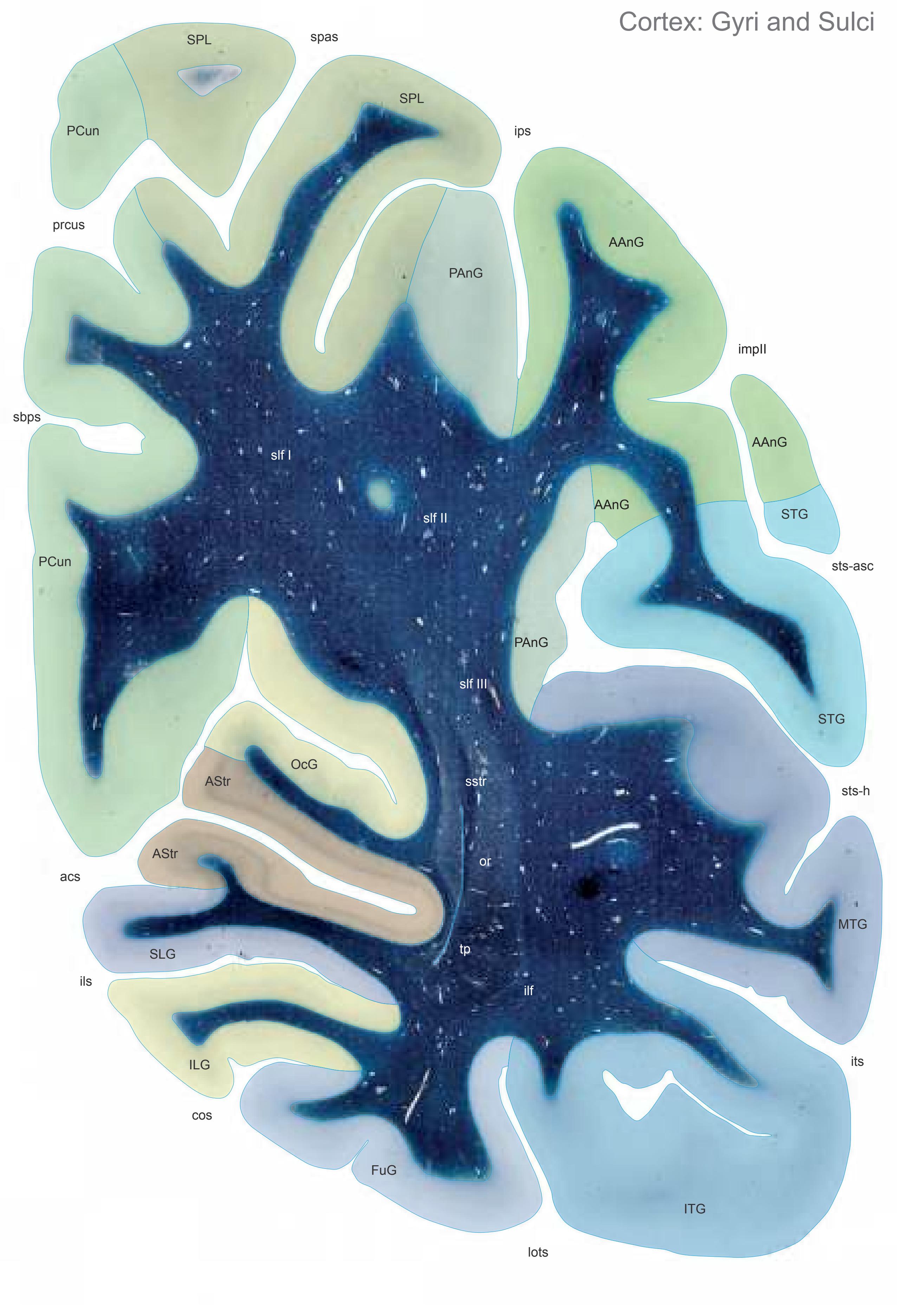
MNI Position y = -66.13 mm AHB Position y = 62.96 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus prcus precuneal sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
branch
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum Fibers
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 80 Slice Nr. 4839
**340**

ICL: 62.96 MCP: 48.22 MNI: -66.13

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impII second intermediate parietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, ascending posterior segment
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**341**


MNI Position y = -67.45 mm AHB Position y = 64.21 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impIII third intermediate parietal sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus prcus precuneal sulcus ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subpavrietal sulcus spas superior parietal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
## Fibers
segment (sts-2)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 81 Slice Nr. 4886
**342**

ICL: 64.21 MCP: 49.47 MNI: -67.45

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
spas superior parietal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**343**

MNI Position y = -67.53 mm AHB Position y = 64.30 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
FuG fusiform gyrus ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part
ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division
SLG superior lingual gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA17 area striata
BA18 area occipitalis
BA19 area praeoccipitalis BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior
BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis BA36 area ectorhinalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis
BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa) PE superior parietal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
TA superior temporal area
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
TH hippocampotemporal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v23 subregion of BA 2
v31 ventral subregion
v23 subregion of BA 23 v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 81 Slice Nr. 4889
**344**

**345**


MNI Position y = -68.91 mm AHB Position y = 65.64 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
## Sulci
impIII third intermediate parietal sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum Fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 82 Slice Nr. 4939
**346**
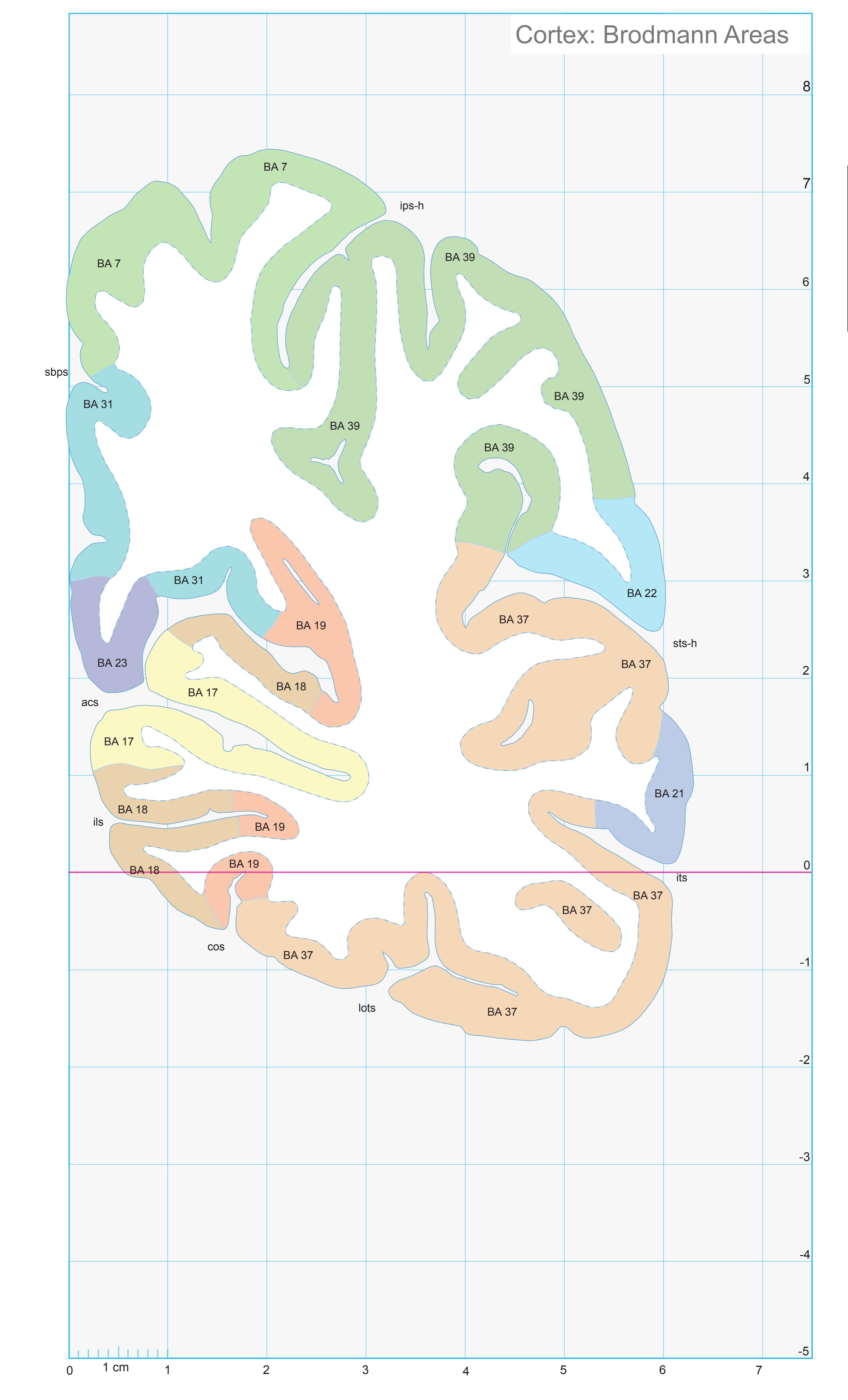
ICL: 65.64 MCP: 50.90 MNI: -68.91

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**347**
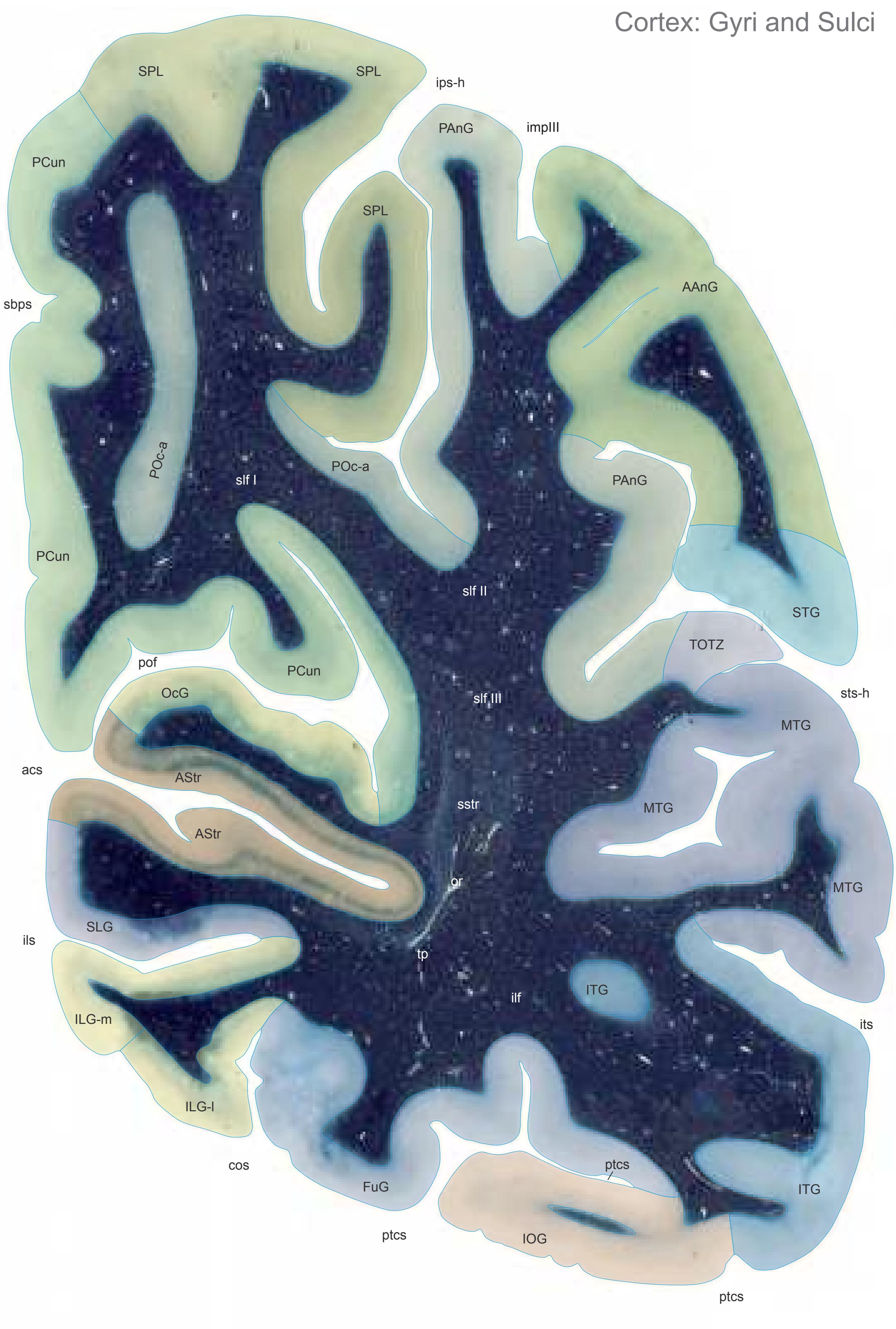
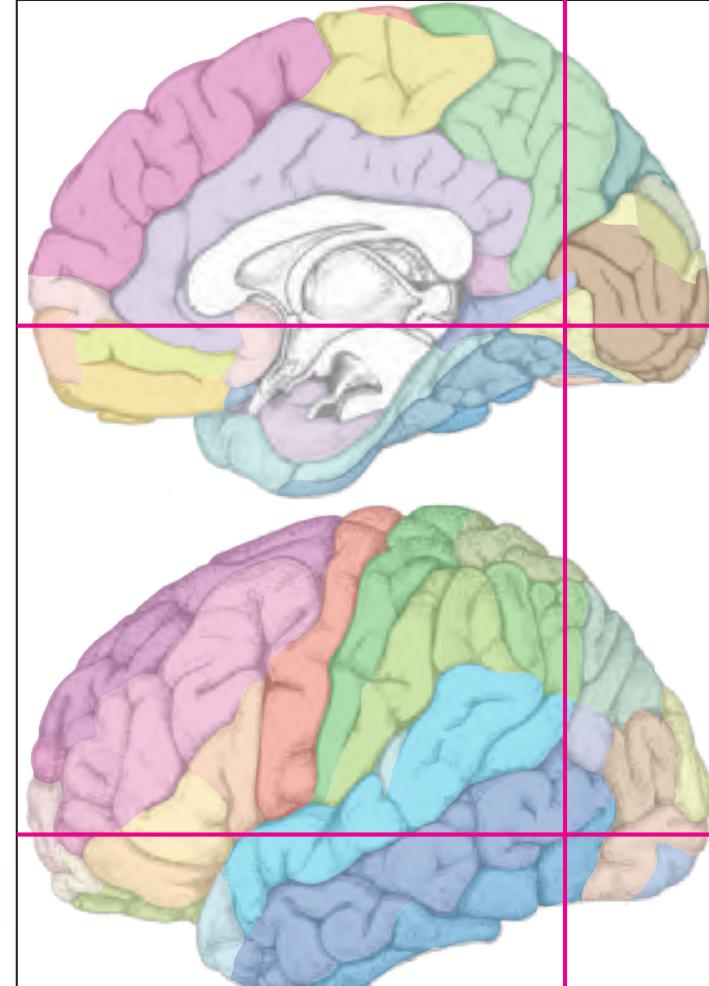
MNI Position y = -70.38 mm AHB Position y = 67.00 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus
ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part
IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division
SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impIII third intermediate parietal sulcus
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus
pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
or optic radiation
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 83 Slice Nr. 4990
**348**

ICL: 67.00 MCP: 52.26 MNI: -70.38

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**349**

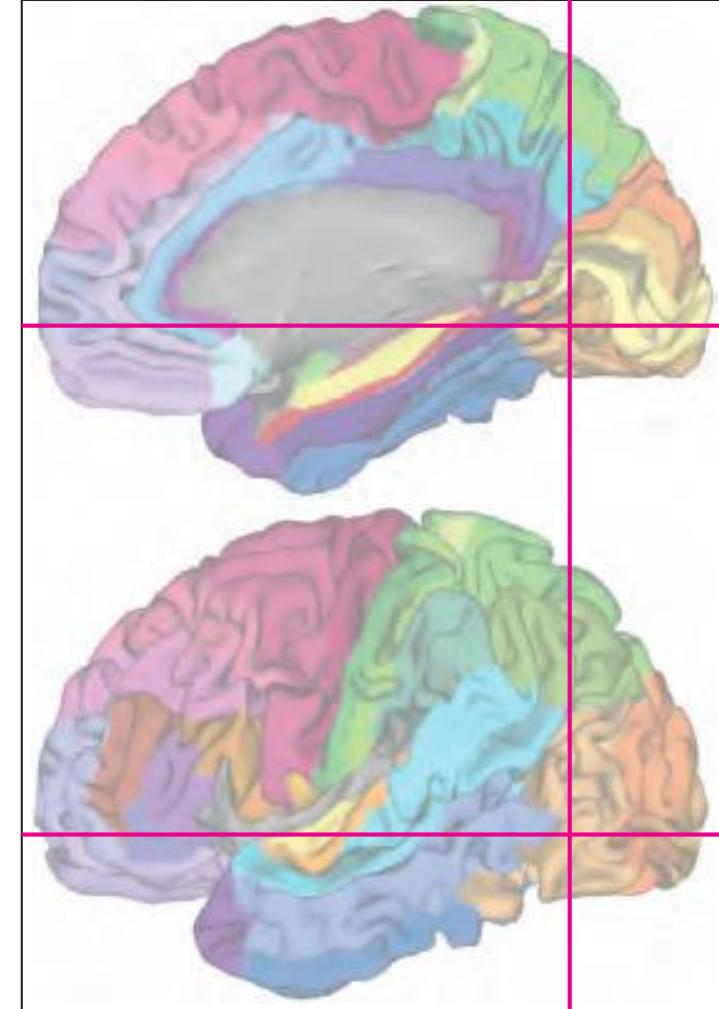
MNI Position y = -70.29 mm AHB Position y = 66.92 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
FuG fusiform gyrus ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part
ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part
IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri
PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division
SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus
TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA17 area striata
BA18 area occipitalis
BA19 area praeoccipitalis
BA21 area temporalis media
BA22 area temporalis superior BA23 area cingularis posterior ventralis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis
BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
LC1 dorsal posterior cingulate area
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa) PE superior parietal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
TA superior temporal area
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 83 Slice Nr. 4987
**350**
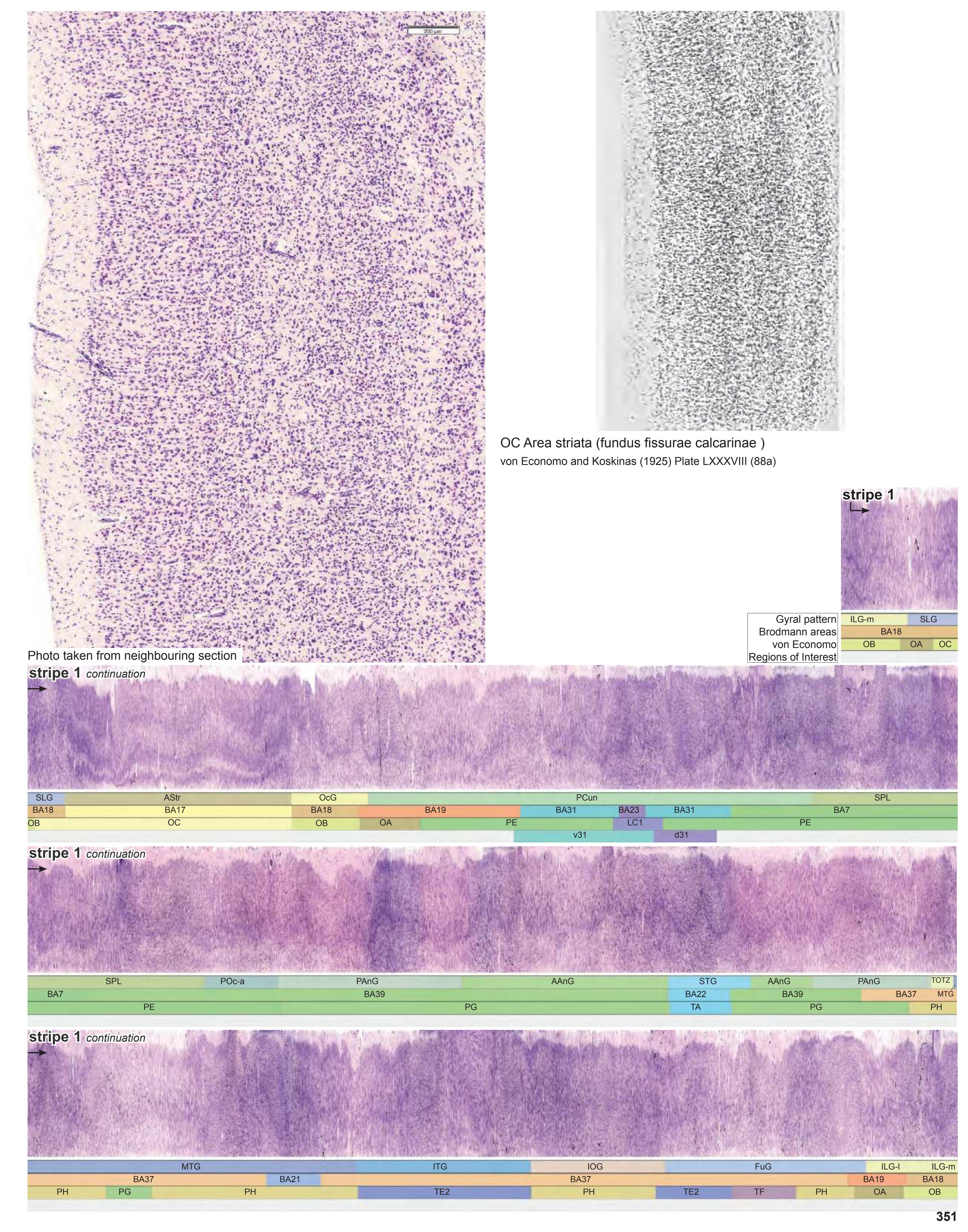


MNI Position y = -71.76 mm AHB Position y = 68.37 mm
\*Cp cuneal point AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
acs calcarine sulcus, central part
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impIII third intermediate parietal sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure
ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 84 Slice Nr. 5041
**352**

ICL: 68.37 MCP: 53.63 MNI: -71.76
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
acs anterior calcarine sulcus cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**353**

MNI Position y = -73.19 mm AHB Position y = 69.68 mm
\*CP cuneal point AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus
## STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
Sulci
SPL superior parietal lobule
cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ils intralingual sulcus impIII third intermediate parietal sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum Fibers
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 85 Slice Nr. 5090
**354**

ICL: 69.68 MCP: 54.94 MNI: -73.19

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
cos collateral sulcus
cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ils intralingual sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment
its inferior temporal sulcus
lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
pof parieto-occipital fissure
ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
posterior segment
**355**
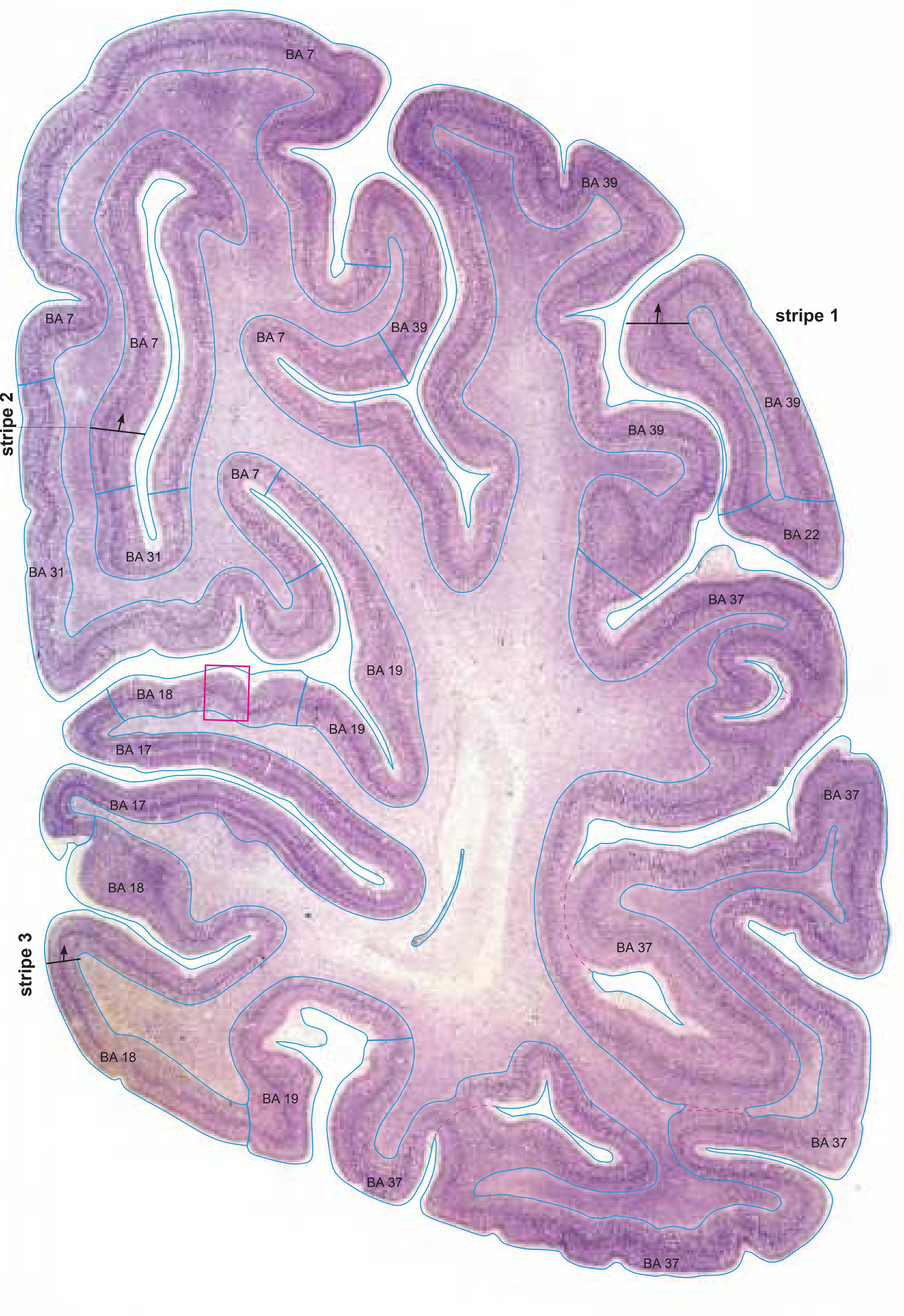

MNI Position y = -73.22 mm AHB Position y = 69.71 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
CuP cuneal point
FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part
ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part
ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus
ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri
PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division
SLG superior lingual gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule
STG superior temporal gyrus
TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA17 area striata
BA18 area occipitalis
BA19 area praeoccipitalis BA22 area temporalis superior
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis
BA38 area temporopolaris BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
VON Economics
OA peristriate area
OA peristriate area OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa)
PE superior parietal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area TA superior temporal area
TE2 inferior temporal area proper
TF fusiform area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 85 Slice Nr. 5091
**356**

**357**
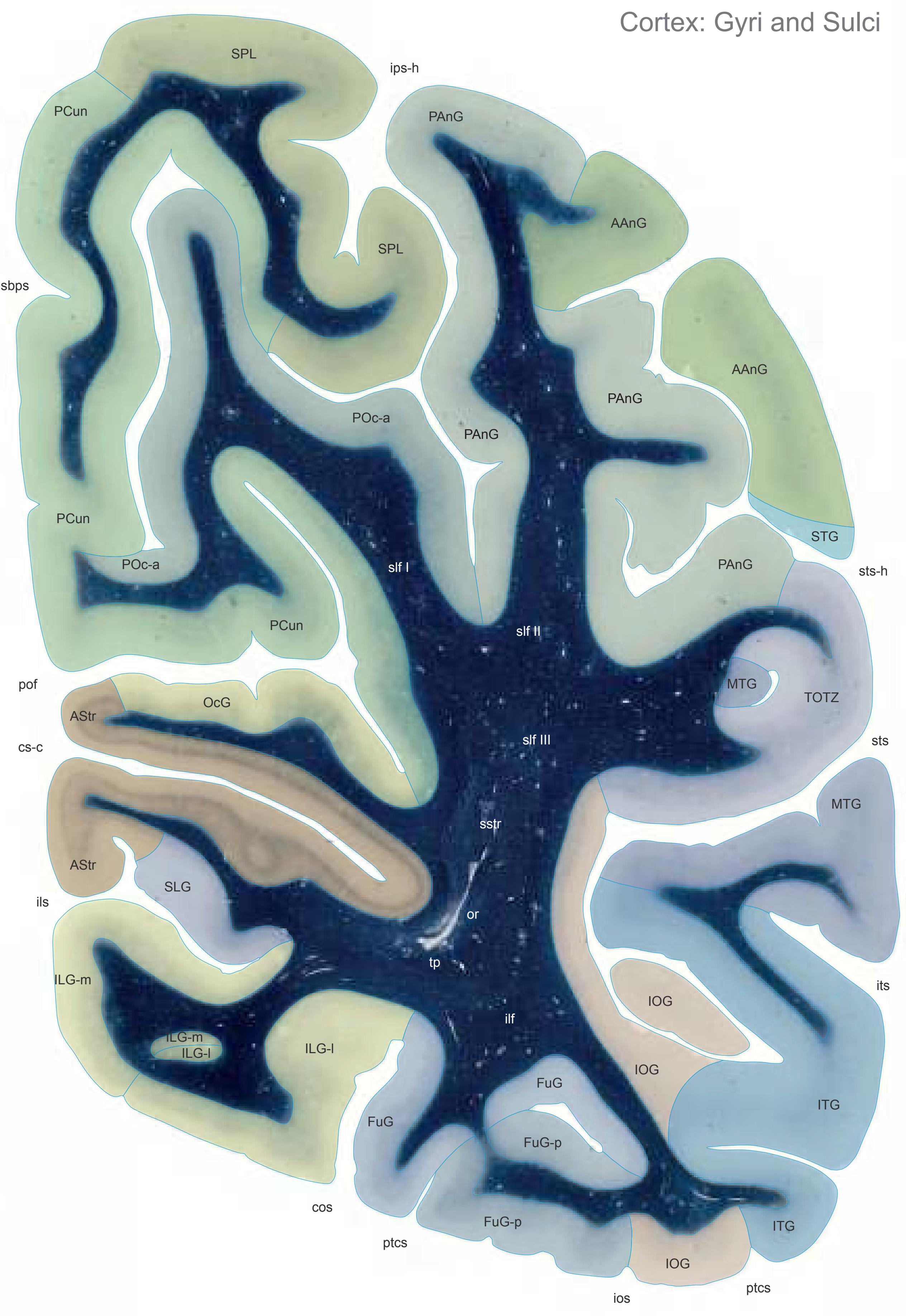

MNI Position y = -74.57 mm AHB Position y = 71.00 mm
AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part
IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus
AAnG angular gyrus
PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part
ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure
ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus
sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle
or optic radiation
slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp.
sstr sagittal stratum
tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 86 Slice Nr. 5139
**358**
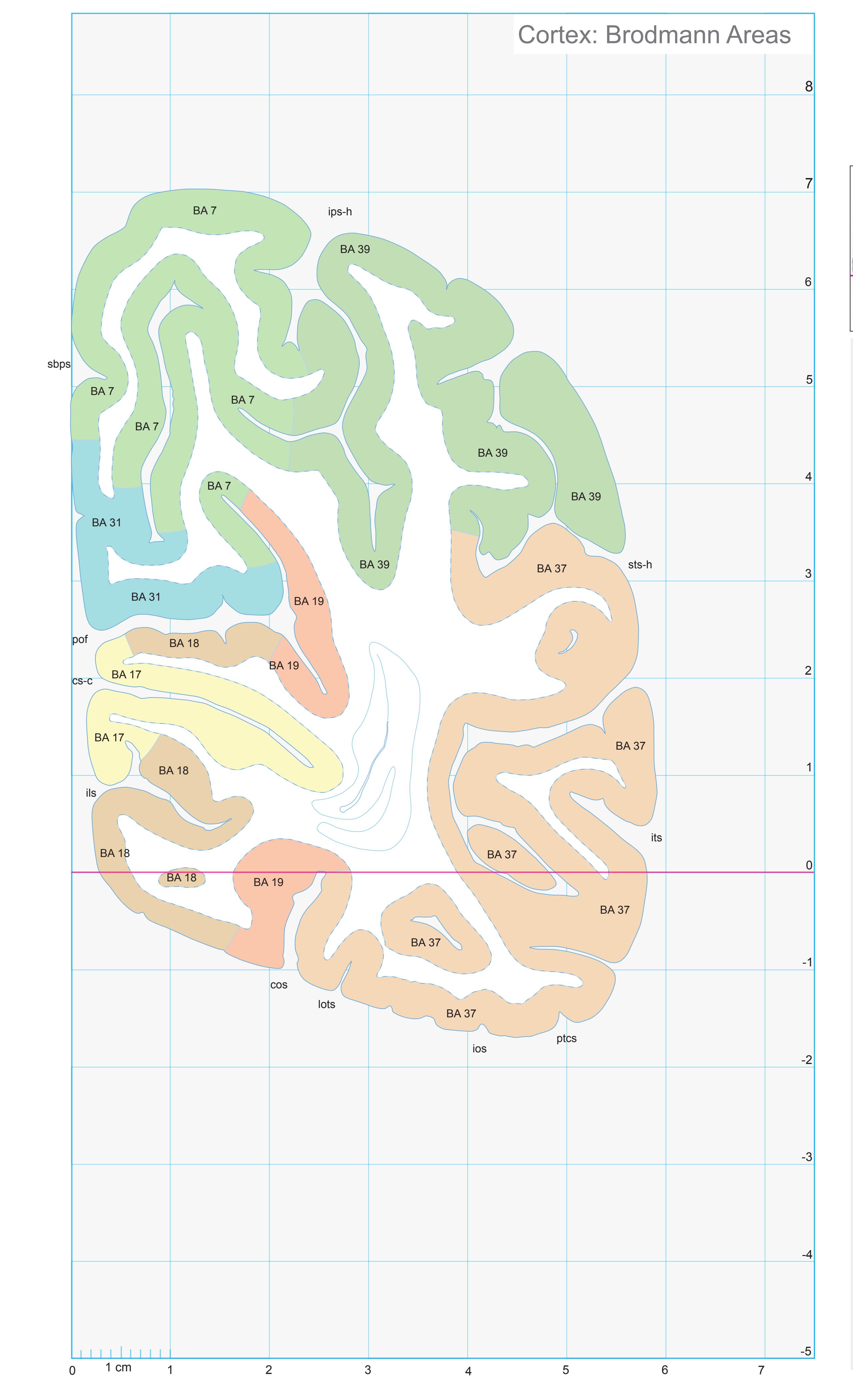
ICL: 71.00 MCP: 56.26 MNI: -74.57

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus
ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus lots lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus
sbps subparietal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**359**
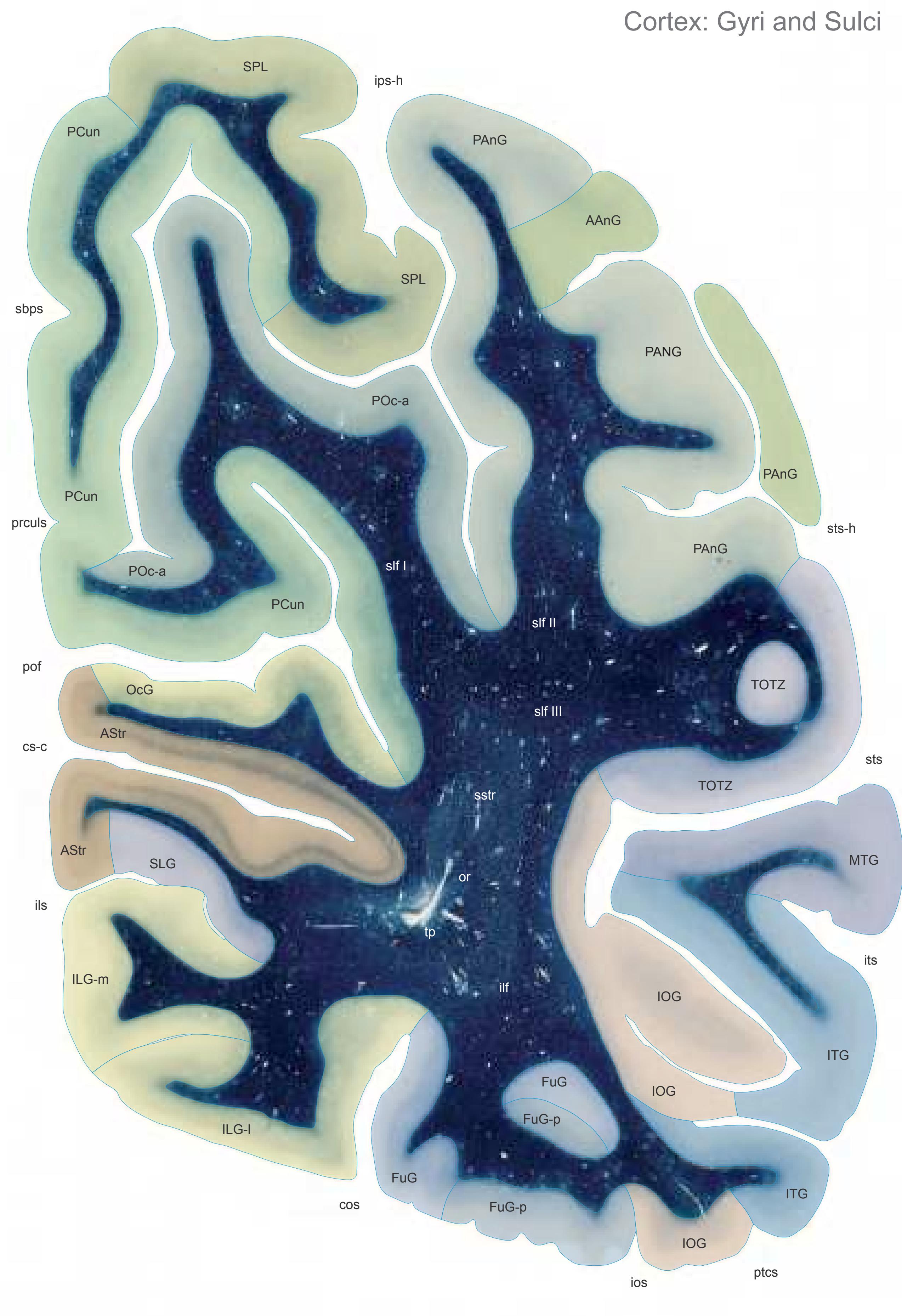

MNI Position y = -76.04 mm AHB Position y = 72.39 mm
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus
segment (sts-2)
cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 87 Slice Nr. 5191
**360**
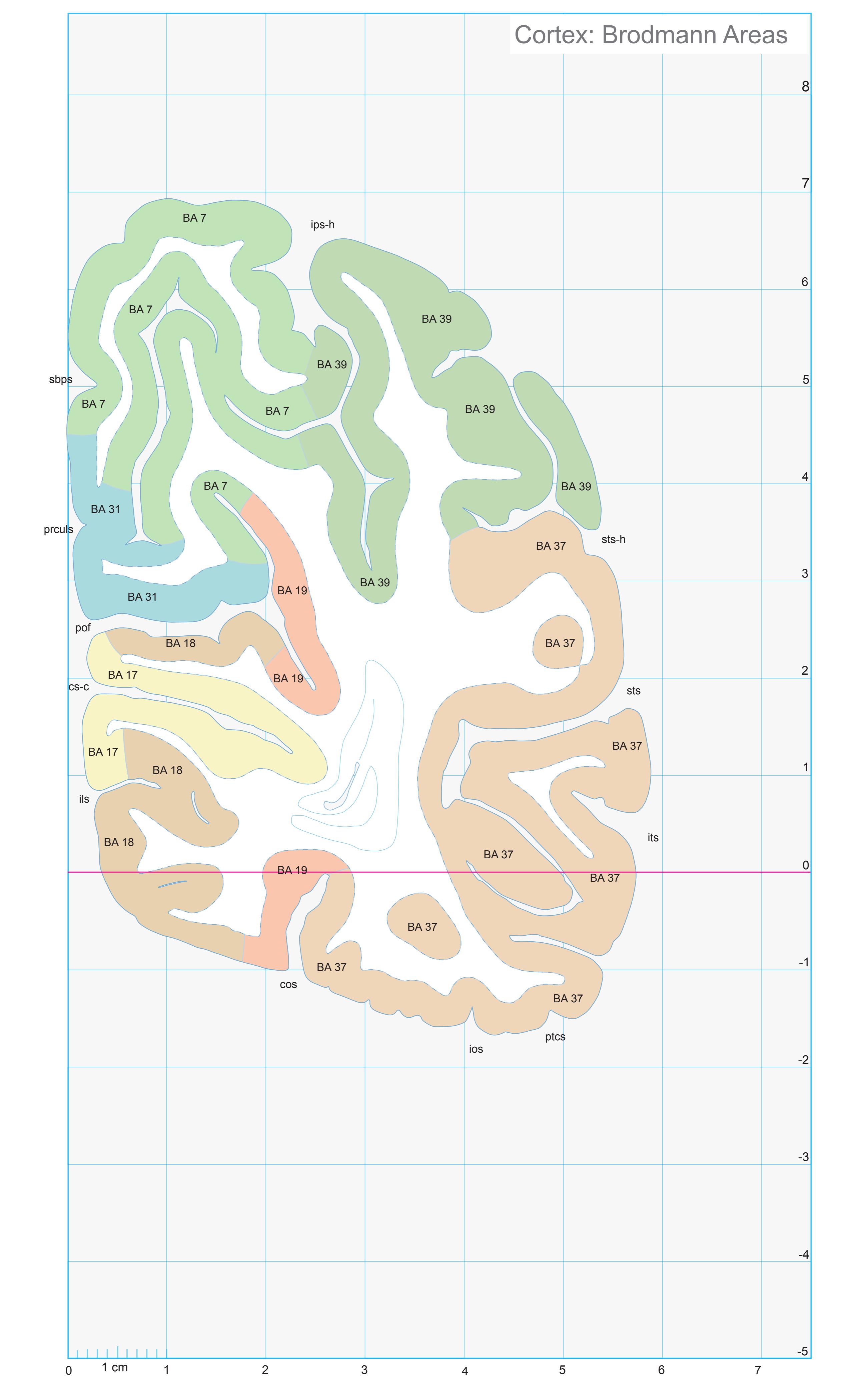
ICL: 72.39 MCP: 57.65 MNI: -76.04
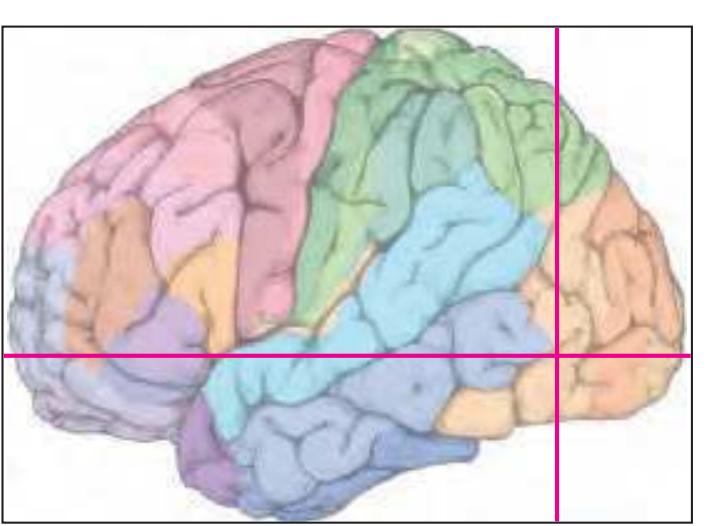
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**361**
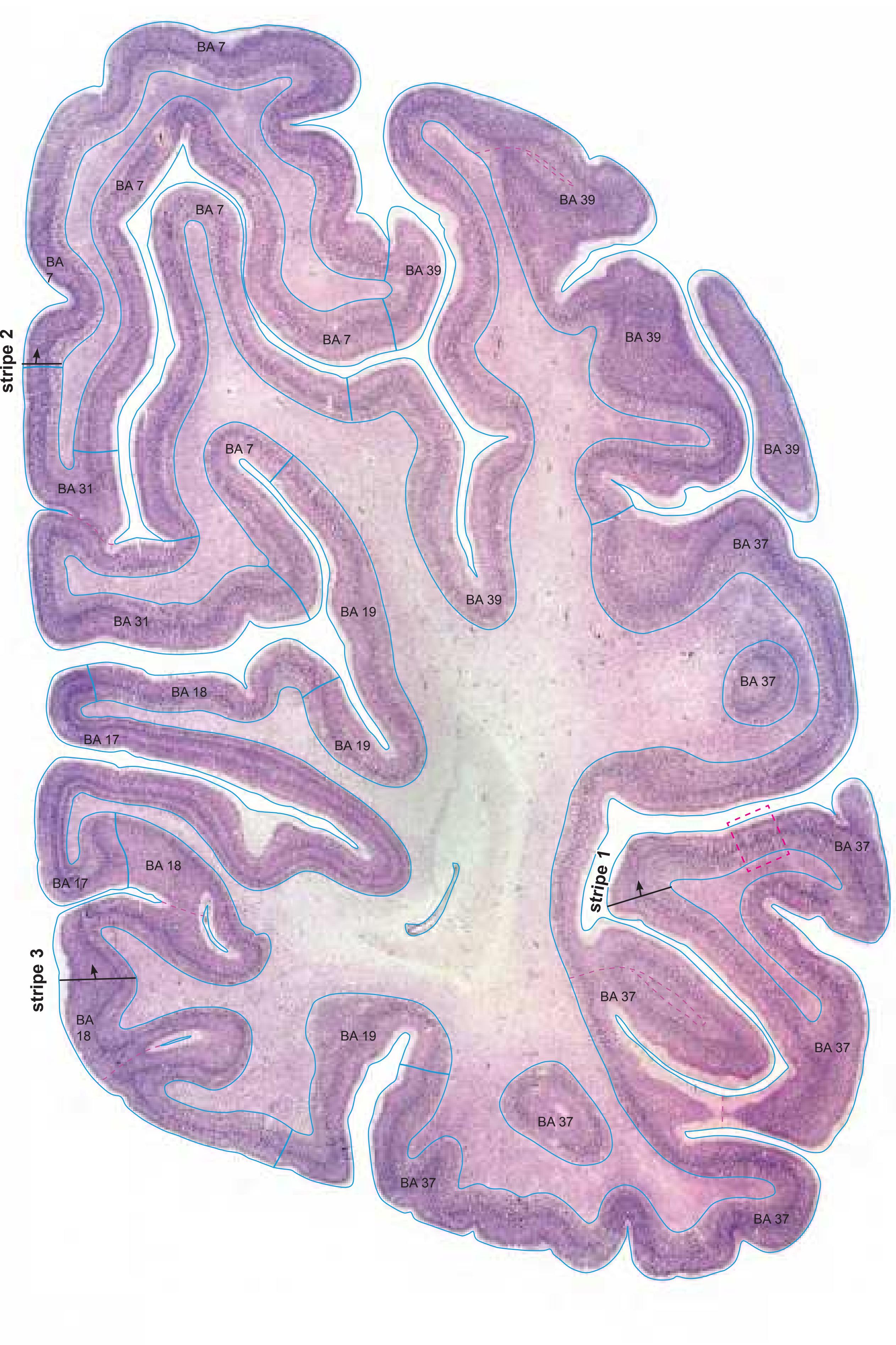
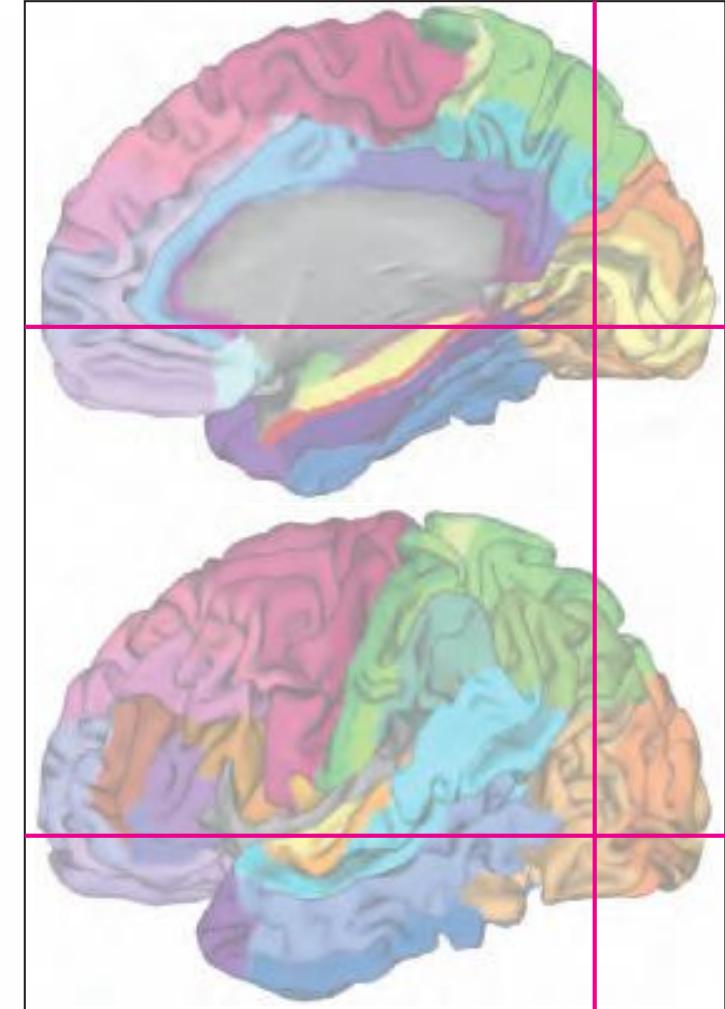
MNI Position y = -76.01 mm AHB Position y = 72.36 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AAnG angular gyrus AStr striate area
FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part
ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus
MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri
PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus
POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division
SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
BA7 area parietalis superior
BA17 area striata
BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis
BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
BA37 area occipito-temporalis
BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa) PE superior parietal area
PE superior parietal ar
PG angular area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area TE2 inferior temporal area proper
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 87 Slice Nr. 5190
**362**
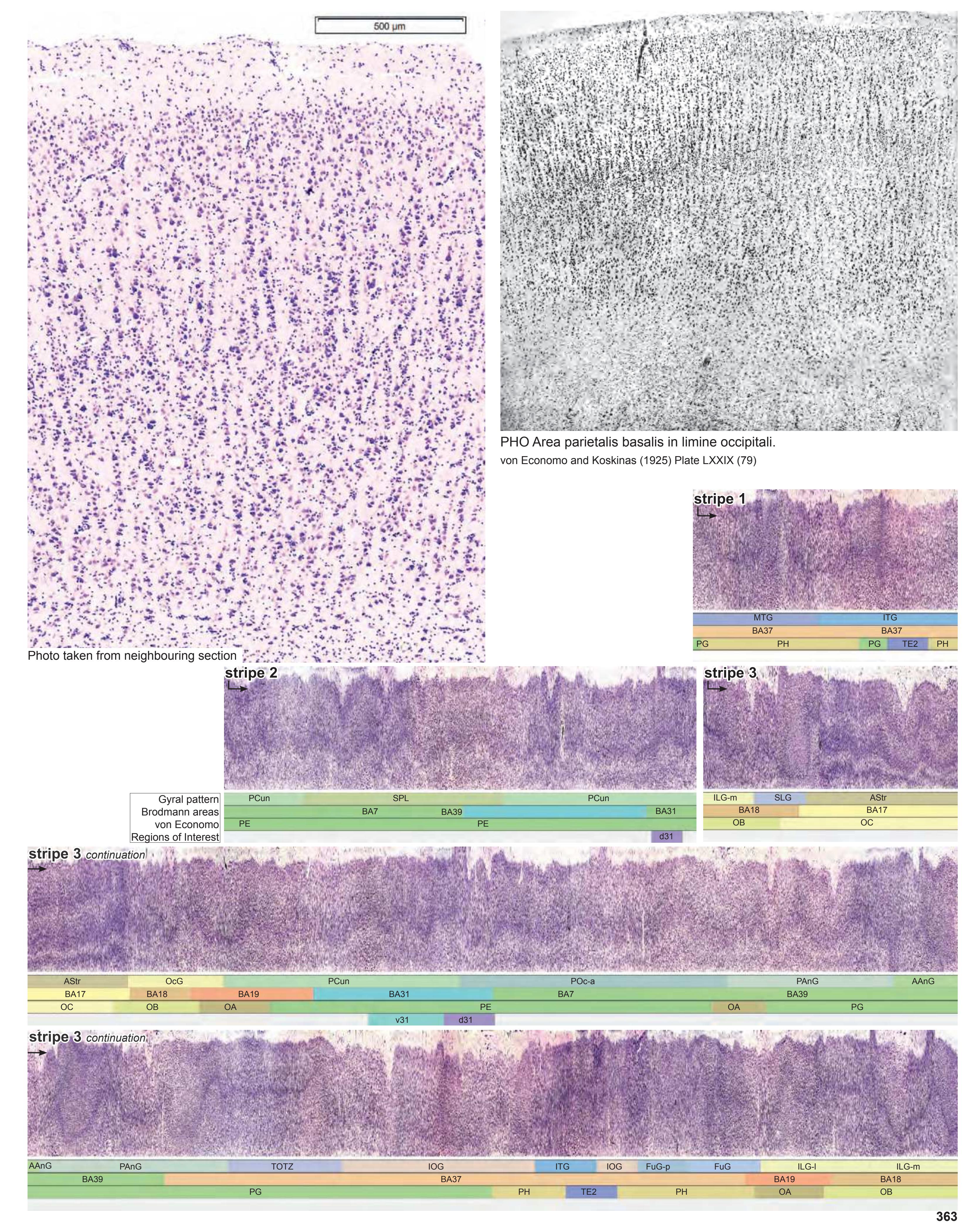


MNI Position y = -77.42 mm AHB Position y = 73.62 mm
AStr striate area AAnG anterior angular gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, posterior part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment (sts-2)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 88 Slice Nr. 5237
**364**

ICL: 73.62 MCP: 58.88 MNI: -77.42

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ils intralingual sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus sts-h superior temporal sulcus, horizontal posterior segment
**365**
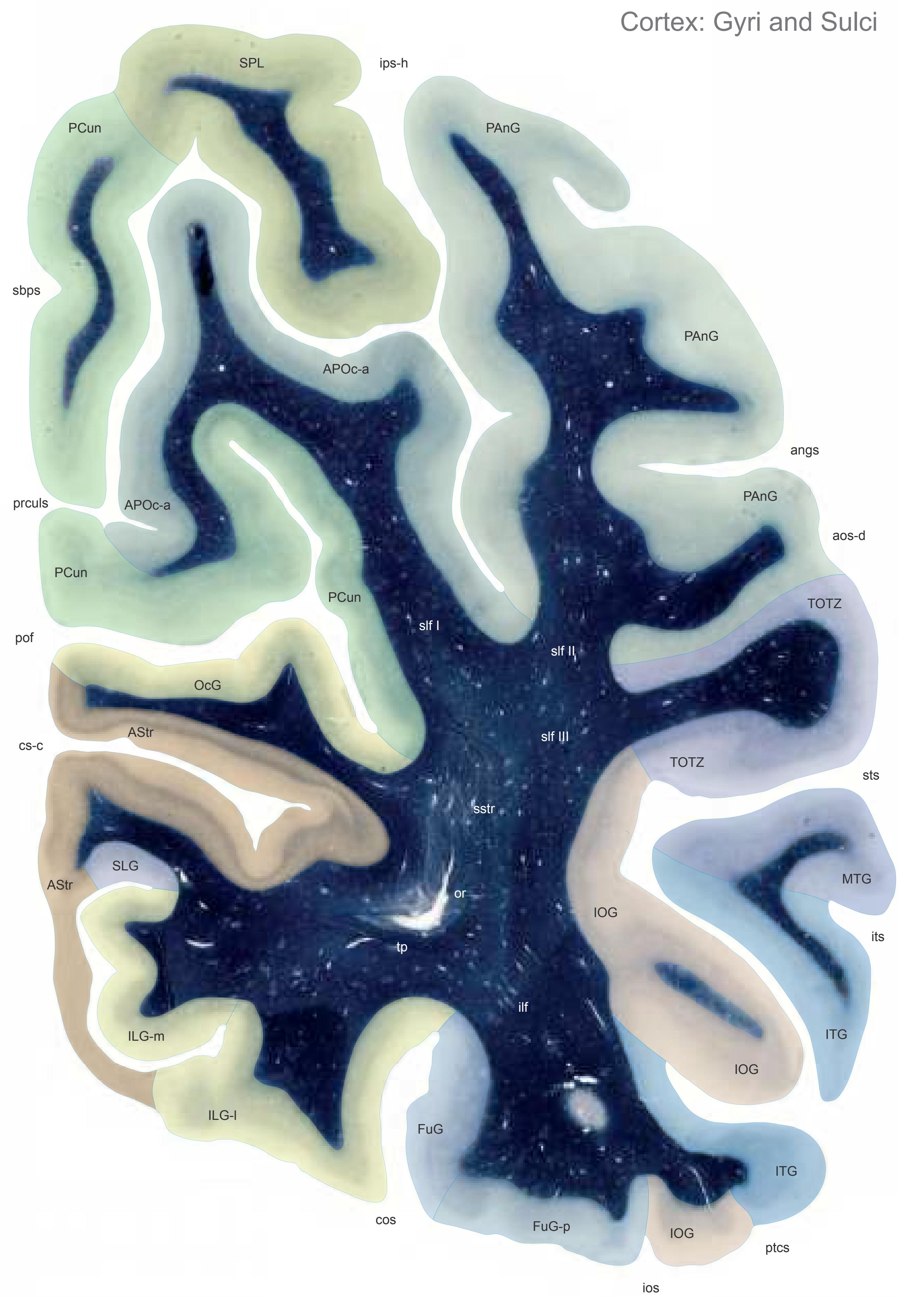

MNI Position y = -78.77 mm AHB Position y = 75.12 mm
AStr striate area APOc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 89 Slice Nr. 5293
**366**
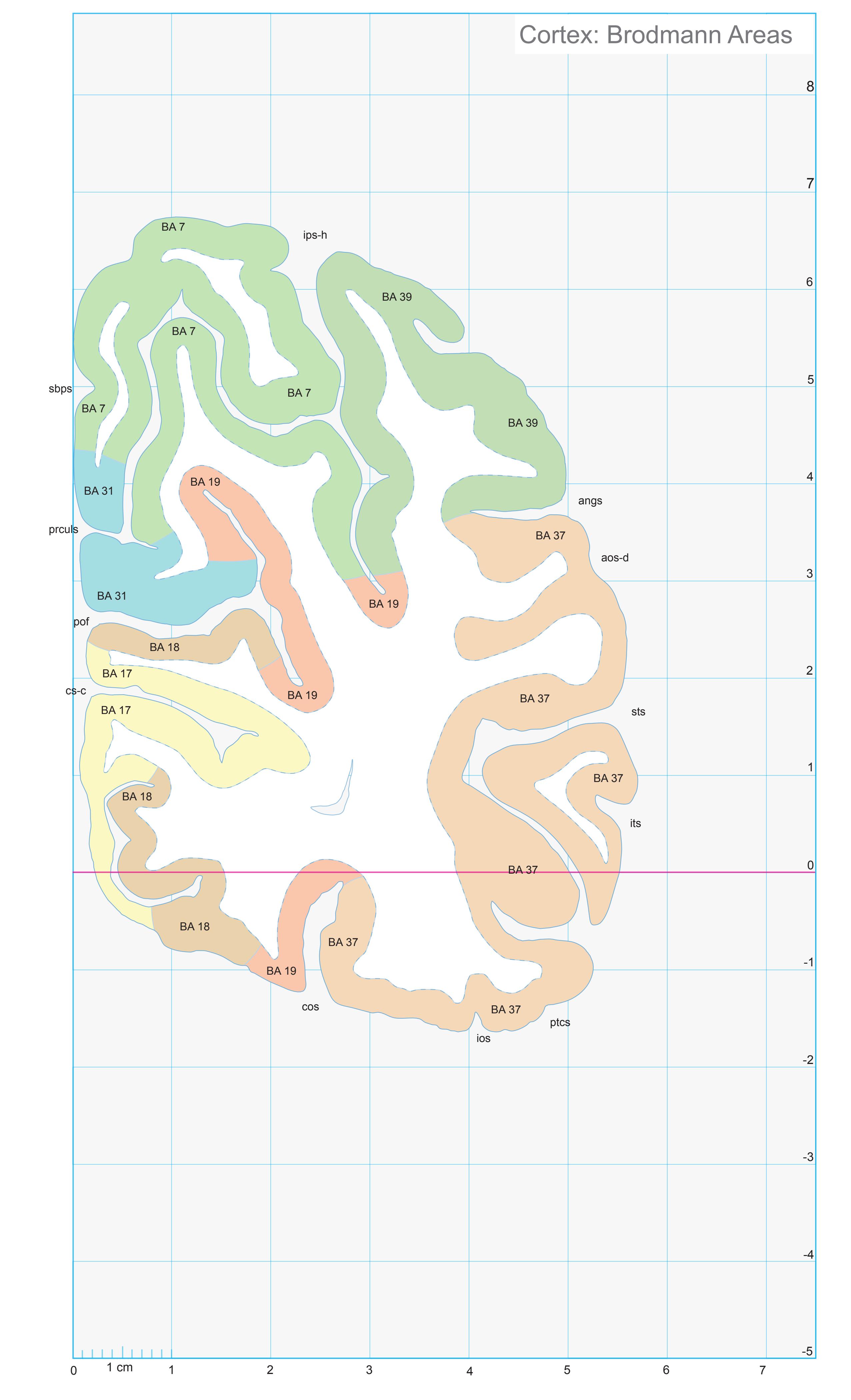
ICL: 75.12 MCP: 60.38 MNI: -78.77

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus ptcs posterior transverse collateral sulcus sbps subparietal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
**367**


MNI Position y = -78.12 mm AHB Position y = 74.37 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AStr striate area APOc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyri PAnG posterior angular gyrus
PCun precuneus SLG superior lingual gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
- BA7 area parietalis superior
- BA17 area striata
- BA18 area occipitalis
- BA19 area praeoccipitalis
- BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
- BA37 area occipito-temporalis BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa)
PE superior parietal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
d31 dorsal subregion of BA 31
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 89 Slice Nr. 5265
**368**

**369**


MNI Position y = -82.26 mm AHB Position y = 78.31 mm
AStr striate area APOc-a Arcus parieto-occipitalis, ant. division FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part ITG inferior temporal gyrus IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus SPL superior parietal lobule
TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus
aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure
prculs precuneal limiting sulcus
## - Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II superior longitudinal fascicle II, central comp. slf III superior longitudinal fascicle III, vent. comp. sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 90 Slice Nr. 5412
**370**

ICL: 78.31 MCP: 63.57 MNI: -82.26
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment its inferior temporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus
**371**


MNI Position y = -85.10 mm AHB Position y = 80.99 mm
AStr striate area FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division SPL superior parietal lobule
TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipital sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure ppa posterior marginal parietal sulcus (Vogt) prculs precuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior part
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle or optic radiation slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II/III superior longitudinal fascicle II/III sstr sagittal stratum tp tapetum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 91 Slice Nr. 5512
**372**
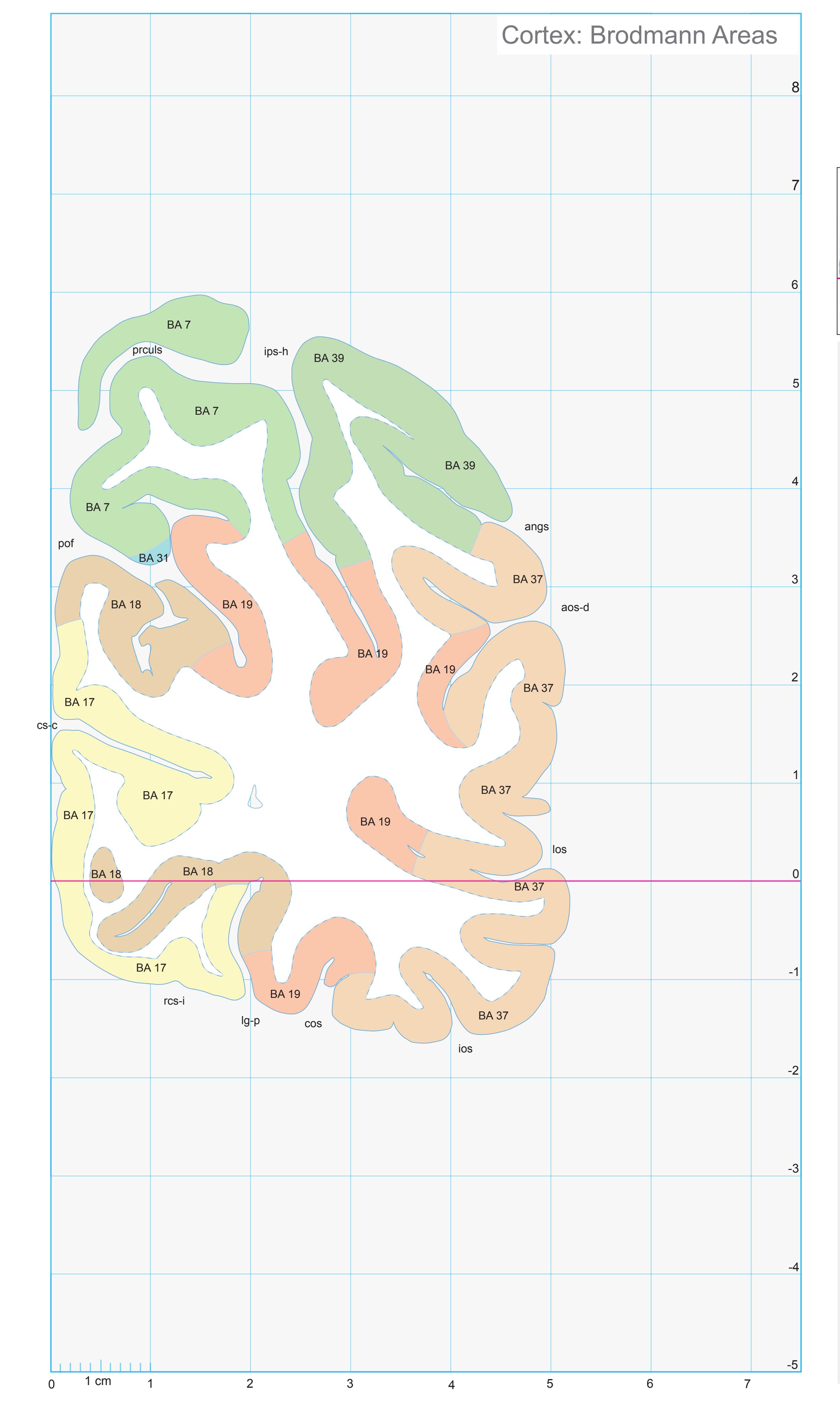
ICL: 80.99 MCP: 66.25 MNI: -85.10

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch
**373**
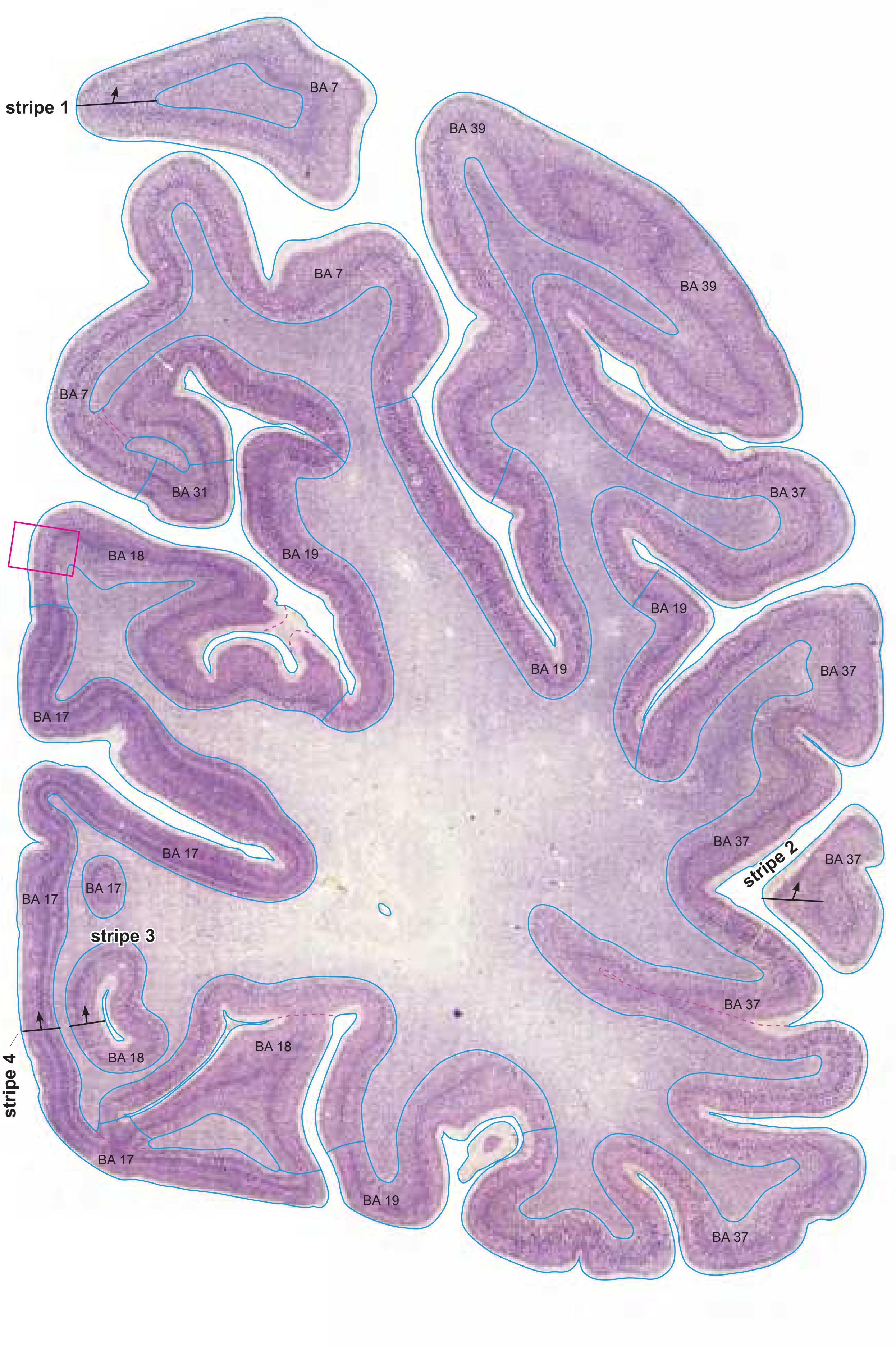

MNI Position y = -83.78 mm AHB Position y = 79.76 mm
## AStr striate area Gyral Pattern
FuG fusiform gyrus FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus
OcG occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus
POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone
## Brodmann Areas
- BA7 area parietalis superior
- BA17 area striata
- BA18 area occipitalis
- BA19 area praeoccipitalis
- BA31 area cingularis posterior dorsalis
- BA37 area occipito-temporalis
- BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area
OB parastriate area
OC striate area (granulosa) PE superior parietal area
PG angular area
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
## Regions of Interest
B. Vogt:
v31 ventral subregion of BA 31
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 91 Slice Nr. 5466
**374**

**375**


MNI Position y = -87.89 mm AHB Position y = 83.67 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part MOG medial occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part culs cuneal limiting sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipital sulcus (lunate ?) pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior part sss superior sagittal sulcus (vEconomo/Koskinas)
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II/III superior longitudinal fascicle II/III sstr sagittal stratum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 92 Slice Nr. 5612
**376**

ICL: 83.67 MCP: 68.93 MNI: -87.89
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch sss superior sagittal sulcus
**377**


MNI Position y = -90.73 mm AHB Position y = 86.38 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part MOG medial occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division
## Sulci
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcus, dorsal segment culs cuneal limiting sulcus cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment iss inferior sagittal sulcus lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipital sulcus pof pariero-occipital sulcus (posterior ramus) prculs percuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior part sss superior sagittal sulcus
## Fibers
ilf inferior longitudinal fascicle slf I superior longitudinal fascicle I, dorsal comp. slf II/III superior longitudinal fascicle II/III sstr sagittal stratum
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 93 Slice Nr. 5713
**378**
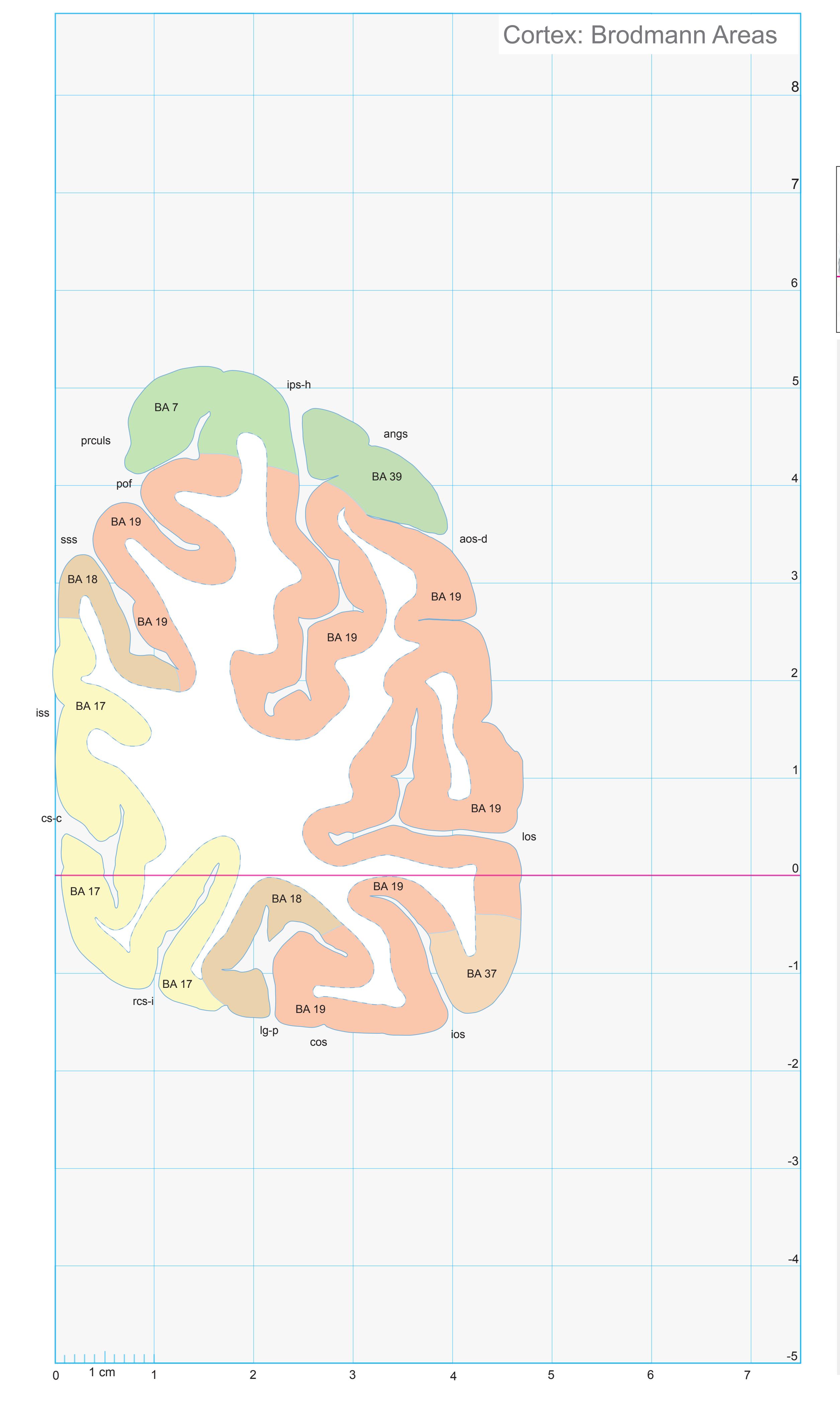
ICL: 86.38 MCP: 71.64 MNI: -90.73
BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus aos-d anterior occipital sulcis, dorsal segment cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p. ios inferior occipital sulcus ips-h intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment iss inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior) lg-p lingual sulcus, posterior ramus los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure prculs precuneal limiting sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch sss superior sagittal sulcus
**379**


MNI Position y = -89.35 mm AHB Position y = 85.07 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part MOG medial occipital gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division
## Brodmann Areas
- BA7 area parietalis superior
- BA17 area striata
- BA18 area occipitalis
- BA19 area praeoccipitalis
- BA37 area occipito-temporalis
- BA39 area angularis
## von Economo and Koskinas
- OA peristriate area
- OB parastriate area OC striate area (granulosa)
- PE superior parietal area
- PG angular area
-
PH basal (temporooccipital) parietal area
## Regions of Interest
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 93 Slice Nr. 5664
**380**


OA2(m) Area peristriata anterior magnocellularis. von Economo and Koskinas (1925) Plate LXXXI (81)

PE OA PG OA PG OA PH OA OB OC BA7 BA19 BA39 BA19 BA37 BA19 BA18 BA17 POc-p MOG PAnG MOG IOG FuG-p ILG-l ILG-m AStr
**381**


MNI Position y = -93.55 mm AHB Position y = 89.03 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-m inferior lingual gyrus, medial part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lateral part SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Sulci
culs cuneal limiting sulcus cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part ios inferior occipital sulcus iss inferior sagittal sulcus los lateral occipital sulcus pof parietooccipital sulcus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior part sos superior occipital sulcus sss superior sagittval sulcus tos transverse occipital sulcus
## Fibers
-
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 94 Slice Nr. 5812
**382**
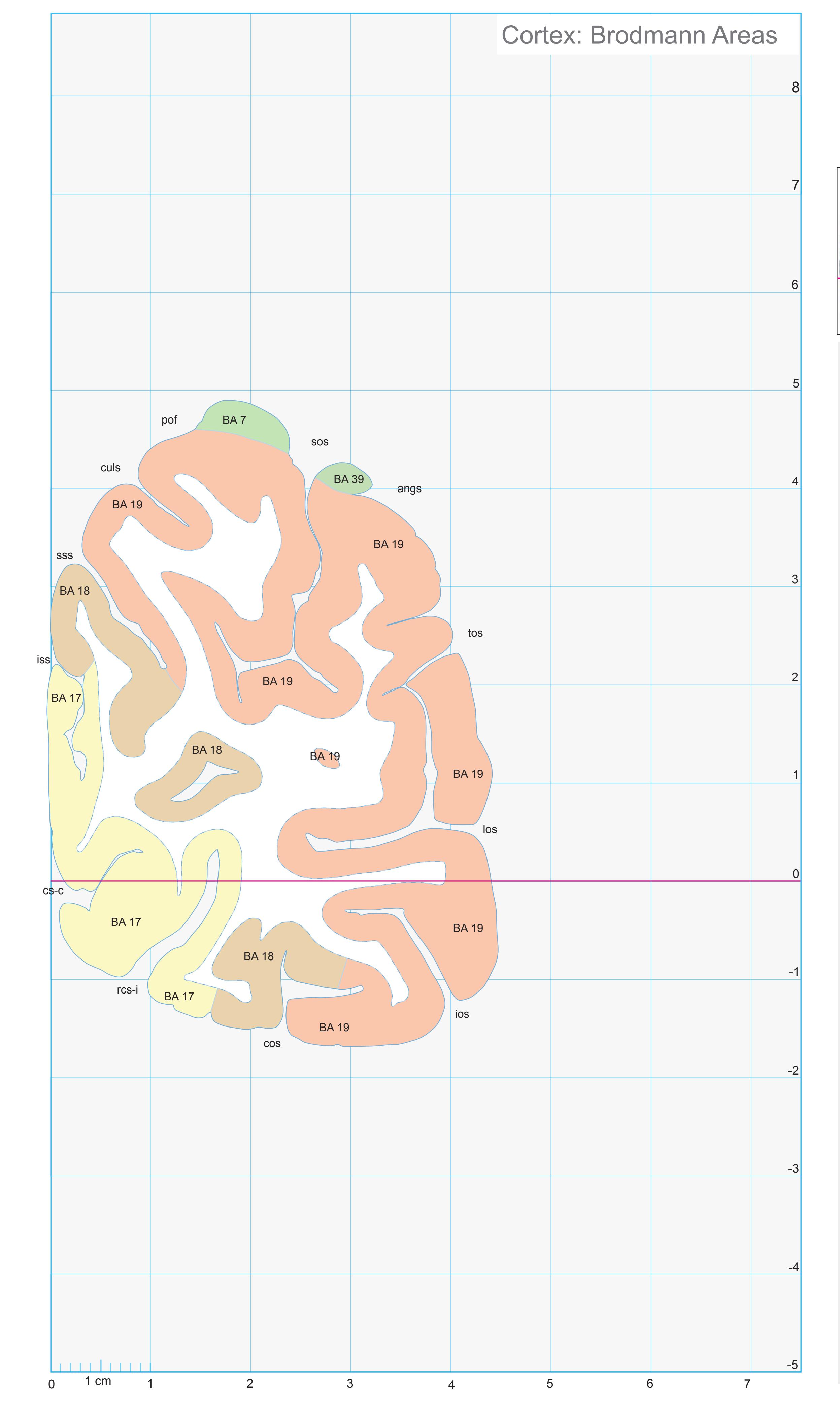
ICL: 89.03 MCP: 74.29 MNI: -93.55

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
angs angular sulcus
cos collateral sulcus cs-c calcarine sulcus, central p.
culs cuneal limiting sulcus
ios inferior occipital sulcus iss inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior)
los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure
rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch
sos superior occipital sulcus
sss superior sagittal sulcus tos transverse occipital sulcus
**383**


MNI Position y = -96.33 mm AHB Position y = 91.71 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lateral part
SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Sulci
cos collateral sulcus culs cuneal limiting sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus iss inferior sagittal sulcus los lateral occipital sulcus (lunate ?) rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, superior part sss superior sagittal sulcus tos transverse occipital sulcus tos-l transverse occipital sulcus, lateral part
tos-m transverse occipital sulcus, medial part
## Fibers
-
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 95 Slice Nr. 5912
**384**
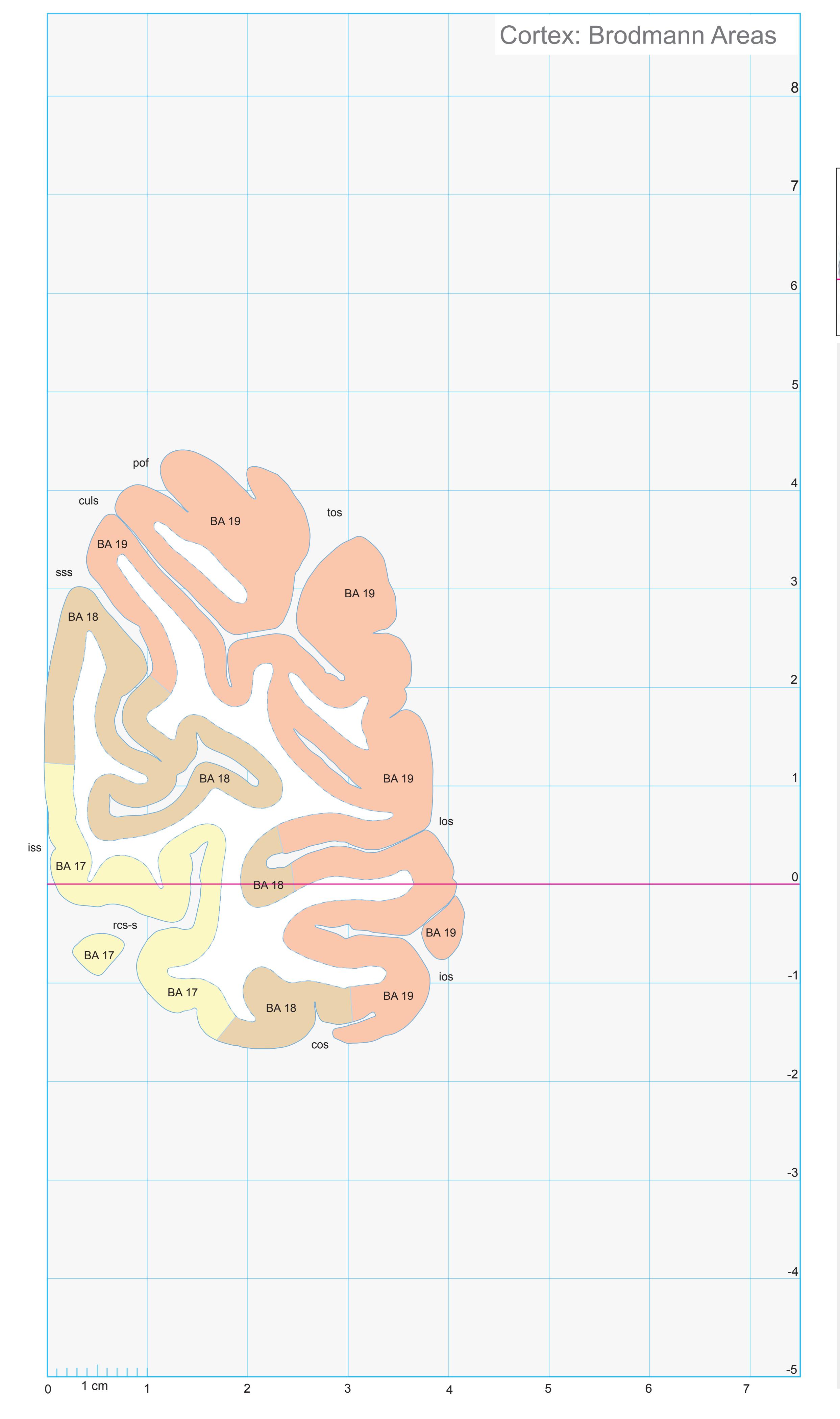
ICL: 91.71 MCP: 76.97 MNI: -96.33

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
cos collateral sulcus culs cuneal limiting sulcus ios inferior occipital sulcus iss inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior) los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus pof parieto-occipital fissure rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch sss superior sagittal sulcus
tos transverse occipital sulcus
**385**
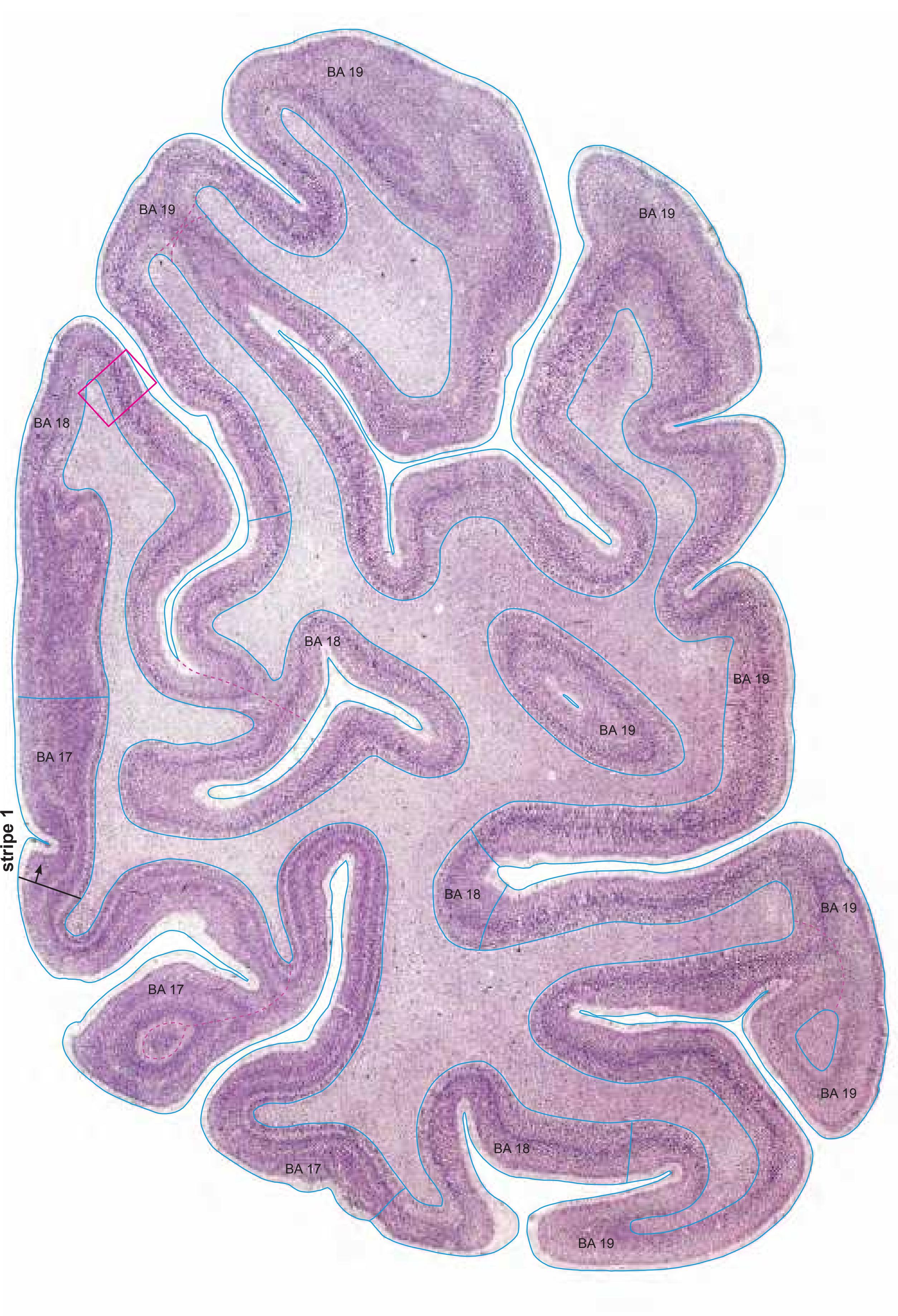

MNI Position y = -94.98 mm AHB Position y = 90.43 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lateral part SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Brodmann Areas
BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis
## von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area OB parastriate area OC striate area (granulosa)
Regions of Interest
-
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 95 Slice Nr. 5864
**386**

**387**
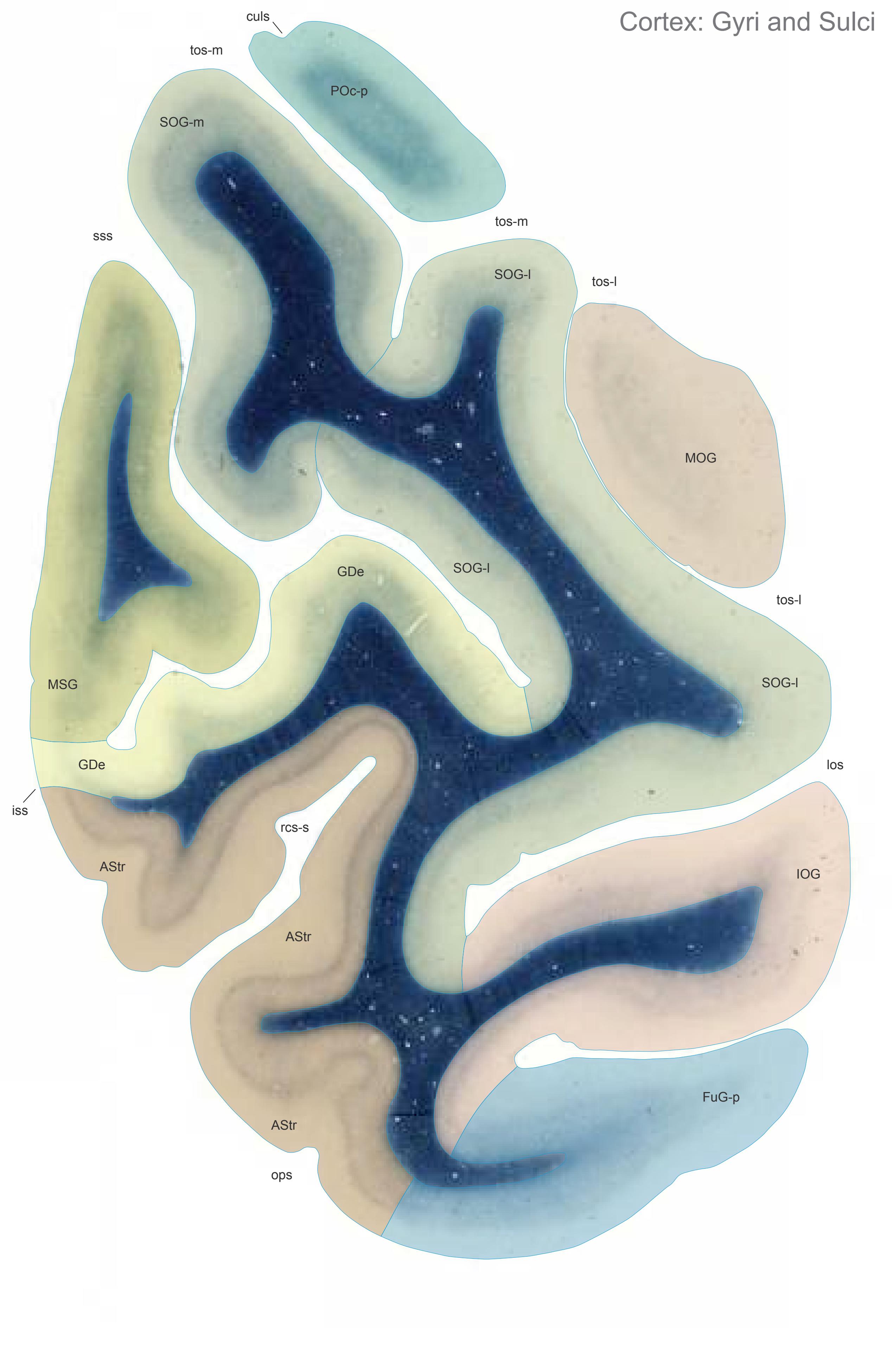

MNI Position y = -99.18 mm AHB Position y = 94.42 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens IOG inferior occipital gyrus MOG medial occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus POc-p Arcus parieto-occipitalis, post. division SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lat. part SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Sulci
culs cuneal limiting sulcus iss inferior sagittal sulcus los lateral occipital sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, superior part sss superior sagittal sulcus tos-l transverse occipital sulcus, lateral part tos-m transverse occipital sulcus, medial part
## Fibers
-
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 96 Slice Nr. 6013
**388**

ICL: 94.42 MCP: 79.68 MNI: -99.18

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
culs cuneal limiting sulcus
iss inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior)
los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of
Seitz) rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch
tos-m transverse occipital sulcus, medial ramus
sss superior sagittal sulcus tos-l transverse occipital sulcus, lateral ramus
**389**
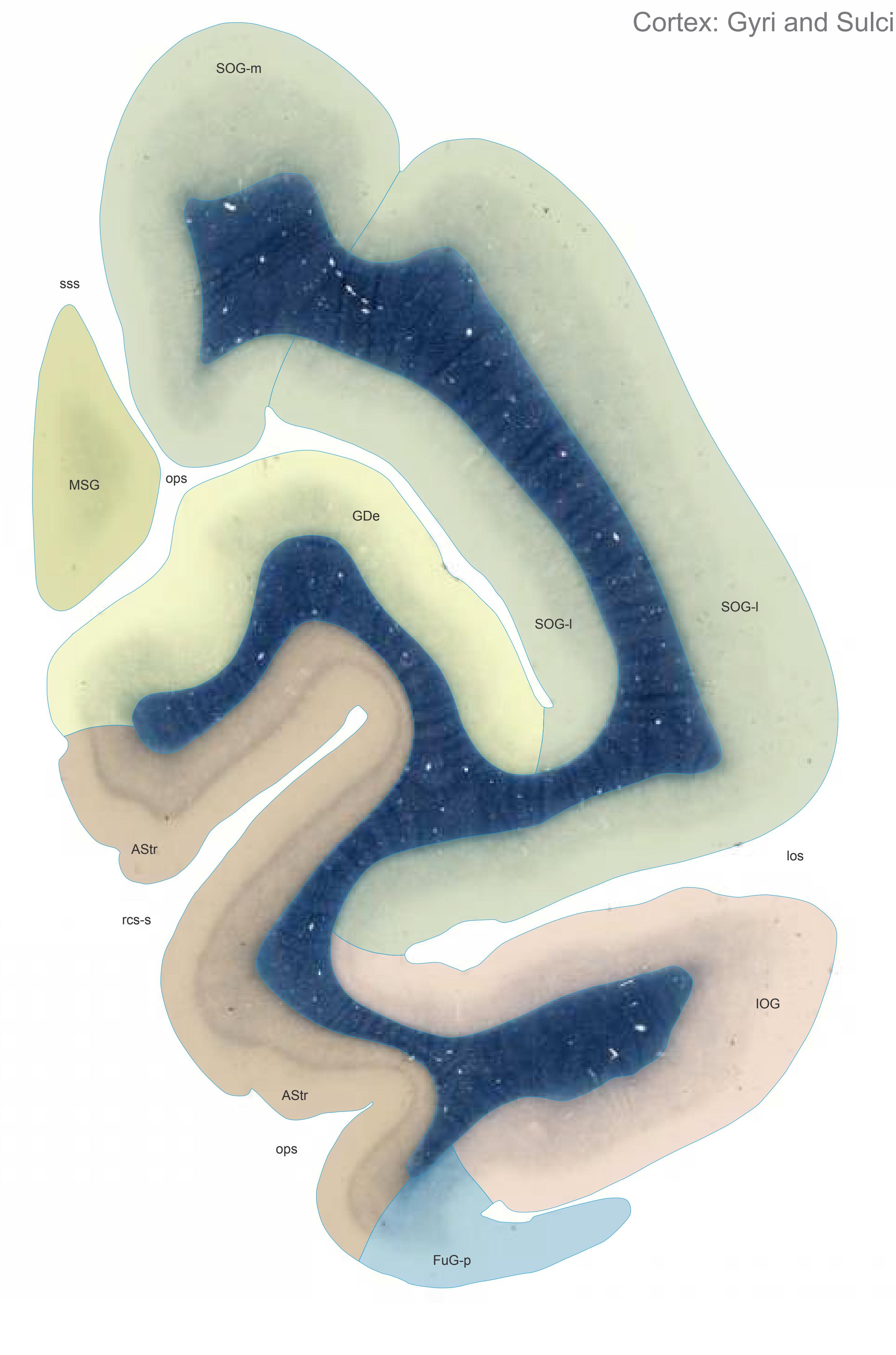

MNI Position y = -101.99 mm AHB Position y = 97.10 mm
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens IOG inferior occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lat. part SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Sulci
los lateral occipital sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, superior part sss superior sagittal sulcus
## - Fibers
This is a blank image. There is no text to extract.
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 97 Slice Nr. 6113
**390**
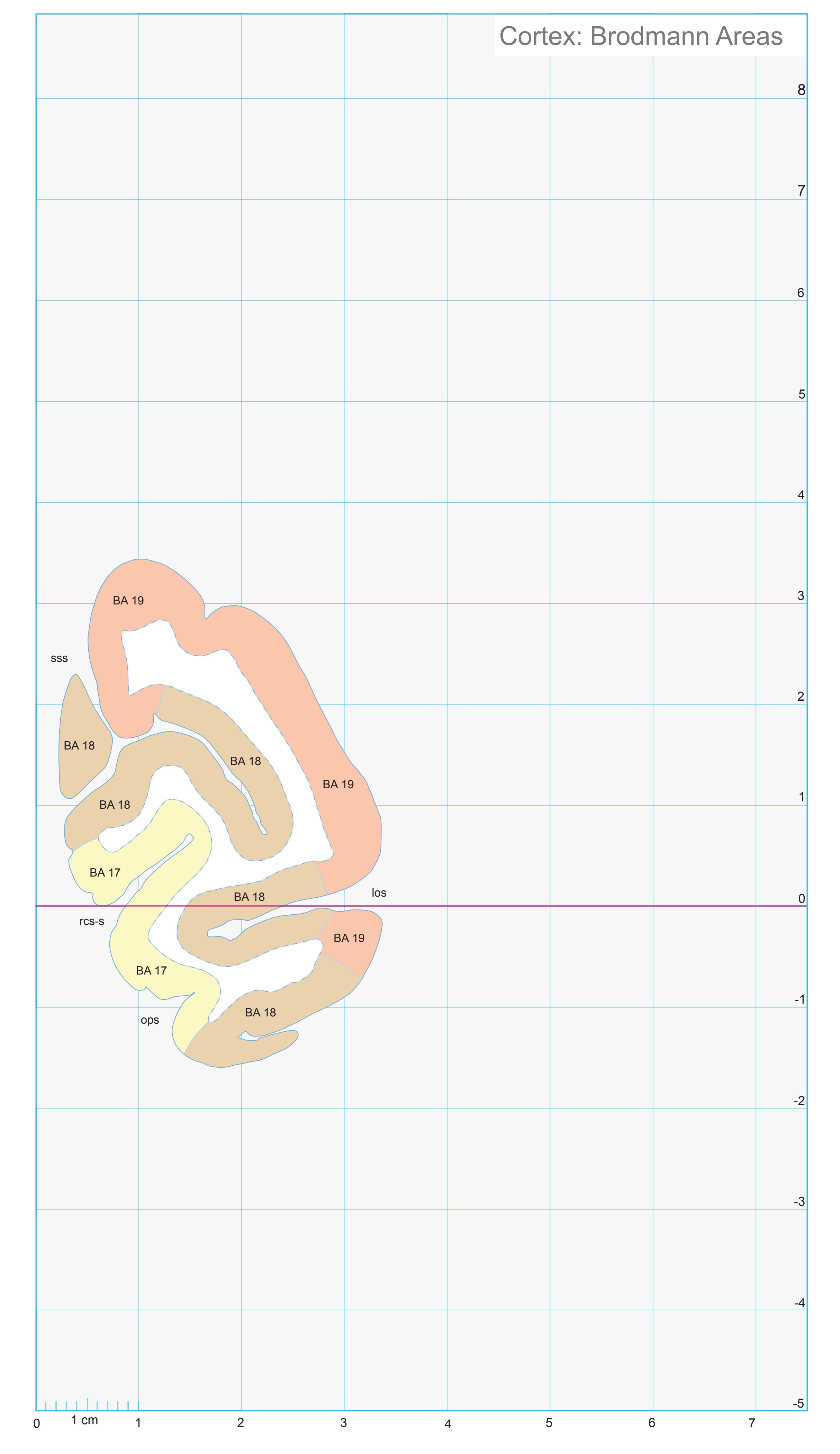
ICL: 97.10 MCP: 82.36 MNI: -101.99

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of Seitz)
rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch sss superior sagittal sulcus
**391**


MNI Position y = -100.61 mm AHB Position y = 95.79 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AStr striate area FuG-p fusiform gyrus, post. part GDe gyrus descendens IOG inferior occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, lat. part SOG-m superior occipital gyrus, medial part
## Brodmann Areas
BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis
## von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area OB parastriate area OC striate area (granulosa)
Regions of Interest
-
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 97 Slice Nr. 6064
**392**

Regions of Interest
OB gamma Limes parastriatus gigantopyramidalis. OC Area striata. von Economo and Koskinas (1925) Plate LXXXVI (86)
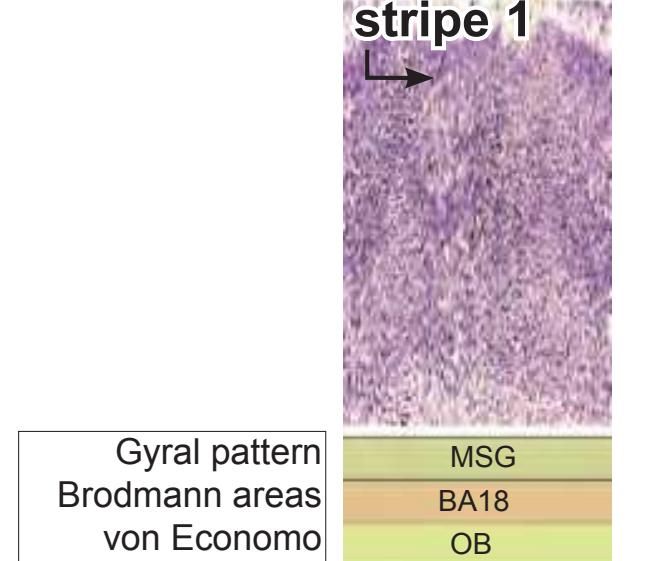

**393**


MNI Position y = -104.78 mm AHB Position y = 99.75 mm
ASTr striate area GDe gyrus descendens IOG inferior occipital gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus
## Sulci
los lateral occipital sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, superior part
## Fibers
-
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 98 Slice Nr. 6212
**394**

ICL: 99.75 MCP: 85.01 MNI: -104.78

BA1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 ( see p. 101)
los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus ops occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of Seitz) rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch
**395**


MNI Position y = -107.62 mm AHB Position y = 102.43 mm
AStr striate area IOG inferior occipital gyrus GDe gyrus descendens
## Sulci
los lateral occipital sulcus
Fibers
-
Fiber stain (Weigert) Section Nr. 99 Slice Nr. 6312
**396**

ICL: 102.43 MCP: 87.69 MNI: -107.62

BA17,18 Brodmann areas 17,18 ( see p. 101) los lateral occipitotemporal sulcus
**397**


MNI Position y = -106.24 mm AHB Position y = 101.15 mm
## Gyral Pattern
AStr striate area IOG inferior occipital gyrus GDe gyrus descendens
## Brodmann Areas
- BA17 area striata BA18 area occipitalis BA19 area praeoccipitalis
- von Economo and Koskinas
OA peristriate area OB parastriate area OC striate area (granulosa)
Regions of Interest
-
Cell stain (Nissl): Section Nr. 99 Slice Nr. 6264
**398**

Gyrus descendens Ecker.
OB Area parastriata.
OC Area striata.
OB (gamma) Limes parastriatus gigantopyramidalis.
von Economo and Koskinas (1925) Plate LXXXVII (87)
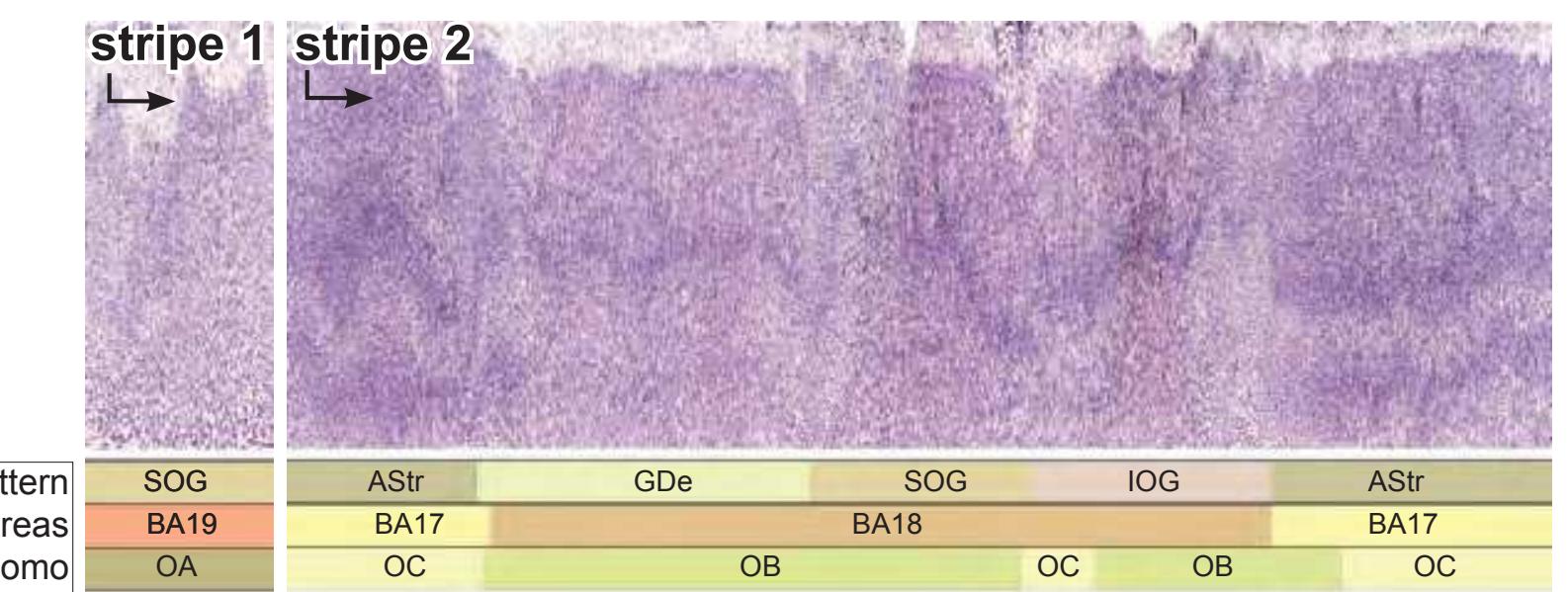
Gyral pattern Brodmann areas von Economo Regions of Interest
**399**
This page intentionally left blank
# **2.4 Horizontal and Sagittal Diagrams with Reduced Detail**

The diagrams of the sections in the axial and sagittal planes were produced from the 3D reconstruction of the *Atlas* brain in the MNI space using the methodology described in section 2.1.10. The distance between the axial sections is 4 mm and in the sagittal series 4 mm.
Since the contour lines defining the pial and ventricular surfaces of the brain as well as the subcortical structures were automatically generated the plates may be more thoroughly checked if stereotaxic applications are intended.
**401**
**Fig.: A-1** Position z = 84.00 mm

**Fig.: A-2** Position z = 80.00 mm
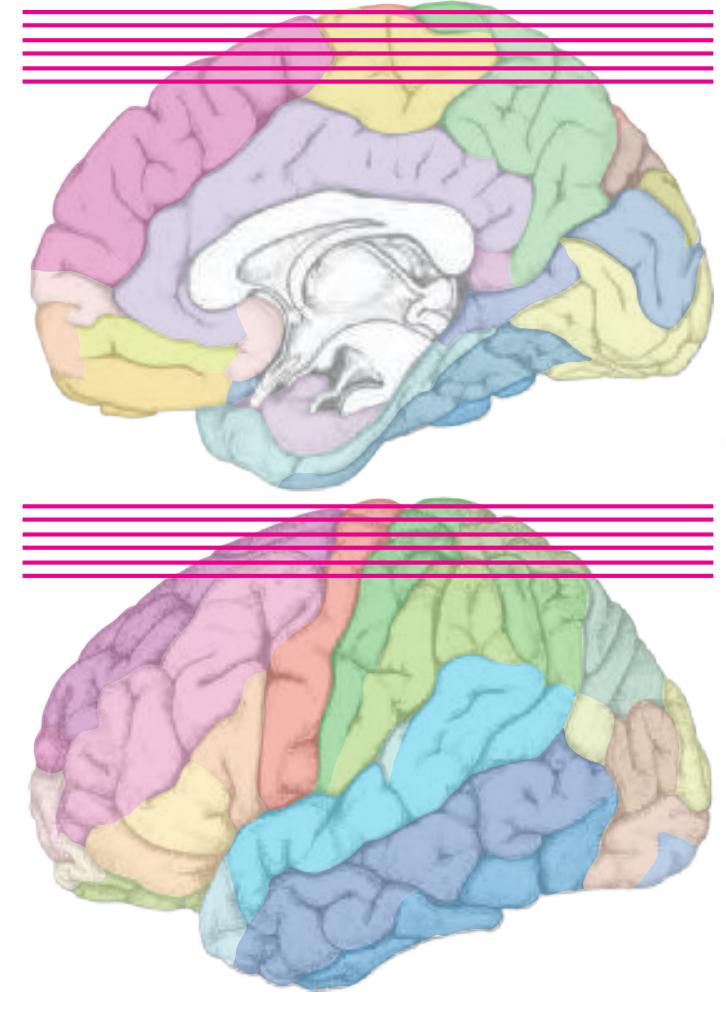
AAnG angular gyrus, anterior division MFG middle frontal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial division SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
SFG
PrG
SPL
PoG
PCL


SFGL PoG PrG SMG MFG AAnG PAnG PCun PCL SFGM SPL **Fig.: A-5** Position z = 68.00 mm
SPL
**402**
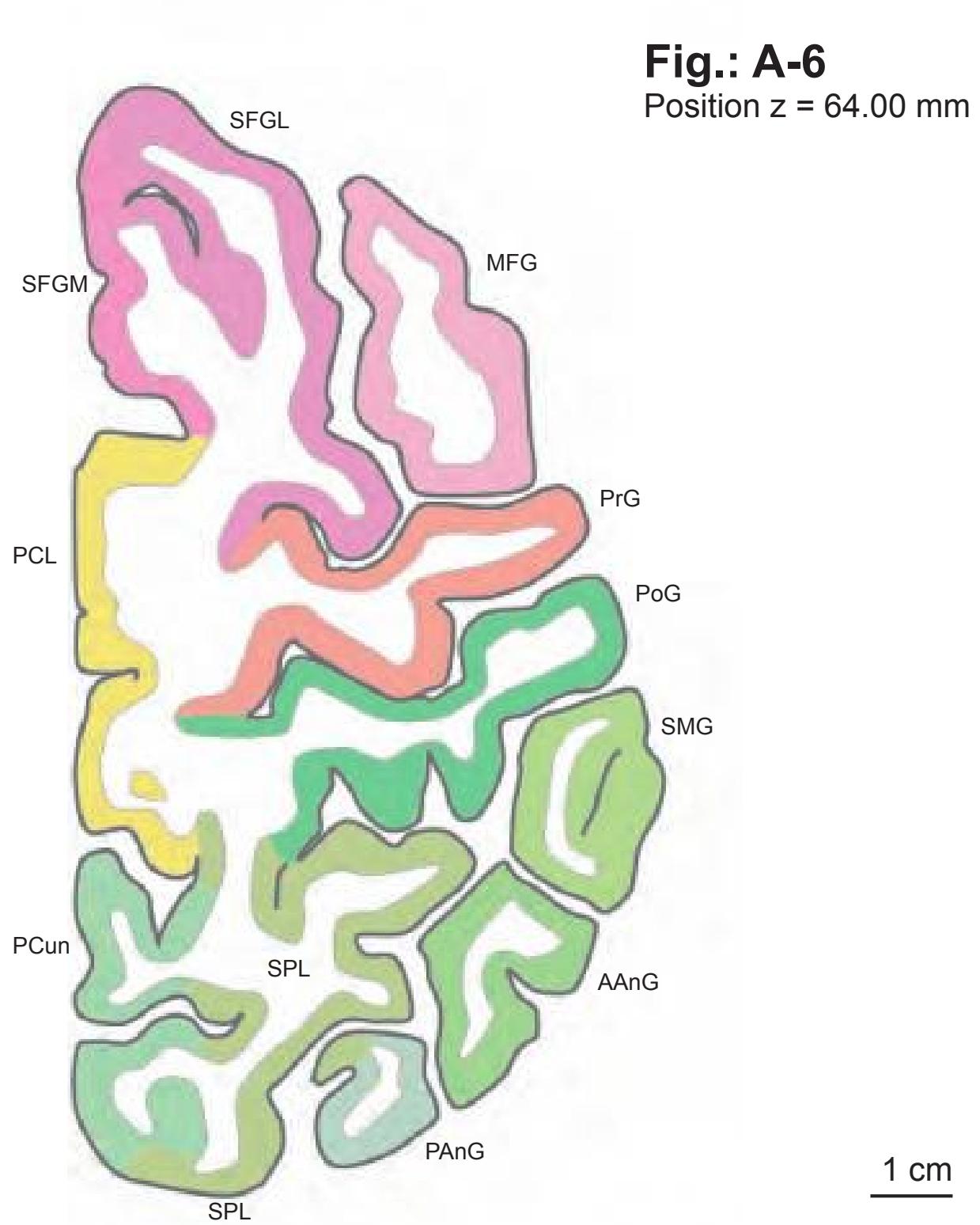
**Fig.: A-7** Position z = 60.00 mm
**Fig.: A-8** Position z = 56.00 mm

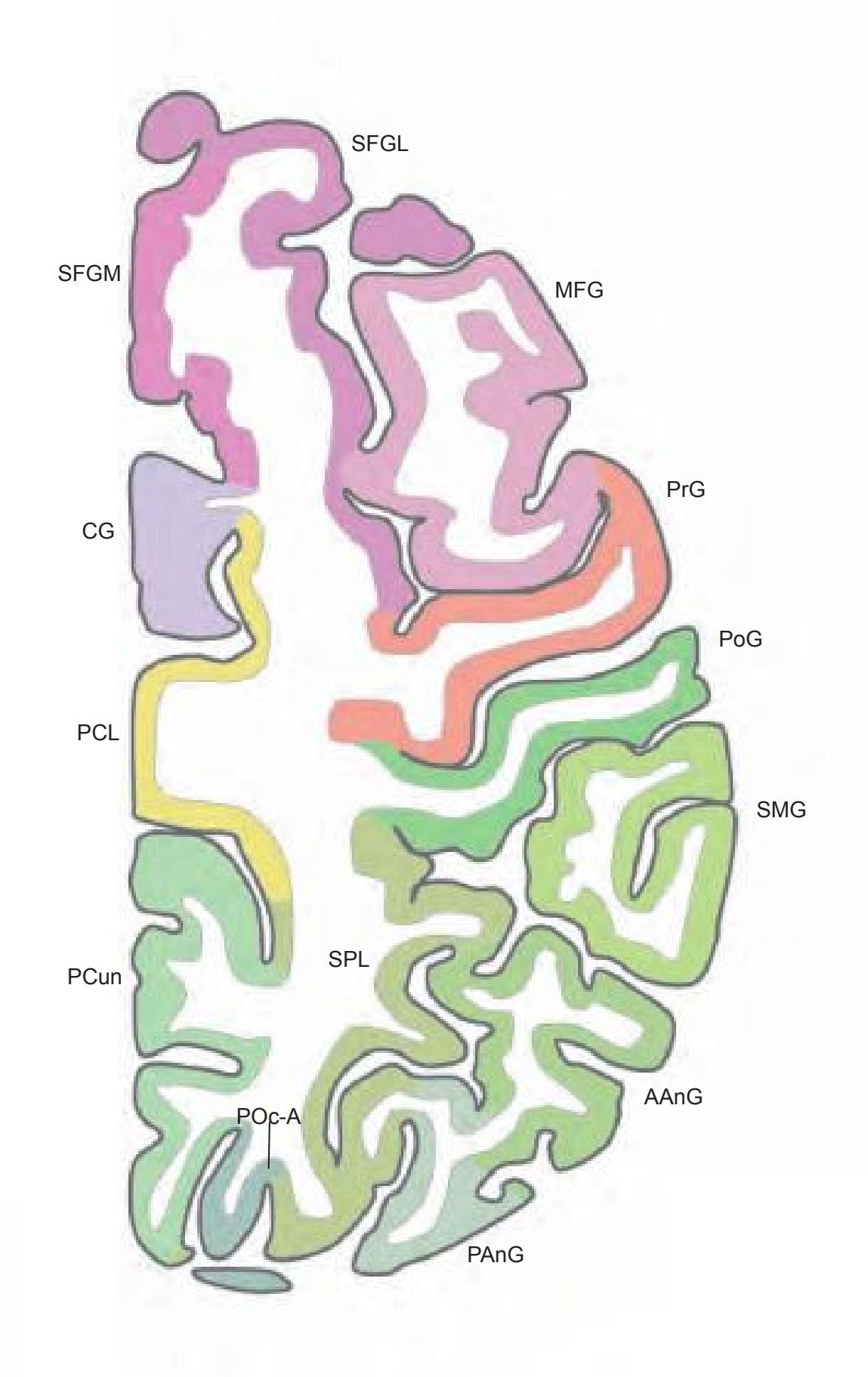

AAnG angular gyrus, anterior division CG cingulate gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus POc-A parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-P parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial division SMG supramarginal gyrus
SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus
**Fig.: A-9** Position z = 52.00 mm
**Fig.: A-10** Position z = 48.00 mm


1 cm
**403**


Cd caudate nucleus CG cingulate gyrus COp-p posterior central operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part Ins insula MFG middle frontal gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus POc-P parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PrG precentral gyrus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial division SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule
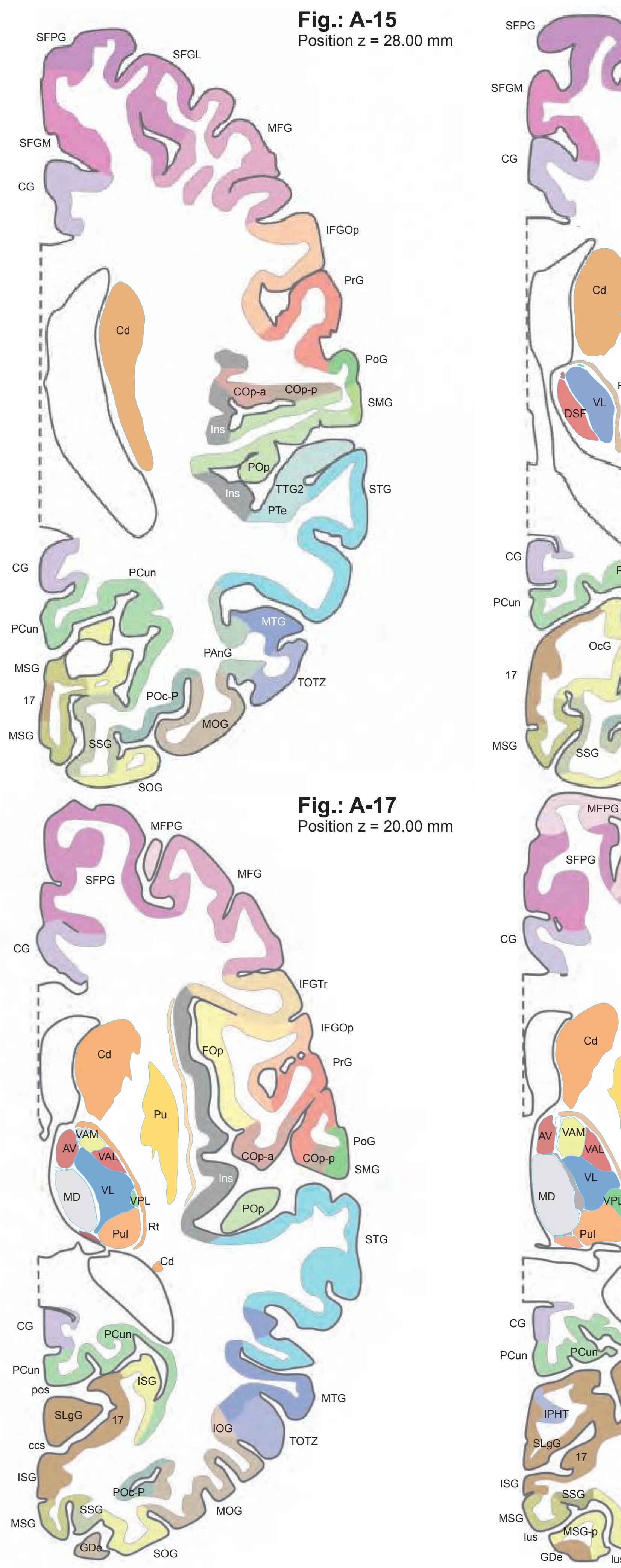


17 striate area AV anteroventral thalamic nucleus ccs calcarine sulcus, central part Cd caudate nucleus CG cingulate gyrus COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum DSF dorsal superficial nucleus FOp frontal operculum GDe gyrus descendens IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part Ins insula IOG inferior occipital gyrus IPHT isthmo-parahippocampal transition ISG inferior sagittal gyrus LIGI long insular gyrus I lus lunate sulcus MD medial dorsal thalamic nucleus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus MSG-p middle sagittal gyrus, posterior part MTG middle temporal gyrus OcG occipital gyrus OFOp orbitofrontal operculum PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus POc-P parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum pos parieto-occipital sulcus PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pu putamen Pul pulvinar Rt reticular thalamic nucleus SFGL superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial division SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SLgG superior lingual gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus SSG superior sagittal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone TTG transverse temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 post. transverse temporal gyrus VAL lateral ventroanterior nucleus VAM medial ventroanterior nucleus VL ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VPL ventroposterior lateral thalamic nucleus
**405**

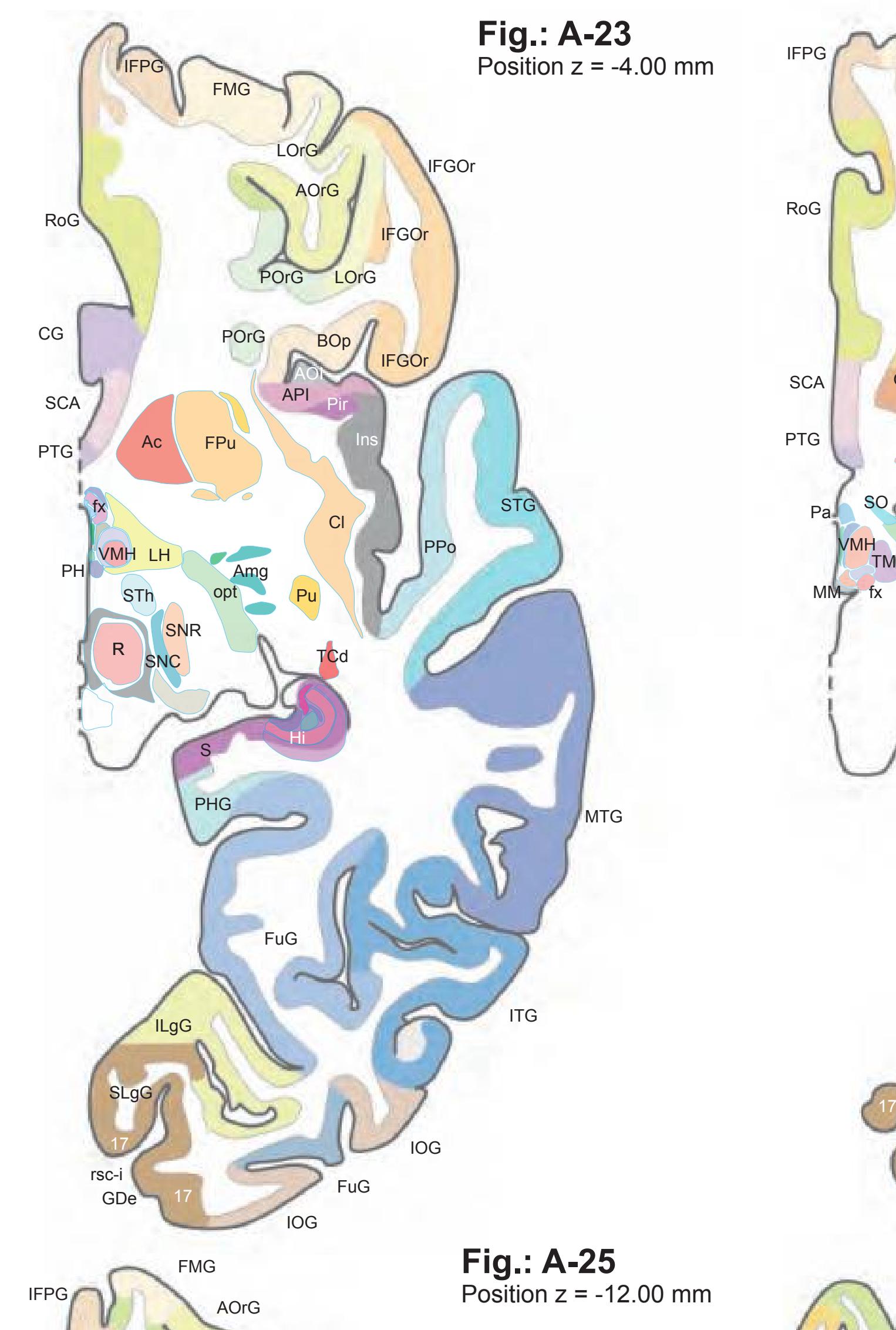

FMG
ITG
ITG
MTG
MTG
STG
**Fig.: A-24**
Position z = -8.00 mm
IFGOr
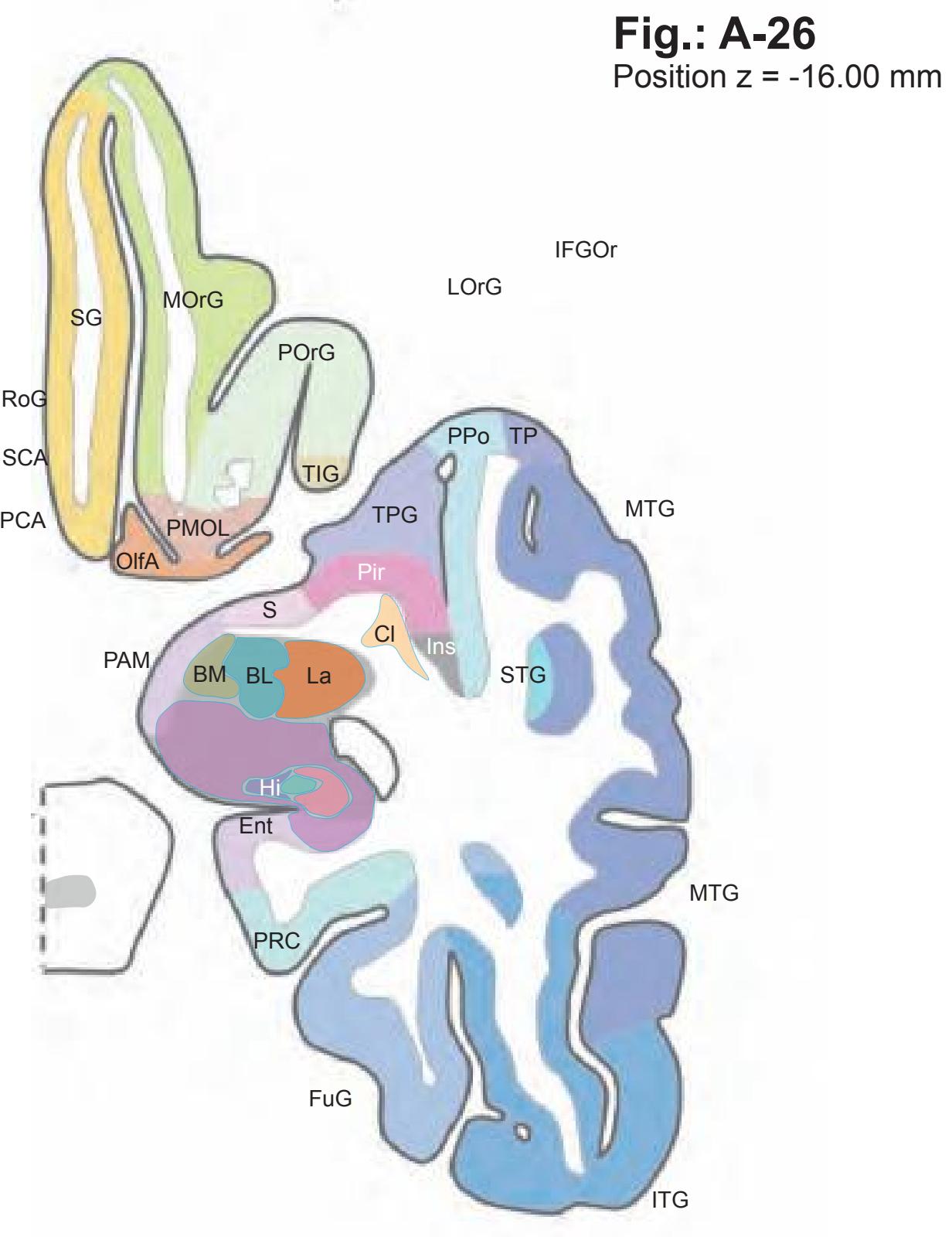

17 striate area Ac accumbens nucleus Amg amygdala AOI area orbitoinsularis AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus API area piriformis insulae BL basolateral amygdaloid nucl. BM basomedial amygdaloid nucl. BOp basal operculum CG cingulate gyrus Cl claustrum Ent entorhinal gyrus FMG frontomarginal gyrus FPu fundus region of putamen FuG fusiform gyrus fx fornix (column and body) GDe gyrus descendens Hi hippocampus IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus ILgG inferior lingual gyrus Inf infundibular nucleus Ins insula IOG inferior occipital gyrus IPo insular pole ITG inferior temporal gyrus La lateral amygdaloid nucleus LgG lingual gyrus LH lateral hypothalamic area LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MM medial mammillary nucleus MOrG medial orbital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus OlfA olfactory area opt optic tract ox optic chiasma Pa paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus PAM periamygdaloid cortex PCA precommissural archicortex PCo post. cortical amygdaloid nucleus PH posterior hypothalamic area PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pir piriform cortex PirF piriform cortex, frontal part PirT piriform cortex, temporal part PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POrG posterior orbital gyrus PPo planum polare PRC perirhinal cortex PTG paraterminal gyrus Pu putamen R red nucleus RoG rostral gyrus rsc-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior branch SCA subcallosal area SG straight gyrus SLgG superior lingual gyrus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SO supraoptic nucleus STG superior temporal gyrus STh subthalamic nucleus S subiculum TCd tail of caudate nucleus TIG transverse insular gyrus TM tuberomammillary nucleus TP temporal pole TPG temporopolar gyrus Un uncus
VMH ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
ITG FuG LgG IOG PHG
FuG
Cl
TIG
AOrG
Ins
IPo
PPo
STG
BOp
LOrG
RoG TP
PirF PirT
POrG
MOrG
Ent
Un
La PCo BL
PMOL
MOrG
SCA
PCA
ox
Inf VMH OlfA
Un PAM
SG
MTG
MTG
1 cm
**407**
ITG MTG FuG PPo MTG Hi TPG PRC SG MOrG Ent PMOL Ent Cl La BL **Fig.: A-27** Position z = -20.00 mm
ITG MTG FuG PPo TPG PRC SG MOrG Ent
AG ambiens gyrus BL basolateral amygdaloid nucl. Cl claustrum Ent entorhinal gyrus
FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus ITG inferior temporal gyrus La lateral amygdaloid nucleus MOrG medial orbital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule
PPo planum polare PRC perirhinal cortex SG straight gyrus S subiculum TP temporal pole TPG temporopolar gyrus
Fig.: A-30
Position z = -3
**Fig.: A-28**
Position z = -24.00 mm
ITG MTG FuG TP TPG PRC Ent
**Fig.: A-30** Position z = -32.00 mm

**Fig.: A-29**
**Fig.: A-31**
Position z = -28.00 mm


**Fig.: A-32** Position z = -40.00 mm
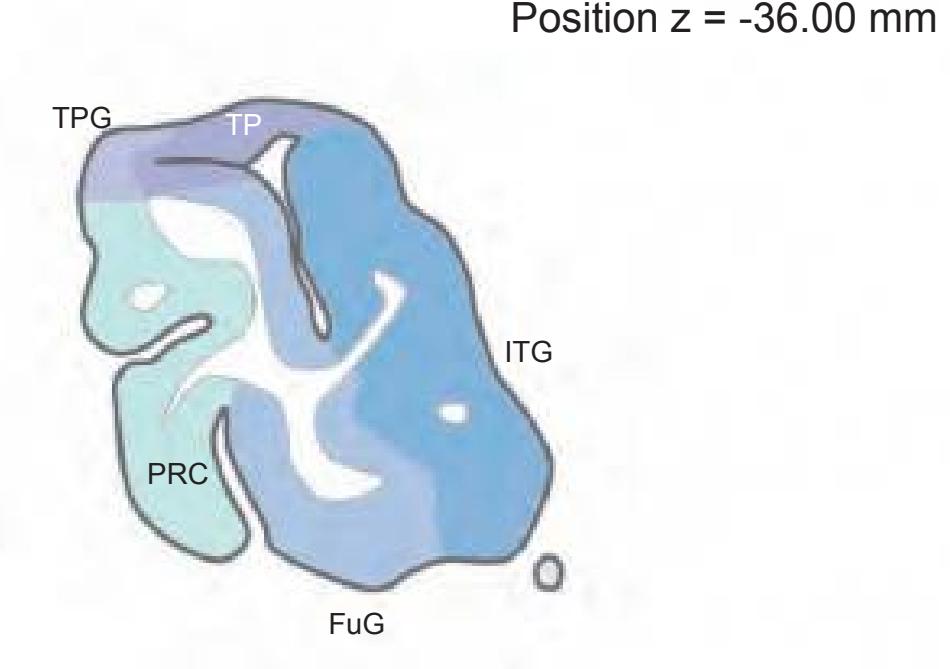
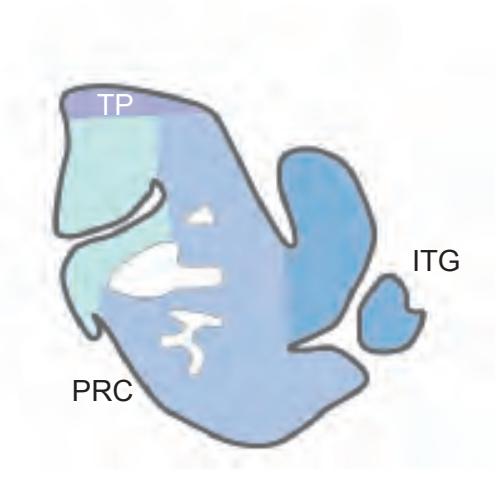
1 cm
**408**




17 striate area 1p olfactory peduncle Ac accumbens nucleus ac anterior commissure AV anteroventral thalamic nucleus bc brachium conjuctivum Cd caudate nucleus CG cingulate gyrus CM centromedian thalamic nucleus CM-PF centromedian parafascicular nucleus crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-thalamic tract) DMH dorsomed. hypothalamic nucleus DSF dorsal superficial nucleus FCd fundus region of caudate nucleus FMG frontomarginal gyrus fx fornix (column and body) GDe gyrus descendens h2 lenticular fascicle IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus IL intralaminar nuclei and lamina ILgG inferior lingual gyrus Inf infundibular nucleus ISG inferior sagittal gyrus LH lateral hypothalamic area MD medial dorsal thalamic nucleus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MM medial mammillary nucleus, med. part MOrG medial orbital gyrus MPO medial preoptic nucleus MSG middle sagittal gyrus MSG-p middle sagittal gyrus, posterior part OcG occipital gyrus OlfA olfactory area opt optic tract ox optic chiasma Pa paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus pc posterior commissure PCA precommissural archicortex PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus Pe periventricular hypothalamic nucleus PH posterior hypothalamic area PHG parahippocampal gyrus POc-A parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-P parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus PrG precentral gyrus Pul pulvinar R red nucleus rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior branch rcs-s retrocalcarine sulcus, superior branch RoG rostral gyrus SCA subcallosal area scs subcalcarine sulcus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFGM superior frontal gyrus, medial division SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SG straight gyrus SLgG superior lingual gyrus SN substantia nigra SO supraoptic nucleus SPL superior parietal lobule
SSG superior sagittal gyrus STh subthalamic nucleus VA ventroanterior thalamic nucleus VAb basal ventroanterior thalamic nucleus VMH ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
1 cm
**409**

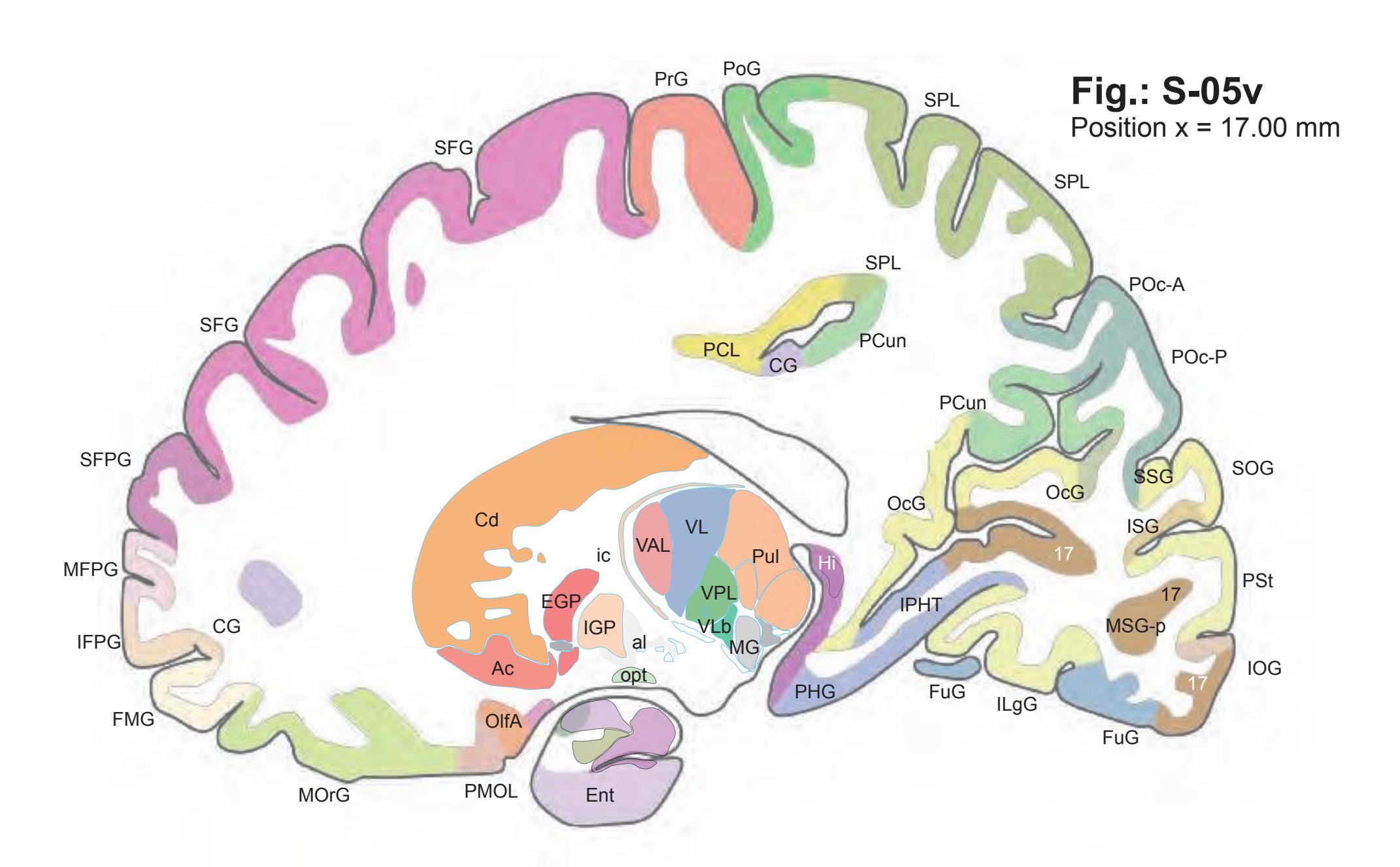

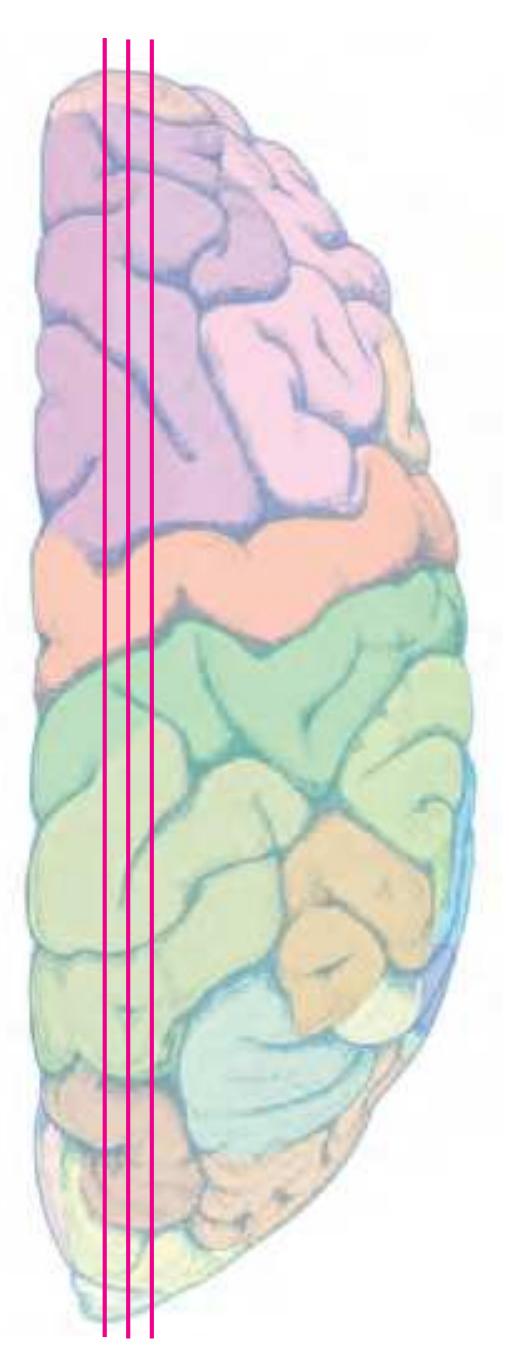
17 striate area ac anterior commissure Ac accumbens nucleus al ansa lenticularis AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus Cd caudate nucleus CG cingulate gyrus CM centromedian thalamic nucleus DSF dorsal superficial nucleus EGP external globus pallidus Ent entorhinal gyrus FCd fundus region of caudate nucleus FMG frontomarginal gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus GDe gyrus descendens Hi hippocampus ic internal capsule IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus IGP internal globus pallidus ILgG inferior lingual gyrus IOG inferior occipital gyrus IPHT isthmo-parahippocampal transition ISG inferior sagittal gyrus LG lateral geniculate nucleus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MG medial geniculate nucleus MOrG medial orbital gyrus MSG middle sagittal gyrus MSG-p middle sagittal gyrus, posterior part OcG occipital gyrus OlfA olfactory area opt optic tract PCL paracentral lobule PCun precuneus PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pir piriform cortex PMOL posteromedial orbital lobule POc-A parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-P parieto-occipital arc, posterior part PoG postcentral gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PrG precentral gyrus PSt parastriate area Pul pulvinar RoG rostral gyrus RSp retrosplenial cortex SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SLgG superior lingual gyrus SNC substantia nigra, pars compacta SNR substantia nigra, pars reticulata SOG superior occipital gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule SSG superior sagittal gyrus TP temporal pole VAL lateral ventroanterior nucleus VAM medial ventroanterior nucleus VL ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VLb basal ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VPL lateral ventroposterior thalamic nucleus
1 cm
**410**
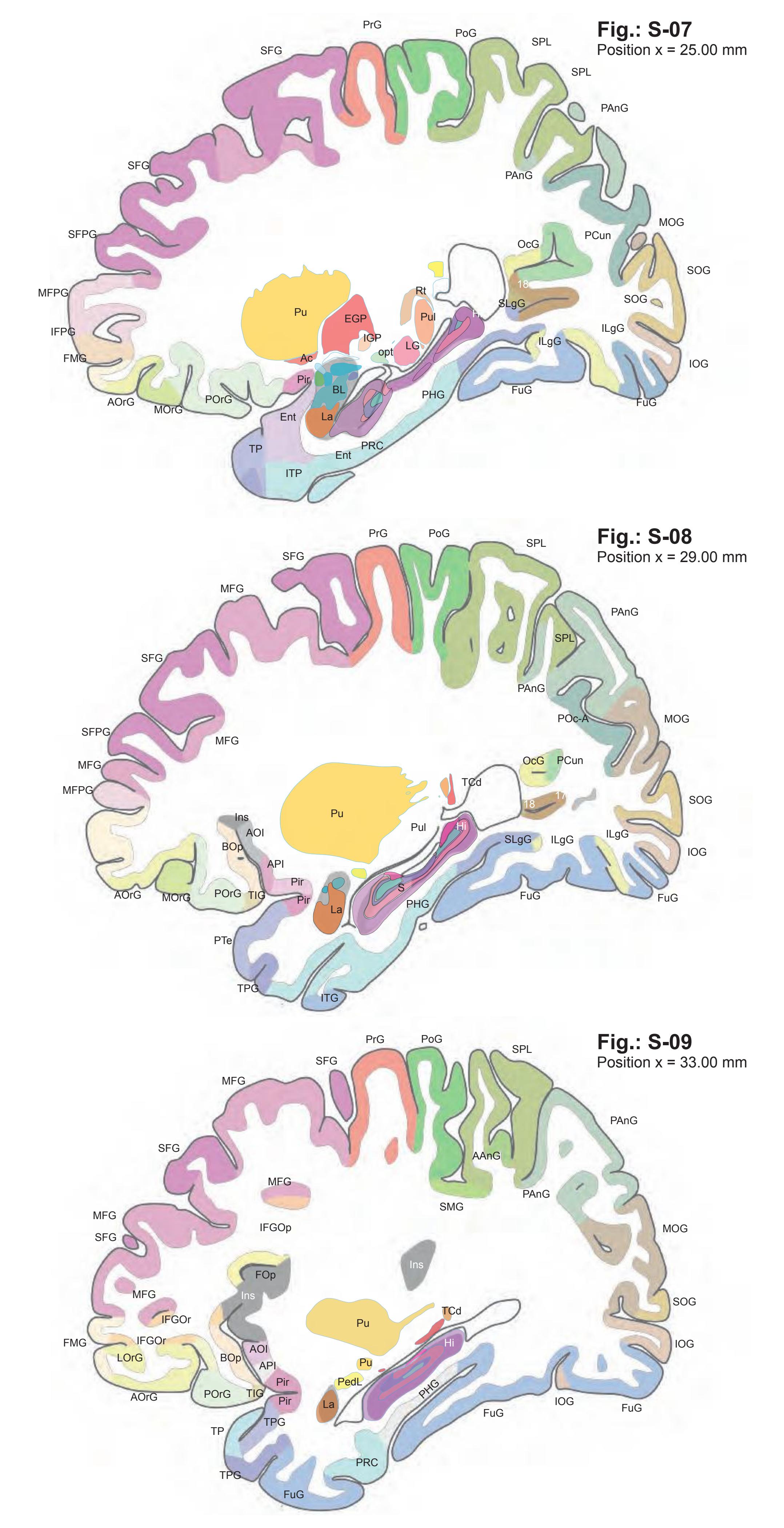

17 striate area 18 area 18 AAnG angular gyrus, anterior division Ac accumbens nucleus ac anterior commissure AOI area orbitoinsularis AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus API area piriformis insulae BL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus BOp basal operculum EGP external globus pallidus Ent entorhinal gyrus FMG frontomarginal gyrus FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFPG inferior frontopolar gyrus IGP internal globus pallidus ILgG inferior lingual gyrus Ins insula IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus ITP inferior temporopolar region La lateral amygdaloid nucleus LG lateral geniculate nucleus LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MFPG middle frontopolar gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MOrG medial orbital gyrus OcG occipital gyrus opt optic tract PAnG posterior angular gyrus PCun precuneus Pedl peduncle of lentiform nucleus PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pir piriform cortex POc-A parieto-occipital arc, anterior part PoG postcentral gyrus POrG posterior orbital gyrus PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale Pu putamen Pul pulvinar Rt reticular thalamic nucleus SFG superior frontal gyrus SFPG superior frontopolar gyrus SLgG superior lingual gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule S subiculum TCd tail of caudate nucleus TIG transverse insular gyrus TP temporal pole TPG temporopolar gyrus
1 cm
**411**

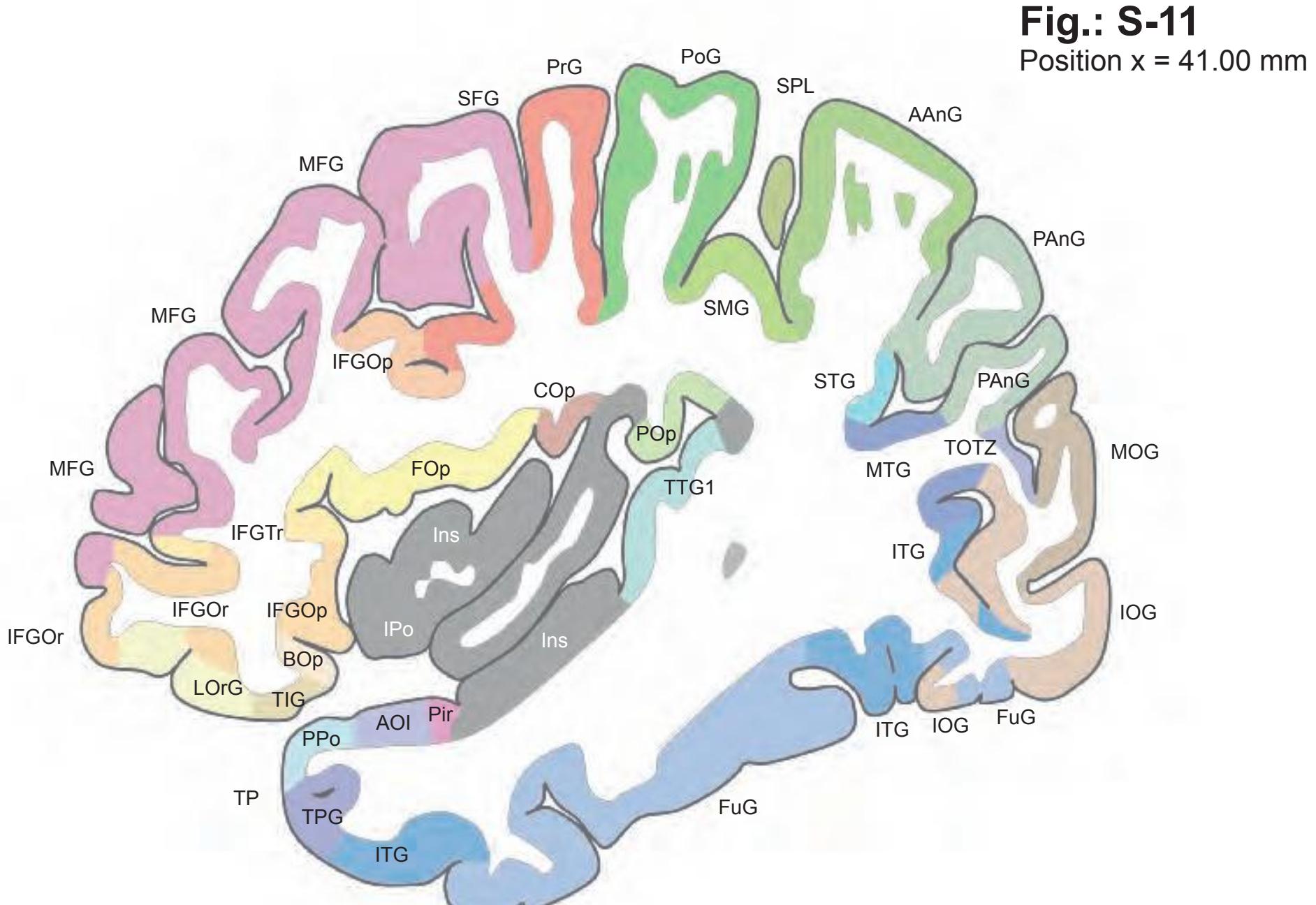
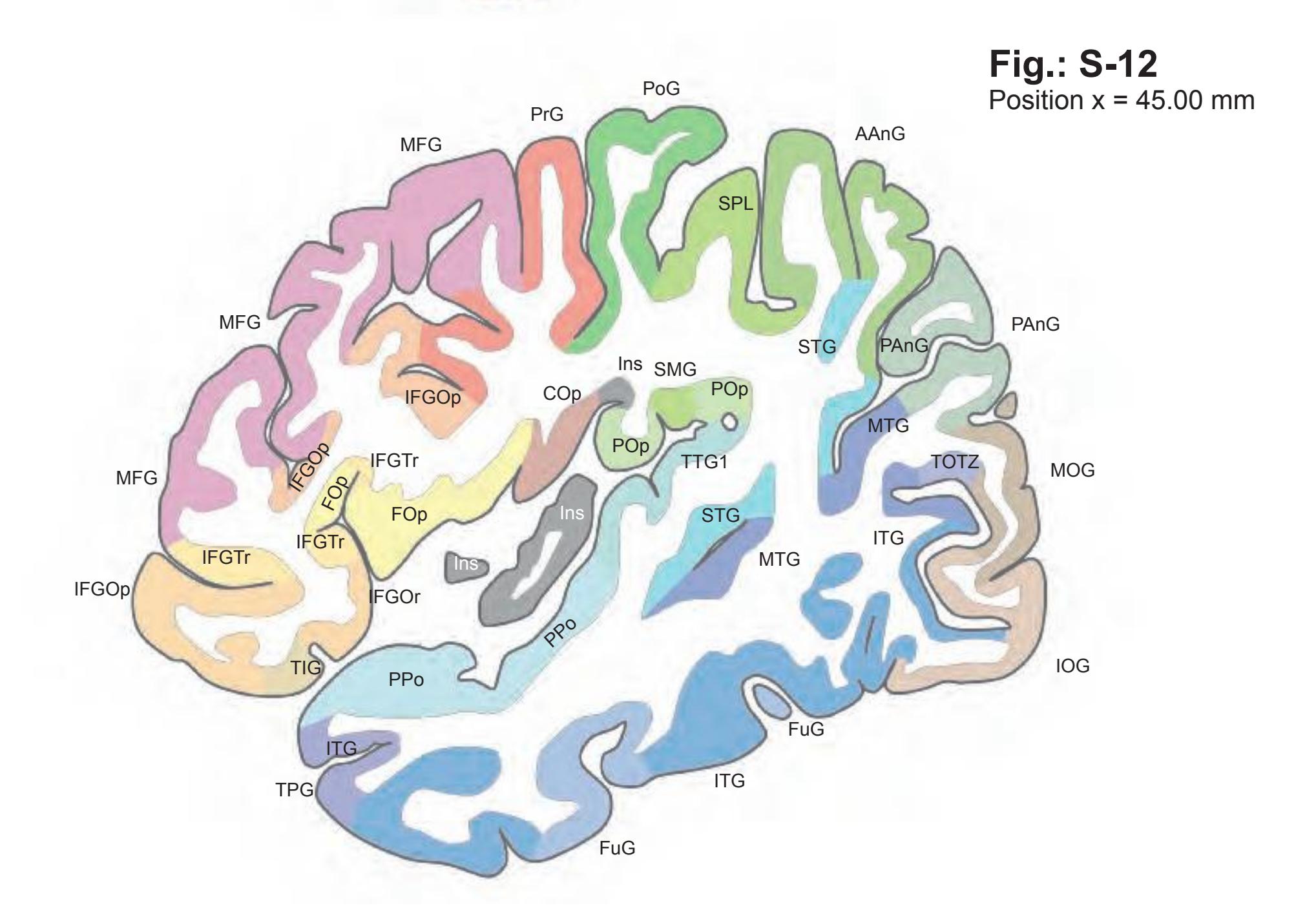

AAnG angular gyrus, anterior division AOI area orbitoinsularis AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus BOp basal operculum COp central operculum (Rolandi) FOp frontal operculum FuG fusiform gyrus Hi hippocampus IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part Ins insula IOG inferior occipital gyrus IPo insular pole ITG inferior temporal gyrus LOrG lateral orbital gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MTG mammillo-tegmental tract PAnG posterior angular gyrus PHG parahippocampal gyrus Pir piriform cortex PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PPo planum polare PRC perirhinal cortex PrG precentral gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus SMG supramarginal gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TIG transverse insular gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone TP temporal pole TPG temporopolar gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
1 cm
**412**
MFG PoG MTG PrG SPL SMG PAnG IOG TOTZ TPG MOG MFG ITG IFGOp TTG1 AAnG Ins IFGTr IFGOr IFGOp PPo ITG STG STG POp COp POp FOp IFGOp SMG PTe MTG IOG COp **Fig.: S-13** Position x = 49.00 mm
MFG PoG MTG PrG TOTZ TPG ITG TTG1 AAnG IFGTr IFGOr IFGOp PPo ITG STG STG POp COp-a FOp IFGOp SMG PTe MTG COp-p MTG **Fig.: S-14** Position x = 53.00 mm
**Fig.: S-15** Position x = 57.00 mm


AAnG angular gyrus, anterior division COp central operculum (Rolandi) COp-a anterior central operculum COp-p posterior central operculum FOp frontal operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGTr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part Ins insula IOG inferior occipital gyrus ITG inferior temporal gyrus MFG middle frontal gyrus MOG middle occipital gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PAnG posterior angular gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PPo planum polare PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus SPL superior parietal lobule STG superior temporal gyrus TOTZ temporooccipital transition zone TPG temporopolar gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
1 cm
**413**
**Fig.: S-16** Position x = 61.00 mm

**Fig.: S-17** Position x = 65.00 mm

**Fig.: S-18** Position x = 69.00 mm
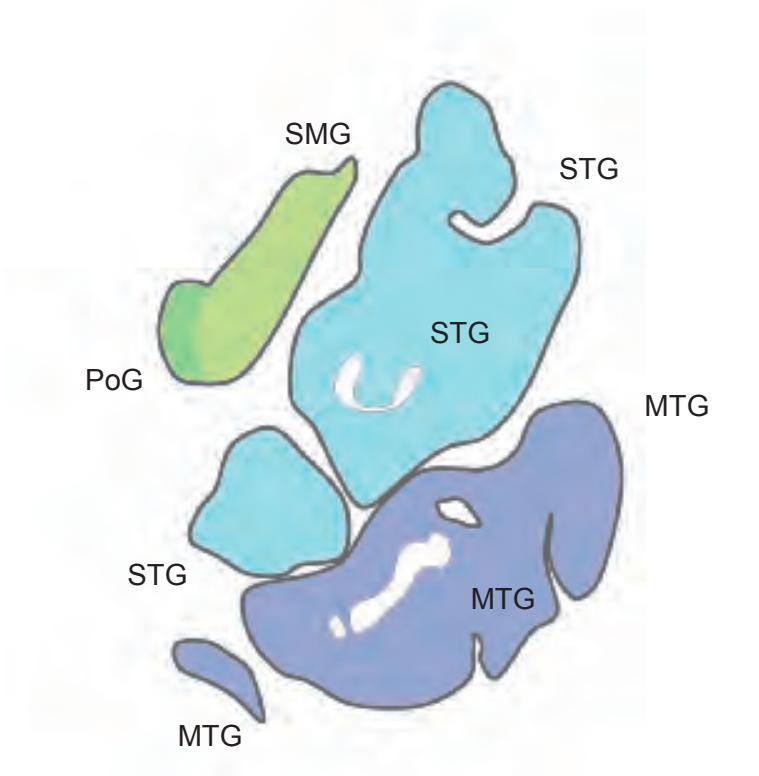
COp-p posterior central operculum IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part ITG inferior temporal gyrus MTG middle temporal gyrus PoG postcentral gyrus POp parietal operculum PPo planum polare PrG precentral gyrus PTe planum temporale SMG supramarginal gyrus STG superior temporal gyrus TTG1 ant. transverse temporal gyrus
1 cm
**414**
# **2.5 Maps of Subcortical Areas**

This part presents maps of the thalamus and of the hypothalamus of the right hemisphere of the *Atlas* brain. The images are shown at higher magnification than in the main *Atlas*. The delineations were curated by F. Forutan and Y. Koutcherov. The nomenclature is arranged systematically to facilitate orientation.
Importantly, these images were not transformed to fit the stereotaxic (Talairach or MNI) space. They are identical to the actual mounted sections and to the photographs that can evaluated by "virtual microscopy" in the internet (www.thehumanbrain.info).
## **References:**
Koutcherov, Y., Mai, J.K., Ashwell, K.W.S., Paxinos, G.: The organization of the human paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 423: 299-318 (2000).
Koutcherov, Y., Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G.: Hypothalamus of the human fetus. J. Chemical Neuroanatomy, 26; 253-270 (2003).
Koutcherov, Y., Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G.: Hypothalamus of the human fetus. In: The Human Nervous System. Academic Press, San Diego, USA (2004).
Koutcherov, Y., Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G.: Organisation of the human dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus. NeuroReport: 15 (1), 107-111 (2004)
Koutcherov, Y. Paxinos, G. Mai, J.: The organization of the human medial preoptic nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 503:392–406 (2007).
Mai, J.K. and Forutan, F.: Thalamus. In: The Human Nervous System. Academic Press, San Diego, USA 620-679 (2012).
**415**
## **2.5.1 Thalamus by F. Forutan**
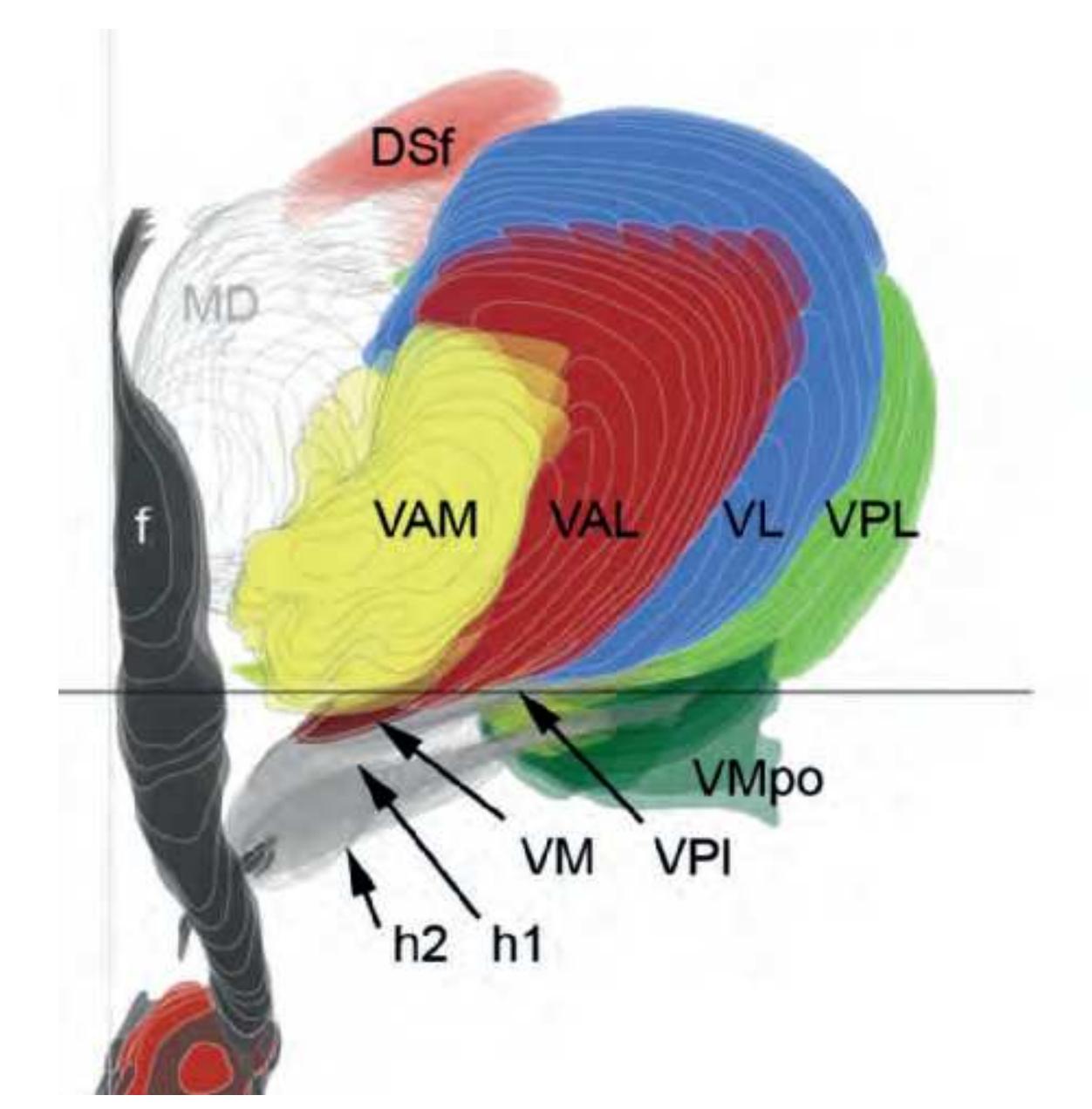
### **Superior Region (anterior group nuclei)**
AV anteroventral nucleus (anteroprincipal nucleus)
AM anteromedial nucleus AD anterodorsal nucleus DSf dorsal superficial nucleus
## **Medial Region**
**MD mediodorsal nucleus**
MDMC magnocellular mediodorsal nucleus, (medial MD; Ncl. medialis fibrosus) MDPC parvicellular mediodorsal nucleus, (central MD; Ncl. medialis fasciculosus) MDPL paralaminar (paralamellar) mediodorsal nucleus,
(lateral MD; Ncl. densocellularis / multiformis)
### **Lateral Region**
#### **Motor Thalamus**
**VA ventroanterior nucleus** (ventral anterior nucleus) VAM medial ventroanterior nucleus (nigral afferents) VAMC magnocellular ventroanterior nucleus VAL lateral ventroanterior nucleus (pallidal afferents) VAb basal ventroanterior nucleus [VM] (entry zone of nigral and amygdaloid afferents)
**VL ventrolateral nucleus**
VLA anterior ventrolateral nucleus (medial oral division) VLP posterior ventrolateral nucleus (lateral caudal division) VLPI posterior ventrolateral nucleus, internal part VLPE posterior ventrolateral nucleus, external part VLb basal (inferior) ventrolateral nucleus [VPI] (entry zone of the cerebellar fibers)
#### **Sensory Thalamus**
**VP ventroposterior nucleus** or complex VPL lateral ventroposterior nucleus; VPM medial ventroposterior nucleus VPS superior ventroposterior nucleus (Kaas) VPPC ventroposterior nucleus, parvicellular part VPMPC medial ventroposterior nucleus, parvicellular part VPb basal ventroposterior nucleus [VMpo] (entry zone of sensory afferents)
## **Intralaminar Formation**
ILA anterior group of the intralaminar nuclei
CeMe central medial nucleus CL central lateral nucleus PC paracentral nucleus Cuc cucullar nucleus
#### **ILC central group of intralaminar nuclei**
CM centromedian nucleus PF parafascicular nucleus SPf subparafascicular nucleus ILP posterior intralaminar group Lim limitans nucleus SGe suprageniculate nucleus
### **Periventricular Formation** (midline nuclei)
dorsal component of the periventricular formation
PT paratenial nucleus PV paraventricular nucleus
#### ventral component of the periventricular formation
Re reuniens nucleus SM submedius nucleus PeV periventricular nucleus
### **Posterior Region**
Pul pulvinar nucleus (pulvinar-LP complex)
Pul pulvinar nucleus (pulvinar-LP complex) APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus)
IPul inferior pulvinar nucleus IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal part ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate part IVPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, ventral part IGPul intergeniculate pulvinar nucleus
LPul lateral pulvinar nucleus MPul medial pulvinar nucleus MLPul mediolateral pulvinar nucleus SFPul superficial pulvinar nucleus SPul superior pulvinar nucleus
### **Prethalamus**
PRt prereticulate nucleus Rt reticulate nucleus Fa fasciculosus nucleus
### **Epithalamus**
HB habenular nucleus HBL lateral habenular nucleus HBM medial habenular nucleus
### **Metathalamus**
LG lateral geniculate nucleus MG medial geniculate nucleus
## Fibers
| ac | anterior commissure | lenf | lenticular fasciculus |
|------|---------------------------------|-------|---------------------------------|
| al | ansa lenticularis | ll | lateral lemniscus |
| ap | ansa peduncularis | mfb | medial forebrain bundle |
| ar | acoustic radiation | ml | medial lemniscus |
| bic | brachium of the inf. colliculus | mp | mammillary peduncle |
| cmg | capsule of MGN | mt | mammillothalamic tract |
| cr | capsule of nucleus ruber | opt | optic tract |
| csc | commissure of sup. colliculus | or | optic radiation |
| eml | external medullary lamina | palhy | pallidohypothalamic tract |
| FF | Field of Forel | pc | posterior commissure |
| fr | fasciculus retroflexus | prf | principal mammillary fasciculus |
| fx | fornix | slf | sublenticular fascicle |
| h1 | thalamic fascicle | sm | stria medullaris |
| h2 | lenticular fascicle | sox | supraoptic commissure |
| hbc | habenular commissure | st | stria terminalis |
| iml | internal medullary lamina | sumx | supramammillary commissure |
| ithp | inferior thalamic peduncle | vaf | ventral amygdaloid fibers |
Other abbreviations: see Index
**416**
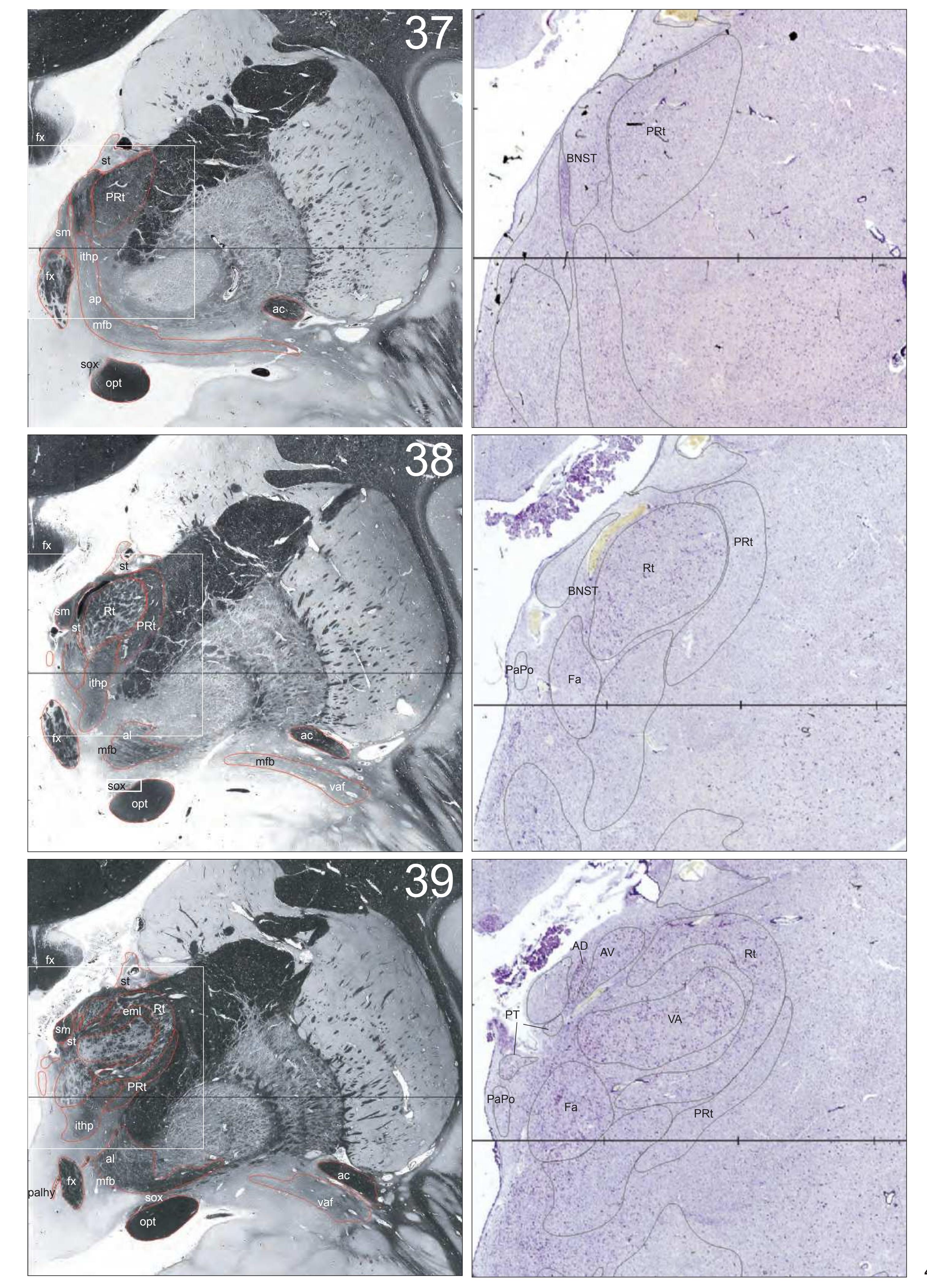
**417**

**418**
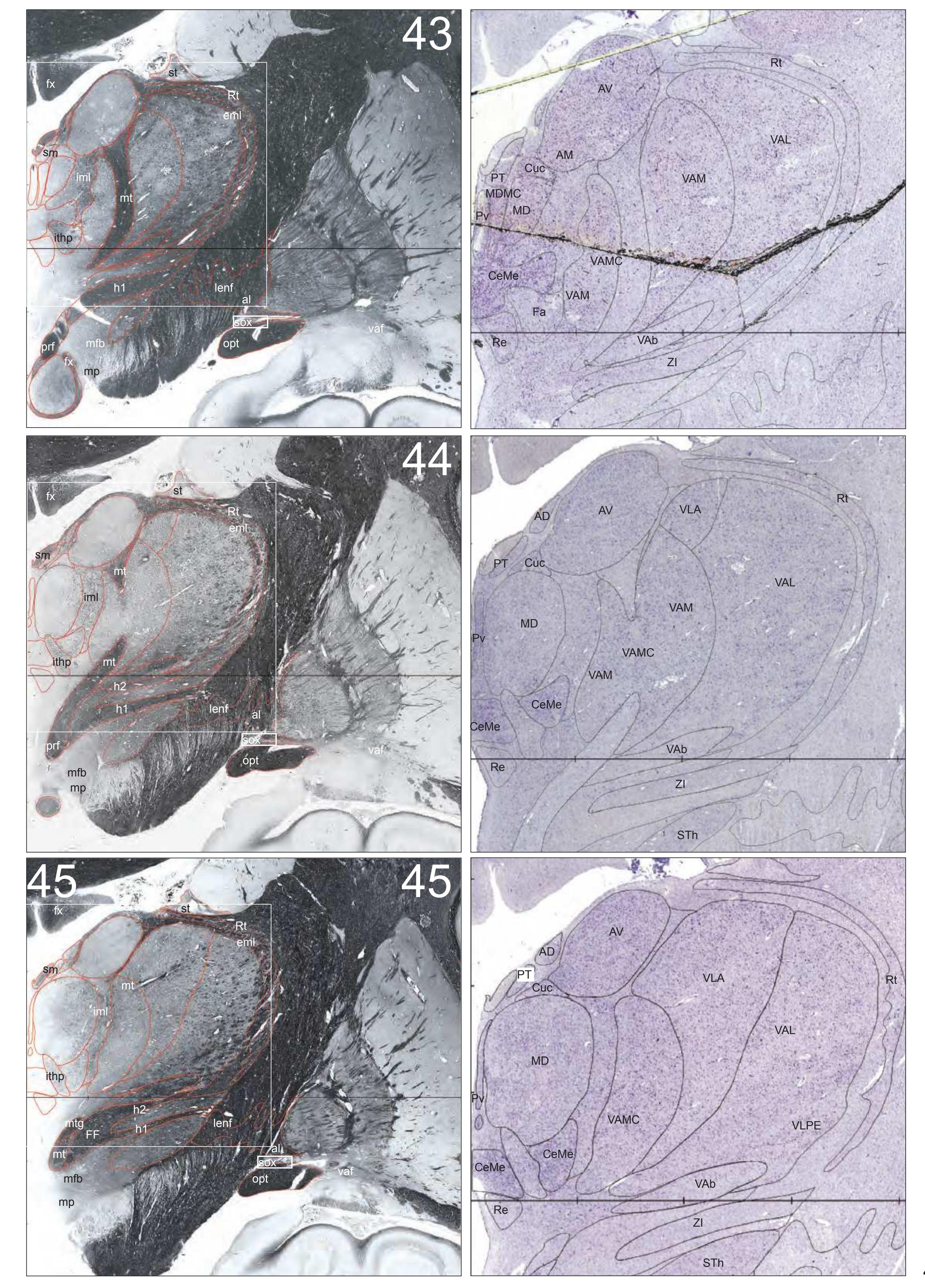
**419**
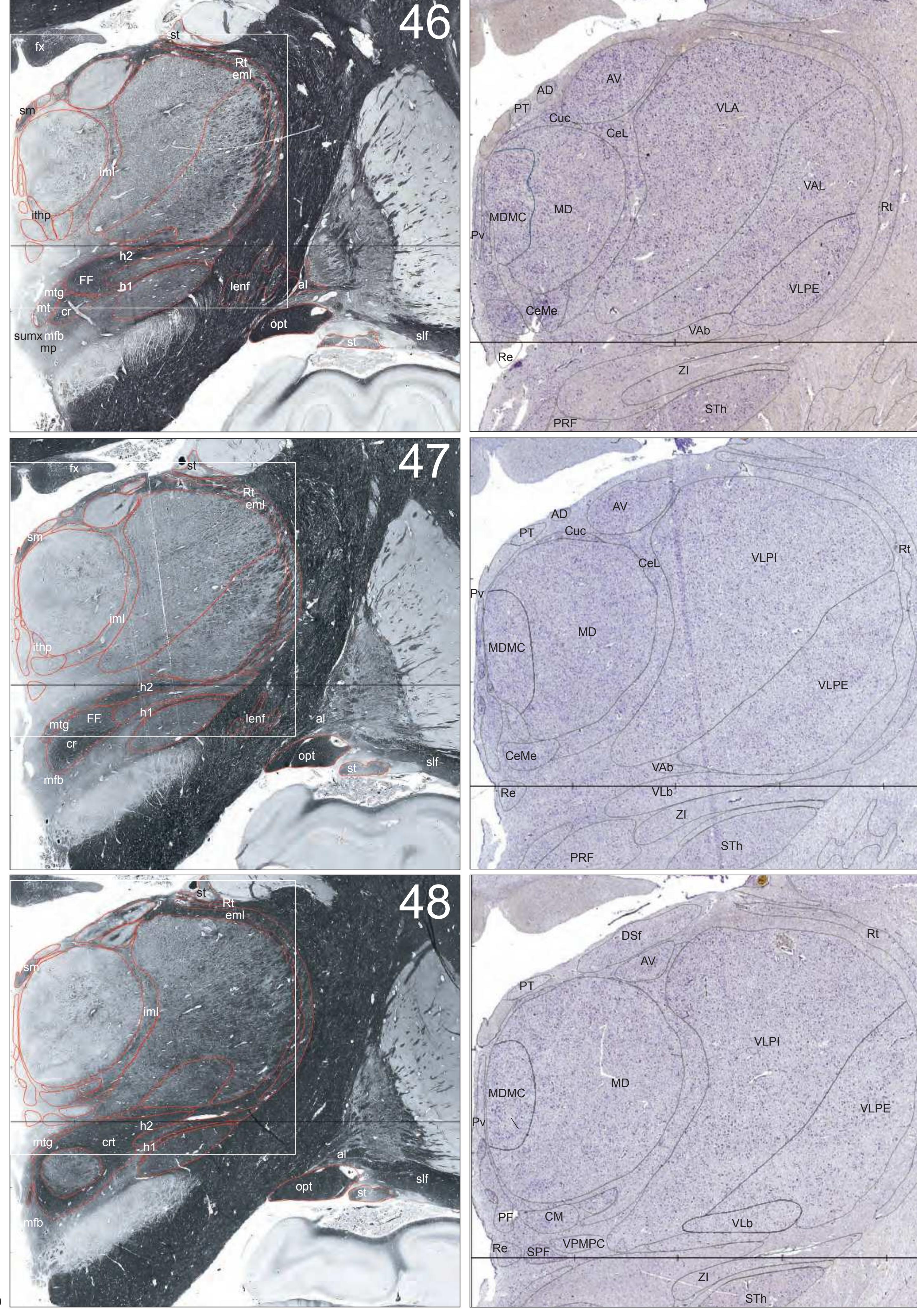
**420**

**421**

**422**
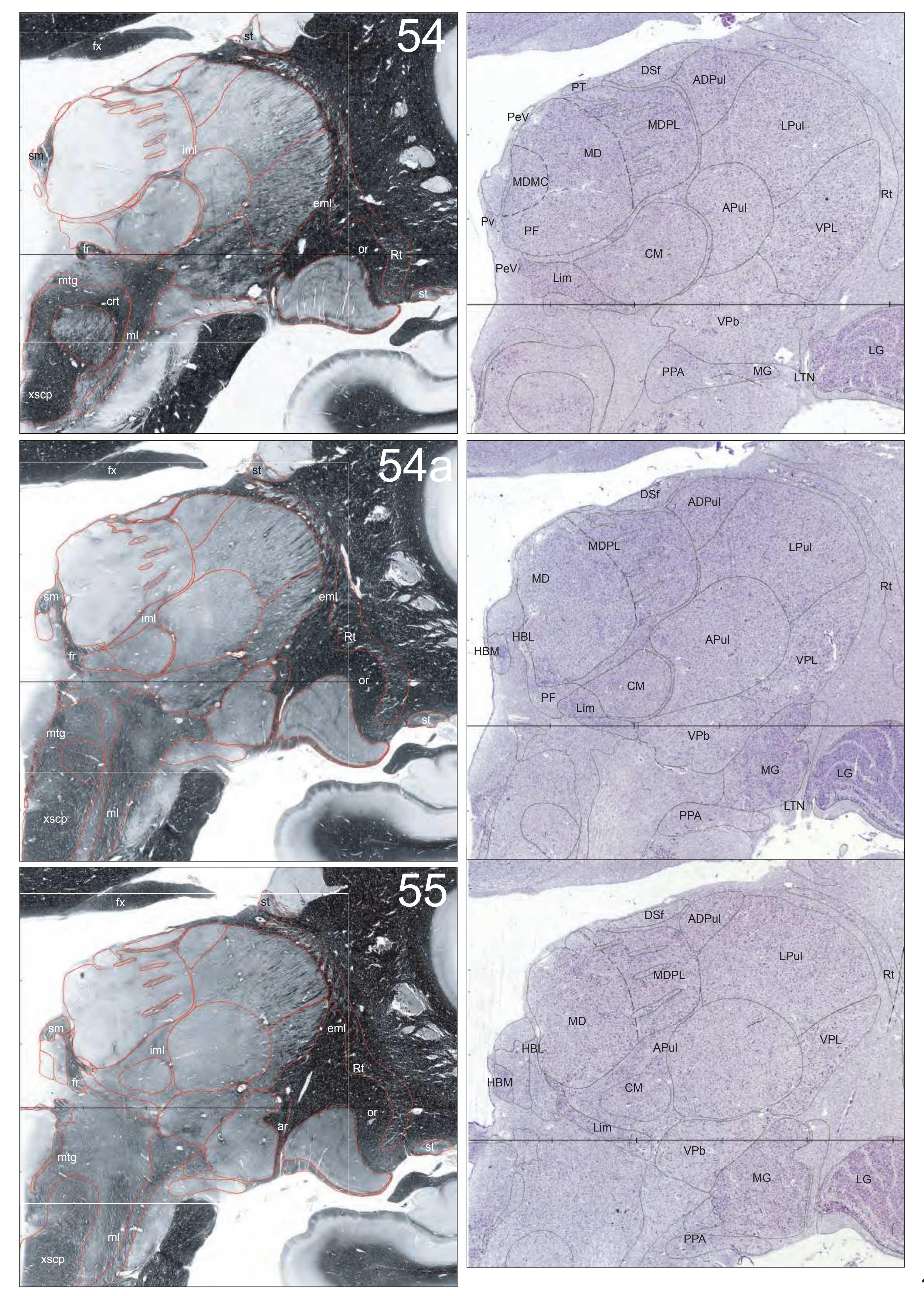
**423**

**424**
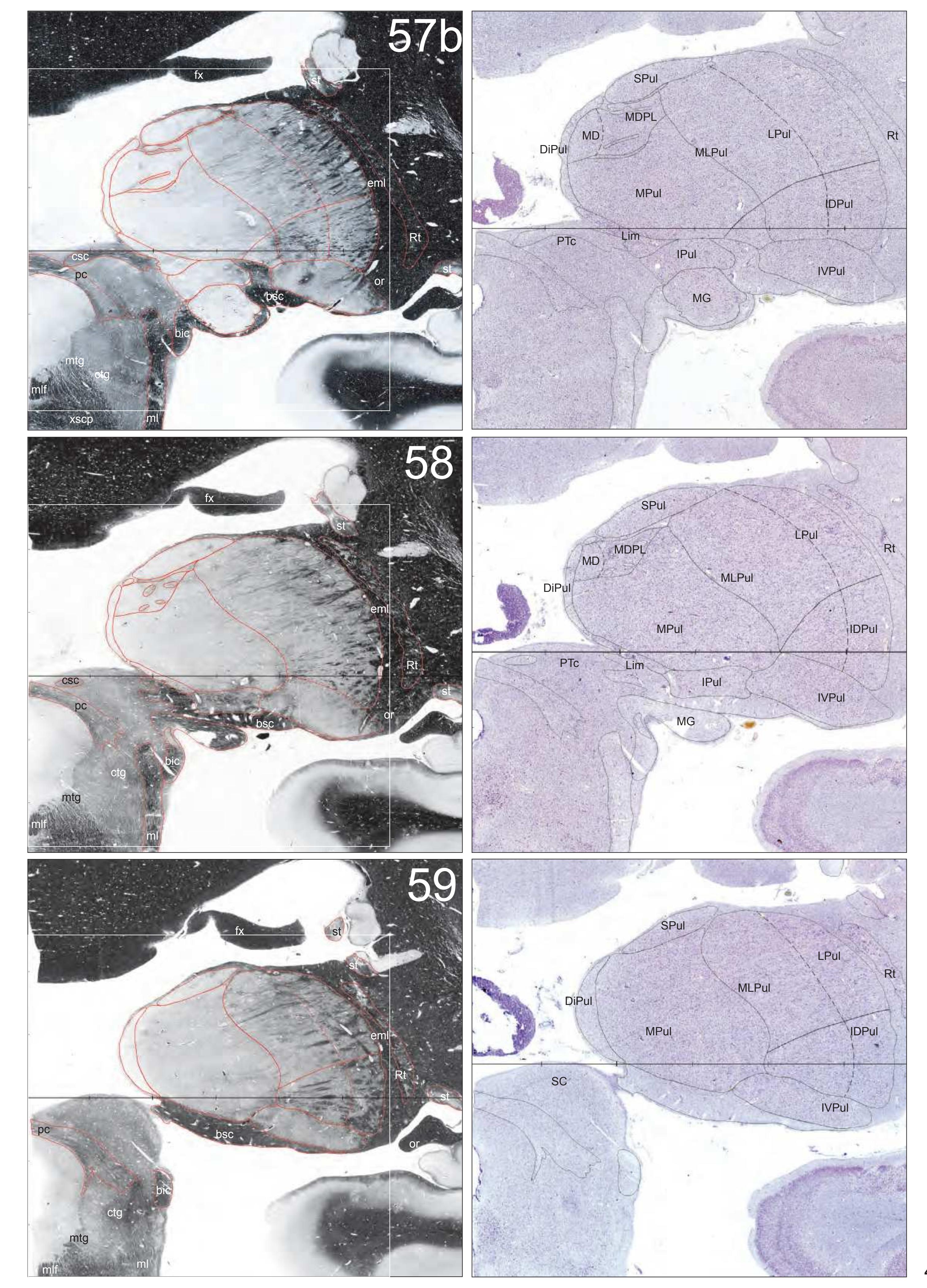
**425**

**426**
## **2.5.2 Hypothalamus by Y. Koutcherov**
### **Preoptic Area**
#### Pe periventricular hypothalamic nuclei
- VMPe ventromedial preoptic nucleus
- DPe dorsomedial periventricular nucleus
- AVPe anteroventral periventricular nucleus
#### MPO medial preoptic nucleus
- MPOL medial preoptic nucleus, lateral part
- MPOM medial preoptic nucleus, medial part
#### IMH intermediate hypothalamic cell groups
- InM intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (SxD)
- Unn uncinate nucleus
### **AHA Anterior Hypothalamic Area**
## SCh suprachiasmatic nucleus
- SChC central, compact division
- SChD dorsal division
#### Pa paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus
- PaAP anterior parvocellular part
- PaD dorsal part
- PaMC magnocellular part
- PaPC parvicellular part
- PaPo posterior part
#### SO supraoptic nucleus
- SODL dorsolateral part
- SOVM ventromedial part
- SOT tuberal part
- SOP posterior part
### **IHA Infundibular (Tuberal) Hypothalamic Region**
#### VMH ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- VMHDM dorsomedial part
- VMHVL ventrolateral part
- VMS shell
#### DMH dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
- DMHD diffuse part
- DMHC compact part
## Inf infundibular nucleus
Inf infundibular nucleus
### **MHA Mammillary Region**
#### MB mammillary body
- SuM supramammillary nucleus
- MM medial mammillary nucleus, medial part
- ML medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part
- LM lateral mammillary nucleus
#### TM tuberomammillary complex (Brockhaus, 1942)
- TM tuberomammillary nucleus, principal part
- PeF perifornical nucleus
#### LTu lateral tuberal nucleus
LTu lateral tuberal nucleus
### **LH Lateral Hypothalamic Area**
- LH lateral hypothalamic area, anterior part
- LH lateral hypothalamic area, tuberal part
- LH lateral hypothalamic area, posterior part
- PalHy pallidohypothalamic nucleus
### **PH Posterior Hypothalamic Area**
PH posterior hypothalamic area
### **DH Dorsal Hypothalamic Area**




Reconstruction of the human hypothalamus. Posterior view of rostrocaudal divisions (from top to bottom: preoptic, anterior, tuberal and mammillary region).
**427**
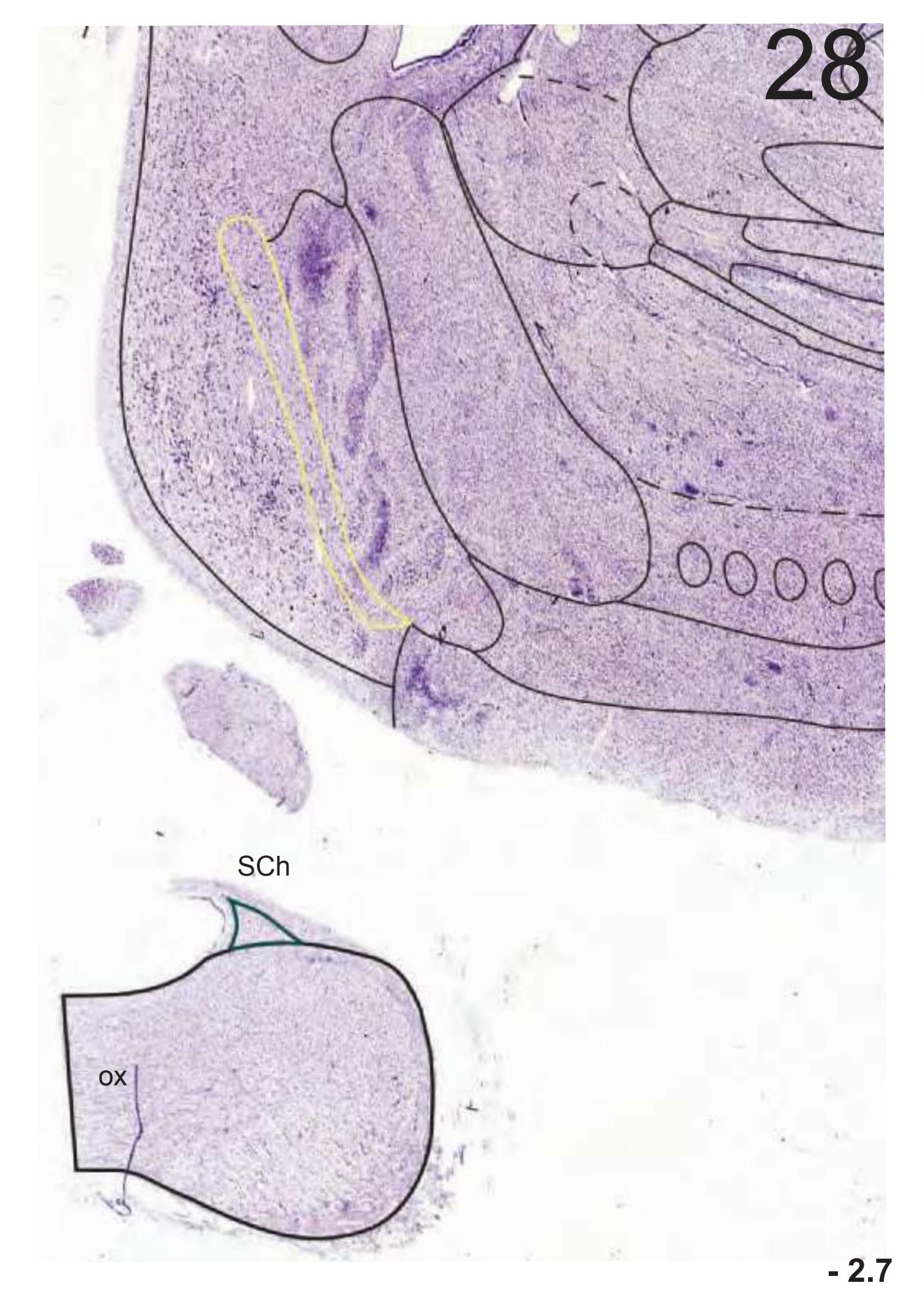

**- 2.0**


**- 1.3 - 0.6**
**428**


**429**
**+ 2.7 + 4.0**
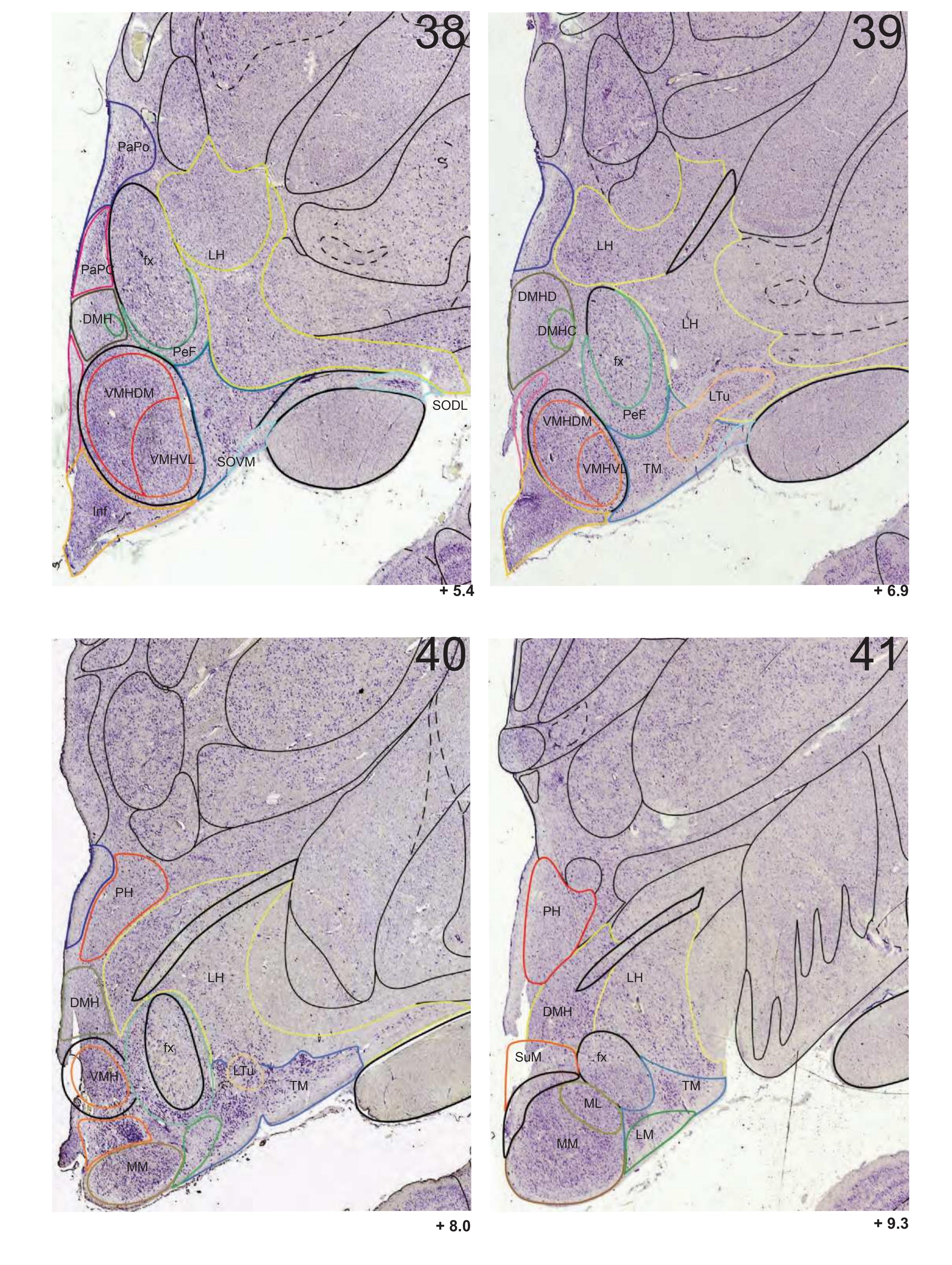
**430**
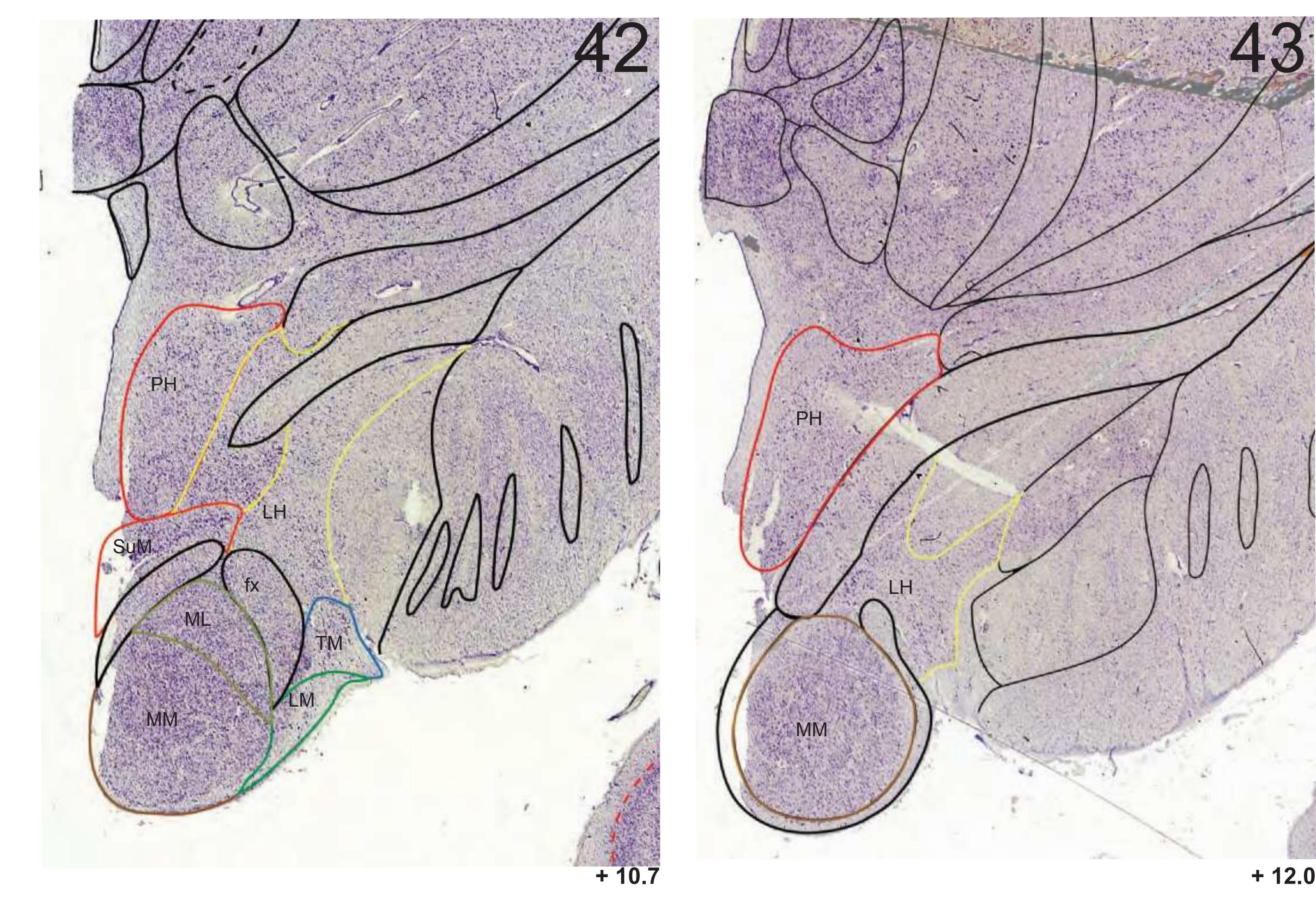

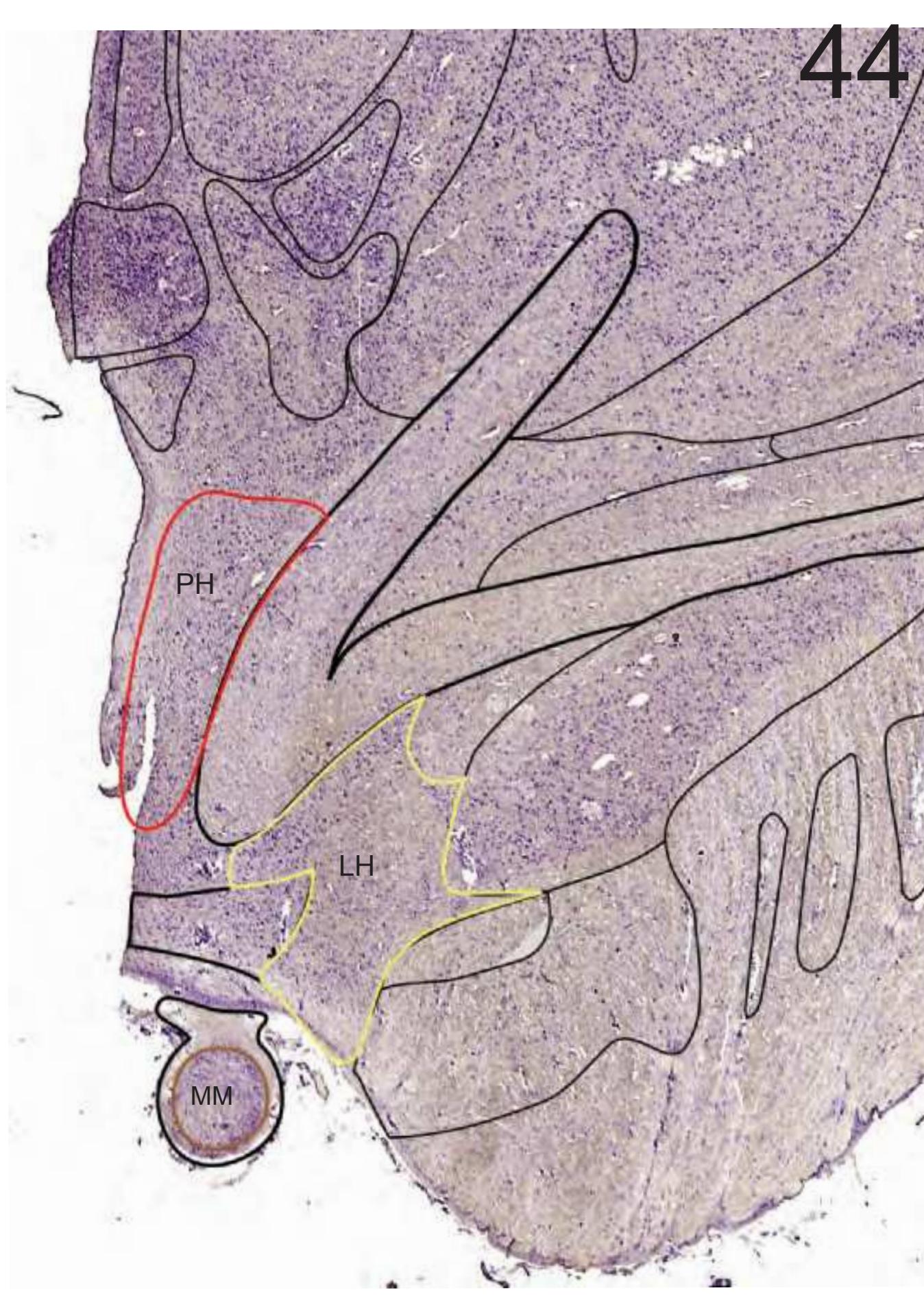
**+ 13.3**
**431**
This page intentionally left blank
# **2.6 Published Studies**
# **Referring to the Brain Represented in the Atlas of the Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates**
Numerous descriptive and quantitative studies have been performed on the very same brain represented in the *Atlas of the Brain in Stereotaxic coordinates*. The material on the following pages illustrates that almost all relevant structures and areas of the brain have undergone intensive studies. These include not only detailed morphological and architectural but also morphometric analyses. Relevant published delineations of structures and quantitative data concerning fresh volume, volume of serial sections, numeric cell density, volumetric cell density, absolute cell numbers
etc., have been assembled. References pertinent to these data are to be found at the end of this section. Most of the cited literature is available in full, including figures, in an editable format on the website: www.thehumanbrain.info. Therefore, the additional information from the various authors can be counter referenced to the *Atlas*. It is noteworthy that many of such studies were performed in order to quantify morphological changes associated with either neurologic or psychiatric diseases. The 3-D reconstructions shown in this section were derived from *Atlas* sections.
# **2.6.1 Histological, Morphometric and Histochemical Studies**
## BRAIN
## **Weight, Volume and Linear Dimensions**
| Brain weight (in formalin) | 1383 |
|----------------------------|------|
| Fresh volume (cm3) | 1316 |
| | R | L |
|-------------|-----|-----|
| Length (L)* | 171 | 170 |
| Width (W)* | 71 | 71 |
| Height (H)* | 97 | 96 |
| Length + | 120 | 122 |
| Width + | 63 | 64 |
| Height + | 82 | 82 |
**R**: right hemisphere, **L**: left hemisphere
## **Shrinkage Factors (SF)**
| | R | L |
|---------------------------|------|------|
| SFw Lange, Thörner (1974) | 2.13 | 2.22 |
| SFl Lange, Thörner (1974) | 1.89 | 1.81 |
| SFl Sievert (1992) | 1.74 | 1.82 |
SFw (Weight related shrinkage factor ) = [(Bw \* 0,88 /1,0365) / serial section volume of hemisphere], where Bw = brain weight, Factor 0,88 = [ weight of hemisphere ] / [ brain weight], Factor 1.0365 = mean specific brain weight).
SF : Loss of volume from the fixed autopsy brains to the histological material.
SFl : Linear calculated volume shrinkage factor = [ L\*W\*H (autopsy brain in formaline) ] / [ L\*W\*H (serial paraffin sections) ], where L = length of hemisphere; W = width of hemisphere; H = height of hemisphere.
Hopf, A., Gihr, M., Kraus, C. (1967).
| | R | L |
|---------------------------------|-----|-----|
| Fresh volume (cm3) | 549 | 527 |
| Volume of serial sections (cm3) | 267 | 262 |
| | R | L |
| Fresh volume (cm3) | 297 | 303 |
| Volume of serial sections (cm3) | 144 | 139 |
Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979); Albring, K.M. (1983); Lange, H., Thörner, G. (1974).
## PROSENCEPHALON CEREBRAL CORTEX
Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979); Albring, K.M. (1983); Lange, H., Thörner, G. (1974).
**433**
\* Formalin fixed brain; + after histological preparation
## CEREBRAL CORTEX
fresh volume of cortical regions (3 cm)
| | R | L |
|--------------------------------------------------------|-----|-----|
| Brain weight (in formalin) | 261 | 277 |
| Isocortex (ICx) | | |
| Isocortex frontalis (ICx.f.) | 101 | 103 |
| ICx.f. convexitatis | 63 | 64 |
| ICx.f. medialis | 22 | 22 |
| ICx.f. opercularis dorsalis | 3.6 | 3.2 |
| ICx.f. opercularis basalis | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| ICx.f. basalis | 11 | 12 |
| Area (A.) gigantocellularis (gc) | 5.1 | 5.5 |
| A. gc. convexitatis | 3.8 | 4.0 |
| A. gc. medialis | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| ICx.parietalis (ICx.pa) | 44 | 42 |
| ICx.pa. convexitatis | 24 | 22 |
| ICx.pa. medialis | 16 | 15 |
| ICx.pa. opercularis | 4.9 | 5.1 |
| Regio postcentralis (R.p) | 13 | 15 |
| R.p. convexitatis | 11 | 12 |
| R.p. medialis | 2.1 | 2.5 |
| ICx. temporalis (ICx.t) | 41 | 49 |
| ICx. t. dorsalis | 7.7 | 7.8 |
| R. temporalis transversalis (R.tv) | 2.6 | 2.2 |
| R.tv. | 1.9 | 1.6 |
| R.tv.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| Parieto-temporal convexity | 38 | 38 |
| ICx. occipitalis | 37 | 43 |
| A18 + A19 | 30 | 35 |
| A17 | 7.6 | 7.9 |
| Allocortex (with Proisocortex) | | |
| Claustro-Cx. temporalis | 1.2 | 0.7 |
| Claustro-Cx. insularis | 7.4 | 7.3 |
| Tbc. olfactorium, R. praepiriformis | | |
| frontalis, Peri-Palaeo-Cx. frontalis | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| Palaeo-Cx. temporalis | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Archi-Cx. frontalis | 7.3 | 7.0 |
| Archi-Cx. parietalis | 5.6 | 4.4 |
| Archi-Cx. temporalis | 7.3 | 6.2 |
| Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979); Albring, K.M. (1983). | | |
**Further studies:**
Beheim-Schwarzbach, D. (1952); Braitenberg G. V. (1952); Brockhaus, H. (1940); Busch, K.-T. (1960); Heinze, G. (1954); Sanides, F. (1952); Schulze, H.A (1960).
## HIPPOCAMPAL FORMATION
Reconstruction of the human hippocampus of the *Atlas* brain. Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M.
## **Further study:**
Falkai, P (1989).

## CLAUSTRUM

Brockhaus, H. (1949).
**434**
## AMYGDALOID COMPLEX

**Further study:**
Sanides, F. (1957).

Brockhaus, H. (1938). Oblque view on the reconstruction of the human amygdaloid complex of the *Atlas* brain. BL: basolateral nucleus; BLVM: basolateral nucleus, ventral part; BM: basomedial nucleus; BMDM: basomedial nucleus, dorsomedial part; BMVM: basomedial nucleus, ventromedial part; L: lateral nucleus; BL: basolateral nucleus; PCo: posterior cortical nucleus. Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M. (2014).
## SEPTAL NUCLEI AND BED NUCLEUS OF STRIA TERMINALIS

Subareas of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis as distinguished by immunoreactivity for different neuropeptides (NT: neurotensin, NPY: neuropeptide Y; SOM: somatostatin; ENK: L- and M-enkephalin; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal
# NPH SP VIP ENK
polypeptide; SP: Substance P; NPH Neurophysin I,II. (modified from: Walter, A., Mai, J.K., Lanta, L., Görcs, T., 1991).
#### **Further study:**
Brockhaus, H. (1942).
## BASAL NUCLEAR COMPLEX

## **Further studies:**
Buttlar-Brentano, K.v. (1954,1955,1956); Morres S. A., Mai J. K., Teckhaus L. (1992).

Brockhaus, H. (1942): Schema of the human basal nuclear complex. Reconstruction of the human basal nuclear complex of the *Atlas* brain together with the anterior commissure (orange) and optic chiasma and tract (yellow). MS: medial septal nucleus; DB: diagonal nucleus; Ch4: basal nucleus of Meynert. Original data from Morres et al., 1992. Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M. (2014).
**435**
## MESENCEPHALON
## **STRIATUM**
| STRIATUM | | |
|---------------------------------------------|------|------|
| | R | L |
| Volume of serial sections (10 mm3) | | |
| Caudate nucleus | 298 | 269 |
| Putamen | 360 | 343 |
| Numeric cell density (number / mm3) | | |
| Small neurons (x10) | 2029 | 2248 |
| Large neurons | 156 | 156 |
| Glial cells (x10) | 7360 | 7835 |
| Volumetric neuronal density (10-2 %) | 454 | 393 |
#### **Nuclear diameter** (10-2 �075m)
Small neurons 859 891
Albring, K.M. (1983); Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979); Lange, H., Thörner, G. (1974); Lange, H., Thörner G., Hopf, A. (1975a,b; 1976); Lange, H., Thörner, G., Hopf, A., Schröder, K.F.(1976).
## **CAUDATE NUCLEUS**
| Numeric cell density (number / mm3) | |
|-------------------------------------|--------|
| Macroneurons (L) | 270 |
| Microneurons (S) | 22,663 |
| L/S | 1/83 |
| Average diameter in μm | 10.78 |
## **PUTAMEN**
#### **Numeric cell density** (number / mm3)
| Macroneurons (L) | 163 |
|------------------------|--------|
| Microneurons (S) | 19,953 |
| L/S | 1/119 |
| Average diameter in μm | 9.47 |
Dom. R. (1976); Dom, R., De Saedeleer, J., Bogerts, B., Hopf, A. (1981).
#### **Further studies:**
Brockhaus, H. (1942); Namba, M. (1957); Sanides, F. (1957).
## HYPOTHALAMUS
Wahren, W. (1952), modified. The diagram shows the positions of the sections of the left hemisphere of the *Atlas* brain as delineated by W. Wahren in Schaltenbrand G. and Wahren, W.: Atlas for Stereotaxy of the Human Brain. IInd ed. G. Thieme, Stuttgart (1977).
#### **Further studies:**
Brockhaus, H. (1942); Buttlar-Brentano, K.v. (1954); Mai, J.K., Kedziora, O., Teckhaus, L. & M.V. Sofroniew (1991). 3-D reconstructions of individual hypothalamic nuclei also based on the Atlas brain have been published Koutcherov, I.et al., (2000; 2004; 2007).

Oblique anterior view of the human striatum. Mai, J.K., Majtanik, M. (2014).
## **GLOBUS PALLIDUS**
| | | R | L |
|-------------------------------------|-----|-----|-----|
| Volume of serial sections (mm3) | | | |
| External globus pallidus | EGP | 656 | 560 |
| Internal globus pallidus | IGP | 289 | 238 |
| Numeric cell density (number / mm3) | | | |
| Neurons | EGP | 763 | 994 |
| | IGP | 625 | 588 |
| Glial cells (*103 ) | EGP | 124 | 132 |
| | IGP | 118 | 120 |
| Volumetric cell density (10-3 %) | | | |
| Neurons | EGP | 290 | 380 |
| | IGP | 210 | 270 |
| Glial cells | EGP | 450 | 620 |
| | IGP | 510 | 580 |
Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979).

Reconstruction of the human hypothalamus (posterior-anterior view). Koutcherov, Y. (2008); Mai J.K., Majtanik, M. (2014).
**436**
## THALAMUS
#### **Numeric cell density** (number / mm3 )
| Small neurons | anterior thalamus | 3,522 |
|---------------|--------------------|-------|
| | medial thalamus | 4,544 |
| | lateral thalamus | 1,012 |
| | posterior thalamus | 4,686 |
| Large neurons | anterior thalamus | 6,177 |
| | medial thalamus | 5,538 |
| | lateral thalamus | 3,248 |
| | posterior thalamus | 7,618 |
Dom, R. et al.(1981); Dom. R. (1976).
**Further studies:**
**anterior ncl.:** Fünfgeld, E.W. (1952, 1954)
**mediodorsal ncl.:** Bäumer, H. (1952); Namba, M. (1958) **lateral ncl.:** Bäumer, H. (1952,1954); Dom, R. (1976).
## SUBTHALAMUS
## **SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS**
| | | R | L |
|-------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|
| Fresh volume (cm3) | | 0.139 | 0.119 |
| Volumes of serial sections (mm3) | | | |
| Subthalamic ncl., med. part | SThM
SThL
total | 31.7
35.7
67.4 | 31.2
26.6
57.9 |
| Numeric cell density (number / mm3) | | | |
| Neurons (*10) | SThL
SThM | 375
591 | 357
516 |
| Volumetric cell density | | | |
| Neurons (10-2 %) | SThL
SThM | 142
162 | 199
223 |
| Volumetric cell density (%) | | | |
| Neurons: | SThL | 2.48 | |
| Glia | SThM
SThL
SThM | 1.87
0.99
0.923 | |
| Numeric cell density (number / mm3) | | | |
| | SThL
SThM | 7,417
8,046 | |
| Absolute cell numbers | | 232
287 | 700
600 |
Füssenich, M.S.U. (1967).
#### **Further studies:**
Brockhaus, H. (1942); Klatzo, I. (1954); Lange, H., Thörner, G. (1974); Lange, H., Thörner G., Hopf, A. (1975a,b; 1976); Lange, H., Thörner, G., Hopf, A., Schröder, K.F. (1976); Marani, E., Tjitske, H., Lakke, E.A.J.F., Usunoff K.G. (2008).

Reconstruction of the human thalamus of the *Atlas* brain. Am, AV,DSF: anterior group nuclei; VAM, VAL, VL, VPL: lateral nuclei; LG, MG geniculate nuclei; Pul: pulvinar; opt: optic chiasma and tract; st; stria terminalis. Mai, J.K., Forutan, F. (2013).
## **Zona incerta**
Brockhaus, H. (1942, modified): Delineations derived from the left hemisphere (L4) of the *Atlas* brain. Abbrev.: h1+h2: thalamic and lenticular fascicles; R: red nucleus; SN: substantia nigra; STh: subthalamic nucleus.
**437**
## MESENCEPHALON
## **RED NUCLEUS**
#### **Volumes of serial sections** (mm3)
| Dorsomedial quadrant | r1 | 26.6 |
|------------------------|----|------|
| Dorsolateral quadrant | r2 | 35.9 |
| ventrolateral quadrant | r3 | 35.8 |
| ventromedial quadrant | r4 | 35.2 |
#### **Numeric cell density** (number/mm3 )
| | | R | L |
|-------------|----|-----|-----|
| Neurons | r1 | 171 | 172 |
| | r2 | 124 | 95 |
| | r3 | 104 | 103 |
| | r4 | 104 | 104 |
| Glial cells | r1 | 446 | 421 |
| | r2 | 384 | 336 |
| | r3 | 320 | 402 |
| | r4 | 309 | 308 |
#### **Volumetric density** (%)
| Neurons | r1 | 57 | 51 |
|-------------|----|----|----|
| | r2 | 28 | 24 |
| | r3 | 25 | 27 |
| | r4 | 21 | 23 |
| Glial cells | r1 | 78 | 69 |
| | r2 | 74 | 58 |
| | r3 | 74 | 60 |
| | r4 | 72 | 56 |
values without shrinkage factor-correction
Herbel, W. (1979); Sander, H.A. (1981).
## LOWER BRAINSTEM
**Locus coeruleus:** Wünscher, W. (1956);
**Superior olive:** Beheim-Schwarzbach, D. (1955); Wünscher, W.
(1956).
## CELL STUDIES
Hempel, K.-J., Treff, W.M. (1959); Klatzo, I. (1954); Schiffer, D.(1954); Treff, W.M., Hempel, K.-J. (1959).
## NEUROACTIVE SUBSTANCES
Mai, J.K., Kedziora, O., Teckhaus, L., Sofroniew M.V. (1991); Mai, J.K., Stephens, P., A. Hopf, Cuello A.C. (1986); Mai, J. K., Reifenberger, G. (1988); Pioro, E.P., Mai, J. K., Cuello, A.C. (1990); Walter, A., Jimenez-Härtel, W., Mai J.K. (1990); Walter, A., Mai, J.K., Lanta, L., Görcs T. (1991).
## **SUBSTANTIA NIGRA**

#### **Further studies:**
Bogerts, B., Häntsch, J., Herzer, M. (1982); Solcher, H. (1956).
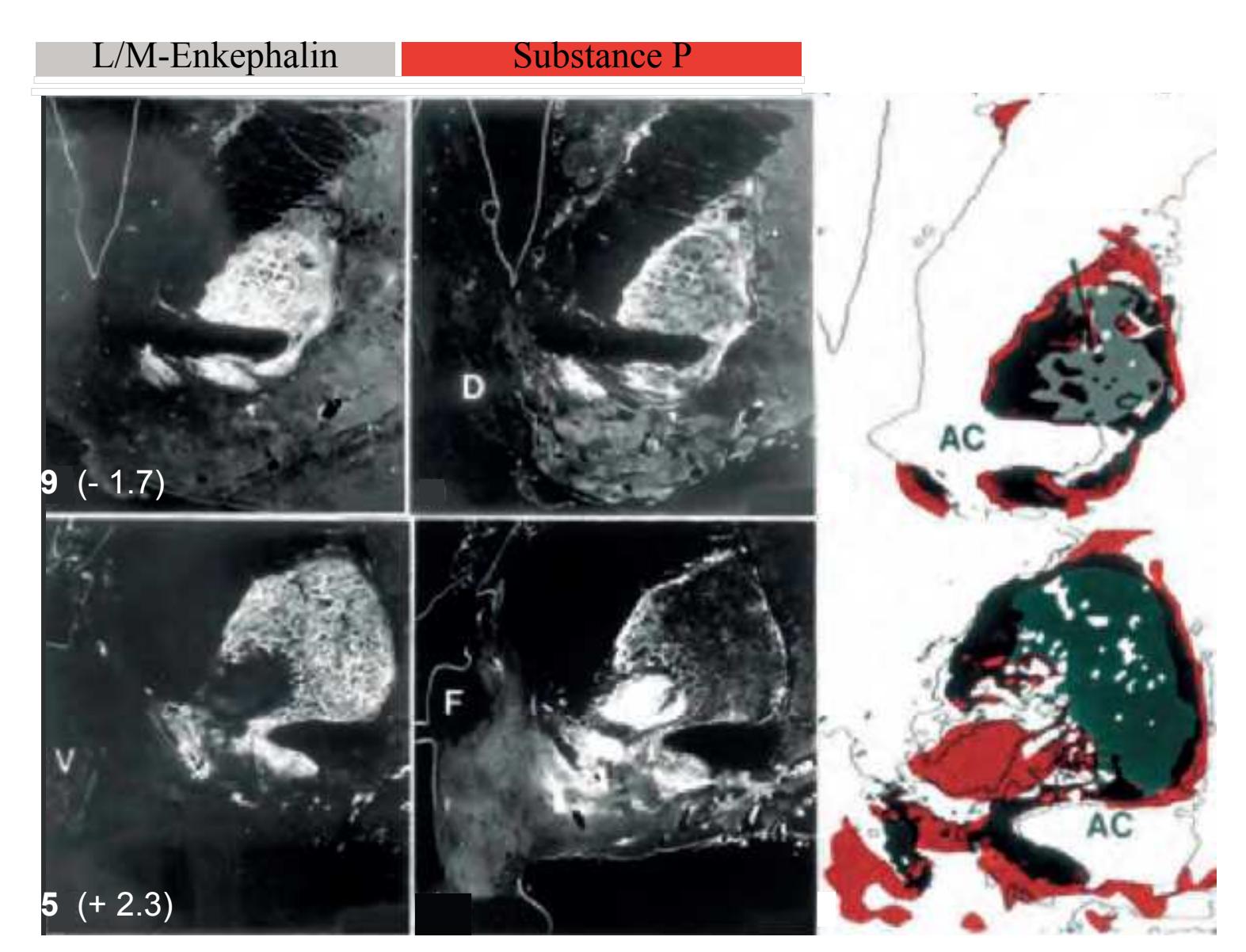
Mai, J.K., Stephens, P., A. Hopf, Cuello A.C. (1986).
**438**
## **2.6.2 References**
- The full text of the references which are indicated by an asterisk (\*) are available on the website: www.thehumanbrain.info
- Albring, K.M. (1983) Quantitative Untersuchungen 33 Rindenregionen des menschlichen Gehirns. Thesis, Univ. of Düsseldorf.
- \*Bäumer, H. (1952) Untersuchungen am Ncl. medialis und lateralis thalami bei Schizophrenie.Proc. I st Intl. Congr. Neuropathol. Rom. Rosenberg & Sellier, Torino. Vol. 3, pp. 636-647.
- \*Bäumer, H. (1954) Veränderungen des Thalamus bei Schizophrenie. J. Hirnforsch. 1, 156-172.
- Beheim-Schwarzbach, D. (1952) Anatomische Veränderungen im Schläfenlappen bei "funktionellen" Psychosen. Proc. I st. Intl. Congr. Neuropathol. Rom. Rosenberg & Sellier, Torino.Vol. 3, pp. 609-620.
- Beheim-Schwarzbach, D. (1955) Lebensgeschichte der melaninhaltigen Nervenzellen des Ncl. coeruleus unter normalen und pathogenen Bedingungen. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 62-95.
- Bogerts, B., Häntsch, J., Herzer, M. (1982) A morphometric study of the dopaminecontaining cell groups in the mesencephalon of normals,Parkinson patients and schizophrenics. Thesis, Düsseldorf.
- \*Braitenberg, G. V. (1952) Ricerche istopatologiche sulla corteccia frontale di schizofrenici. Proc. I st. Intl. Cong. Neuropathol. Rom. Rosenberg & Sellier, Torino. Vol. 3, pp. 621-626.
- \*Brockhaus, H. (1938) Zur normalen und pathologischen Anatomie des Mandelkerngebietes. J. Psychol. Neurol. 49, 1-136.
- \*Brockhaus, H. (1940) Die Cyto- und Myeloarchitektonik des Cortex claustralis und des Claustrum beim Menschen. J. Psychol. Neurol. 49, 249-348.
- \*Brockhaus, H. (1942) Beitrag zur normalen Anatomie des Hypothalamus und der Zona incerta beim Menschen. J. Psychol. Neurol. 51, 96-195.
- \*Brockhaus, H. (1942) Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen über den Basalkernkomplex. J. Psychol. Neurol. 51, 57-95.
- \*Brockhaus, H. (1942) Zur feinen Anatomie des Septum und des Striatum. J. Psychol. Neurol. 51, 1-56. Translated in: Human Brain Dissection. Pope A. ed. (1983) U.S. Government Printing Office Publ. 381-132: 3096.
- \*Busch, K.-T. (1960) Individuelle architektonische Differenzen der Area striata. J. Hirnforsch. 4, 535-552.
- \*Buttlar-Brentano, K.v. (1954) Zur Lebensgeschichte des Ncl. basalis, tuberomammillaris, supraopticus und paraventricularis unter normalen und pathogenen Bedingungen. J. Hirnforsch. 1, 337-419.
- \*Buttlar-Brentano, K.v. (1955) Das Parkinsonsyndrom im Lichte der lebensgeschichtlichen Veränderungen des Nucleus basalis. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 55-76.
- Buttlar-Brentano, K.v. (1956) Zur weiteren Kenntnis der Veränderung des Basalkerns bei Schizophrenen. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 271-291.
- \*Dom, R., De Saedeleer, J., Bogerts, B., Hopf, A. (1981) Quantitative cytometric analysis of basal ganglia in catatonic schizophrenics. In: Biological Psychiatry (eds. Perris, C. Struwe, G & Jansson B), Elsevier, North-Holland pp. 723-726.
- \*Dom. R. (1976) Neostriatal and Thalamic Inter-neurons. Their role in the pathophysiology of Huntington's chorea, Parkinson's disease and catatonic schizophrenia. Thesis, Univ. of Leuven.
- \*Falkai, P. (1988). Hippocampal pathology in schizophrenia. A morphometric study. Thesis, Düsseldorf.
- \*Fünfgeld, E.W. (1952) Pathologisch-anatomische Untersuchungen im Nucleus anterior thalami bei Schizo phrenie, Proc. I st . Intl. Cong. Neuropathol. Rom. Rosenberg & Sellier, Torino. Vol. 3, pp. 648-659.
- \*Fünfgeld, E.W. (1954) Der Nucleus anterior thalami bei Schizophrenie. J. Hirnforsch. 1, 146-155.
- Füssenich, M.S.U. (1967) Vergleichend anatomische Studien über den Nucleus subthalamicus (Corpus Luysi) bei Primaten.Thesis, Univ. of Freiburg.
- \*Hassler, R. (1937) Zur Normalanatomie der Substantia nigra. Versuch einer architektonischen Gliederung. J. Psychol. Neurol. 48, 1-55.
- Hassler R (1938) Zur Pathologie der Paralysis agitans und des postencephali-
- tischen Syndroms. J. Psychol. Neurol. 48: 387-476. \*Heinze G. (1954) Zytoarchitektonische Untergliederung der Area occipitalis. J. Hirnforsch. 1: 173-198.
- \*Hempel, K.-J. (1958) Histopathologische Untersuchungen am Supranucleus medialis-dorsalis thalami bei Schizophrenie J. Hirnforsch. 4, 371-411.
- \*Hempel, K.-J., Treff, W.M. (1959) Die Gliazelldichte bei klinisch Gesunden und Schizophrenen. J. Hirnforsch. 4, 371-411.
- \*Herbel, W. (1979) Zur Neuroanatomie und Neuro-pathologie des Nucleus ruber beim Menschen. Thesis, University of Düsseldorf.
- \*Hopf, A., Gihr, M., Kraus, C. (1967) Vergleichende Architektonik des Primatenthalamus. Progr. Primatol. I. Congress of the International Primatological Society, Frankfurt, pp.120-127.
- Klatzo, I. (1954) Über das Verhalten des Nukleolar-apparates in den menschlichen Pallidumzellen. J. Hirnforsch. 1, 47-60.
- Koutcherov, I., Mai, J.K., Ashwell, K.W.S., Paxinos, G.:(2000) The organization of the human paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 423: 299-318.
- Koutcherov, I., Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G. (2004) Organisation of the human dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus. NeuroReport: 15 (1), 107-111.
- Koutcherov, Y. Paxinos, G. Mai, J. (2007) The organization of the human medial preoptic nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 503:392–406.
- \*Lange, H., Albring, K.M. (1979) Quantitative Untersuchungen an 33 Rindenregionen des menschlichen Gehirns. Verh. Anat. Ges. 73, 107-109.
- \*Lange, H., Thörner, G. (1974) Zur Neuroanatomie und Neuropathologie des Corpus striatum, Globus pallidus und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen, Thesis, Düsseldorf.
- \*Lange, H., Thörner G., Hopf, A. (1975) Morphometrisch-statistische Strukturanalysen des Striatum, Pallidum und Nucleus subthalamicus beimMenschen, Teil 1, J. Hirnforsch. 16, 333-350.
- \*Lange, H., Thörner G., Hopf, A. (1975) Morphometrisch-statistische Strukturanalysen des Striatum, Pallidum und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen, Teil 2, [Morphometrical-statistical structure analysis of human striatum, pallidus and subthalamic nucleus. II. Globus pallidus]. J. Hirnforsch. 16, 401-413. German. PMID: 1214059
- Lange, H., Thörner, G., Hopf, A. (1976) Morphometrisch-statistische Strukturanalysen des Striatum, Pallidum und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen, Teil 3, [Morphometric-statistical structure analysis of human striatum, pallidum and nucleus subthalamicus. III. Nucleus subthalamicus]. J. Hirnforsch. 17(1), 31–41. German. PMID: 965719
- \*Lange, H., Thörner, G., Hopf, A., Schröder, K.F. Morphometric studies of the neuropathological changes in choreatic diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 28, 401-425. (1976)
- Mai, J. K., Reifenberger, G. (1988): Distribution of the carbohydrate epitope 3-fucosyl-Nacetyl-lactosamine (FAL) in the adult human brain. J. Chem. Anat. 1, 255-285.
- Mai, J.K., Forutan, F. (2012) Thalamus. In: The Human Nervous System, 3rd Ed., Eds. Mai, J.K. and Paxinos, G.: Academic Press/Elsevier, San Diego, pp. 620-679.
- Mai, J.K., Kedziora, O., Teckhaus, L., Sofroniew, M.V. (1991). Evidence for subdivisions in the human suprachiasmatic nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 305: 508-525.
- Mai, J.K., Stephens, P., A. Hopf, Cuello A.C. (1986): Substance P in the human brain. Neuroscience 17, 709-739.
- Marani, E., Tjitske, H., Lakke, E.A.J.F., Usunoff K.G. (2008) The Subthalamic Nucleus: Part I: Development, Cytology, Topography and Connections (Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology) Springer, Berlin, Germany.
- Morres S. A., Mai J. K. Teckhaus L. (1992) Expression of the CD15 Epitope in the Human Magnocellular Basal Forebrain System. Histochem. J., 24: 902-910.
- \*Namba, M. (1958) Über die feineren Strukturen des medio-dorsalen Supranucleus und der Lamella medialis des Thalamus beim Menschen. J.Hirnforsch. 4, 1-41.
- \*Namba, M.(1957) Cytoarchitektonische Untersuchung am Striatum. J. Hirnforsch. 3, 24-48.
- Pioro, E.P., Mai, J. K., Cuello, A. C. (1990): Distribution of substance P- and enkephalinimmunoreactive neurons and fibers. in: The Human Nervous System. G. Paxinos (ed.), Academic Press, 1051-1094.
- \*Rabl, R. (1958) Strukturstudien an der Massa intermedia des Thalamus. J. Hirnforsch. 4, 76-112.
- \*Sander, H.A. (1981) Morphometrische Analyse der neuropathologischen Veränderungen im Nucleus ruber bei Parkinson'scher Krankheit. Thesis, Univ. of Düsseldorf.
- \*Sanides, F. (1957) Die Insulae terminales des Erwachsenengehirns des Menschen. J. Hirnforsch. 3, 243-273.
- \*Sanides, F. (1957) Untersuchungen über die histologische Struktur des Mandelkerngebietes. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 354-390.
- Sanides, F. (1962). Die Architektur des menschlichen Stirnhirns. Zugleich eine Darstellung der Prinzipien seiner Gestaltung als Spiegel der stammesgeschichtlichen Differenzierung der Großhirnrinde. Monogr., Ges. Neurol. Psychat. 98, 1-203, Springer, Berlin, Göttingen, Heidelberg.
- Schiffer, D. (1954) Sur l'action reparatrice du noyau des cellules nerveuses. J. Hirnforsch. 1, 326-336.
- Schröder, K.F. (1970) Quantitativ-morphologische Untersuchungen zur Genese verschiedener Choreaformen. Thesis, University of Marburg.
- Schröder, K.F., Hopf, A, Lange, H, Thörner, G. (1975) Morphometrisch-statistische Strukturanalysen des Striatum, Pallidum und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen. I Striatum. [Morphometrical-statistical structure analysis of human striatum, pallidum and subthalamic nucleus]. J Hirnforsch. 16(4):333-350. German. PMID: 1214057.
- Schulze, H. A. (1960) Zur individuellen cytoarchitektonischen Gestaltung der linken und rechten Hemisphäre des Lobulus parietalis inferior. J.Hirnforsch. 4, 486-534.
- Solcher, H. (1956) Zur Pathologie des Niger reticulatus und zu seiner Stellung im extrapyramidalen System. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 391-401.
- Strasburger, E.H. (1937) Die myeloarchitektonische Gliederung des Stirnhirns beim Menschen und Schimpansen. J. Psychol. Neurol. 47: 565-606.
- Thörner G, Lange H, Hopf A. (1975) Morphometrisch-statistische Strukturanalysen des Striatum, Pallidum und Nucleus subthalamicus beim Menschen. II Pallidum. [Morphometrical-statistical structure analysis of human striatum, pallidus and subthalamic nucleus. II. Globus pallidus]. J Hirnforsch. 16(5):401-413. German. PMID: 1214059.
- Treff, W.M., Hempel, K.-J. (1959) Quantitative Untersuchungen über relative Zell- und Zellkernvolumina bei klinisch Gesunden und Schizophrenen. J. Hirnforsch. 4, 412-454.
- \*Vogt, C., Vogt, O. (1941) Thalamusstudien I-III. J. Psychol. Neurol. Heft 1 u. 2. 50: 32- 154.
- Vogt, C., Vogt, O. (1942) Morphologische Gestaltungen. J. Psychol. Neurol. 50, 1-504. \*Wahren, W. (1952) The changes of hypothalamic nuclei in schizophrenia. Proc. I st . Intl. Congr. Neuropathol. Rom. Rosenberg and Sellier, Torino. Vol. 3, pp. 660-673.
- Walter, A., Jimenez-Härtel, W., Mai, J.K. (1990) Mapping of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the human forebrain. Brain Res. Bull. 24, 297-311.
- Walter, A., Mai, J.K., Lanta, L., Görcs, T. (1991) Differential distribution of histochemical markers in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the human brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 4: 281-298.
- Wünscher, W. (1956) Cytoarchitektonik und Involution einiger Hirnstammkerne mit vegetativen Funktionen und der oberen Olive. J. Hirnforsch. 2, 354-390.
- Yilmazer-Hanke, D.M. (2012) Amygdala. In: The Human Nervous System, 3rd ed., Eds. Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G.: Academic Press/Elsevier, San Diego, pp. 761-823.
**439**
# **Index**
## List of Structures
Names of structures are listed separately for different regions( Cortex regions; Gyri, Surface Morphology; Sulcii; ... ). Each name is followed by the abbreviation of the structure.
#### **Cortex regions**
agranular insular cortex (claustrocortex insularis) AIn amygdalohippocampal area AHi
#### **Gyri, Surface Morphology**
ambiens gyrus AG amygdalostriatal transition area AStr
...
#### **Cortex regions**
```
agranular insular cortex (claustrocortex insularis) AIn
amygdalohippocampal area AHi
anterior cingulate cortex (B.Vogt) ACC
anterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) aMCC
area orbitoinsularis AOI
area piriformis insulae API
Brodmann areas 1-52 BA1-52
CA1 field of hippocampus CA1
CA2 field of hippocampus CA2
CA3 field of hippocampus CA3
cortico-amygdaloid transition area CxA
dorsal presubiculum dPrS
dorsal temporopolar region DTP
entorhinal cortex EC
entorhinal cortex Ent
entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield ECL
entorhinal cortex, caudal subfield Ec
entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield EI
entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield ELC
entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield ELR
entorhinal cortex, medial intermediate subfield EMI
entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield Eo
entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield ER
fascia dentata FD
fields of hippocampus CA1-3
fimbria of the hippocampus fi
frontal limbic area FLA
frontopolar cortex (or gyrus) FrP
hippocampal head HiH
hippocampo amygdaloid transitional area HATA
hippocampus Hi
insula Ins
lateral temporopolar cortex TPCl
lingual-parahippocampal transition area LPHT
margo denticulatus MDe
medial temporopolar cortex TPCm
olfactory area OlfA
parahippocampal area TF TF
parahippocampal area TH TH
parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area PHA
parainsular region PIR
parastriate area PStr
parasubiculum PaS
parietooccipital transition zone POTZ
periamygdalar area PAA
periamygdaloid cortex PAC
periamygdaloid cortex PAM
perirhinal cortex PRC
perirhinal cortex, BA 35 PRC35
perirhinal cortex, BA 36 PRC36
perisplenial cortex(B.Vogt ) PSC
piriform cortex Pir
piriform cortex, frontal part PirF
piriform cortex, temporal part PirT
postcentral insular cortex PCI
posterior cingulate cortex (B.Vogt) PCC
posterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) pMCC
precommissural archicortex PCA
precuneiform area PrCuF
precuneus PCun
presubiculum PrS
retrosplenial cortex RSC
retrosplenial limbic gyri RSG
striate area AStr
subcallosal area SCA
subiculum S
temporooccipital transition zone TOTZ
```
## **Gyri, Surface Morphology**
ambiens gyrus AG
amygdalostriatal transition area AStr angular gyrus AnG angular gyrus, anterior division AAnG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrGL anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus, medial part AOrGM anterior angular gyrus AAnG anterior central operculum COp-a anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, medial part AOrG-m anterior subcentral gyrus ASCe anterior transverse temporal gyrus TTG1 arcus parieto-occipitalis, anterior division APOc-a arcus parieto-occipitalis, posterior division APOc-p basal operculum BOp brainstem BSt central operculum (Rolandi) COp cerebellar hemisphere CH cerebellum Cb cingulate gyrus CG cuneal point \*CP cuneolingual gyrus (in depth) \*X cuneus Cun dentate gyrus DG diverticulum unci du fasciolar gyrus FG frontal dimple fd frontal lobe FL frontal operculum FOp frontal pole FP frontomarginal gyrus FMG fusiform gyrus FuG fusiform gyrus, posterior part FuG-p gyri Andreae Retzii ARG gyrus ambiens GA gyrus descendens GDe gyrus semilunaris GSL gyrus uncinate GU inferior frontal gyrus IFG inferior frontal gyrus, ascending part IFG-asc inferior frontal gyrus, basilar part IFG-ba inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part IFGOp inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part IFGOr inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part IFGTr inferior frontopolar gyrus IFPG inferior lingual gyrus ILG inferior lingual gyrus ILgG inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part ILG-l inferior lingual gyrus, medial part ILG-m inferior occipital gyrus IOG inferior parietal lobule IPL inferior rostral gyrus IRoG inferior sagittal gyrus ISG inferior temporal gyrus ITG inferior temporopolar region ITP infundibular stalk InfS insular gyrus IG insular pole IPo intermediate orbital gyrus IOrG isthmus I isthmus of cingulate gyrus ICG lamina terminalis LT lateral fusiform gyrus LFuG lateral orbital gyrus LOrG limen insulae Li lingual gyrus (O5) LgG medial fusiform gyrus MFuG
medial orbital gyrus MOrG
medulla oblongata Md middle frontal gyrus MFG middle frontopolar gyrus MFPG middle occipital gyrus MOG middle sagittal gyrus MSG middle temporal gyrus MTG occipital gyrus (gyri) OcG occipital pole OcP occipito-temporal gyrus OTG olfactory bulb OB olfactory trigone OTr optic papilla pap orbital gyrus/gyri OrG orbitofrontal gyri OFG paracentral fossa pcf paracentral lobule PCL paracingulate gyrus PCg parahippocampal gyrus PHG paraterminal gyrus PTG parietal operculum POp parieto-occipital arc (first parieto-occipital « plis de passage » of Gratiolet) POc parieto-occipital arc, anterior part POc-A parieto-occipital arc, posterior part POc-P perisplenial gyri (von Economo) PSG planum polare PPo planum polare, lateral part PPo-l planum temporale PTe pons Pons postcentral gyrus PoG posterior angular gyrus PAnG posterior central operculum COp-p posterior orbital gyrus POrG posterior subcentral gyrus PSCe posterior transverse temporal gyrus TTG2 posteromedial orbital lobule PMOL precallosal gyrus PCG precentral gyrus PrG preoccipital notch pi radiation of straight gyrus rsg radiation of straight gyrus sgr rostral gyrus RoG spinal cord Spinal straight gyrus SG striate area (Brodmann area 17) 17 subcallosal gyrus SCG subsplenial gyrus SSpG superior frontal gyrus SFG superior frontal gyrus, lateral part SFGL superior frontal gyrus, medial part SFGM superior frontopolar gyrus SFPG superior lingual gyrus SLG superior lingual gyrus SLgG superior medullary velum SMV superior occipital gyrus SOG superior occipital gyrus, lat part SOG-l superior occipital gyrus, medial part SOG-m superior parietal lobule SPL superior rostral gyrus SRoG superior sagittal gyrus SSG superior sagittal gyrus, anterior part SSG-a superior sagittal gyrus, posterior part SSG-p superior temporal gyrus STG supramarginal gyrus SMG temporal lobe TL temporal operculum TOp temporal pole TP temporopolar gyrus TPG transverse insular gyrus TIG transverse temporal gyrus/gyri TTG
uncal notch unn
**440**
temporopolar cortex TPC
uncus Un vermis of cerebellum Ver
#### **Sulci**
accessory callosal sulcus acals accessory superior frontal sulcus asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus asfs-m accessory supraorbital sulcus asos angular sulcus angs anterior intermediate parietal sulcus (Jensen) impI anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen imI anterior occipital sulcus aos anterior occipital sulcus, dorsal segment aos-d anterior occipital sulcus, inferior ramus aos-i anterior occipital sulcus, superior ramus aos-s anterior parietal sulcus (Vogt), (precuneal limiting sulcus) apa anterior parolfactory sulcus aps anterior parolfactory sulcus, inferior branch apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, superior branch apss anterior subcentral sulcus ascs anterior transverse collateral sulcus atcos calcarine sulcus cs calcarine sulcus, anterior part acs calcarine sulcus, central part ccs calcarine sulcus, central part cs-c callosal sulcus cals central sulcus ce choroidal fissure chf cingulate sulcus cgs cingulate sulcus, anterior p cgs-a cingulate sulcus, posterior p cgs-p circular insular sulcus cis collateral sulcus (medial occipitotemporal sulcus) cos collateral sulcus, occipital ramus cos-o collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus cos-ph collateral sulcus, temporal ramus cos-t cuneal limiting sulcus culs diagonal sulcus dgs endorhinal sulcus ers fragmentosus sulcus frs frontal paramidline sulcus fmps frontal paramidline sulcus fpms frontomarginal sulcus fms fronto-orbital sulcus fors frontopolar sulcus fps Heschl sulcus sH hippocampal fissure hf inferior cingulate sulcus cgs-i inferior frontal sulcus ifs inferior frontopolar sulcus ifps inferior occipital sulcus ios inferior postcentral sulcus ipocs inferior precentral sulcus iprs inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior) iss inferior temporal sulcus its intermediate frontal sulcus imfs intermediate orbital sulcus imos intermediate orbital sulcus iors intralingual sulcus ils intraparietal sulcus ips intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment ips-h intrarhinal sulcus irhs intrarhinal sulcus irs lateral (Sylvian) fissure lf lateral fissure, horizontal segment lf-h lateral fissure, anterior segment lf-a lateral fissure, middle segment lf-m lateral fissure, posterior segment lf-p lateral fissure, vertical segment lf-v lateral frontomarginal sulcus lfms lateral occipitotemporal sulcus lots lateral orbital sulcus lors lateral occipital sulcus los lingual sulcus lgs lingual sulcus, posterior ramus lg-p lunate sulcus lus marginal precentral sulcus maprs marginal segment of cingulate sulcus cgs-mg medial frontomarginal sulcus mfms middle frontopolar sulcus mfps middle orbital sulcus mors midfusiform sulcus mfs occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of Seitz) ops olfactory sulcus olfs orbital sulcus ors paracentral sulcus pacs paracingulate sulcus pcgs paraterminal sulcus pts parieto-occipital fissure pof polar sulcus ps postcentral sulcus pocs posterior orbital sulcus pors posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch porsm posterior paramidline sulcus ppms posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt) ppa posterior parolfactory sulcus pps posterior transverse collateral sulcus ptcos postreme subcallosal sulcus posc precentral sulcus prs
precuneal limiting sulcus prculs precuneal sulcus prcus preolfactory transverse sulcus polfs preopercular sulcus prop pretriangular sulcus prts radiate sulcus (Eberstaller) ras retrocalcarine sulcus, lower branch rcs-i retrocalcarine sulcus, upper branch rcs-s rhinal sulcus rhs rostral sulcus ros rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch ros-i rostral sulcus, superior (upper) branch ros-s second intermediate parietal sulcus imII semiannular sulcus sas subcalcarine sulcus scs subparietal sulcus sbps sulcus acusticus acus sulcus semiannularis ssa superior frontal sulcus sfs superior frontopolar sulcus sfps superior occipital sulcus sos superior parietal sulcus spas superior postcentral sulcus spcs superior precentral sulcus sprs superior sagittal sulcus sss superior temporal sulcus sts superior temporal sulcus, anterior segment sts-a superior temporal sulcus, ascending segment sts-asc superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment sts-h superior temporal sulcus, posterior segment sts-p supraorbital sulcus sors third intermediate parietal sulcus imIII transverse occipital sulcus tos transverse occipital sulcus, lateral ramus tos-l transverse occipital sulcus, medial ramus tos-m transverse orbital sulcus tors transverse temporal sulcus tvt triangular sulcus ts uncal sulcus us vertical ramus of lateral fissure lfv
#### **Ventricular system, CSF**
arachnoid granulations argr calcar avis cal cavity of septum pellucidum CSP central part of lateral ventricle CLV cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius) Aq choroid plexus chpx cistern Ci fourth ventricle 4V frontal horn of lateral ventricle FLV great (cerebellomedullary) cistern GrCi interpeduncular cistern IPCi interpeduncular fossa IPF interventricular foramen IVF lateral ventricle LV occipital horn of lateral ventricle OLV pontine cistern PoCi preoptic recess of the third ventricle P3V subarachnoid space SArS tela choroidea of the lateral ventricle tclv temporal horn of lateral ventricle TLV tenia of fimbria tfi tenia of fornix tfx tenia of thalamus tt tenia semicircularis tsc third ventricle 3V trigone of lateral ventricle TrLV velum terminale vt
## **Nuclei and Subcortical Brain Areas**
accessory basal amygdaloid nucleus AB accumbens nucleus Ac accumbens nucleus, central part AcC accumbens nucleus, lateral part AcL accumbens nucleus, medial part AcM amygdala Amg amygdaloid island (extended amygdala) AI anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus APul anterior amygdaloid area AAA anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal part ACoD anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part ACoV anterior hypothalamic area AHA anterior lateral preoptic nucleus ALPO anterior medial preoptic nucleus AMPO anterior olfactory nucleus (retrobulbar region) AO anterior olfactory nucleus, posterior part AOP anterior perforated substance APS anterior thalamic nucleus ATh anterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VLA anterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, external part VLAE anterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, internal part VLAI anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus) ADPul anterodorsal thalamic nucleus AD anteromedial thalamic nucleus AM
anteroprincipal (anteroventral) thalamic nucleus APr anteroventral nucleus (anteroprincipal nucleus) AV
anteroventral periventricular hypothalamic nucleus AVPe arcuate nucleus Arc basal (inferior) ventrolateral thalamic nucleus [VPI] (entry zone of the cerebellar fibers) VLb basal nucleus, compact part BC basal nucleus, diffuse part BD basal ventroanterior thalamic nucleus [VM] (entry zone of nigral and amygdaloid afferents) VAb basal ventroposterior nucleus [VMpo] (entry zone of sensory afferents) VPb basolateral amygdaloid nucleus BL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal (magnocellular) part BLD basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, intermediate part BLI basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, paralaminar part BLPL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventrolateral part BLVL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventromedial part BLVM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus BM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, centromedial part BMCM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, dorsolateral part BMDL basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, dorsomedial part BMDM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, ventromedial part BMVM bed nucleus of the stria terminalis BST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, central division BSTC bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division BSTL bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, juxtacapsular part BSTLJ bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division BSTM bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, posterior division BSTP bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, posterior division, lateral part BSTPL bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, posterior division, medial part BSTPM bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, ventral division BSTV body of caudate nucleus BCd capsule of red nucleus cr caudate nucleus Cd central amygdaloid nucleus Ce central amygdaloid nucleus, lateral part CeL central amygdaloid nucleus, medial part CeM central medial thalamic nucleus CeMe centromedian thalamic nucleus CM claustrum Cl commissural nucleus Co compact insular claustrum CoCl cucullaris nucleus Cuc cuneiform area CuA cuneiform nucleus CuF dentate nucleus Dt diffuse insular claustrum DiCl diffuse pulvinar nucleus DiPul dorsal claustrum DCl dorsal hypothalamic area DH dorsal hypothalamic nucleus DoH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic nucleus DPeH dorsal raphe nucleus DR dorsal superficial nucleus DSF dorsal tegmental nucleus DTg dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus DMH dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, compact part DMHC Edinger-Westphal nucleus EW entopeduncular nucleus EP extended amygdala EA external globus pallidus EGP fasciculosus nucleus Fa fundus region of caudate nucleus FCd fundus region of putamen FPu fundus striati FStr globus pallidus GP great terminal island GTI habenula Hb head of caudate nucleus HCd H-field of Forel H horizontal limb of the diagonal band HDB hypothalamus Hy indusium griseum IGr inferior colliculus IC inferior olive IO inferior pulvinar nucleus IPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal part IDPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate part ILPul inferior pulvinar nucleus, ventral p IVPul infundibular nucleus Inf interfascicular nucleus IF intergeniculate pulvinar nucleus IGPul internal globus pallidus IGP interpeduncular nucleus IP interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure IPAC interthalamic adhesion IThA lateral amygdaloid nucleus La lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal anterior part LaDA lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal lateral part LaDL lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsomedial part LaDM lateral amygdaloid nucleus, intermediate part LaI lateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part LaV lateral caudate nucleus CdL lateral dorsal thalamic nucleus LD lateral geniculate nucleus LG lateral habenular nucleus LHb lateral hypothalamic area LH lateral mammillary nucleus LM
**441**lateral pulvinar nucleus LPul lateral septal nucleus, dorsal part LSD lateral septal nucleus, intermediate part LSI lateral septal nucleus, ventral part LSV lateral terminal nucleus of the accessory optic system LTN lateral thalamic nuclear region LTh lateral tuberal nucleus LTu lateral ventroanterior thalamic nucleus VAL lateral ventroposterior thalamic nucleus VPL laterodorsal nucleus, oral part LDO laterodorsal nucleus, superficial part LDSF laterodorsal tegmental nucleus LDTg limitans claustrum LiCl limitans nucleus Lim limitans putamen PuLi locus coeruleus LC mammillary body MB medial amygdaloid nucleus Me medial amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part MeA medial caudate nucleus CdM medial geniculate nucleus MG medial geniculate nucleus, dorsal posterior part MGDP medial geniculate nucleus, fibrosus part MGFi medial geniculate nucleus, limitans part MGLi medial geniculate nucleus, magnocellular part MGMC medial geniculate nucleus, parvocellular part MGPC medial habenular nucleus MHb medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part ML medial mammillary nucleus, medial part MM medial preoptic nucleus MPO medial preoptic nucleus, lateral part MPOL medial pulvinar nucleus MPul medial putamen PuM medial septal nucleus MS medial ventroanterior thalamic nucleus VAM medial ventroposterior thalamic nucleus VPM medial ventroposterior thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part VPMPC median eminence ME median preoptic nucleus MnPO median raphe nucleus MnR mediodorsal thalamic nucleus MD mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part MDMC mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, paralamellar part MDPL mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part MDPC mediolateral pulvinar nucleus MLPul mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus Me5 microcellular tegmental nucleus MiTg nucleus Darkschewitsch Dk nucleus of the diagonal band DB nucleus of the diagonal band, angular part ADB olfactory tubercle Tu pallidohypothalamic nucleus PalHy parabigeminal nucleus PBG parabrachial pigmented nucleus PBP parafascicular thalamic nucleus PF paranigral nucleus PN paraoptic nucleus PaO paratenial thalamic nucleus PT paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus Pa paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, anterior parvocellular part PaAP paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, dorsal part PaD paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, fornical part PaFo paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, magnocellular part PaMC paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, parvocellular part PaPC paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, posterior part PaPo paraventricular thalamic nucleus PV peduncle of lentiform nucleus PedL periaqueductal gray PAG perifornical nucleus PeF peripeduncular area PPA peripeduncular nucleus PP periventricular nucleus Pe pineal gland Pi posterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus PCo posterior hypothalamic area PH posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VLP posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, external part VLPE posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, internal part VLPI preamygdalar claustrum PACl prepiriform claustrum PPCl prereticular zone PRt pretectal area PTc pulvinar thalami Pul putamen Pu quadrigeminal plate QP red nucleus R red nucleus, parvocellular part RPC reticular thalamic nucleus Rt reticular thalamic nucleus Rt reuniens thalamic nucleus Re rostral linear nucleus RLi septofimbrial nucleus SFi septum pellucidum SptP sexual dimorphic nucleus SxD striatal cell bridge(s) SB subcaudate terminal island SCTI
subparafascicular thalamic nucleus SPF substantia gliosa (subependymal gray) SGl substantia nigra SN substantia nigra, pars compacta SNC substantia nigra, pars reticulata SNR substriatal terminal island SSTI subthalamic nucleus STh superficial pulvinar nucleus SFPul superior colliculus SC superior pulvinar nucleus SPul superior ventroposterior thalamic nucleus (Kaas) VPS supracapsular part of the globus pallidus SCGP suprachiasmatic nucleus SCh suprageniculate nucleus SGe supramammillary nucleus SuM supraoptic nucleus SO supraoptic nucleus, dorsolateral part SODL supraoptic nucleus, ventromedial part SOVM tail of caudate nucleus TCd tectum of midbrain Tec temporal claustrum TCl thalamus Th triangular septal nucleus TS tubercular terminal islands TuTI tuberomammillary complex TMC tuberomammillary nucleus TM ventral caudate nucleus CdV ventral claustrum VCl ventral extension of BSTC BSTCV ventral pallidum VGP ventral periventricular hypothalamic nucleus VPeH ventral putamen PuV ventral tegmental area VTA ventroanterior thalamic nucleus (ventral anterior nucleus) VA ventroanterior thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part VAMC ventrointermedius nucleus VIM ventrolateral thalamic nucleus VL ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus VMH ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part VMHDM ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part VMHVL ventroposterior thalamic nucleus VP ventroposterior thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part VPPC vertical limb of the diagonal nucleus VDB zona incerta ZI zona incerta, dorsal part ZID zona incerta, ventral part ZIV **Fibers**
alveus of the hippocampus alv
angular bundle Ab
ansa cervicalis ancer ansa lenticularis al ansa peduncularis ap anterior commissure ac anterior commissure, anterior (olfactory) limb aco anterior corona radiata acr anterior limb of the internal capsule aic anterior longitudinal ligament all anterior thalamic peduncle athp anterior thalamic radiation atr apical ligament of dens ald arcuate fasciculus arc auditory radiation aud band of Giacomini bG body of corpus callosum bcc body of fornix bfx brachium of the inferior colliculus bic brachium of the superior colliculus bsc capsule of medial geniculate nucleus cmg central tegmental tract ctg cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-thalamic tract) crt cerebral peduncle cp cingulum bundle cgb column of fornix cfx comb system comb commissure of the inferior colliculi cic commissure of the superior colliculi csx corpus callosum cc corticospinal tract cst crus of fornix crfx decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles xscp diagonal band (Bandeletta diagonalis, Broca) db dorsal hippocampal commissure dhx dorsal tegmental decussation dtx dorsal trigeminothalamic tract tth external capsule ec external medullary lamina of the thalamus eml extreme capsule ex fasciculus mammillaris princeps mpr fasciculus retroflexus (habenulo-interpeduncular tract) fr forceps major of the corpus callosum fmj forceps minor of the corpus callosum fmi fornix fx fornix longus fxl genu of fornix gfx genu of the corpus callosum gcc
genu of the internal capsule gic
habenular commissure hbx hippocampal commissure hx incomplete medullary lamina of the globus pallidus icml inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus ifo inferior longitudinal fasciculus ilf inferior thalamic peduncle ithp internal capsule ic internal medullary lamina of the thalamus iml internal sagittal stratum isst lateral lemniscus ll lateral longitudinal stria lls lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus lml lateral olfactory tract lo lenticular fasciculus h2 lenticular fasciculus lenf limiting medullary lamina of the globus pallidus liml longitudinal stria ls mammillotegmental tract mtg mammillothalamic tract mt medial forebrain bundle mfb medial lemniscus ml medial longitudinal fasciculus mlfc medial longitudinal stria mls medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus mml medial olfactory radiation molf middle cerebellar peduncle mcp middle longitudinal fasciculus mlf olfactory peduncle 1p olfactory radiation olfr olfactory tract olf optic chiasma ox optic radiation or optic tract opt orbitofrontal fibers ofr pallidohypothalamic fibers palhy pallidosubthalamic fibers psf pontine fibers pons posterior commissure pc posterior corona radiata pcr posterior limb of the internal capsule pic posterior thalamic radiation ptr precommissural fornix pcfx principal mammillary fasciculus prf pyramidal tract py radiation of corpus callosum racc rostrum of corpus callosum rcc sagittal stratum sstr spinothalamic tract spth splenium of the corpus callosum scc stria medullaris of thalamus sm stria terminalis st subcallosal fasciculus scal subcallosal stratum SCS subependymal stratum SEpS sublenticular part of the internal capsule slic sublenticular stria sls superficial medullary stratum sms superior cerebellar peduncle scp superior corona radiata scr superior fronto-occipital fasciculus sfo superior longitudinal fasciculus slf superior longitudinal fasciculus I, dorsal component slfI superior longitudinal fasciculus II, central component slfII superior longitudinal fasciculus III, ventral component slfIII superior occipitofrontal fasciculus sof superior thalamic stria str supramammillary commissure sumx supraoptic commissure sox tapetum tp thalamic fasciculus h1 thalamic radiation (corona radiata) thr
## Nerves, Ganglia
triangular area (Wernicke) TrA uncinate fasciculus unc
ventral amygdalofugal fibers (pathway) vaf ventral tegmental decussation vtx
abducens nerve or its root 6n accessory nerve 11n auriculotemporal nerve 5au buccal nerve bucn carotid plexus cpx cervical nerve cern cervical plexus cerpx chorda tympani cty facial nerve or its root 7n frontal nerve 5fr glossopharyngeal nerve 9n greater occipital nerve gocn greater petrosal nerve 7gp hypoglossal nerve or its root 12n inferior alveolar artery, vein and nerve ial inferior alveolar nerve 5ial infraorbital nerve 5ior lacrimal nerve 5lac lingual nerve 5lg mandibular nerve 5man maxillary nerve 5mx motor root of trigeminal nerve 5mo mylohyoid nerve myhy
**442**
subfornical organ SFO
nasociliary nerve 5nc occipital artery, vein and (greater occipital) nerve occ oculomotor nerve 3n oculomotor nerve (inferior branch) 3ni oculomotor root 3r ophthalmic nerve 5oph optic nerve 2n optic tract opt otic ganglion Otic palatine nerve (s) paln parotid plexus papx pharyngeal branches phar posterior superior alveolar nerve psan pterygopalatine ganglion PtgPal superior cervical ganglion SCGn superior laryngeal nerve sln supratrochlear nerve sutrn sympathetic trunk Symp trigeminal ganglion 5Gn trigeminal nerve 5n trochlear nerve or its root 4n vagus nerve 10n ventral root vr
### Arteries, Veins and Sinuses
vestibulocochlear nerve 8n
(anterior) choroidal artery cha angular artery anga angular artery and vein ang angular vein angv anterior auricular artery aaua anterior cerebral artery acer anterior inferior cerebellar artery aica ascending palatine artery apala ascending pharyngeal artery aph basilar artery bas callosal vein calv cavernous sinus cavs central artery of retina cret common carotid artery cctd confluence of sinuses cosi deep cervical artery and vein dpc deep lingual artery and vein dlg deep temporal artery dta descending palatine artery dpala diploic vein dip emissary vein emi external carotid artery ectd external jugular vein ejugv facial artery (glandular branches) fac facial vein facv greater palatine artery gpala greater palatine artery, vein and nerve gpal greater palatine vein gpalv inferior alveolar artery iala inferior alveolar artery, vein and nerve ial inferior alveolar vein ialv inferior labial artery and vein ilab inferior petrosal sinus ipets inferior sagittal sinus issi inferior temporal artery ita infraorbital artery iora internal carotid artery ictd internal cerebral vein icv internal jugular vein (sigmoid sinus/jugular bulb) ijugv internal nasal vein inav internal vertebral venous plexus ivvpx labial artery lab lacrimal artery lac lacrimal vein lacv lingual artery lga lingual vein lgv maxillary artery mxa maxillary vein mxv middle cerebral artery mcer middle meningeal artery mm middle meningeal artery, frontal branch mmf middle meningeal artery, parietal branch mmp nasopalatine artery (sphenopalatine artery) npal occipital artery occa occipital artery, vein and (greater occipital) nerve occ occipital vein occv ophthalmic artery opha ophthalmic vein ophv posterior auricular artery paua posterior auricular artery and vein pau posterior auricular vein pauv posterior cerebral artery pcer posterior communicating artery pcoma posterior inferior cerebellar artery pica posterior nasal artery pna posterior superior alveolar artery psa posterior superior alveolar nerve psan pterygoid plexus ptgpx retroarticular (venous) plexus rapx retromandibular vein rmv septal vein sv sphenopalatine artery sphpal straight sinus ss sublingual artery slga
sublingual vein slgv submental artery sma submental vein smv superficial temporal artery sta superficial temporal vein stv superior cerebellar artery sca superior ophthalmic vein sophv superior posterior alveolar artery spala superior sagittal sinus sssi superior temporal artery, frontal branch staf superior temporal artery, middle branch stam superior temporal artery, posterior branch stap superior thyroid artery sthy superior thyroid vein sthyv supraorbital artery sora supratrochlear artery sutra supratrochlear vein sutrv temporal vein(s) tv thalamostriate vein tsv transverse facial artery tfa transverse facial vein tfv transverse sinus trs vein v vertebral artery vert
### **Muscles**
anterior cervical intertransversarii muscles AceIT anterior rectus capitis muscle AReCa aryepiglotticus muscle AryE buccinator muscle BucM cervical interspinal muscle CISM ciliaris muscle CilM corrugator supercilii muscle CSCil depressor anguli oris muscle DpAO depressor labii inferioris muscle DpLb depressor supercilii muscle DpSCil digastric muscle Dig digastric muscle, tendon DigT genioglossus muscle GeGl geniohyoid muscle GeHy greater zygomaticus muscle MjZyg hyoglossus muscle HyGl iliocostalis cervicis muscle ICCe inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx ICM inferior oblique capitis muscle IObCa inferior oblique muscle (tendon) IOb inferior rectus muscle IRec interspinalis muscle ISM intertransversarii muscles InTrM lateral pterygoid muscle LPtg lateral pterygoid muscle, lateral belly LPtgL lateral pterygoid muscle, medial belly LPtgM lateral rectus capitis muscle LReCa lateral rectus muscle LRec levator anguli oris muscle LAngO levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle LLbAN levator labii superioris muscle LLb levator palpebrae superioris muscle LPal levator scapulae muscle LSc levator veli palatini muscle LeVePal longissimus capitis muscle LgsCa longissimus cervicis muscle LgsCe longissimus cervicis muscle, tendon LgsCeT longus capitis and colli muscles LgC longus capitis muscle LgCa longus colli muscle LgCo masseter muscle MasM medial pterygoid muscle MPtg medial rectus muscle MRec mentalis muscle MentM middle constrictor muscle of the pharynx MCM middle scalenus muscle MScal minor zygomaticus muscle MiZyg multifidus cervicis muscle Mul mylohyoid muscle MyHy nasalis muscle Nas occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly OcFrF occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly OcFrO omohyoid muscle OmHy orbicularis oculi muscle OO orbicularis oris muscle OOr palatoglossus muscle PalGl palatopharyngeus muscle PalPh platysma Plat posterior auricular muscle PAu rectus capitis posterior major muscle RePMj rectus capitis posterior minor muscle RePMi risorius muscle RisM salpingopharyngeus muscle SalPh scalenus muscle ScalM semispinal cervicis muscle SSpCe semispinalis capitis muscle SSpCa spinalis muscle SpM splenius capitis and cervicis muscle SplM splenius capitis muscle SplCa splenius cervicis muscle SplCe sternohyoid muscle StHy sternomastoid muscle StM sternomastoid muscle, tendon StT styloglossus muscle StyGl
stylohyoid muscle StyHy stylopharyngeus muscle StyPh superior and middle constrictor muscle S/MCM superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx SCM superior constrictor muscle, pterygopharyngeal part SCMPP superior oblique capitis muscle SObCa superior oblique muscle SOb superior rectus muscle SRec temporalis muscle TempM temporalis muscle, tendon TempT tensor tympani muscle TenT tensor veli palatini muscle TeVePal thyrohyoid muscle ThHy trapezius muscle TzM zygomatic muscle(s) ZygM
### Bones, Joints, Soft (connective) Tissue (tendons, ligaments, fascia, skin, fibrous tissues, fat, and synovial membranes)
anterior arch of atlas AAT articular disc of temporo-mandibular joint Disc articular tubercle ATub atlanto-axial membrane AtAxMe atlantooccipital joint AtOc atlantooccipital membrane AtOcMe atlas (C1 vertebra) Atlas auditory tube Aud axis (C2 vertebra) Axis body of hyoid bone BHy body of mandible BMan buccal fat pad BFat cartilage of auditory tube CAT cervical vertebra Vert common anular tendon CAnT condylar process of the mandible Cond coronoid process of the mandible Cor crista galli CGal dens axis DAx diaphragma sellae DS dura mater Dura epiglottis EGl ethmoidal cell(s) EthC external auditory meatus EAud eyeball eye falx cerebri FxC frontal bone Fro frontal bone, nasal part FroN frontal bone, orbital part FroO frontal bone, squamosal part FroSq frontal bone,crest FroC frontal sinus FrS galea aponeurotica (epicranial aponeurosis) gapo greater horn of hyoid bone GHHy greater palatine foramen GPalF hamulus of the pterygoid bone HPtg hyoid bone Hyoid hypoglossal canal 12C incisive canal IncC inferior nasal concha INaC infraorbital canal IOrC infraorbital foramen IOrF internal auditory meatus IAud jugular process JugP lacrimal gland Lac lambdoid suture lds lateral lamina of pterygoid process LLPt lens Lens lingual follicle LgFo lingual gland Lg lingual septum LgSpt lymph node Ly major alar cartilage MjAC mandible Man mandibular canal ManC mandibular fossa ManF mastoid antrum MaA mastoid cells MstC mastoid process of temporal bone Mst maxilla Mx maxillary sinus MxS medial lamina of pterygoid process MLPt middle nasal concha MNaC nasal bone Na nasal septum NSpt nasolacrimal duct nlac nasopharyngeal tonsil NPhT nuchal fascia nuf nuchal ligament nl occipital bone Occ occipital sinus occs occipito-mastoid suture ocm oral cavity Oral orbital fat body OFat palatine bone Pal palatine gland(s) PalG palatine tonsil PtT parietal bone Par parotid duct ptdd parotid gland Ptd
perpendicular plate PeP
**443**
pharyngeal opening of auditory tube oaud pharyngeal recess PhRe piriform recess PirR pituitary gland Pit posterior arch of atlas PAT prevertebral fascia pvf pterygoid canal PtgC pterygoid process Ptg pterygopalatine fossa PtPF salpingopalatinal fold SPalF salpingopharyngeal fold SPhF semicircular canals SCC semicircular ducts SCD septal nasal cartilage SeC sigmoid sinus sigs soft palate SPal sphenoid bone Sph
sphenoid sinus SphS sphenoid, greater wing SphGW sphenomandibular ligament sphml sphenoparietal sinus sphps sphenozygomatic suture sphzg spinous process of axis SpAx stylohyoid ligament shl styloid process Sty sublingual duct sld sublingual gland (and duct) SL submandibular duct smd submandibular gland SM superior horn of thyroid cartilage SHThC superior petrosal sinus spets temporal bone Temp temporal bone, petrosal part TempP temporal fascia tf
temporomandibular disc TMD tentorium cerebelli TCb thyrohyoid membrane ThHyMe thyroid cartilage ThC torus levatorius TLev torus tubarius TTub transverse ligament of atlas tla transverse process of fourth vertebra TrP4 transverse process of the atlas TrPAt tympanic cavity TyC uvula Uv vocal ligament vl vomer Vom zygomatic arch ZygA zygomatic bone Zyg
**444**
# List of Abbreviations
The abbreviations are listed in alphabetical order. Each abbreviation is followed by the structure name and the pages on which the abbreviation appears. However, for the sake of legibility we use the tilde symbol " **~** " in those cases where a structure appears in successive photographs or diagrams but not on every page.
```
*CP cuneal point 97, 354
*SP Sylvian point 96
*X cuneolingual gyrus (in depth) 97
10n vagus nerve 31, 33, 36~40, 55, 57, 76, 77
11n accessory nerve 34~39, 57, 77
12C hypoglossal canal 80, 81
12n hypoglossal nerve or its root 30~38, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 76, 77, 79-
81
17 striate area (Brodmann area 17) 17~25, 66-68, 405-407, 409-411
1p olfactory peduncle 97, 139, 143~171, 409
2n optic nerve 26, 27, 47, 49, 51, 80-83
3n oculomotor nerve 27, 51, 53, 55, 216~251, 256~264, 271
3N oculomotor nucleus 263, 265, 269, 271
3ni oculomotor nerve (inferior branch) 28, 29, 30
3V third ventricle 21-25, 54~58, 197~211, 229~241
4n trochlear nerve or its root 27, 51, 280, 282
4V fourth ventricle 26, 29, 58
5au auriculotemporal nerve 30, 31
5fr frontal nerve 26, 27, 47
5Gn trigeminal ganglion 28, 29, 53, 80, 81
5ial inferior alveolar nerve 31-33, 49, 51, 76-79
5ior infraorbital nerve 30, 31, 33, 34, 45, 47, 49, 79
5lg lingual nerve 30-36, 49, 51, 76-79
5man mandibular nerve 79
5mo motor root of trigeminal nerve 30, 31
5mx maxillary nerve 29, 51
5n trigeminal nerve 27, 55, 80
5nc nasociliary nerve 80
5oph ophthalmic nerve 28, 29
6n abducens nerve or its root 51
7gp greater petrosal nerve 29, 55
7n facial nerve or its root 28, 29, 30, 31, 33, 55, 73
8n vestibulocochlear nerve 29
9n glossopharyngeal nerve 34, 36-38, 49, 51, 53, 57, 76, 78
AAA anterior amygdaloid area 209
AAnG anterior angular gyrus 95, 96, 300~364, 402-404, 411-413
AAT anterior arch of atlas 82
aaua anterior auricular artery 55
AB accessory basal amygdaloid nucleus 193
Ac accumbens nucleus 52, 406-411
ac anterior commissure 54, 55, 79~84, 97, 184~235, 406, 409, 417,
418
acals accessory callosal sulcus 97, 136-139, 142, 144, 148, 150, 154
AcC accumbens nucleus, central part 169, 173, 175, 179~191
ACC anterior cingulate cortex (B.Vogt) 97
ACeIT anterior cervical intertransversarii muscle 55
acer anterior cerebral artery 12~26, 46~66
AcL accumbens nucleus, lateral part 155~187, 193, 406
AcM accumbens nucleus, medial part 169~193, 406
aco anterior commissure, anterior (olfactory) limb 186, 187, 190-193,
196
ACo anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus 203~214
ACoD anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal part 209, 211, 215
ACoV anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part 209, 211, 215
acr anterior corona radiata 148
acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part 97, 214-216, 286~353
acus sulcus acusticus 96, 220-222, 226
AD anterodorsal thalamic nucleus 217~227, 233~241, 417-420
ADB nucleus of the diagonal band, angular part 193, 428
ADPul anterodorsal pulvinar nucleus (lateral posterior nucleus) 257~269,
422, 423
AG ambiens gyrus 52, 53, 97, 178~234, 408
AH anterior hypothalamic area 203, 205, 209, 211
AHi amygdalohippocampal area 227, 229
AI amygdaloid island (extended amygdala) 209, 211, 221
aic anterior limb of the internal capsule 23, 150~209
aica anterior inferior cerebellar artery 26, 55, 57
AIn agranular insular cortex (claustrocortex insularis) 78-80
al ansa lenticularis 208~256, 410, 417-422
ald apical ligament of dens 82, 83
all anterior longitudinal ligament 37, 38, 83
Alv alveolar process of maxilla 45
alv alveus of the hippocampus 80, 216~247, 259, 263, 293-295, 298,
300, 304
AM anteromedial thalamic nucleus 221, 223, 227, 418, 419, 436
aMCC anterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) 97
Amg amygdala 26, 27, 54-57, 78-80, 239~251, 407, 435
AMPO anterior medial preoptic nucleus
ancer ansa cervicalis 39, 40, 55
ang angular artery and vein 30, 31
AnG angular gyrus 14-19, 63-68, 73-77
anga angular artery 29, 32, 33
angs angular sulcus 95, 96, 364-367, 370-373, 376-379, 383
angv angular vein 27-29
AO anterior olfactory nucleus (retrobulbar region) 52, 151~167
AOI area orbitoinsularis 150~160, 406~412
AOrG anterior (intermediate) orbital gyrus 95, 97, 406~412
AOrG-l anterior orbital gyrus, lateral part 97, 114~138
AOrG-m anterior orbital gyrus, medial part 97, 114~124
aos anterior occipital sulcus 96
aos-d anterior occipital sulcus, dorsal segment 366~379
aos-i anterior occipital sulcus, inferior ramus 96
aos-s anterior occipital sulcus, superior ramus 95, 96
ap ansa peduncularis 208-211, 216, 217, 417
apa anterior parietal sulcus (Vogt), (precuneal sulcus) 95-97
apala ascending palatine artery 33-38
aph ascending pharyngeal artery 36-38, 53
API area piriformis insulae 162~171, 406, 407, 411
APr anteroprincipal (anteroventral) thalamic nucleus see anteroventral
thalamic nucleus
aps anterior parolfactory sulcus 97, 162, 163
APS anterior perforated substance 25
apsi anterior parolfactory sulcus, inferior branch 166-169
apss anterior parolfactory sulcus, superior branch 166-169, 173
APul anterior (oral) pulvinar nucleus 257~271, 406, 421-424
Aq cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius) 25, 265, 269~277
ar acoustic radiation 423
arc arcuate fasciculus 118~294
Arc arcuate nucleus 209~217
AReCa anterior rectus capitis muscle 31, 33, 80
ARG gyri Andreae Retzii 289, 292, 294-296
argr arachnoid granulations 59
AryE aryepiglotticus muscle 51
ASCe anterior subcentral gyrus 96
ascs anterior subcentral sulcus 96, 174~184, 196~226
asfs accessory superior frontal sulcus 95, 96, 108~119, 139
asfs-l accessory superior frontal sulcus, lateral ramus 120~143
asfs-m accessory superior frontal sulcus, medial ramus 120~136
asos accessory supraorbital sulcus 97, 108~125
ASt amygdalostriatal transition area 211~223, 229~257
AStr striate area 322~399
AtAx atlanto-axial membrane 83
atcos anterior transverse collateral sulcus 95, 97
ATh anterior thalamic nucleus 23, 55, 56
athp anterior thalamic peduncle
Atlas atlas (C1 vertebra) 33-35, 55~59, 83, 84
AtOc atlantooccipital joint 33, 57, 81
AtOcMe atlantooccipital membrane 83
atr anterior thalamic radiation 154~214
ATub articular tubercle 75
aud auditory radiation 79
Aud auditory tube 51, 78~81
AV anteroventral (anteroprincipal) nucleus 217~245, 259, 263, 405,
406, 409, 417-420, 436
AVPe anteroventral periventricular hypothalamic nucleus 191, 193, 428
Axis axis (C2 vertebra) 37, 55~59, 82, 84
BA 1-52 Brodmann areas 1-52 101~399
bas basilar artery 26-29, 55
bc brachium conjunctivum 406, 409
BC basal nucleus, compact part 193~209, 215, 221~233, 429
bc brachium conjunctivum 409
bcc body of corpus callosum 97, 162~268
BCd body of caudate nucleus 58
BD basal nucleus, diffuse part 203, 205, 209, 211
BFat buccal fat pad 45, 49
bfx body of fornix 56-58, 223~269
bG band of Giacomini 235, 239-242, 245
BHy body of hyoid bone 40
bic brachium of the inferior colliculus 265~287, 424-426
BL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus 203~211, 217, 229, 233, 407~411,
435
BLD basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal (magnocellular) part 215,
221, 223, 227
BLI basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, intermediate part 215, 221, 223,
227
BLPL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, paralaminar part 215, 221, 223,
227
BLVL basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventrolateral part 215, 223, 227
BLVM basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventromedial part 197~223,435
BM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus 197~233, 407, 435
BMan body of mandible 47
BMCM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, centromedial part 221
BMDL basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, dorsolateral part 221
BMDM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, dorsomedial part 221, 435
BMVM basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, ventromedial part 221, 435
BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis 83, 417, 428, 429, 435
BOp basal operculum 144~160, 406~412
bsc brachium of the superior colliculus 265, 270, 271, 274-277, 280,
283, 424, 425
BSt brainstem 95,
BSTC bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, central division 185~199, 203,
205, 209, 435
BSTCV ventral extension of BSTC 209, 435
BSTL bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division 185, 191~199
BSTLJ bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, juxtacapsular
part 187, 203, 205, 209
BSTM bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division 187, 191, 193,
197, 199, 435
BSTP bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, posterior division 203, 205, 209
BSTV bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, ventral division 197, 199, 203,
205, 435
BucM buccinator muscle 34-40, 45, 47, 76-79
bucn buccal nerve 30~38
CA1 CA1 field of hippocampus 223~308
CA1-3 fields of hippocampus
CA2 CA2 field of hippocampus 241~299
CA3 CA3 field of hippocampus 229~302
cal calcar avis 313
cals callosal sulcus 97, 144~317
calv callosal vein 149, 151, 155, 157, 161
CAnT common anular tendon 29
CAT cartilage of auditory tube 33
cavs cavernous sinus 27, 28, 51, 53
Cb cerebellum 78-80
cc corpus callosum 54~58, 82, 167~193, 229, 235, 239~271
ccs calcarine sulcus, central part 95, 97, 405, 406
cctd common carotid artery 39, 40, 53, 55
Cd caudate nucleus 80, 81, 149, 221~283, 404-406, 409, 410, 436
CdL lateral caudate nucleus 151~215
CdM medial caudate nucleus 151~217
CdV ventral caudate nucleus 185~209
Ce central amygdaloid nucleus 211, 215, 217, 235
ce central sulcus 55, 95-97, 214~299
ceis central insular sulcus 178~232
CeL central amygdaloid nucleus, lateral part 221, 223, 227, 229, 233,
420-422
CeM central amygdaloid nucleus, medial part 221, 223, 227, 229, 233
CeMe central medial thalamic nucleus 223, 229, 233, 235, 239, 418-420
cern cervical nerve 39, 40
cern1 cervical nerve1 80, 81
cern2 cervical nerve2 35, 55, 57, 80, 81
cern3 cervical nerve3 55, 80, 81
cerpx cervical plexus 55
cfx column of fornix 196, 198, 202, 204
CG cingulate gyrus 16-25, 49-63, 80-84, 97, 118~322, 403-410
CGal crista galli 27, 45, 47
cgb cingulum bundle 124~322
cgh cingulum (hippocampal part) 222~312
cgs cingulate sulcus 157, 232, 234, 235, 238-241, 244-247, 256~277
cgs-a cingulate sulcus, anterior part 97, 120~205
cgs-i inferior cingulate sulcus 97, 124~161, ~
cgs-mg marginal segment of cingulate sulcus 96, 97, 286~325
cgs-p cingulate sulcus, posterior part 97, 208~283
CH cerebellar hemisphere 57-60
cha (anterior) choroidal artery 22, 26, 52~58
chf choroidal fissure 234~268, 282
chpx choroid plexus 21~25, 57, 60
Ci cistern
cic commissure of the inferior colliculi 280, 282, 286, 287
CilM ciliaris muscle 29
cis circular insular sulcus 150~287
CISM cervical interspinal muscle 61
Cl claustrum 23, 25, 52-54, 55-57, 78, 79, 151~163, 247~257, 407,
408, 434
CLi caudal linear nucleus 263, 265, 269, 271
CLV central part of lateral ventricle 54, 56, 57
CM centromedian thalamic nucleus 56, 57, 82, 245~265, 406, 409,
410, 420~423
cmg capsule of medial geniculate nucleus 274, 275
CM-PF centromedian-parafascicular thalamic complex 406, 409
CnF cuneiform nucleus 277
Co commissural nucleus 229, 233, 241
CoCl compact insular claustrum 167~241
comb comb system 222~246
Cond condylar process of the mandible 30, 31, 53
COp central operculum (Rolandi) 96, 412, 413
COp-a anterior central operculum 214, 216~244, 405, 406, 413
COp-p posterior central operculum 228~255, 404, 405, 413, 414
Cor coronoid process of the mandible 31
cos collateral sulcus (medial occipitotemporal sulcus) 97, 268~385
cosi confluence of sinuses 25, 65
cos-o collateral sulcus, occipital ramus 97
cos-ph collateral sulcus, parahippocampal ramus 95, 97, 220~265
cos-t collateral sulcus, temporal ramus 95, 97, 210, 214, 216, 217
cp cerebral peduncle 25, 55-57, 80, 81, 226~268
cpx carotid plexus 39
cr capsule of red nucleus 239, 241, 245, 247, 251, 420
cret central artery of retina 47
crfx crus of fornix 270, 271~300
crt cerebello-rubro thalamic fibers (dentato-thalamic tract) 238~262,
409, 420-423
cs calcarine sulcus
cs-c calcarine sulcus, central part 354~383
csc commissure of the superior colliculi 271~277, 424, 425
CSCil corrugator supercilii muscle 26, 27
CSP cavity of septum pellucidum 163, 167, 169, 203, 209
ctg central tegmental tract 264, ~271, 424, 425
cty chorda tympani 31, 32
CuA cuneiform area 275
Cuc cucullaris nucleus 229~239, 419, 420
CuF cuneiform nucleus 281, 283
culs cuneal limiting sulcus 97, 376, 378, 382-385, 388, 389
Cun cuneus 20, 63-68, 80, 81, 82, 84, 97
CxA cortico-amygdaloid transition area 203, 205
DAx dens axis 33, 82, 84
dB diagonal band (Bandeletta diagonalis, Broca) 156~184, 197, 199
DB nucleus of the diagonal band 53, 435
DCl dorsal claustrum 203~223, 229, 233, 245
DG dentate gyrus 25, 78, 79, 81, 229~299
dgs diagonal sulcus 96, 154, 156
DH dorsal hypothalamic area 209, 215
dhx dorsal hippocampal commissure 268~289
DiCl diffuse insular claustrum 179~233
Dig digastric muscle 30-40, 45, 47, 51, 53, 55, 57, 74-82
DigT digastric muscle, tendon 38, 39, 49, 78, 79
dip diploic vein 57
DiPul diffuse pulvinar nucleus 424, 425, 426
Disc articular disc of temporo-mandibular joint 30, 31, 75
Dk nucleus Darkschewitsch 251
dlg deep lingual artery and vein 45
DMH dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus 211, 215, 217, 221, 409, 429,
430
DMHC dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, compact part 217, 429, 430
DMHD dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, diffuse part 427, 430
DoH dorsal hypothalamic nucleus 203, 205
dpala descending palatine artery 32, 33, 47, 49, 80, 81
DpAO depressor anguli oris muscle 38, 39, 40, 78
DPe dorsomedial periventricular hypothalamic nucleus 428
dpc deep cervical artery and vein 32-40
DPeH dorsal periventricular hypothalamic nucleus 191, 193, 197, 199
DpLb depressor labii inferioris muscle 40, 78
dPrS dorsal presubiculum 227
DpSCil depressor supercilii muscle 28, 29, 30, 31
```
**445**
| DR | dorsal raphe nucleus 275, 277 | HDB | horizontal limb of the diagonal band 191, 193, 428, 429 | JugP | jugular process 78, 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|-------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-------|-----|------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|--------------------------------|--|----|--|-------------------------------------------------------|--|
| DS | diaphragma sellae 53 | hf | hippocampal fissure 228~269, 268, 75~288, 292, 293 | La | lateral amygdaloid nucleus 193~227, 407, 408, 411 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DSf | dorsal superficial nucleus see DSF | Hi | hippocampus 22-27, 54-59, 79, 80, 195, 201, 207, 213, 219, 225, 231, 237, 243, 249, 255, 261, 267, 273, 279, 285, 291, 297~306, 406~412, 434 | lab | labial artery 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DSF | dorsal superficial nucleus 82, 241, 245, 247, 251~265, 405, 409, 410, 420~424, 436 | HiH | hippocampal head 216, 217, 220, 222, 226, 228, 232 | lac | lacrimal artery 47 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dt | dentate nucleus 60 | HPtg | hamulus of the pterygoid bone 35, 49 | Lac | lacrimal gland 26, 27, 45 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| dta | deep temporal artery 30, 31, 47, 49 | Hy | hypothalamus 24, 25, 54, 436 | lacv | lacrimal vein 29 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DTg | dorsal tegmental nucleus 281, 283 | HyGl | hyoglossus muscle 37-40, 45, 47, 49, 80 | LaDA | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal anterior part 215, 217, 221 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DTP | dorsal temporopolar region | Hyoid | hyoid bone 49, 51, 53, 79-81 | LaDL | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal lateral part 211, 215, 217 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| dtx | dorsal tegmental decussation 262 | I | isthmus 97, 406 | LaDM | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsomedial part 215 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| du | diverticulum unci 220, 221 | ial | inferior alveolar artery, vein and nerve 35-38, 47 | LaI | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, intermediate part 215, 221 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dura | dura mater 81 | iala | inferior alveolar artery 34, 49, 51, 76 | LAngO | levator anguli oris muscle 33-37, 78, 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EA | extended amygdala 203, 205 | ialv | inferior alveolar vein 34 | LaV | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part 221 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EAud | external auditory meatus 73, 75 | IAud | internal auditory meatus 78, 79 | LC | locus coeruleus 83 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ec | entorhinal cortex, caudal subfield 235, 236, 239 | IC | inferior colliculus 275, 280, 281, 283, 287, 426 | LD | lateral dorsal thalamic nucleus 57, 82 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EC | entorhinal cortex 179, 181-183 | ic | internal capsule 52, 54-57, 80-82, 192, 197~222, 410 | lds | lambdoid suture 25, 26, 27 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ec | external capsule 23, 148~257 | ICCe | iliocostalis cervicis muscle 40 | LDTg | laterodorsal tegmental nucleus 281, 283 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ECL | entorhinal cortex, caudal limiting subfield 241, 242, 245, 247, 248, 251, 253, 254 | ICG | isthmus of cingulate gyrus 298~333 | lenf | lenticular fasciculus 220~240, 419, 420 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ectd | external carotid artery 34-39, 53, 74-77 | ICM | inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx 39, 40, 53, 80 | Lens | lens 78, 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EGl | epiglottis 51, 81, 82, 84 | icml | incomplete medullary lamina of the globus pallidus 214-217, 220-223 | LeVePal | levator veli palatini muscle 32, 33, 51, 53, 80, 81 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EGP | external globus pallidus 54, 55, 179~251, 406, 410, 411 | ictd | internal carotid artery 26-39, 51, 53, 55, 76-82 | lf | lateral (Sylvian) fissure 95, 96, 144~289 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EI | entorhinal cortex, intermediate subfield 215~233 | icv | internal cerebral vein 59 | lf-a | lateral fissure, anterior segment 96 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ejugv | external jugular vein 55, 73 | IDPul | inferior pulvinar nucleus, dorsal part 275, 277, 281, 283, 425, 426 | lf-h | lateral fissure, horizontal segment 95, 96, 97, 127~151 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ELC | entorhinal cortex, lateral caudal subfield 217~233 | IF | interfascicular nucleus 253, 257, 259 | lf-m | lateral fissure, middle segment 96 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ELR | entorhinal cortex, lateral rostral subfield 185~215 | IFG | inferior frontal gyrus 17, 24, 25, 45-57, 73-79 | lfms | lateral frontomarginal sulcus 95, 106-109, 112-114, 118, 120 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| emi | emissary vein 29, 59, 61 | IFG-asc | inferior frontal gyrus, ascending part 96 | lf-p | lateral fissure, posterior segment 96 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EMI | entorhinal cortex, medial intermediate subfield 209~224 | IFG-ba | inferior frontal gyrus, basilar part 96 | LFuG | lateral fusiform gyrus 97 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| eml | external medullary lamina of the thalamus 204, 208, 216~287, 417-426 | IFGOp | inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part 18-25, 49-59, 95, 96, 142~208, 404~414 | lf-v | lateral fissure, vertical segment 96, 142~160 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ent | entorhinal cortex 24-27, 51-59, 95, 97, 166~261, 406-408, 410, 411 | IFGOr | inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part 20-23, 95-97, 112~160, 406~413 | LG | lateral geniculate nucleus 79, 253~271, 406, 410, 411, 422-424, 436 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Eo | entorhinal cortex, olfactory subfield 193, 194, 197, 199, 200, 203, 205, 206 | IFGTr | inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part 18-23, 95-97, 126~160, 405~413 | Lg | lingual gland 39, 49 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EP | entopeduncular nucleus 223, 227 | ifo | inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus 166~204 | lga | lingual artery 38-40, 47, 49, 51, 78-81 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ER | entorhinal cortex, rostral subfield 193~212 | IFPG | inferior frontopolar gyrus 95, 97, 102~118, 406~411 | LgC | longus capitis and colli muscles 78-81 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EthC | ethmoidal cell(s) 28, 29, 45, 47, 49 | ifps | inferior frontopolar sulcus 95, 97, 102~113 | LgCa | longus capitis muscle 30-40, 53, 55 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EW | Edinger-Westphal nucleus 257, 259, 263, 265 | ifs | inferior frontal sulcus 95, 96, 112~167 | LgCo | longus colli muscle 30, 35-40 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ex | extreme capsule 23, 148~226, 234~257 | IG | insular gyrus 148~172 | LgFo | lingual follicle 81 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| eye | eyeball 27, 29, 45 | IGP | internal globus pallidus 54, 55, 209~241, 406~411 | LgG | lingual gyrus (O5) 80, 95, 97, 288~327, 407 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fa | fasciculosus nucleus 215, 217, 221, 223, 227, 417-419 | IGPul | intergeniculate pulvinar nucleus 271, 424 | lg-p | lingual sulcus, posterior ramus 372, 373, 376-379 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fac | facial artery (glandular branches) 34-40, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 75-77, 79 | IGr | indusium griseum 149~247, 257, 277, 289, 293~301 | lgs | lingual sulcus 97, 406 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| facv | facial vein 33-37, 40, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 75, 76, 79 | ijugv | internal jugular vein (sigmoid sinus/jugular bulb) 31, 33-40, 55, 57, 76-79 | LgsCa | longissimus capitis muscle 32-40, 57, 59, 61, 74-77 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FCd | fundus region of caudate nucleus 155~169, 173~185, 406, 409, 410 | IL | intralaminar thalamic nuclei and lamina 406, 409 | LgsCe | longissimus cervicis muscle 36-40 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fcl | fasciculus circumligatus 244, 246, 250, 252 | ilab | inferior labial artery and vein 39, 40 | LgsCeT | longissimus cervicis muscle, tendon 37, 38 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FD | fascia dentata 240~252 | ilf | inferior longitudinal fasciculus 178~378 | LgSpt | lingual septum 45 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fd | frontal dimple 95, 102, 103, 106 | ILG | inferior lingual gyrus 328~340 | lgv | lingual vein 47, 49, 51 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fds | fimbriodentate gyrus 250, 252, 268, 288 | ILgG | inferior lingual gyrus 97, 406~411 | LH | lateral hypothalamic area 197~233, 407, 409, 428-431 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FF | Field of Forel 416, 419, 420 | ILG-l | inferior lingual gyrus, lateral part 342~387 | LHb | lateral habenular nucleus 265, 269, 271 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FG | fasciolar gyrus 60, 81, 292 | ILG-m | inferior lingual gyrus, medial part 342~382 | Li | limen insulae 80, 82, 83, 178-181, 184-187, 191 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fi | fimbria of the hippocampus 23, 25, 78, 241~292 | ilgs | intralingual sulcus 95 | LiCl | limitans claustrum 197, 203~233 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FL | frontal lobe 47 | ILPul | inferior pulvinar nucleus, intermediate part 275, 277, 283, 287 | LIGI | long insular gyrus I 405, 406 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FLA | frontal limbic area 48-56 | ils | intralingual sulcus 328~365 | Lim | limitans nucleus 265, 269, 271, 275, 406, 423-425 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FLV | frontal horn of lateral ventricle 21, 23, 51, 149, 155~169, 175, 187~199 | imfs | intermediate frontal sulcus 136~149 | liml | limiting medullary lamina of the globus pallidus 216, 217, 220-222, 226, 227 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FMG | frontomarginal gyrus 95-97, 102~118, 406~411 | iml | internal medullary lamina of the thalamus 220~271, 418-424 | ll | lateral lemniscus 270, 274, 275, 276, 280, 282, 286, 426 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fmi | forceps minor of the corpus callosum 21, 143~169 | impI | anterior intermediate parietal sulcus of Jensen 96, 301~335 | LLb | levator labii superioris muscle 32, 33, 35, 78, 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fmj | forceps major of the corpus callosum 21, 286~318 | impII | second intermediate parietal sulcus 96, 322~341 | LLbAN | levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle 33 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fmps | frontal paramidline sulcus 96 | impIII | third intermediate parietal sulcus 96, 342, 346, 348, 352, 354 | LLPt | lateral lamina of pterygoid process 49 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fms | frontomarginal sulcus 96, 97 | INaC | inferior nasal concha 33, 45 | lls | lateral longitudinal stria 144~228, 234, 235, 240, 250, 262, 292-295, 298-300 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FOp | frontal operculum 20, 21, 76-79, 96, 148~225, 405, 406, 411-413 | inav | internal nasal vein 51 | LM | lateral mammillary nucleus 221, 223, 227, 430, 431 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fors | fronto-orbital sulcus 96 | IncC | incisive canal 37 | lml | lateral medullary lamina of the globus pallidus 178~253 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FP | frontal pole 96 | Inf | infundibular nucleus 407, 409, 429, 430 | lo | lateral olfactory tract 178, 180, 184-187, 190-193, 196, 197, 199 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fp | frontopolar fibers 108, 112 | InfS | infundibular stalk 53, 197, 199, 203, 205 | lObCa | inferior oblique capitis muscle 35 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fpms | frontal paramidline sulcus 95, 150~210 | InM | intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (sexual dimorphic nucleus) 427, 429 | LOrG | lateral orbital gyrus 97, 118~142, 406, 407, 411, 412 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fps | frontopolar sulcus 103 | Ins | insula 20-25, 50-60, 76, 77, 153, 159, 165, 171~186, 192, 196~228, 231~292, 404~413 | lors | lateral orbital sulcus 96, 97, 108~143 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fpt | frontopontine tract 240, 244, 246, 250 | InTrM | intertransversarii muscles 36, 37, 38 | los | lateral occipital sulcus 96, 372~397 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FPu | fundus region of putamen 155~209, 406, 407 | IO | inferior olive 57, 82 | LOTG | lateral occipitotemporal gyrus 26, 27 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fr | fasciculus retroflexus (habenulo-interpeduncular tract) 238~269, 421-424 | IOb | inferior oblique muscle (tendon) 30, 31, 45, 78, 81 | lots | lateral occipitotemporal sulcus 95, 97, 156~226, 244~359 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fro | frontal bone 25 | IObCa | inferior oblique capitis muscle 34, 57, 59, 61, 76-84 | LPal | levator palpebrae superioris muscle 26, 27, 45, 47, 49, 80 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FroC | frontal bone, crest 45, 75 | IOG | inferior occipital gyrus 95-97, 342~399, 405-407, 410-413 | LPHT | lingual-parahippocampal transition area 97 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FroN | frontal bone, nasal part 26, 27 | iora | infraorbital artery 31-33, 45, 47, 49, 79 | LPtg | lateral pterygoid muscle 32, 33, 49, 51, 53, 76, 77, 79 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FroO | frontal bone, orbital part 26, 27, 45 | IOrC | infraorbital canal 45, 47 | LPtgL | lateral pterygoid muscle, lateral belly 30, 31 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FroSq | frontal bone, squamosal part 47 | IOrF | infraorbital foramen 79 | LPtgM | lateral pterygoid muscle, medial belly 30, 31 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FrP | frontopolar cortex (or gyrus) 45, 46, 47, 96 | IOrG | intermediate orbital gyrus | LPul | lateral pulvinar nucleus 259~287, 406, 422-426 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| frs | fragmentosus sulcus 97, 124, 125-127, 130-133, 136 | iors | intermediate orbital sulcus 97 | LRec | lateral rectus muscle 28, 29, 45, 47, 49, 78 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FrS | frontal sinus 25, 28, 45, 47 | ios | inferior occipital sulcus 95-97, 354~385 | LReCa | lateral rectus capitis muscle 32, 33, 55, 74 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FStr | fundus striati 25, 82, 83 | IP | interpeduncular nucleus 154, 156, 160, 251~265 | ls | longitudinal stria 301 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FuG | fusiform gyrus 23, 49-64, 75-80, 95-97, 166~375, 406-408, 410-412 | IPAC | interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure 215 | LSc | levator scapulae muscle 36-40, 57, 59, 74, 75 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FuG-p | fusiform gyrus, posterior part 352~393 | ipcs | inferior postcentral sulcus 96 | LSD | lateral septal nucleus, dorsal part 187~221 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fus | midfusiform sulcus 300~304, 318~329 | ipets | inferior petrosal sinus 29, 55, 77, 81 | LSI | lateral septal nucleus, intermediate part 187~221 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fx | fornix 21, 23, 54, 55, 59, 84, 193~223, 406, 407, 409, 417~431 | IPF | interpeduncular fossa 24, 25, 55, 82, 241, 253 | LSV | lateral septal nucleus, ventral part 175, 185, 187, 191, 193, 197, 199, 203 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| FxC | falx cerebri 45, 49 | IPHT | isthmo-parahippocampal transition area 405, 406, 410 | LT | lamina terminalis 25, 84, 179, 181, 185, 187 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| fxl | falx cerebri 45, 49 | IPL | inferior parietal lobule 16~20 | LTh | lateral thalamic nuclear region 80, 82 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | IPs | insular pole 407, 412 | LTN | lateral terminal nucleus of the accessory optic system 269, 423 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | IPul | interpeduncular nucleus 251~265 | LTu | lateral tuberal nucleus 217, 221, 430 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Ips | insular pole 407, 412 | LuG | lunate gyrus 96 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Ips | insular pole 407, 412 | lus | lunate sulcus 95, 96, 405, 406 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Ips | insular pole 407, 412 | LV | lateral ventricle 18~26, 53, 58, 59, 203~211, 229~287 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | FxC | | | Ips | falx cerebri 45, 49 | | insular pole 407, 412 | lv | IPL | | lymph node 27, 40, 47, 55, 74, 76 | inferior parietal lobule 16-20 | | LV | | lateral ventricle 18~26, 53, 58, 59, 203~211, 229~287 | |
| fxl | | fornix longus 156~174, 186, 196, 198~216 | | IPo | | insular pole 407, 412 | | Ly | | lymph node 37-40, 47, 55, 74-76 | | | | | | | |
| GA | | gyrus ambiens see AG | | ipocs | | inferior postcentral sulcus 232~239, 264~287 | | MaA | | mastoid antrum 57 | | | | | | | |
| gapo | | galea aponeurotica (epicranial aponeurosis) 25 | | iprs | | inferior precentral sulcus 95, 96, 168~209 | | Man | | mandible 32, 33, 35, 36, 37, 39, 49, 75-83 | | | | | | | |
| gcc | | genu of the corpus callosum 21, 23, 97, 144~163 | | ips | | intraparietal sulcus 95, 96, 298~341 | | ManC | | mandibular canal 40, 45, 47, 49 | | | | | | | |
| GDe | | gyrus descendens 95, 97, 382~399, 405~410 | | ips-a | | intraparietal sulcus, ascending segment 96 | | ManF | | mandibular fossa 75 | | | | | | | |
| GeGl | | genioglossus muscle 38-40, 45, 47, 82-84 | | ips-d | | intraparietal sulcus, descending segment 96 | | maprs | | marginal precentral sulcus 222, 226-229, 232-235, 238-240, 244 | | | | | | | |
| GeHy | | geniohyoid muscle 40, 45, 47, 83, 84 | | ips-h | | intraparietal sulcus, horizontal segment 96, 300~313, 342~379 | | MasM | | masseter muscle 31-38, 45, 47, 49, 51, 73-75 | | | | | | | |
| GHHy | | greater horn of hyoid bone 38, 39, 40 | | IPul | | inferior pulvinar nucleus 277, 283, 287, 406, 424, 425 | | MB | | mammillary body 25, 55 | | | | | | | |
| gic | | genu of the internal capsule 23, 222, 226, 229 | | IRec | | inferior rectus muscle 28-31, 45, 47, 49 | | mcer | | middle cerebral artery 16~26, 46, 48, 52-58, 60, 62, 64, 77 | | | | | | | |
| gocn | | greater occipital nerve 25, 29-36, 78-81 | | irhs | | intrarhinal sulcus 168~199 | | MCM | | middle constrictor muscle of the pharynx 39, 40, 51, 53 | | | | | | | |
| GP | | globus pallidus 23, 56, 57, 79-81, 436 | | IRoG | | inferior rostral gyrus 46-50 | | mcp | | middle cerebellar peduncle 56, 57, 80 | | | | | | | |
| gpal | | greater palatine artery, vein and nerve 45 | | irs | | intrarhinal sulcus 217, 233 | | MD | | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus 56, 57, 82, 229~275, 405, 406, 409, | | | | | | | |
| gpala | | greater palatine artery 34-37 | | ISG | | inferior sagittal gyrus 97, 405, 406, 409, 410 | | | | 419-425 | | | | | | | |
| GPalF | | greater palatine foramen 47 | | isgs | | inferior sagittal sinus 55, 57, 97 | | Md | | medulla oblongata 31 | | | | | | | |
| GrCi | | great (cerebellomedullary) cistern 59 | | ISM | | interspinalis muscle 36-40 | | MDMC | | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part 235~263, 418- | | | | | | | |
| GSL | | gyrus semilunaris 203, 205, 209, 211, 215, 221 | | iss | | inferior sagittal sulcus (S. limitans superior) 55, 57, 378~389 | | | | 423 | | | | | | | |
| GTI | | great terminal island 179~199 | | isst | | internal sagittal stratum 301, 305, 307 | | MDPC | | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part 239~257, 265 | | | | | | | |
| GU | | gyrus uncinate 229, 230 | | ita | | inferior temporal artery 24 | | MDPL | | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, paralamellar part 251~265, 422- | | | | | | | |
| H | | H-field of Forel 233 | | ITG | | inferior temporal gyrus 22-27, 49-64, 73-79, 95-97, 156~375, | | | | 425 | | | | | | | |
| h1 | | thalamic fasciculus 232~252, 418~422 | | | | 406~414 | | Me | | medial amygdaloid nucleus 227, 229, 233, 235 | | | | | | | |
| h1-h2 | | h1 and h2 fasciculi 406 | | IThA | | interthalamic adhesion 223, 227 | | ME | | median eminence 217 | | | | | | | |
| h2 | | lenticular fasciculus 220, 221-223, 226-229, 232-235, 238, 239, | | ithp | | inferior thalamic peduncle 211~239, 417-420 | | Me5 | | mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus 281, 283 | | | | | | | |
| | | 240, 409, 419-422 | | ITP | | inferior temporopolar region 147~177, 411 | | MeA | | medial amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part 211, 215, 217 | | | | | | | |
| HATA | | hippocampo amygdaloid transitional area 227, 229, 230, 233 | | its | | inferior temporal sulcus 96, 97, 156~371 | | MentM | | mentalis muscle 40 | | | | | | | |
| Hb | | habenula 23 | | its-a | | inferior temporal sulcus, anterior segment 96 | | mfb | | medial forebrain bundle 180~234, 417-422 | | | | | | | |
| HBL | | lateral habenular nucleus 423, 424 | | its-p | | inferior temporal sulcus, posterior ramus 96 | | MFG | | middle frontal gyrus 11-23, 45-60, 76-81, 95, 96, 106~225, 402- | | | | | | | |
| HBM | | medial habenular nucleus 423, 424 | | IVF | | interventricular foramen 209, 211 | | | | 406, 411-413 | | | | | | | |
| hbx | | habenular commissure 424 | | IVPul | | inferior pulvinar nucleus, ventral part 275, 425 | | mfms | | medial frontomarginal sulcus 95, 97, 102~118 | | | | | | | |
| HCd | | head of caudate nucleus 21, 23, 54, 55, 82, 83 | | ivvpx | | internal vertebral venous plexus 35, 38, 57, 59, 79 | | MFPG | | middle frontopolar gyrus 95-97, 102~129, 405, 406, 409-411 | | | | | | | |
| 446 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
**446**
| mfps
mfs | middle frontopolar sulcus 102, 103, 106-109, 112, 114
midfusiform sulcus 97, 305 | Pal
PalG | palatine bone
palatine gland(s) 35, 36, 45, 47 | prs
PrS | precentral sulcus 95, 96
presubiculum 224~293 | | | | | | |
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--|---------------------------------|--|------------------|-----------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------|
| MFuG | medial fusiform gyrus 97 | PalGl | palatoglossus muscle 37 | PRt | prereticular zone 191~221, 417, 418 | | | | | | |
| MG | medial geniculate nucleus 80, 263, 406, 410, 423, 424, 425 | palhy | pallidohypothalamic fibers 220, 221, 417, 418 | prts | pretriangular sulcus 95, 96, 112-115, 118, 119 | | | | | | |
| MGDP
MGFi | medial geniculate nucleus, dorsal posterior part 271
medial geniculate nucleus, fibrosus part 265, 269, 271 | PalHy
paln | pallidohypothalamic nucleus 221, 223, 227
palatine nerve (s) 47 | ps
psa | polar sulcus 150~175
posterior superior alveolar artery 32, 33, 45, 47, 79 | | | | | | |
| MGLi | medial geniculate nucleus, limitans part 265, 269, 271 | PalPh | palatopharyngeus muscle 38, 51, 80 | psan | posterior superior alveolar nerve 33 | | | | | | |
| MGMC
MGPC | medial geniculate nucleus, magnocellular part 265, 269
medial geniculate nucleus, parvocellular part 265 | PalT
PAM | palatine tonsil 51, 80
periamygdaloid cortex 27, 80, 191-194, 196, 198, 202, 203, 205,
407 | PSCe
pscs
PSR | posterior subcentral gyrus 96
posterior subcentral sulcus 228, 232, 234
perisplenial region(B.Vogt) 97 | | | | | | |
| MHb | medial habenular nucleus 265, 269 | PaMC | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, magnocellular part 197,
199, 203, 205, 209, 211, 429 | PSt
PStr | parastriate area 95, 406, 410
parastriate area 318, 321, 322, 324, 327, 328, 330, 333 | | | | | | |
| MiTg | microcellular tegmental nucleus 277 | PAnG | posterior angular gyrus 95, 96, 330~382, 402-405, 411-413 | PT | paratenial thalamic nucleus 215~251, 257, 417-423 | | | | | | |
| MiZyg | minor zygomaticus muscle 32, 33, 34, 35 | PaO
pap | paraoptic nucleus 215
optic papilla 45 | PTc
ptcos | pretectal area 265, 269, 271, 275, 424, 425
posterior transverse collateral sulcus 95, 97 | | | | | | |
| MjAC | major alar cartilage 33, 34 | PaPC | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, parvocellular part 203,
205, 209, 211, 428-430 | ptcs | posterior transverse collateral sulcus 342~367 | | | | | | |
| MjZyg
ml | greater zygomaticus muscle 32-38, 45, 73-75
medial lemniscus 246~277, 423-425 | PaPo | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, posterior part 211, 215,
217, 221, 417, 430 | Ptd
ptdd
PTe | parotid gland 31-33, 35-38, 53, 55, 73-77
parotid duct 35, 36, 47, 49, 51, 73, 75, 76
planum temporale 20-25, 50-61, 73-77, 228~298, 405, 411, 413, 414 | | | | | | |
| ML | medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part 223, 227, 430, 431 | papx | parotid plexus 31 | PTG | paraterminal gyrus 52, 53, 97, 168, 171~180, 407 | | | | | | |
| mlf | middle longitudinal fasciculus 178~294, 424, 425 | Par
PaS | parietal bone 25, 26
parasubiculum 234~278 | PTg | pedunculopontine nucleus 269, 271, 277 | | | | | | |
| mlfc
MLPt | medial longitudinal fasciculus 264, 268, 270, 271, 274-277
medial lamina of pterygoid process 49 | PAT
pau | posterior arch of atlas 82
posterior auricular artery and vein 34, 35 | Ptg
PtgC | pterygoid process 32, 33
pterygoid canal 51 | | | | | | |
| MLPul | mediolateral pulvinar nucleus 275, 277, 281, 283, 287, 425, 426 | PAu | posterior auricular muscle 28 | PtgPal
ptgpx
PtPF | pterygopalatine ganglion 30, 31, 49
pterygoid plexus 31, 51, 75, 76, 78, 79
pterygopalatine fossa 49, 80, 81 | | | | | | |
| mls | medial longitudinal stria 144~241, 250, 262, 294, 298, 300, 304 | paua
pauv | posterior auricular artery 53, 55, 57
posterior auricular vein 26-29, 57, 59 | ptpt
ptr | parieto-temporopontine tract 240, 244, 246, 250
posterior thalamic radiation 298, 300, 304 | | | | | | |
| MM | medial mammillary nucleus, medial part 221~233, 407, 409, 430, 431 | PBG
PBP | parabigeminal nucleus 287
parabrachial pigmented nucleus 247~259, 265 | pts
Pu | paraterminal sulcus 97
putamen 23, 52-57, 78-80, 151~277, 405-407, 411, 436 | | | | | | |
| mm | middle meningeal artery 28, 29, 53, 55 | pc
PCA
PCC | posterior commissure 97, 264~271, 406, 409, 424-426
precommissural archicortex 97, 172~181, 407, 409
posterior cingulate cortex (B.Vogt) 97 | Pul
PuLi
PuV | pulvinar thalami 23, 58, 59, 79, 80, 82, 405, 409-411
limitans putamen 235
ventral putamen 217~251 | | | | | | |
| mmf | middle meningeal artery, frontal branch 27, 51 | PCe
pcer | paracentral thalamic nucleus 421, 422
posterior cerebral artery 18~26, 54-60, 62, 64, 66 | PV
pvf | paraventricular thalamic nucleus 215~259, 418-423
prevertebral fascia 33 | | | | | | |
| mml | medial medullary lamina of the globus pallidus 196~239, 241 | pcf
pcfx | paracentral fossa 97, 250~281
precommissural fornix 178-181, 184, 185, 187, 190-192 | py
QP | pyramidal tract 57, 84, 240, 244, 246, 250
quadrigeminal plate 59 | | | | | | |
| mmp
MNaC | middle meningeal artery, parietal branch 55, 59
middle nasal concha 45 | PCG
pcgs | precallosal gyrus 97, 142~159
paracingulate sulcus 97, 142 | R
racc | red nucleus 24, 56, 57, 82-84, 245, 406, 407, 409, 438
radiation of corpus callosum 138~240, 301, 305, 307 | | | | | | |
| MnPO | median preoptic nucleus 193 | PCI
pcis | postcentral insular cortex 222~244
posterior central insular sulcus 190~246 | rapx
ras | retroarticular (venous) plexus 30, 31
radiate sulcus (Eberstaller) 95, 96, 120~132 | | | | | | |
| MnR | median raphe nucleus 269, 271, 275 | PCL
PCo | paracentral lobule 14, 16, 17, 59-65, 97, 208~310, 402-404, 409, 410
posterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus 217, 221, 223, 227, 229, 230, 407, 435 | rcc
rcs-i | rostrum of corpus callosum 51, 97, 154, 156, 160, 162, 166
retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior (lower) branch 95, 97, 372~383, 409 | | | | | | |
| MOG | middle occipital gyrus 95, 96, 370~388, 404-406, 411-413 | pcoma
pcr | posterior communicating artery 26
posterior corona radiata 244~282 | rcs-s | retrocalcarine sulcus, superior (upper) branch 95, 97, 384~395, 406, 409 | | | | | | |
| molf
MOrG | medial olfactory radiation 173, 175
medial orbital gyrus 97, 108~159, 407-411 | pcs
PCun | postcentral sulcus 95-97, 240~263, 286
precuneus 16, 20-23, 62-68, 80-84, 97, 286~370, 402-405, 409-411 | Re
RePMi
RePMj | reuniens thalamic nucleus 223~257, 418-422
rectus capitis posterior minor muscle 30-33, 61, 63, 80, 81
rectus capitis posterior major muscle 32-35, 61, 63, 76-81 | | | | | | |
| mors | middle orbital sulcus 97, 112-115, 118-121, 124, 125 | Pe
PedL | periventricular nucleus 209, 211, 215, 217, 409
peduncle of lentiform nucleus 223, 227, 229, 233, 411 | rhs
RisM | rhinal sulcus 97, 166~253
risorius muscle 38, 39 | | | | | | |
| MOTG | medial occipitotemporal gyrus 26, 27 | PeF
PeP | perifornical nucleus 211, 215, 217, 429, 430
perpendicular plate 45 | RLi | rostral linear nucleus 245, 253, 257, 259 | | | | | | |
| mp | mammillary peduncle 222, 226, 228, 419, 420 | PeV | periventricular nucleus 421, 422, 423 | rmv | retromandibular vein 34-36, 38, 51, 53, 73-77 | | | | | | |
| MPO
MPOL | medial preoptic nucleus 191, 193, 197, 199, 203, 205, 409, 428
medial preoptic nucleus, lateral part 197, 429 | PF
PH | parafascicular thalamic nucleus 245~263, 420-423
posterior hypothalamic area 221~233, 407, 409, 430, 431 | rmx
RoG | retromammillary commissure 232, 233, 234, 235, 238, 239
rostral gyrus 97, 118~154, 406~410 | | | | | | |
| MPOM | medial preoptic nucleus, medial part 191, 429 | PHA | parahippocampal-amygdaloid transition area 204, 208-211, 214-217 | ros
ros-i
ros-s | rostral sulcus 97, 124~151
rostral sulcus, inferior (lower) branch 97, 108~121
rostral sulcus, superior (upper) branch 97 | | | | | | |
| MPtg | medial pterygoid muscle 32-38, 49, 51, 76-81 | phar
PHG | pharyngeal branches 51, 53
parahippocampal gyrus 23-25, 78-80, 95, 97, 210~316, 406, 407, 409-412 | RPC
RSC
rcs-i | red nucleus, parvocellular part 247, 251, 253, 257, 259, 263
retrosplenial cortex 277~307
retrocalcarine sulcus, inferior branch 407 | | | | | | |
| MPul | medial pulvinar nucleus 271, 275, 277, 281, 283, 287, 406, 424-426 | PhRe
Pi | pharyngeal recess 53
pineal gland 23, 58, 59, 271, 275, 277, 281, 283 | RSG
RSp | retrosplenial limbic gyri (von Economo) 97
retrospenial cortex 410 | | | | | | |
| MRec | medial rectus muscle 28, 29, 45, 47, 49, 80 | pi
pic | preoccipital notch 96, 97
posterior limb of the internal capsule 23, 228~276 | Rt
S/MCM
S | reticular thalamic nucleus 56-59, 215~287, 405, 406, 417~426
superior and middle constrictor muscle 37, 38, 39
subiculum 24, 25, 54-59, 221~307, 406, 407, 408, 411 | | | | | | |
| MS | medial septal nucleus 197, 199, 203, 205, 209, 211, 215, 217, 435 | pica
PIR | posterior inferior cerebellar artery 26, 57, 61
parainsular region 178, 180, 184, 186 | SalPh
SArS
sas | salpingopharyngeus muscle 33
subarachnoid space 35
semiannular sulcus 204~232 | | | | | | |
| MScal | middle scalenus muscle 35, 36 | Pir
PirF | piriform cortex 52, 53, 80, 169~189, 201, 207, 407, 410-412
piriform cortex, frontal part 168~206, 407 | SB
sbps | striatal cell bridge(s) 54~58, 80, 155, 157, 167, 187, 221, 227, 235, 239, 247, 253
subparietal sulcus 97, 292~367 | | | | | | |
| MSG | middle sagittal gyrus 97, 376~393, 404, 405, 409, 410 | PirR
PirT | piriform recess 51
piriform cortex, temporal part 174~209, 407 | SC
SCA | superior colliculus 271~287, 425, 426
subcallosal area 52, 84, 97, 156~181, 406, 407, 409 | | | | | | |
| MSG-p | middle sagittal gyrus, posterior part 405, 406, 409, 410 | Pit
Plat | pituitary gland 27, 53, 84
platysma 37-40, 45, 47, 49, 73, 75-78, 80, 82 | sca
scal
ScalM | superior cerebellar artery 24, 26, 29, 55, 57, 59
subcallosal fasciculus 155~169, 187~193, 197, 271, 275
scalenus muscle 36-40, 55, 57, 59, 77 | | | | | | |
| Mst | mastoid process of temporal bone 57, 73-75 | pm
pMCC | principal mammillary fasciculus 223
posterior midcingulate cortex (B.Vogt) 97 | SCC
scc | semicircular canals 57
splenium of the corpus callosum 21, 59, 60, 97, 270~310 | | | | | | |
| MstC | mastoid cells 73, 74 | PMOL | posteromedial orbital lobule 97, 160, 162, 165, 166, 168, 407, 408, 410 | SCD
SCG | semicircular ducts 76
subcallosal gyrus 149, 166 | | | | | | |
| mt | mammillothalamic tract 227-229, 232-234, 418-420 | PN
pna | paranigral nucleus 245, 263, 265
posterior nasal artery 49 | SCGn
SCGP | superior cervical ganglion 36, 37, 38
supracapsular part of the globus pallidus 179~209, 217 | | | | | | |
| mtg
MTG | mammillotegmental tract 226~241, 247, 253, 257, 259, 419-426
middle temporal gyrus 19-27, 49-64, 73-79, 95-97, 156~375, 405-408, 412-414 | POc
POc-a | parieto-occipital arc (first parieto-occipital « plis de passage » of Gratioloet) 96
parieto-occipital arc, anterior part 95-97, 403, 342~370, 409-411 | SCh
SChC
SChD | suprachiasmatic nucleus 185~205, 428, 429
suprachiasmatic nucleus, compact division 427, 428
suprachiasmatic nucleus, dorsal division 427, 428 | | | | | | |
| mts | middle temporal sulcus 202 | PoCi
POc-p | pontine cistern 27, 29, 55
parieto-occipital arc, posterior part 95-97, 372~388, 403-405, 409, 410 | SCM
SCMPP | superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx 32-37, 78, 79
superior constrictor muscle, pterygopharyngeal part 80 | | | | | | |
| Mul | multifidus cervicis muscle 36-40, 59, 80 | pof
PoG | parietooccipital fissure 96, 97, 348~385
postcentral gyrus 11-23, 55-66, 73-84, 95-97, 220~309, 402~414 | scp
scr
scs | superior cerebellar peduncle 58, 246~263, 270~283, 426
superior corona radiata 150~226
subcalcarine sulcus 97, 262, 409 | | | | | | |
| Mx | maxilla 31, 33, 35-37, 78, 82, 84 | polfs
Pons | preolfactory transverse sulcus 95, 97
pons 27, 29, 55-57, 82, 84, 235~263 | SCS
SCTI | subcallosal stratum 143~167, 173~203, 211, 229, 233, 241~265, 275
subcaudate terminal island 185 | | | | | | |
| mxa | maxillary artery 30-33, 49, 51, 53, 76-80 | pons
POp | pontine fibers 238, 240, 252
parietal operculum 20, 21, 60, 61, 74-77, 96, 238~298, 404, 405, 412-414 | SeC
SEpS | septal nasal cartilage 33, 35
subependymal stratum 211, 215, 229, 235, 239 | | | | | | |
| MxS | maxillary sinus 30, 31, 45, 47, 49, 78-81 | POrG
pors | posterior orbital gyrus 97, 130~166, 406, 407, 410, 411
posterior orbital sulcus 97, 136~168 | SFG
SFGL
SFGM | superior frontal gyrus 11-23, 45-61, 78-84, 95, 96, 106, 108, 111, 402, 409-412
superior frontal gyrus, lateral part 112~244, 402-405
superior frontal gyrus, medial part 97, 112~225, 402-405, 409 | | | | | | |
| mxv | maxillary vein 53 | pors-m
pos | posterior orbital sulcus, middle branch 97, 144~160
praeolfactory sulcus 108, 109, 112, 113 | | | | | | | | |
| MyHy
myhy | mylohyoid muscle 37-40, 45, 47, 78-84
mylohyoid nerve 39, 49, 51 | posc
PP | postreme subcallosal sulcus 97
peripeduncular nucleus 259, 269 | | | | | | | | |
| Na | nasal bone 29, 31 | PPA
ppa | peripeduncular area 259, 263, 265, 269, 422, 423
posterior parietal sulcus (Vogt) 95, 96, 97 | | | | | | | | |
| Nas | nasalis muscle 30-35 | PPCl | prepiriform claustrum 161~191 | | | | | | | | |
| nl | nuchal ligament 31, 33, 35 | | | | | | | | | | |
| nlac | nasolacrimal duct 31 | | | | | | | | | | |
| npal | nasopalatine artery (sphenopalatine artery) 35, 84 | | | | | | | | | | |
| NPhT | nasopharyngeal tonsil 83 | | | | | | | | | | |
| NSpt | nasal septum 31, 45, 47 | | | | | | | | | | |
| nuf | nuchal fascia 29, 31, 33, 37 | | | | | | | | | | |
| oaud | pharyngeal opening of auditory tube 82 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OB | olfactory bulb 47 | | | | | | | | | | |
| occ | occipital artery, vein and (greater occipital) nerve 26-29 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Occ | occipital bone 25-27, 29, 31, 33, 82 | | | | | | | | | | |
| occa
occs | occipital artery 25, 30-37, 53~67, 74, 76-78
occipital sinus 26, 59, 61, 63 | | | | | | | | | | |
| occv | occipital vein 25, 31, 34, 63, 65, 73, 74 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OcFrF | occipito-frontal muscle, frontal belly 45, 47, 73~82 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OcFrO | occipito-frontal muscle, occipital belly 65, 67, 73, 75, 76 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OcG | occipital gyrus (gyri) 15-25, 58, 60-68, 74-84, 288~375, 405, 406, 409-411 | | | | | | | | | | |
| ocm | occipito-mastoid suture 29 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OcP | occipital pole 96, 97 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OFat | orbital fat body 45, 47 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OFG | orbitofrontal gyri 45-51, 76-84 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OFOp | orbitofrontal operculum 405, 406 | | | | | | | | | | |
| ofr | orbitofrontal fibers 144~196 | | | | | | | | | | |
| olf | olfactory tract 26, 49, 51, 169, 172, 173 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OlfA | olfactory area 156~180, 407, 409, 410 | | | | | | | | | | |
| olfr | olfactory radiation 168, 172, 173 | | | | | | | | | | |
| olfs | olfactory sulcus 97, 112~169 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OLV | occipital horn of lateral ventricle 21, 23, 62-65, 79 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OmHy | omohyoid muscle 40, 49, 51 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OO | orbicularis oculi muscle 26-33, 45, 73-80 | | | | | | | | | | |
| OOr | orbicularis oris muscle 36-40, 77-80, 82 | | | | | | | | | | |
| opha | ophthalmic artery 45, 47, 49, 80, 81 | | | | | | | | | | |
| ophv | ophthalmic vein 49 | | | | | | | | | | |
| ops | occipitopolar sulcus (extreme fissure of Seitz) 95, 97, 388-391, 394, 395 | | | | | | | | | | |
| opt | optic tract 24, 25, 52, 54, 55-57, 80, 197~252, 407~411, 417-421 | | | | | | | | | | |
| or | optic radiation 23, 79, 252~271, 298~372, 423-425 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oral | Oral | oral cavity 78, 80, 82 | oral cavity 78, 80, 82 | | PPCI | | prepari form claustrum 161~191 | | SFGM | | superior frontal gyrus, medial part 97, 112~225, 402-405, 409 |
| OrG | orbital gyrus/gyri 24-27, 96 | ppms | posterior paramidline sulcus 96, 276~335 | SFi | septofimbrial nucleus 185, 187, 191, 193 | | | | | | |
| ors | orbital sulcus 169 | PPo | planum polare 55, 56, 148~249, 406-408, 412-414 | sfms | superficial medullary stratum 259, 263, 271, 275 | | | | | | |
| Otic | otic ganglion 53 | PPo-l | planum polare, lateral part 184~225 | SFO | subfornical organ 203, 205, 209, 211, 217 | | | | | | |
| ox | optic chiasma 26, 52, 53, 84, 178~199, 407, 409, 428 | pps | posterior parolfactory sulcus 97, 168~180 | sfo | superior fronto-occipital fasciculus 136~268, 274~294 | | | | | | |
| P3V | preoptic recess of the third ventricle 84, 179~193 | PRC | perirhinal cortex 95, 97, 168~256, 407, 408, 411, 412 | SFPG | superior frontopolar gyrus 95-7, 102~124, 404-406, 409-411 | | | | | | |
| Pa | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus 407, 409 | PRC35 | perirhinal cortex, BA 35 158~255 | sfps | superior frontopolar sulcus 95, 97, 106-109, 112-115, 118-121 | | | | | | |
| PaAP | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, anterior parvocellular part 191, 193, 428 | PRC36 | perirhinal cortex, BA 36 169~255 | SFPul | superficial pulvinar nucleus 269~287 | | | | | | |
| PAC | periamygdaloid cortex 179~224 | PrCuF | precuneiform area | sfs | superior frontal sulcus 95, 96, 108~223 | | | | | | |
| PACl | preamygdalar claustrum 185~215 | prculs | precuneal limiting sulcus 331~343, 360~379 | SG | straight gyrus 26, 27, 45-52, 82, 83, 95, 97, 112~171, 407, 408, 409 | | | | | | |
| pacs | paracentral sulcus 95-97, 192~239 | prcus | precuneal sulcus 330, 334, 336, 340, 342 | SGe | suprageniculate nucleus 257, 271, 275, 424 | | | | | | |
| PaD | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, dorsal part 197, 199, 203, 205, 209, 211 | PRF | prerubral field 420 | SGl | substantia gliosa (subependymal gray) 143~169, 197, 205, 209, 211 | | | | | | |
| PaFo | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, fornical part 203, 205 | prf | principal mammillary fasciculus 227, 228, 233, 235, 418, 419 | sgr | radiation of straight gyrus 118~166 | | | | | | |
| PAG | periaqueductal gray 269, 271, 275, 277, 281, 283, 287 | PrG | precentral gyrus 11-23, 54-64, 74-84, 95-97, 168~279, 402-406, 409-414, 422 | sH | Heschl sulcus 228~270 | | | | | | |
| | | prop | preopercular sulcus 95 | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| shl
stylohyoid ligament 49, 51 | sta | superficial temporal artery 25-33, 73 | TS | triangular septal nucleus 191, 193, 197, 199 | | | | | | | |
| SHThC superior horn of thyroid cartilage 39, 40 | staf | superior temporal artery, frontal branch 49, 51 | ts | triangular sulcus 96 | | | | | | | |
| sigs
sigmoid sinus 26-31, 57, 59, 61, 75 | stam | superior temporal artery, middle branch 53 | tsc | tenia semicircularis 217, 239, 247, 253, 277 | | | | | | | |
| SL
sublingual gland (and duct) 39, 40, 45, 47, 80, 81 | stap | superior temporal artery, posterior branch 53 | tsv | thalamostriate vein 21, 58, 191~241, 247, 251, 257, 263, 283, 287 | | | | | | | |
| sld
sublingual duct 80 | STG | superior temporal gyrus 17-25, 49-65, 73-77, 79, 95, 96, 156~358, | tt | tenia of thalamus 217, 227, 239, 253 | | | | | | | |
| slf I
superior longitudinal fasciculus I, dorsal component 114~378 | | 403-407, 412-414 | TTG | transverse temporal gyrus/gyri 20-23, 54-61, 73-77, 405, 406 | | | | | | | |
| slf II
superior longitudinal fasciculus II, central component 114~370 | STh | subthalamic nucleus 56, 57, 233~251, 406, 407, 409, 419, 420, | TTG1 | anterior transverse temporal gyrus 210~292, 405, 412-414 | | | | | | | |
| slf III
superior longitudinal fasciculus III, ventral component 114~370 | | 421, 438 | TTG2 | posterior transverse temporal gyrus 252~292, 404, 405 | | | | | | | |
| slf
superior longitudinal fasciculus 420, 421, 422 | StHy | sternohyoid muscle 47, 49, 79-81 | tth | dorsal trigeminothalamic tract 265 | | | | | | | |
| SLG
superior lingual gyrus 52, 53, 226, 228, 232, 328~369 | sthy | superior thyroid artery 39, 40, 51, 53 | TTub | torus tubarius 82 | | | | | | | |
| slga
sublingual artery 45 | sthyv | superior thyroid vein 51 | Tu | olfactory tubercle 52, 53, 175~205 | | | | | | | |
| SLgG
superior lingual gyrus 97, 405-407, 409-411 | StM | sternomastoid muscle 31-35, 37-40, 53~63, 73-75 | TuTI | tubercular terminal islands 179~199 | | | | | | | |
| slgv
sublingual vein 45 | str | superior thalamic stria 208~244 | tv | temporal vein(s) 26, 27, 29 | | | | | | | |
| slic
sublenticular part of the internal capsule 216~288 | sts | superior temporal sulcus 95, 96, 151~307, 354~371 | tvt | transverse temporal sulcus 96 | | | | | | | |
| sln
superior laryngeal nerve 37, 38, 39, 40 | sts-a | superior temporal sulcus, anterior segment 96 | TyC | tympanic cavity 29, 77 | | | | | | | |
| sls
sublenticular stria 192, 196, 198, 202, 204, 208, 210 | sts-asc | superior temporal sulcus, ascending segment 96, 306~337, 340, | TzM | trapezius muscle 31-40, 65, 67, 76-81 | | | | | | | |
| sm
stria medullaris of thalamus 23, 210~265, 417-424 | | 341 | Un | uncus 53, 54, 95, 97, 178~251, 407, 429 | | | | | | | |
| SM
submandibular gland 37-40, 49, 51, 75, 76, 78 | sts-h | superior temporal sulcus, horizontal segment 96, 306~365 | unc | uncinate fasciculus 120~232 | | | | | | | |
| sma
submental artery 45, 47 | sts-p | superior temporal sulcus, posterior segment 96 | Unn | uncinate nucleus 197, 199, 427, 429 | | | | | | | |
| smd
submandibular duct 39, 40, 45, 47, 49, 82 | StT | sternomastoid muscle, tendon 30, 74 | unn | uncal notch 193~215, 220~232 | | | | | | | |
| SMG
supramarginal gyrus 15-21, 60-65, 73-75, 95, 96, 228~327, 402-405, 411-414 | stv | superficial temporal vein 25, 29, 55, 57 | uns | uncal sulcus (impression) 184, 190~216 | | | | | | | |
| smv
submental vein 51, 53 | Sty | styloid process 30-34, 53 | us | uncal sulcus 95, 97, 221, 241, 245, 247 | | | | | | | |
| SMV
superior medullary velum 58 | StyGl | styloglossus muscle 35-38, 49, 51, 53, 77, 78 | Uv | uvula 33, 35, 36, 37, 49, 51 | | | | | | | |
| SN
substantia nigra 24, 25, 56, 57, 82-84, 269, 409, 438 | StyHy | stylohyoid muscle 35, 36-40, 51, 53, 77-79 | v | vein 37-40 | | | | | | | |
| SNC
substantia nigra, pars compacta 233~265, 407, 410 | StyPh | stylopharyngeus muscle 33, 35-38, 53, 77, 78 | VA | ventroanterior thalamic nucleus (ventral anterior nucleus) 217, 221, 223, 229, 409, 417, 418 | | | | | | | |
| SNR
substantia nigra, pars reticulata 229~265, 407, 410 | SuM | supramammillary nucleus 221, 223, 227, 430, 431 | VAb | basal ventroanterior thalamic nucleus [VM] (entry zone of nigral and amygdaloid afferents) 233~241, 406, 409, 419, 420 | | | | | | | |
| SO
supraoptic nucleus 191~205, 407, 409, 428, 429 | sumx | supramammillary commissure 233, 235, 239, 420 | vaf | ventral amygdalofugal fibers (pathway) 196~216, 417-419 | | | | | | | |
| SOb
superior oblique muscle 27, 45, 47, 49 | sutra | supratrochlear artery 26, 27 | VAL | lateral ventroanterior thalamic nucleus 227, 233~239, 405, 406, 410, 418-420, 435 | | | | | | | |
| SObCa
superior oblique capitis muscle 32, 33, 57, 59, 61, 76, 77 | sutrn | supratrochlear nerve 27 | VAM | medial ventroanterior thalamic nucleus 227, 233, 405, 406, 410, 418, 419, 435 | | | | | | | |
| socv
suboccipital venous plexus 78, 79 | sutrv | supratrochlear vein 26 | VAMC | ventroanterior thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part 227, 229, 233, 235, 418, 419 | | | | | | | |
| SODL
supraoptic nucleus, dorsolateral part 209, 211, 215, 429, 430 | sv | septal vein 145, 163~211 | VCl | ventral claustrum 175~245 | | | | | | | |
| sof
superior occipitofrontal fasciculus 21, 155 | SxD | sexual dimorphic nucleus 197, 199 | VDB | vertical limb of the diagonal nucleus 185, 187, 191 | | | | | | | |
| SOG
superior occipital gyrus 95-97, 394, 399, 404-406, 410-412 | Symp | sympathetic trunk 37-40, 76 | Ver | vermis of cerebellum 23, 58, 60 | | | | | | | |
| SOG-l
superior occipital gyrus, lat part 382, 384, 387, 388, 390, 393 | sz | stratum zonale 232~244 | vert | vertebral artery 30-38, 40, 55, 57, 59, 78-81 | | | | | | | |
| SOG-m
superior occipital gyrus, medial part 376~393 | TCb | tentorium cerebelli 57, 59, 65 | Vert5 | fifth cervical vertebra 39, 40, 55 | | | | | | | |
| sophv
superior ophthalmic vein 26, 27, 29 | TCd | tail of caudate nucleus 21, 23, 55-59, 79, 229~289, 406, 407, 411 | Vert6 | sixth cervical vertebra 40 | | | | | | | |
| sora
supraorbital artery 45 | TCl | temporal claustrum 181~211 | VGP | ventral globus pallidus 187~245 | | | | | | | |
| sors
supraorbital sulcus 97 | tclv | tela choroidea of the lateral ventricle 247 | VL | ventrolateral thalamic nucleus 56, 57, 229, 405, 406, 410, 435 | | | | | | | |
| sos
superior occipital sulcus 95, 96, 102~119, 126, 127, 382, 383 | Tec | tectum of midbrain 58, 82-84 | VLA | anterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus 223, 233, 235, 239, 406, 419, 420 | | | | | | | |
| SOVM
supraoptic nucleus, ventromedial part 209, 211, 215, 429, 430 | Temp | temporal bone 25-27, 31, 55 | VLb | basal (inferior) ventrolateral thalamic nucleus [VPI] (entry zone of the cerebellar fibers) 241~247, 410, 420, 421 | | | | | | | |
| sox
supraoptic commissure 196~215, 220, 221, 417-419 | TempM | temporalis muscle 25-34, 47~61, 73-78 | VLP | posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus 406, 435 | | | | | | | |
| SPal
soft palate 49, 51, 83, 84 | TempP | temporal bone, petrosal part 29 | VLPE | posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, external part 235~253, 419-421 | | | | | | | |
| SPalF
salpingopalatinal fold 83 | TempT | temporalis muscle, tendon 35, 73-75 | VLPI | posterior ventrolateral thalamic nucleus, internal part 241~247, 420, 421 | | | | | | | |
| spas
superior parietal sulcus 95, 96, 322~343 | TenT | tensor tympani muscle 55 | VMH | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus 407, 409, 429, 430 | | | | | | | |
| SpAx
spinous process of axis 35, 36, 61 | TeVePal | tensor veli palatini muscle 32-34, 49, 51, 78, 80, 81 | VMHDM | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part 209~221, 429, 430 | | | | | | | |
| spcs
superior postcentral sulcus 96, 289~307 | TF | parahippocampal area TF 253~297 | VMHVL | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part 209~221, 429, 430 | | | | | | | |
| spets
superior petrosal sinus 55, 57 | tf | temporal fascia 25, 29, 31 | Vom | vomer 31, 33, 34, 45, 49 | | | | | | | |
| SPF
subparafascicular thalamic nucleus 245~257, 420-422 | tfa | transverse facial artery 32, 33, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53 | VP | ventroposterior thalamic nucleus 193~205, 221~245 | | | | | | | |
| Sph
sphenoid bone 26, 27, 29, 31 | tfi | tenia of fimbria 239, 247, 253 | VPb | basal ventroposterior nucleus [VMpo] (entry zone of sensory afferents) 251~269, 406, 422-424 | | | | | | | |
| SPhF
salpingopharyngeal fold 82 | tfp | transverse fibers of the pons 245 | VPL | lateral ventroposterior thalamic nucleus 247~265, 405, 406, 410, 421-424 | | | | | | | |
| SphGW
sphenoid, greater wing 75, 76, 77 | tfv | transverse facial vein 53 | VPM | medial ventroposterior thalamic nucleus 251~259, 406, 421, 422 | | | | | | | |
| sphml
sphenomandibular ligament 51 | tfx | tenia of fornix 217, 239, 253, 277 | VPMPC | medial ventroposterior thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part 245~259, 420-422 | | | | | | | |
| sphpal
sphenopalatine artery 30, 31 | TH | parahippocampal area TH 257~281 | vr2 | ventral ramus 2 57 | | | | | | | |
| sphps
sphenoparietal sinus 26, 27, 28, 29 | Th | thalamus 20-23, 81, 83, 84, 436 | vr4 | ventral ramus 4 57 | | | | | | | |
| SphS
sphenoid sinus 28, 29, 49, 51, 53, 84 | ThC | thyroid cartilage 40, 49, 80, 81 | vt | velum terminale 235 | | | | | | | |
| sphzg
sphenozygomatic suture 27 | ThHy | thyrohyoid muscle 39, 40, 49, 51, 80 | VTA | ventral tegmental area 235~245, 251~259 | | | | | | | |
| Spinal
spinal cord 35 | ThHyMe | thyrohyoid membrane 39, 40 | vtx | ventral tegmental decussation 256, 258 | | | | | | | |
| SPL
superior parietal lobule 11-19, 63-68, 76-79, 95-97, 280~370, 402-404, 409-413 | thr | thalamic radiation (corona radiata) 79 | xscp | decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles 262~275, 423-425 | | | | | | | |
| SplCa
splenius capitis muscle 28-40, 59, 61, 63, 65, 73-79, 81 | TIG | transverse insular gyrus 97, 142~162, 407, 411, 412 | ZI | zona incerta 215~239, 245~259, 406, 418-422, 435 | | | | | | | |
| SplCe
splenius cervicis muscle 36-40, 77 | TL | temporal lobe 28, 29, 51, 55 | ZID | zona incerta, dorsal part 241 | | | | | | | |
| SplM
splenius capitis and cervicis muscle 40 | tla | transverse ligament of atlas 83 | ZIV | zona incerta, ventral part 241 | | | | | | | |
| SpM
spinalis muscle 37-40 | TLev | torus levatorius 82 | Zyg | zygomatic bone 29, 31, 33, 45, 75 | | | | | | | |
| spocs
superior postcentral sulcus 288~306 | TLV | temporal horn of lateral ventricle 27, 54-59, 80, 217~287 | ZygA | zygomatic arch 47, 49, 51, 73 | | | | | | | |
| sprs
superior precentral sulcus 95, 96, 174~235 | TM | tuberomammillary nucleus 215, 217, 221, 223, 407, 430, 431 | ZygM | zygomatic muscle(s) 76, 77 | | | | | | | |
| spth
spinothalamic tract 270, 271, 274, 276, 280 | TMD | temporomandibular disc 53 | | | | | | | | | |
| SptP
septum pellucidum 53, 173 | tongue | tongue 37, 47, 79, 81 | | | | | | | | | |
| SPul
superior pulvinar nucleus 269, 271, 275, 277, 424, 425 | TOp | temporal operculum 74-77, 96 | | | | | | | | | |
| SRec
superior rectus muscle 26, 27, 47, 49, 78-80 | tors | transverse orbital sulcus 97, 126, 127, 130-133, 136 | | | | | | | | | |
| SRoG
superior rostral gyrus 45, 46-51 | tos | transverse occipital sulcus 95, 96, 382-385 | | | | | | | | | |
| ss
straight sinus 61, 63 | tos-l | transverse occipital sulcus, lateral ramus 95, 96, 384, 388, 389 | | | | | | | | | |
| ssa
sulcus semiannularis | tos-m | transverse occipital sulcus, medial ramus 95, 96, 384, 388, 389 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSG
superior sagittal gyrus 404-406, 409, 410 | TOTZ | temporo-occipital transition zone 95, 96, 346~375, 404, 405, 412, 413 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSG-a
superior sagittal gyrus, anterior part 95 | tp | tapetum 216~372 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSG-p
superior sagittal gyrus, posterior part 95 | TP | temporal pole 26, 27, 49, 50, 51, 96, 407, 408, 410-412 | | | | | | | | | |
| ssgs
superior sagittal sinus 47, 51, 57~71, 95, 97, 376~391 | TPC | temporopolar cortex 150, 153, 154 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSpCa
semispinalis capitis muscle 26-40, 59, 61, 63, 65, 76-79, 81 | TPCl | lateral temporopolar cortex 149~177 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSpCe
semispinal cervicis muscle 37-40, 61, 79 | TPCm | medial temporopolar cortex 147~167 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSpG
subsplenial gyrus 299, 300, 303, 304 | TPG | temporopolar gyrus 95, 97, 156~172, 407, 408, 411-413 | | | | | | | | | |
| sss
superior sagittal sulcus (v.Economo/Koskinas) 95, 97, 376~391 | TrA | triangular area (Wernicke) 265, 269 | | | | | | | | | |
| SSTI
substriatal terminal island 169~209, 217 | TrLV | trigone of lateral ventricle 60, 61, 78, 79, 289~307 | | | | | | | | | |
| sstr
sagittal stratum 304~378 | TrP4 | transverse process of fourth vertebra 40 | | | | | | | | | |
| st
stria terminalis 21, 23, 56, 59, 79, 80, 82, 186~287, 417-426 | TrPAt | transverse process of the atlas 34, 35, 77, 79 | | | | | | | | | |
| | st | trs | stria terminalis | transverse sinus 63, 65, 74-76, 78, 79 | 21, 23, 56, 59, 79, 80, 82, 186~287, 417-426 | | trs | | transverse sinus | 63, 65, 74-76, 78, 79 | |
**447**
**448**

## Atlas of the **th** Human Brain
4 **Edition th**
Jürgen K. Mai Milan Majtanik George Paxinos
The fourth edition of *Atlas of the Human Brain* presents the anatomy of the brain at macroscopic and microscopic levels, featuring different aspects of brain morphology and topography. This greatly enlarged new edition provides the most detailed and accurate delineations of brain structure available. It includes features which assist in the new fields of neuroscience – functional imaging, resting state imaging and tractography. Atlas of the Human Brain is an essential guide to those working with human brain imaging or attempting to relate their observations on experimental animals to humans. Totally new in this edition is the inclusion of Nissl plates with delineation of cortical areas (Brodmann's areas), the first time that these areas have been presented in serial histological sections.
Part 1: *The Atlases of the Brain in the Head* (Macroscopic Atlas) displays the brain in the head sectioned in the three cardinal planes. It consists of serial 1 cm thick sections from three human heads that were previously scanned with MRI. This presentation allows for correlation of the brain with bony landmarks, nerves, and blood vessels. In addition, included are X-ray images of the cadaver sections and MR-images from a healthy volunteer showing levels corresponding to those depicted in the atlas plates.
Part 2: *The Atlas of the Brain in MNI Stereotaxic Space* (Microscopic Atlas) consists of a detailed atlas of the isolated brain in MNI stereotaxic coordinates represented by 149 serial histological sections of one hemisphere with meticulous delineations. It displays the myelo- and cytoarchitecture accompanied by detailed diagrammatic delineations.
### New Features of the 4th edition:
- • The contents of the Atlas of the brain in MNI stereotaxic space has been extensively expanded from 143 pages, showing 69 levels through the hemisphere, to 314 pages representing 99 levels.
- • In addition to the fiber-stained (myelin) plates, we now provide fifty new (Nissl) plates covering cytoarchitecture. These are interdigitated within the existing myelin plates of the stereotaxic atlas.
- • All photographic plates now represent the complete hemisphere.
- • All photographs of the cell- and fiber-stained sections have been transformed to fit the MNI-space.
- • Major fiber tracts are identified in the fiber-stained sections.
- • In the Nissl plates cortical delineations (Brodmann's areas) are provided for the first time.
- • The number of diagrams increased to 99. They were now generated from the 3D reconstruction of the hemisphere registered to the MNI- stereotaxic space. They can be used for immediate comparison between our atlas and experimental and clinical imaging results.
- • Parts of cortical areas are displayed at high magnification on the facing page of full page Nissl sections. Images selected highlight those areas which are thought to correspond with those published by von Economo and Koskinas (1925).
- • A novel way of depicting cortical areal pattern is used: The cortical cytoarchitectonic ribbon is unfolded and presented linearly. This linear representation of the cortex enables the comparison of different interpretations of cortecal areas and allows mapping of activation sites.
- • Low magnification diagrams in the horizontal (axial) and sagittal planes are included, calculated from the 3D model of the atlas brain.


